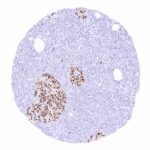
295,00 € – 995,00 €
Product details
Synonyms = AN2; Aniridia type II protein; Oculorhombin; Paired box gene 6 (aniridia keratitis); Paired box homeotic gene 6; Paired box protein Pax-6; Sey; WAGR
Antibody type = Mouse monoclonal / IgG
Clone = MSVA-706M
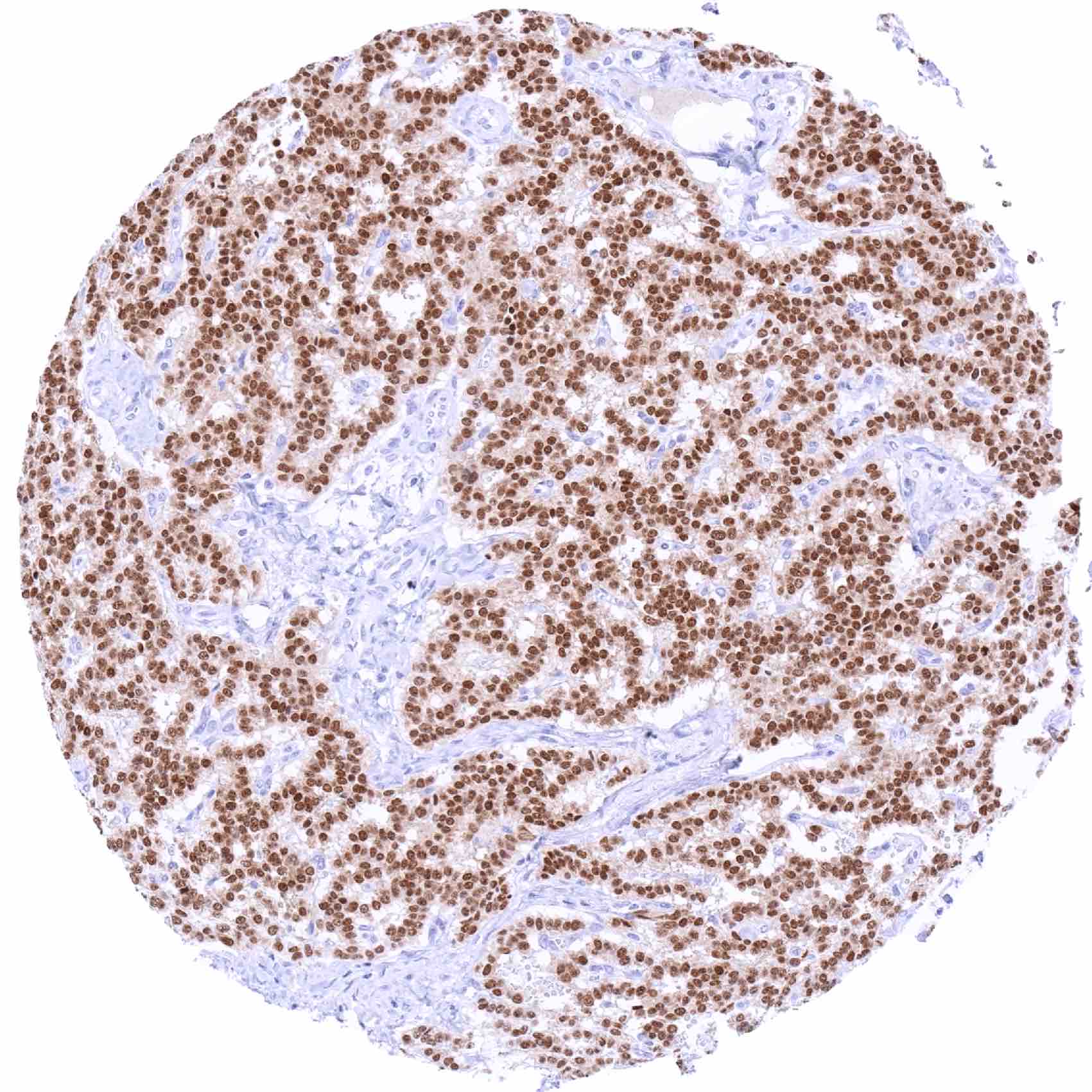
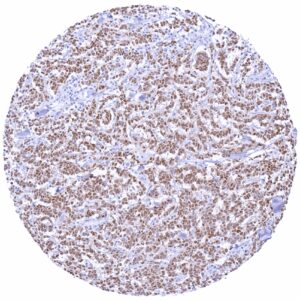
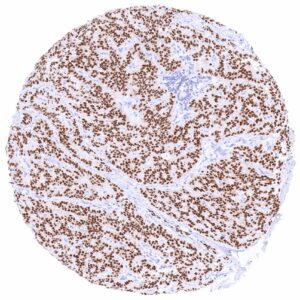
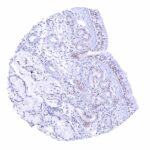
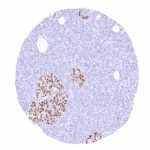
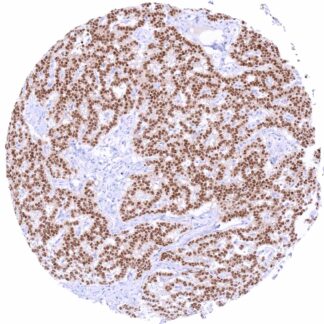
Positive control = Pancreas: A strong PAX6 positivity should be seen in the cells of islets of Langerhans.
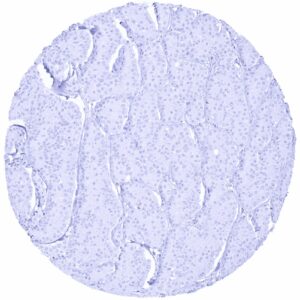
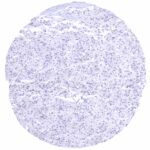
Negative control = Tonsil: PAX6 immunostaining should be absent in all cells.
Cellular localization = Nuclear
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100 – 1:200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
PAX6 is a pivotal protein for neural and pancreatic development.
Biology Behind
PAX6 (paired box protein 6) is a 46 KDa transcription factor protein coded by the PAX6 gene on chromosome 11p13. PAX6 is a key molecule for neural development. It is involved in the regulation of brain patterning and the balance between cell proliferation and neural differentiation in an appropriate manner to developmental timing. PAX6 also plays a role in the development of the pancreas, pituitary gland, and the testes. The function of the PAX6 protein and the factors that regulate its expression are not well known. In the cortex of the brain, PAX6 controls the responsiveness to some secreted molecules such as sonic hedgehog and BMP. Because of its critical role in eye development, the protein has also been termed aniridia type II protein (AN2) or oculorhombin. Heterozygous mutants produce a wide spectrum of ocular defects such as aniridia in humans. In animal models, mutations cause various neurodevelopmental disorders.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
Images describing the PAX6 staining pattern in normal tissues obtained by the antibody MSVA-706M are shown in our “Normal Tissue Gallery”.
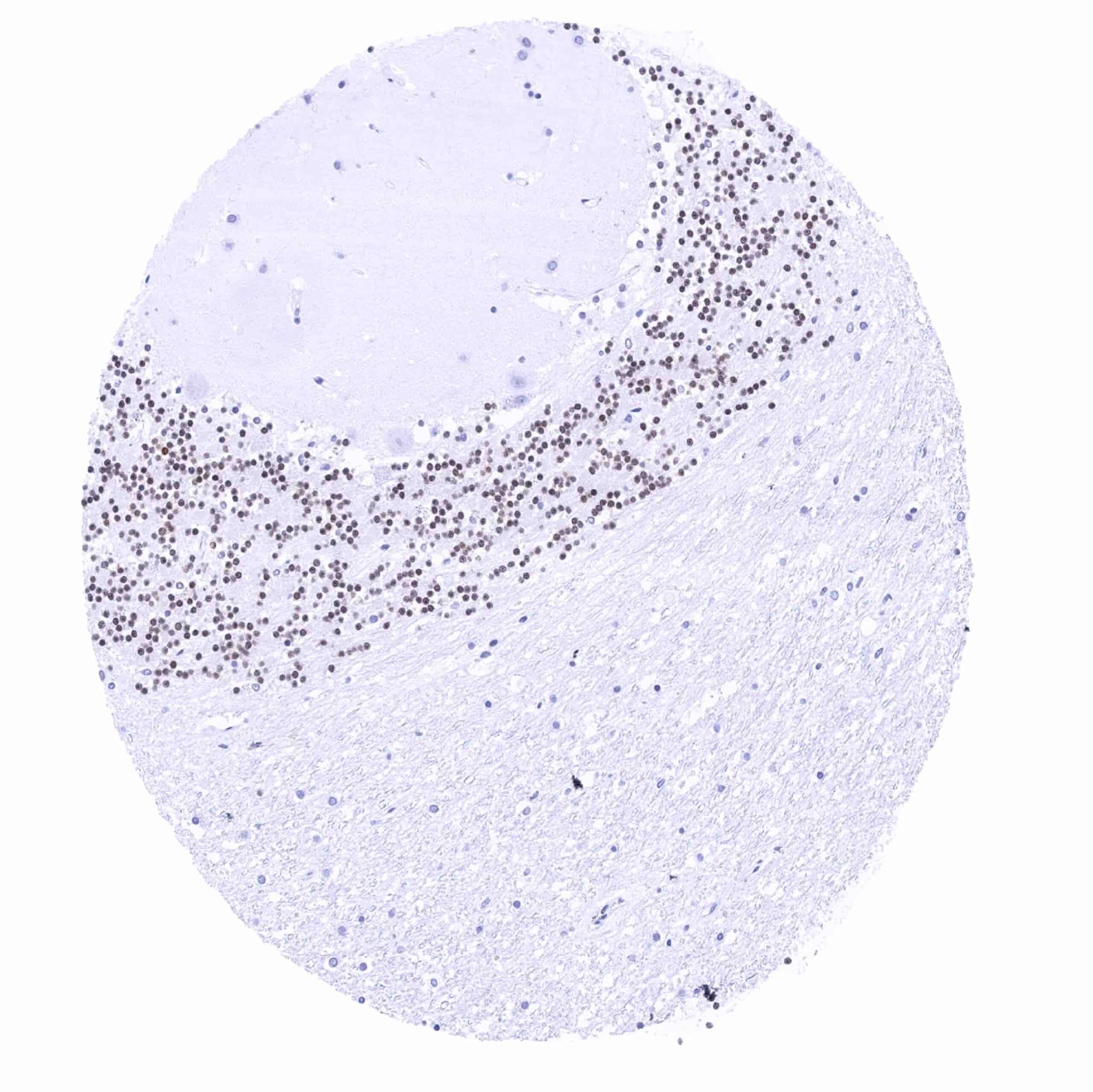
| Brain | Cerebrum | Nuclear Pax6 staining of some glia cells. |
| Cerebellum | Nuclear Pax6 staining of granule cells. | |
| Endocrine Tissues | Thyroid | Negative. |
| Parathyroid | Negative. | |
| Adrenal gland | Negative. | |
| Pituitary gland | Nuclear Pax6 staining of few epithelial cells in the adenohypophysis. | |
| Respiratory system | Respiratory epithelium | Moderate to strong nuclear Pax6 staining of respiratory epithelial cells and of adjacent glandular cells (especially in the paranasal sinus). |
| Lung | Negative. | |
| Gastrointestinal Tract | Salivary glands | Negative. |
| Esophagus | Negative. | |
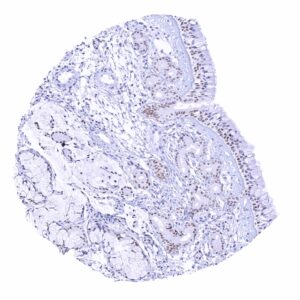
| Stomach | Nuclear Pax6 staining of few (neuroendocrine) cells. | |
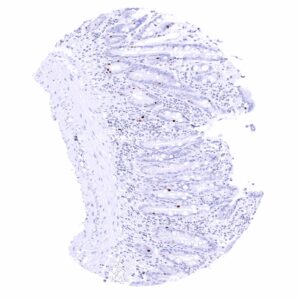
| Duodenum | Nuclear Pax6 staining of few (neuroendocrine) cells. | |
| Small intestine | Nuclear Pax6 staining of few (neuroendocrine) cells. | |
| Appendix | Nuclear Pax6 staining of few (neuroendocrine) cells. | |
| Colon | Nuclear Pax6 staining of few (neuroendocrine) cells. | |
| Rectum | Nuclear Pax6 staining of few (neuroendocrine) cells. | |
| Liver | Negative. | |
| Gallbladder | Negative. | |
| Pancreas | Negative. | |
| Genitourinary | Kidney | Negative. |
| Urothelium | Negative. | |
| Male genital | Prostate | Negative. |
| Seminal vesicles | Negative. | |
| Testis | Negative. | |
| Epididymis | Negative. | |
| Female genital | Breast | Negative. |
| Uterus, myometrium | Negative. | |
| Uterus, ectocervix | Negative. | |
| Uterus endocervix | Negative. | |
| Uterus, endometrium | Negative. | |
| Fallopian Tube | Negative. | |
| Ovary | Negative. | |
| Placenta early | Negative. | |
| Placenta mature | Negative. | |
| Amnion | Negative. | |
| Chorion | Negative. | |
| Skin | Epidermis | Negative. |
| Sebaceous glands | Negative. | |
| Muscle/connective tissue | Heart muscle | Negative. |
| Skeletal muscle | Negative. | |
| Smooth muscle | Negative. | |
| Vessel walls | Negative. | |
| Fat | Negative. | |
| Stroma | Negative. | |
| Endothelium | Negative. | |
| Bone marrow/ lymphoid tissue | Bone marrow | Negative. |
| Lymph node | Negative. | |
| Spleen | Negative. | |
| Thymus | Negative. | |
| Tonsil | Negative. | |
| Remarks |
These findings are largely consistent with the RNA data described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression PAX6)
All organs with documented PAX6 RNA expression (brain, pituitary gland, pancreas, stomach, duodenum, testis) showed IHC positivity for MSVA-706M which was restricted to specific cell types.
Positive control = Pancreas: A strong PAX6 positivity should be seen in the cells of islets of Langerhans.
Negative control = Tonsil: PAX6 immunostaining should be absent in all cells.
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
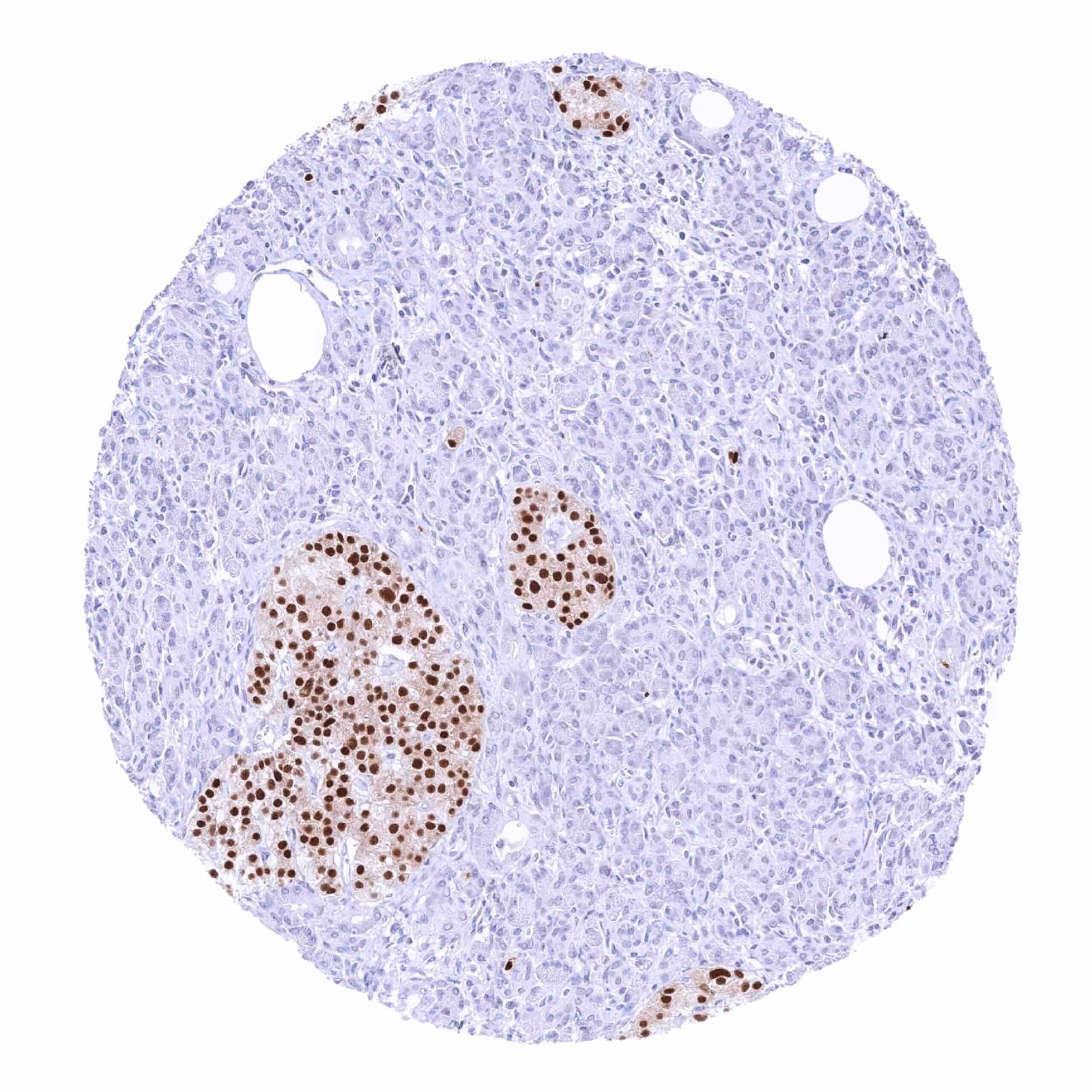
PAX6 immunostaining is particularly strong in neuroendocrine tumors derived from the pancreas and of other organs. PAX6 expression can – less frequently and usually at lower level – also occur in several other tumor entities.
The TCGA findings on PAX6 RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Compatibility of Antibodies
PAX6 (MSVA-706M) publication summary
Relevant publication: Lutz et al. “PAX6 is a useful marker for pancreatic origin of neuroendocrine neoplasms: A tissue microarray study evaluating more than 19,000 tumors from 150 different tumor types” Published in Hum Pathol. 2024 Dec;154:105695. Epub 2024 Nov 19. PMID: 39571690.
A total of 17’224 tumors were analyzed from 150 different tumor categories by using the following protocol: Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 7,8 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. MSVA-706M at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent). This protocol was also used for all stainings depicted in our tumor and normal tissue galleries.
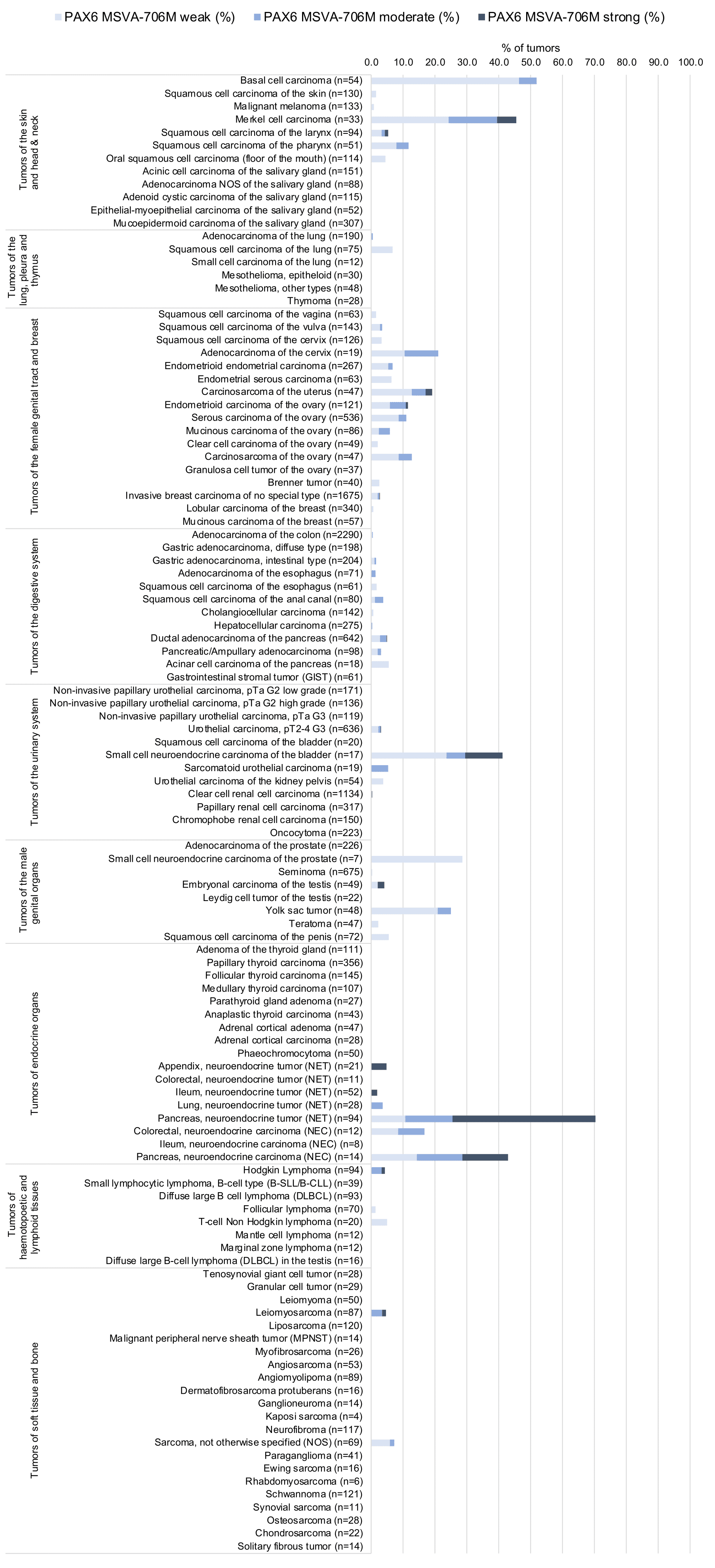
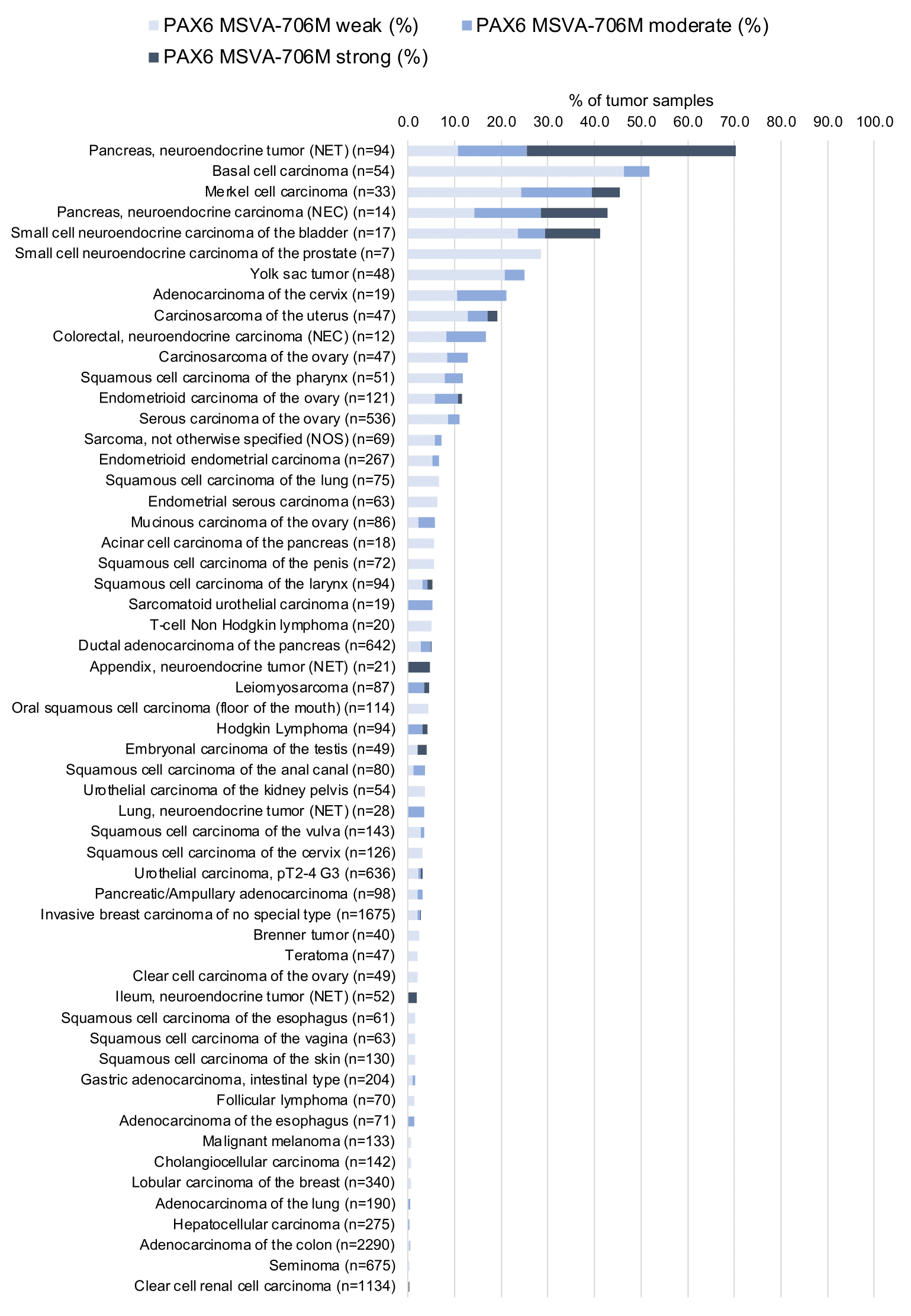
While 60 of 150 tumor categories contained at least one case with weak PAX6 expression there were only 16 tumor categories including at least 1 case with strong PAX6 positivity. The highest PAX6 positivity rates occurred in pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (42.9–70.8%), other neuroendocrine neoplasms (up to 50%), testicular tumors (up to 58%), basal cell carcinomas of the skin (51.9%), squamous cell carcinomas of different organs (1.5–11.8%), and in various gynecological tumors (up to 30%). The distribution of positive staining results is shown in “organ-systematic” and in “ranking order” figures below (images based on data from Lutz et al).
Authors conclusions on diagnostic utility of PAX6 IHC with respect to the distinction of different tumor entities (Lutz et al):
- Within neuroendocrine neoplasms, PAX6 immunostaining can be used to distinguish a pancreatic origin (mostly (69%) PAX6 positive) from tumors from other organs (mostly PAX6 negative)
- Pancreatic origin distinction by PAX6 is best supported in NETs for which extra-pancreatic PAX6 positivity occurred in only 3% of cases as compared to 25% of extra-pancreatic NECs.
- By utilizing GAD2 and progesterone receptor (PR) data from previous studies, it was found that combining PAX6 data with GAD2 and PR further increases the diagnostic performance of PAX6 and especially results in a very high specificity for pancreatic NET/NEC origin. A positivity of two of the three markers PR, PAX6 and GAD2 was associated with a pancreatic NET/NEC origin in >99% of cases. Moreover, only 14% of the 118 neuroendocrine neoplasms with negativity for all three antibodies were of pancreatic origin
Data from the publication: “PAX6 is a useful marker for pancreatic origin of neuroendocrine neoplasms: A tissue microarray study evaluating more than 19,000 tumors from 150 different tumor types”. Published by Lutz et al. in Hum Pathol. 2024 Dec;154:105695. Epub 2024 Nov 19. PMID: 39571690.
Summarized in own graphics:
1. PAX6 staining in tumors “organ-specific” with antibody MSVA-706M
2. PAX6 staining in tumors “ranking order” by positivity with antibody MSVA-706M
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image galleries are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 7,8 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply MSVA-706M at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Potential Research Applications
- The function of PAX6 and its interaction partners are unknown.
- The role of PAX6 in cancer needs to be further investigated.
- The diagnostic utility of PAX6 immunohistochemistry is unclear.
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
There are two ways how the specificity of antibodies can be documented for immunohistochemistry on formalin fixed tissues. These are: 1. Comparison with a second independent method for target expression measurement across a large number of different tissue types (orthogonal strategy), and 2. Comparison with one or several independent antibodies for the same target and showing that all positive staining results are also seen with other antibodies for the same target (independent antibody strategy).
Orthogonal validation: For the antibody MSVA-706M, specificity is suggested by the strong concordance of the immunostaining data with data from three independent RNA screening studies, including the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) RNA-seq tissue dataset, the FANTOM5 project, and the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project, which are all summarized in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression PAX6). Most organs with documented PAX6 RNA expression (brain, pituitary gland, pancreas, stomach, duodenum) showed IHC positivity for MSVA-706M. positivity. Additional PAX6 staining was detected by MSV-xxx in neuroendocrine cells in other gastrointestinal mucosa samples. Given the small number of PAX6 positive cells in these tissues, PAX6 RNA probably remained undetected in analyses involving large tissue samples. Despite of some PAX6 RNA expression in normal testis, MSVA-706M did not show any staining of testicular structures.
Comparison of antibodies: True expression of PAX6 in all cell types for which a nuclear PAX6 staining had been detected by MSVA-706M (brain, pituitary gland, pancreas, gastrointestinal mucosa, paranasal sinus mucosa) was confirmed by comparison with a commercially available independent second antibody (termed “validation antibody”). Similar as MSVA-706M, the validation antibody did not stain any testicular structures.