295,00 € – 995,00 €
Product details
Synonyms = LPFS2; S152; T cell activation antigen S152; T-cell activation antigen CD27; T14; TNFRSF7; TNFSF7; Tp55; Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 7
Antibody type = Mouse monoclonal / IgG1
Clone = MSVA-027M
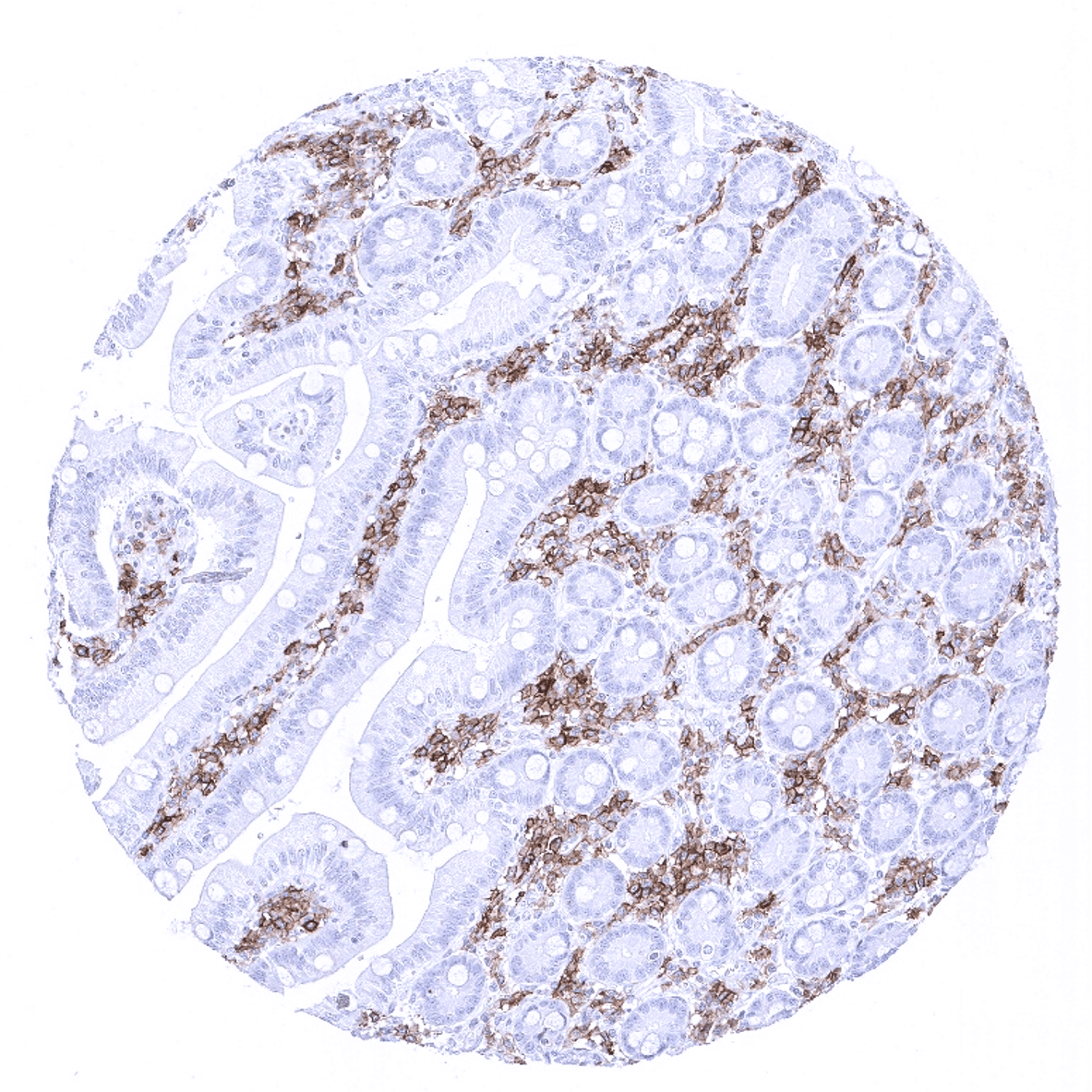
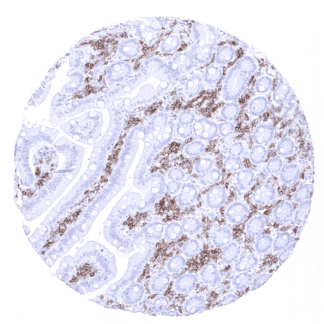
Positive control = Tonsil: A strong, membranous staining should be seen in the majority of interfollicular lymphocytes but also in a fraction of lymphocytes in the germinal centres and the mantle zone.
Negative control = Tonsil: CD27 staining should be absent in all epithelial cells and a fraction of lymphocytes.
Cellular localization = Cell Surface
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100 – 1:200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
Biology Behind
The CD27, a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily, is a homodimeric phosphoglycoprotein of 120 kDa constitutively expressed on thymocytes, naïve T cells, B cells, and NK cells. The ligand for CD27, CD70, is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on antigen presenting cells in response to antigen stimulation. Upon T-cell activation, CD27 is upregulated and appears to induce proliferation and local accumulation of CD8+ T cells. CD27 is later downregulated after several rounds of division and differentiation toward effector cells. CD27 and its ligand CD70 play a major role in the immune response against cancers. Accordingly, Varlilumab, an agonistic antibody that binds to CD27 is an experimental cancer treatment currently in phase I clinical trials. CD27 can also be expressed on various types of T-cell and B-cell lymphomas.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
In the thymus, CD27 is present on the vast majority of medullary but only rarely in cortical lymphocytes. In lymph nodes and the tonsil, CD27 is primarily seen in lymphocytes of the interfollicular area but also present in a considerable fraction of lymphocytes in the germinal centre and the mantle zone. In the spleen, almost all cells of the white pulp, but only few cells in the red pulp are stained. CD27 is also expressed in the majority of mucosa associated lymphocytes in the gastrointestinal and urinary tract and also in the majority of scattered lymphocytes occasionally seen in other tissues including bone marrow. CD27 is not seen in any mesenchymal, epithelial or brain tissues.
These findings are largely comparable with the RNA data described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression CD27) where very small RNA amounts were detected in tissues known for having relatively many mucosa associated lymphocytes. Protein data are not provided in the protein atlas for CD27.
Suggested positive tissue control: Tonsil: A strong, membranous staining should be seen in the majority of interfollicular lymphocytes but also in a fraction of lymphocytes in the germinal centres and the mantle zone.
Suggested negative tissue control: Tonsil: CD27 staining should be absent in all epithelial cells and a fraction of lymphocytes.
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
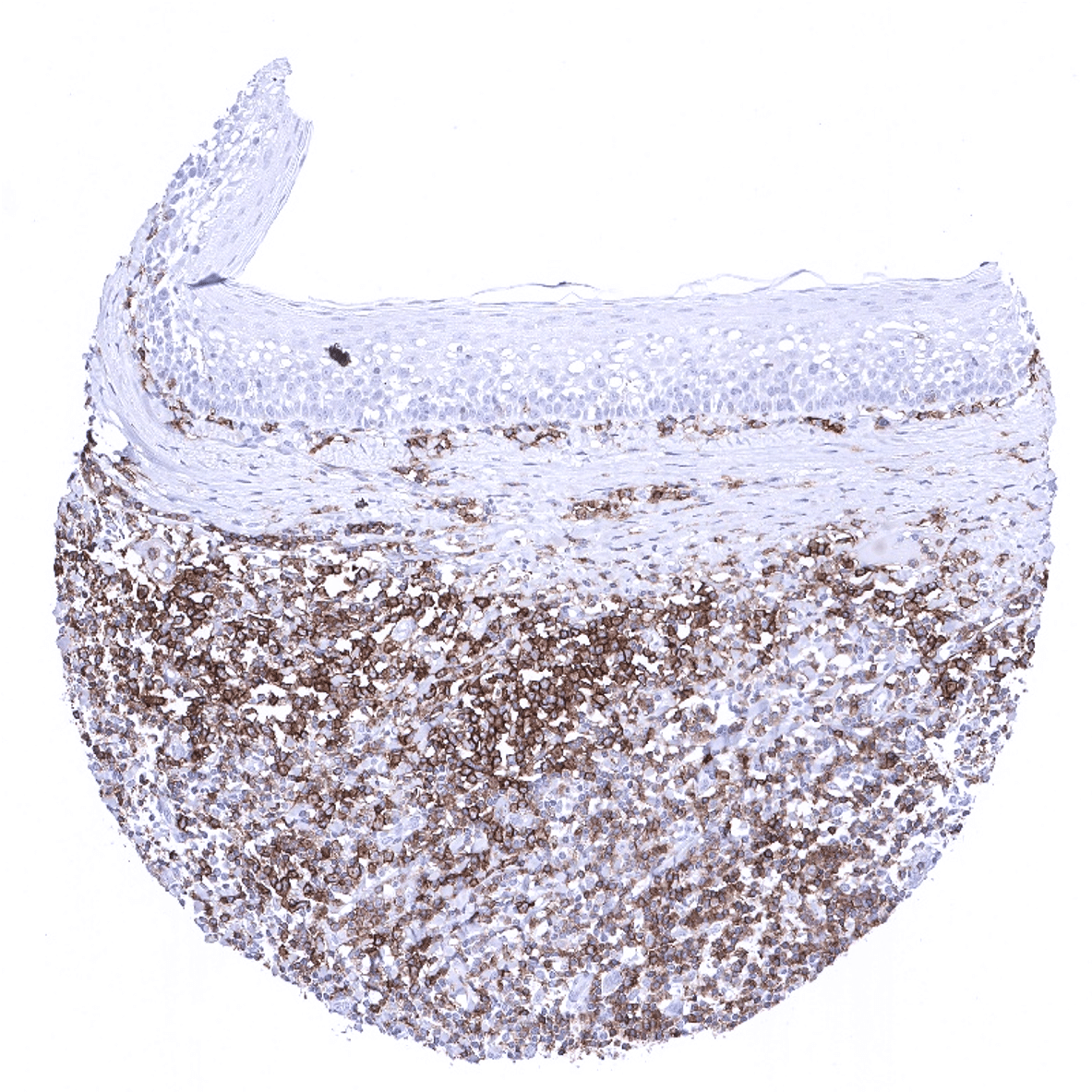
CD27 is expressed in many lymphomas. CD27 positive lymphocytes account for a variable but often large fraction of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in all kinds of solid cancers.
The TCGA findings on CD27 RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Compatibility of Antibodies
No data available at the moment
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image galleries are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH9 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply MSVA-027M at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Impact of pH
MSVA-027M results in strongest staining if pH7,8 is used for slide pretreatment. pH9 is acceptable but lower pH results in a significant deterioration of sensitivity. An example of the impact of pH is shown below for normal kidney tissue.
Potential Research Applications
- CD27 and its ligand CD70 are a “hot topic” in immuno-oncology. The role of these proteins and their interplay with other modulators of the immune system are currently investigated in a high number of laboratories.
- It is currently unclear whether anti-CD27 antibodies may be therapeutically applied in CD27 positive lymphomas.
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
Specificity of MSVA-027M is documented by strong positive staining in cell types that are well documented to express CD27 such as specific lymphocyte subpopulations in combination with complete absence of staining in all tissues known to not express CD27 including all epithelial, mesenchymal and neuronal tissues and also tissues notorious for non-specific IHC background such as kidney, colonic mucosa, and epidermis.