295,00 € – 895,00 €
Product details
Synonyms = Ataxia telangiectasia group D complementing gene (ATDC); Tripartite motif-containing protein 29 (TRIM29)
Antibody type = Mouse monoclonal / IgG
Clone = MSVA-629M
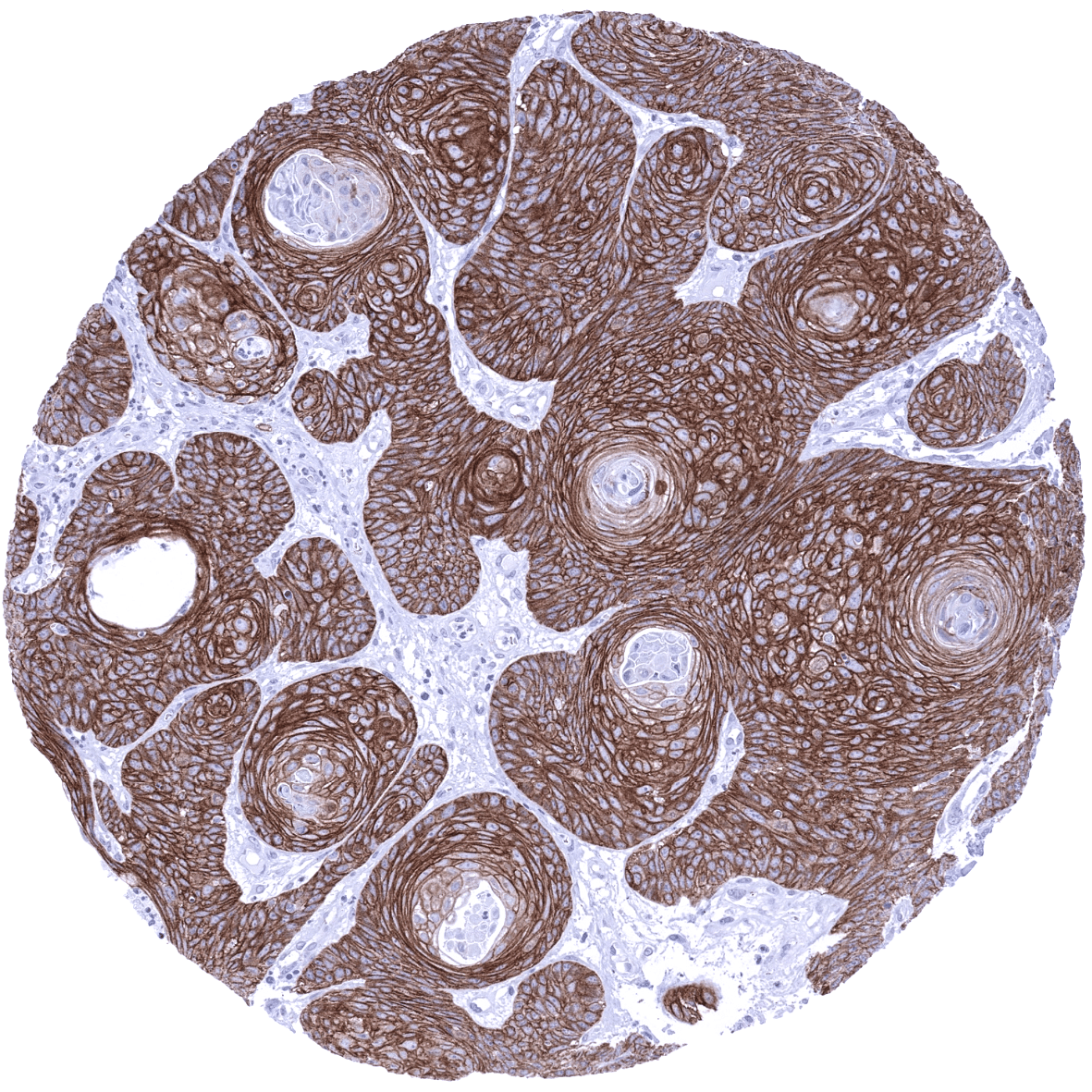
Positive control = Tonsil: A strong membranous and cytoplasmic TRIM29 immunostaining should be seen in squamous epithelial cells.
Negative control = Tonsil: All non-epithelial cells must not show any TRIM29 immunostaining.
Cellular localization = Cytoplasmic and cell surface.
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100-200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
TRIM29 is a multifunctional protein with a role in cancer biology and antiviral innate immunity.
Biology Behind
Tripartite motif proteins (TRIM) embody a family of proteins that contain a RING-Bbox-Coiled Coil motif followed by different C-terminal domains. TRIM family proteins are involved in important cellular processes such as intracellular signaling in innate immunity and carcinogenesis. TRIM29, a 66 kDa protein coded by the TRIM29 gene on the 11q23 is a member of the TRIM protein family. It is an E3 ubiquitin ligase which employs the B-box domain to catalyze substrate ubiquitination instead of the typical RING domain. TRIM29 induced post-translational modifications are involved in diverse signaling events and play a role in a wide range of different cellular processes such as DNA damage response, cancer development and progression, cell adhesion/tumor invasion, autophagy, cell differentiation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and antiviral innate immunity. TRIM29 interacts with multiple different pathways including the Wnt and the PKC–NF-κB signaling pathways. In normal tissues, TRIM29 expression has preferentially been found in squamous epithelial cells and urothelium. Increased expression of TRIM29 has been described in many different cancer types and – depending on the tumor type – both high and low levels of expression have been found to be associated with poor patient prognosis.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
TRIM29 immunostaining is always membranous and cytoplasmic but not nuclear. A strong TRIM29 immunostaining occurs in all squamous epithelia (intensity can decrease towards the surface in some samples, keratin layer is negative), sebaceous glands, squamous epithelium of tonsil and of corpuscles of Hassal’s, urothelium (umbrella cells are negative or only weakly positive) as well as in amnion cells und chorion cells of the placenta. A weak to moderate TRIM29 immunostaining occurs in excretory ducts and myoepithelial cells of breast, salivary and bronchial glands, basal membranes of the cytotrophoblast of the placenta, as well as in basal cells of the prostate, epididymis, seminal vesicles and the endocervix. A weak to moderate TRIM29 staining could occasionally be seen in colon epithelium (one positive gland in one sample) as well as in scattered epithelial cells of the adenohypophysis. TRIM29 staining is not seen in stomach, ileum, duodenum, neurohypophysis, brain, skeletal, heart and smooth muscle, fat, thyroid, parathyroid gland, adrenal gland, ovary, endometrium, fallopian tube, lung, testis, kidney, Brunner gland, colon, appendix, gallbladder, liver, and the pancreas as well in lymphocytes and hematopoietic cells.
A very faint staining of ganglion structures in the gastrointestinal muscular wall and of islet cells of pancreas can occasionally be seen. These findings are not consistent with data obtained by independent antibodies and may thus constitute a (tolerable) antibody cross-reactivity.
These findings are largely consistent with the RNA and protein data described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression TRIM29)
Positive control: Tonsil: A strong membranous and cytoplasmic TRIM29 immunostaining should be seen in squamous epithelial cells.
Negative control: Tonsil: All non-epithelial cells must not show any TRIM29 immunostaining.
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
The TCGA database on RNA expression in cancer has described particularly high levels of TRIM29 RNA in cervical, head & neck, and urothelial carcinomas. However, individual cases with high level TRIM29 expression were also described in most other analyzed tumor entities, including lung, colorectal, gastric, pancreatic, breast, endometrial and ovarian cancers.
The TCGA findings on TRIM29 RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Compatibility of Antibodies
No data available at the moment
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image gallery are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 7,8 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply MSVA-629M at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Agilent / Dako – Autostainer Link 48
Pretreatment in PT-Link for 30 minutes at 95°C (pH high); FLEX peroxidase blocking for 5 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-629M 1:150 for 20 minutes (room temperature), FLEX+ mouse/rabbit (LINKER) for 15 minutes (room temperature), horseradish peroxidase (HRP) for 20 minutes (room temperature), FLEX DAB+Sub-Chromo for 10 minutes (room temperature), FLEX hematoxylin for 5 minutes (room temperature).
These images reflect stainings by the protocol described above. It is of note that a comparable staining result can also be obtained by different protocols. In general, a longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, and a longer incubation time of FLEX+LINKER result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining. Modifications of the protocol with a strengthening effect on staining intensity in combination with changes of other parameters that result in lower staining intensity can result in a comparable result as shown above.
Leica – BOND RX
Dewax at 72°C for 30 seconds; Pretreatment in Bond Epitope Retrieval Solution (ER2 – EDTA pH9) for 20 minutes at 100°C; Peroxidase blocking for 5 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-629M 1:150 for 15 minutes (room temperature), Post primary (rabbit anti mouse) for 8 minutes (room temperature), Polymer (goat anti rabbit) for 8 minutes (room temperature), mixed DAB refine for 10 minutes (room temperature), hematoxylin for 5 minutes (room temperature).
These images reflect stainings by the protocol described above. It is of note that a comparable staining result can also be obtained by different protocols. In general, a longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, a higher temperature during incubation, and a longer incubation time of Post primary and or the Polymer result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining. Modifications of the protocol with a strengthening effect on staining intensity in combination with changes of other parameters that result in lower staining intensity can result in a comparable result as shown above.
Roche – Ventana Discovery ULTRA
Pretreatment for 64 minutes at 100°C (pH 8,4); CM peroxidase blocking for 12 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-629M 1:150 for 20 minutes at 36°C, secondary antibody (anti-mouse HQ) for 12 minutes at 36°C, anti-HQ HRP for 12 minutes at room temperature, DAB at room temperature, hematoxylin II at room temperature for 8 minutes, bluing reagent at room temperature for 4 minutes.
These images depict staining results obtained by the protocol described above. It is of note, that the Ventana machines generally require higher antibody concentrations than other commonly used autostainers because the antibodies are automatically diluted during the procedure. Various other protocols can result in an identical result as shown above. A longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, a higher temperature during incubation, and a longer incubation time of secondary antibody and or the anti-HQ HRP result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining.
Potential Research Applications
- The prevalence and clinical significance of TRIM29 expression in cancer is unknown.
- The role of TRIM29 in immune responses and in immuno oncology is still unclear
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
There are two ways how the specificity of antibodies can be documented for immunohistochemistry on formalin fixed tissues. These are: 1. comparison with a second independent method for target expression measurement across a large number of different tissue types (orthogonal strategy), and 2. Comparison with one or several independent antibodies for the same target and showing that all positive staining results are also seen with other antibodies for the same target (independent antibody strategy).
Orthogonal validation: Specificity of the antibody MSVA-629M for TRIM29 is suggested by the high concordance of its immunostaining pattern with data from three independent RNA screening studies, including the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) RNA-seq tissue dataset, the FANTOM5 project, and the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project, which are all summarized in the human protein atlas Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression TRIM29). Immunostaining by MSVA-629M is detected in all analyzed organs with documented TRIM29 RNA expression (salivary gland, esophagus, bladder, thymus, tonsil, prostate, seminal vesicles, epididymis, breast, skin, placenta). The additional focal staining of selected cell types in respiratory epithelium and of scattered cells in some samples of colon mucosa and the adenohypophysis can be explained by the low overall quantity of these cell types in their respective organs. It is thus very likely, that TRIM29 expression was missed in these RNA analyses.
Comparison of antibodies: That true TRIM29 protein expression is detected by MSVA-629M is also suggested by the similar staining pattern observed by the independent antibody HPA020053 which was used for analyses in the context of the human protein atlas project.
Specifically, HPA020053 also identified TRIM29 immunostaining in basal cells of respiratory epithelium and some colorectal glands. The adenohypophysis was not analyzed by HPA020053, but an own staining with another independent antibody also identified some positive cells in the adenhypophysis sample found positive for MSVA-629M (images see below).
Antibody Comparison: MSVA-629 vs another independent TRIM29 antibody called “Validation Antibody 4r6 “