295,00 € – 895,00 €
Product details
Synonyms = UP1A; UPIA; UPKA; TSPAN21
Antibody type = Mouse monoclonal / IgG
Clone = MSVA-735M
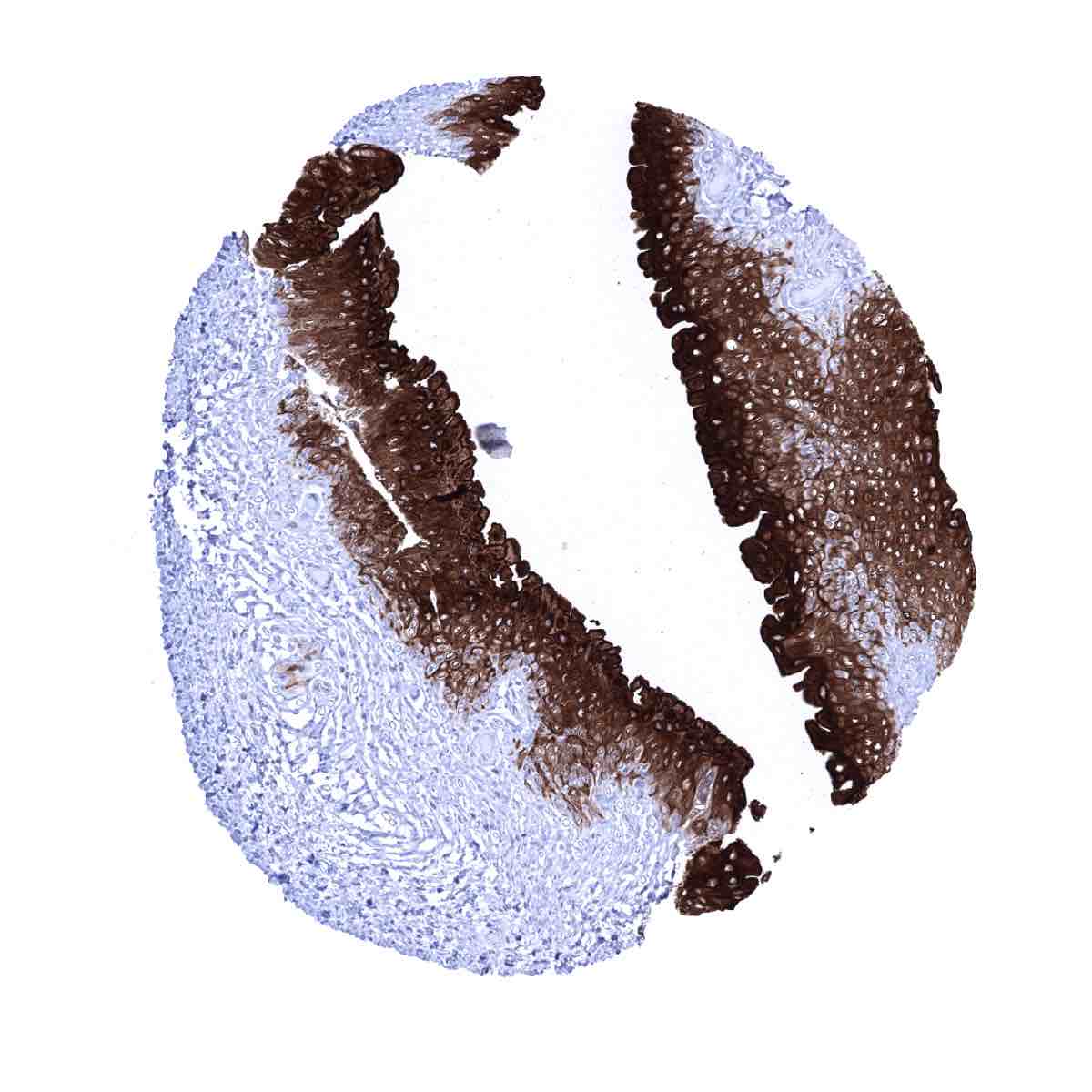
Positive control =Urinary bladder: A strong membranous and cytoplasmic Upk1a immunostaining should be seen in the urothelium (the staining can be limited to the top 1/3 or 2/3 of the urothelium).
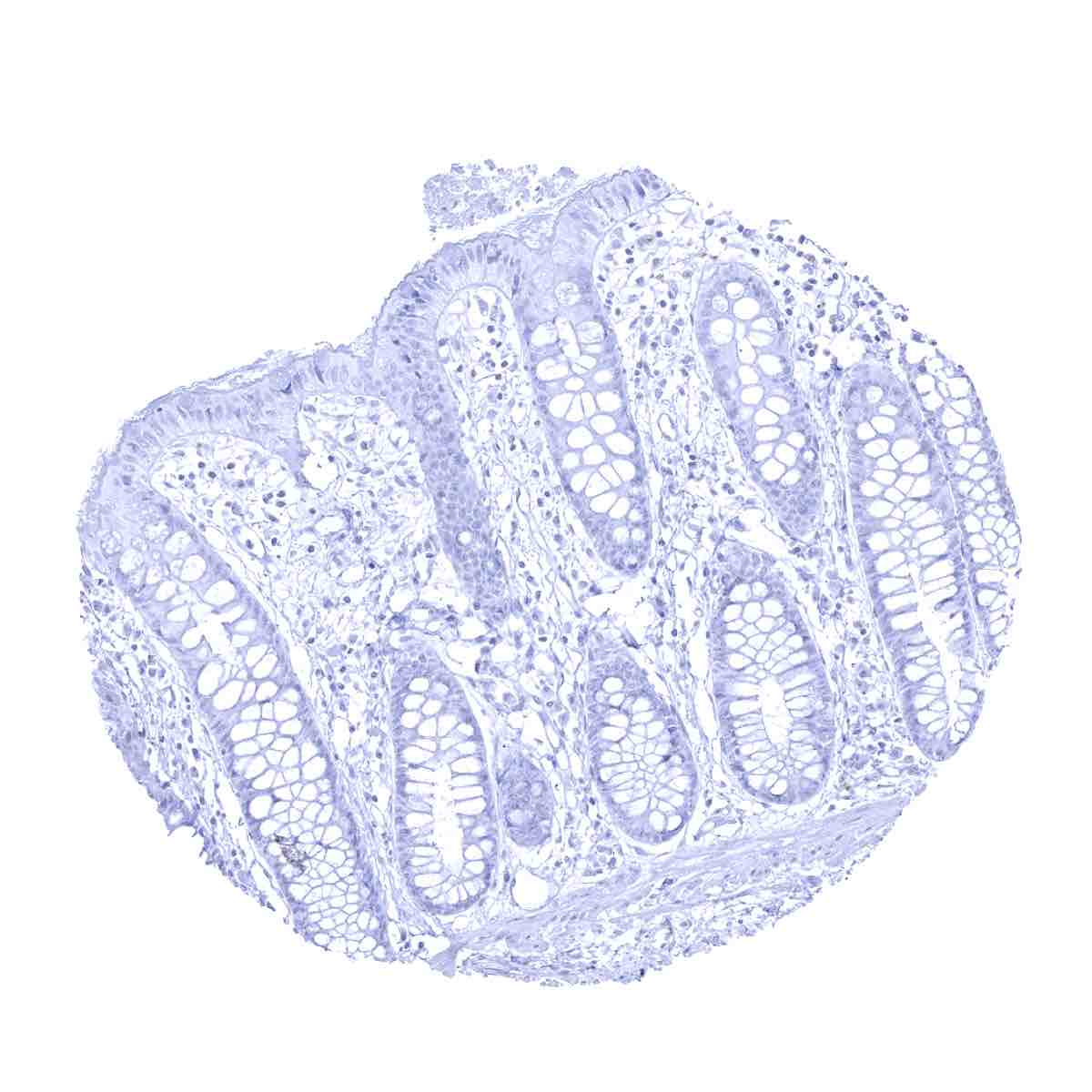
Negative control =Colon: Upk1a immunostaining should be absent in all cells of the colon mucosa.
Cellular localization = Cell surface
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100-1:200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
Uroplakin 1A is marker for urothelium and urothelial tumors.
Biology Behind
The Uroplakin 1A (Upk1a) protein is coded by the UPK1b gene located at 19q13.12. Upk1a is one out of 5 known uroplakin (Upk) protein particles that cooperatively form apical asymmetric unit membrane (AUM) plaques which play an important role in the stabilization and strengthening of epithelial cells that line the bladder. These AUM plaques enable the inner bladder membrane to stretch and prevent urothelial cells from rupturing during bladder distension. Upks are assembled in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where they heterodimerize prior to escaping the ER. Upk1a heterodimerizes with Upk2 and Upk1b heterodimerizes with Upk3. Upk heterodimers subsequently form heterotetramers which then combine as concentric hexameric rings that are packaged into vesicles and trafficked to the cell surface. AUMs and Upk proteins may have a role in mediating membrane permeability and signal transduction events that are involved in the regulation of cell development, activation, growth, and motility.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
Uroplakin 1A staining pattern in Normal Tissues with antibody MSVA-735M (images are shown in our “Normal Tissue Gallery”)
| Brain | Cerebrum | Negative. |
| Cerebellum | Negative. | |
| Endocrine Tissues | Thyroid | Negative. |
| Parathyroid | Negative. | |
| Adrenal gland | Negative. | |
| Pituitary gland | Negative. | |
| Respiratory system | Respiratory epithelium | Negative. |
| Lung | Negative. | |
| Gastrointestinal Tract | Salivary glands | Negative. |
| Esophagus | A faint/weak/moderate Upk1a staining can occur in some cell layers (middle third) of the squamous epithelium. | |
| Stomach | Negative. | |
| Duodenum | Negative. | |
| Small intestine | Negative. | |
| Appendix | Negative. | |
| Colon | Negative. | |
| Rectum | Negative. | |
| Liver | Negative. | |
| Gallbladder | Negative. | |
| Pancreas | Negative. | |
| Genitourinary | Kidney | Negative. |
| Urothelium | Upk1a immunostaining is strongest in the urothelium. Here the staining is particularly strong in the top third cell layers including umbrella cells. Staining is less intense or even absent in basal cell layers. | |
| Male genital | Prostate | A focal weak to moderate UpK1a staining can occur in case of squamous metaplasia in prostatic glands or ducts. |
| Seminal vesicles | A moderate to strong focal UpK1a staining of individual cells or groups of cells can occasionally be seen. | |
| Testis | Negative. | |
| Epididymis | Negative. | |
| Female genital | Breast | Negative. |
| Uterus, myometrium | Negative. | |
| Uterus, ectocervix | A faint/weak/moderate Upk1a staining can occur in some cell layers (middle third) of the squamous epithelium. | |
| Uterus endocervix | Negative. | |
| Uterus, endometrium | Negative. | |
| Fallopian Tube | Negative. | |
| Ovary | Negative. | |
| Placenta early | Negative. | |
| Placenta mature | Negative. | |
| Amnion | Negative. | |
| Chorion | Negative. | |
| Skin | Epidermis | A faint/weak/moderate Upk1a staining can occur in some cell layers (middle third) of the squamous epithelium. |
| Sebaceous glands | Negative. | |
| Muscle/connective tissue | Heart muscle | Negative. |
| Skeletal muscle | Negative. | |
| Smooth muscle | Negative. | |
| Vessel walls | Negative. | |
| Fat | Negative. | |
| Stroma | Negative. | |
| Endothelium | Negative. | |
| Bone marrow/ lymphoid tissue | Bone marrow | Negative. |
| Lymph node | Negative. | |
| Spleen | Negative. | |
| Thymus | Negative. | |
| Tonsil | Negative. | |
| Remarks |
These findings are largely consistent with the RNA and protein data described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression Uroplakin 1A)
Positive control =Urinary bladder: A strong membranous and cytoplasmic Upk1a immunostaining should be seen in the urothelium (the staining can be limited to the top 1/3 or 2/3 of the urothelium).
Negative control =Colon: Upk1a immunostaining should be absent in all cells of the colon mucosa.
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
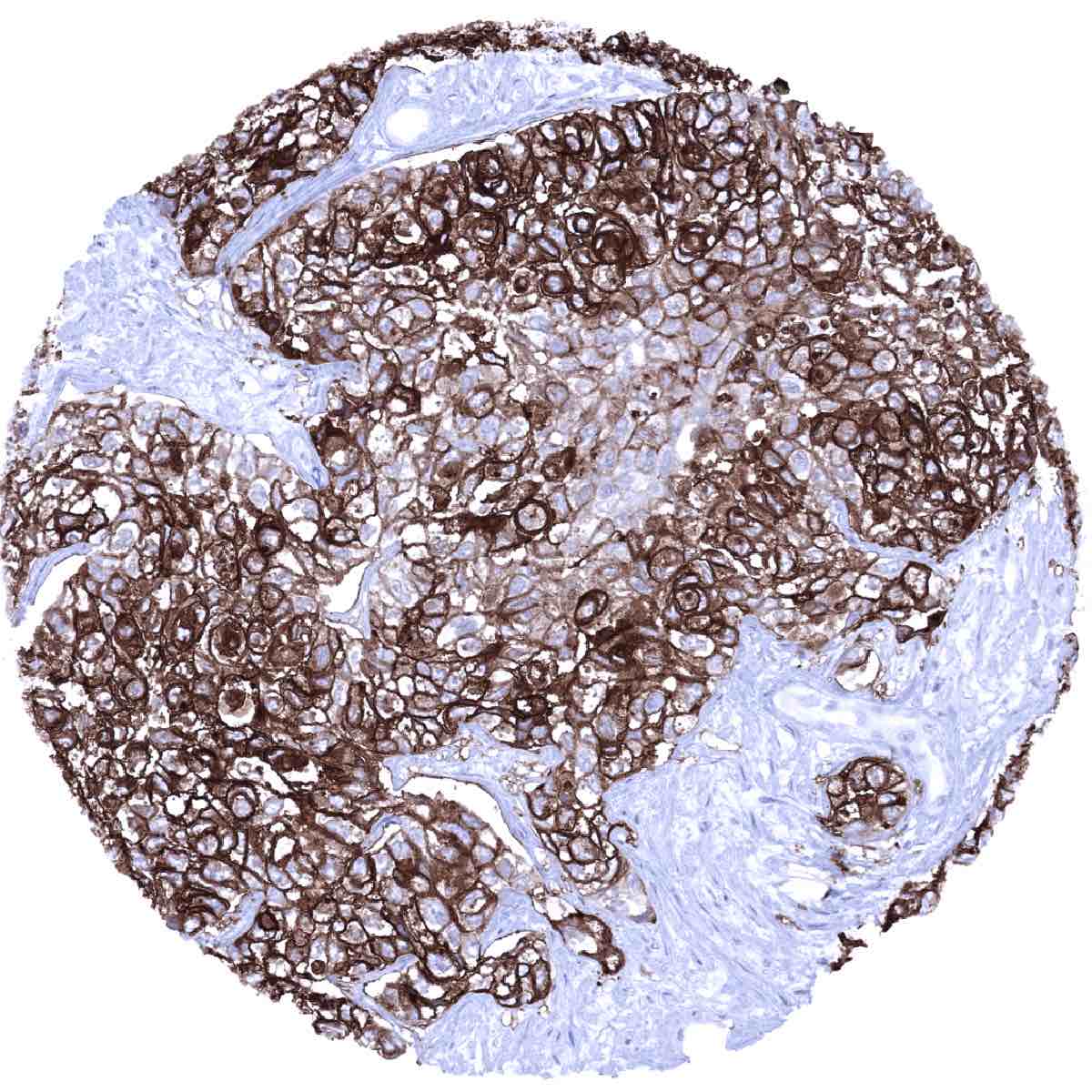
A positive Upk1a immunostaining is most commonly seen in urothelial carcinomas. It can also occur in squamous cell carcinomas and – rarely – in other cancers.
The TCGA findings on Uroplakin 1A RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Compatibility of Antibodies
Uroplakin 1a (MSVA-735M) publication summary
Relevant publication: Reiswich et al. Large-scale human tissue analysis identifies Uroplakin 1a as a putative diagnostic marker for urothelial cancer. Published in Pathology Research and Practice 2022 Jul 18;237:154028. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35872365.
A total of 5’323 tumors were successfully analyzed from 115 different tumor categories by using the following protocol: Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH7,8 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. MSVA-735M at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent). This protocol was also used for all stainings depicted in our tumor and normal tissue galleries.
The study results showed a striking predominance of Upk1a expression in urothelial neoplasms (42.6–98%) including Brenner tumors of the ovary (64.9%), followed by neoplasms of the thyroid gland (31.8–33.3%). The authors also observed Upk1a positivity in up to 15% of cases in 26 additional tumor categories but the staining was usually cytoplasmic and weak (rarely moderate) in these tumors. The distribution of positive staining results is shown in an “organ-systematic” and in a “ranking order” figure below (images based on data from Reiswich et al.). Results on possible associations with histopathological and clinical parameters of tumor aggressiveness are also summarized below (table based on data from Reiswich et al.).
Authors conclusions on diagnostic utility of Upk1a immunohistochemistry with respect to the distinction of different tumor entities (Reiswich et al.):
- Distinction of urothelial carcinoma (positive in about 50%) from prostate cancer (usually negative) or other neoplasms invading the urinary bladder (usually negative).
Authors conclusions on prognostic/predictive role of Upk1a expression (Reiswich et al.):
- Reduced Upk1a expression is linked to high grade in pTa urothelial tumors of the bladder (p<0,02).
- Reduced Upk1a expression is more frequent in pT2-4 than in pTa urothelial carcinomas (p<0,0001).
Data from the publication: Large-scale human tissue analysis identifies Uroplakin 1a as a putative diagnostic marker for urothelial cancer. Published by Reiswich et al. in Pathology Research and Practice 2022 Jul 18;237:154028. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35872365. Summarized in own graphics.
Figure 1. Uroplakin 1A staining in cancer (“organ-systematic”; according to Reiswich et al.)
Figure 2. Uroplakin 1A staining in cancer (“ranking list”; according to Reiswich et al.)
Figure 3. Clinico-pathological associations described by Reiswich et al. (p-value)
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image galleries are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 9 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply MSVA-735M at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Agilent / Dako – Autostainer Link 48
Pretreatment in PT-Link for 30 minutes at 95°C (pH high); FLEX peroxidase blocking for 5 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-735M 1:450 for 20 minutes (room temperature), FLEX+ mouse/rabbit (LINKER) for 15 minutes (room temperature), horseradish peroxidase (HRP) for 20 minutes (room temperature), FLEX DAB+Sub-Chromo for 10 minutes (room temperature), FLEX hematoxylin for 5 minutes (room temperature).
These images reflect stainings by the protocol described above. It is of note that a comparable staining result can also be obtained by different protocols. In general, a longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, and a longer incubation time of FLEX+LINKER result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining. Modifications of the protocol with a strengthening effect on staining intensity in combination with changes of other parameters that result in lower staining intensity can result in a comparable result as shown above.
Leica – BOND RX
Dewax at 72°C for 30 seconds; Pretreatment in Bond Epitope Retrieval Solution (ER2 – EDTA pH9) for 20 minutes at 100°C; Peroxidase blocking for 5 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-735M 1:150 for 15 minutes (room temperature), Post primary (rabbit anti mouse) for 8 minutes (room temperature), Polymer (goat anti rabbit) for 8 minutes (room temperature), mixed DAB refine for 10 minutes (room temperature), hematoxylin for 5 minutes (room temperature).
These images reflect stainings by the protocol described above. It is of note that a comparable staining result can also be obtained by different protocols. In general, a longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, a higher temperature during incubation, and a longer incubation time of Post primary and or the Polymer result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining. Modifications of the protocol with a strengthening effect on staining intensity in combination with changes of other parameters that result in lower staining intensity can result in a comparable result as shown above.
Roche – Ventana Discovery ULTRA
Pretreatment for 64 minutes at 100°C (pH 8,4); CM peroxidase blocking for 12 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-735M 1:150 for 20 minutes at 36°C, secondary antibody (anti-mouse HQ) for 12 minutes at 36°C, anti-HQ HRP for 12 minutes at room temperature, DAB at room temperature, hematoxylin II at room temperature for 8 minutes, bluing reagent at room temperature for 4 minutes.
These images depict staining results obtained by the protocol described above. It is of note, that the Ventana machines generally require higher antibody concentrations than other commonly used autostainers because the antibodies are automatically diluted during the procedure. Various other protocols can result in an identical result as shown above. A longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, a higher temperature during incubation, and a longer incubation time of secondary antibody and or the anti-HQ HRP result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining.
Potential Research Applications
- The prevalence and clinical significance of Upk1a expression in cancer is unknown.
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
There are two ways how the specificity of antibodies can be documented for immunohistochemistry on formalin fixed tissues. These are: 1. Comparison with a second independent method for target expression measurement across a large number of different tissue types (orthogonal strategy), and 2. Comparison with one or several independent antibodies for the same target and showing that all positive staining results are also seen with other antibodies for the same target (independent antibody strategy).
Orthogonal validation: For the antibody MSVA-735M specificity is suggested by the strong concordance of the immunostaining data with data from three independent RNA screening studies, including the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) RNA-seq tissue dataset, the FANTOM5 project, and the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project, which are all summarized in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression Uroplakin 1A). RNA expression was almost exclusively detected in organs covered by squamous epithelium (esophagus, vagina, cervix, skin) or containing urothelium (bladder, prostate).
Comparison of antibodies: True expression of Upk1a in urothelium and squamous epithelium as well as in individual samples of seminal vesicle and the prostate is also confirmed by the independent product candidate called “Validation Antibody” which was eventually discarded because of a fibrillar cross-reactivity in the brain.