295,00 € – 995,00 €
Product details
Synonyms = DNA mismatch repair protein Msh6; G/T mismatch-binding protein; GTBP; GTMBP; hMSH6; HNPCC5; HSAP; MSH6; mutS (E. coli) homolog 6; MutS alpha 160kDa subunit; MutS-alpha 160kDa subunit; p160; Sperm associated protein
Antibody type = Recombinant Rabbit monoclonal / IgG
Clone = MSVA-906R
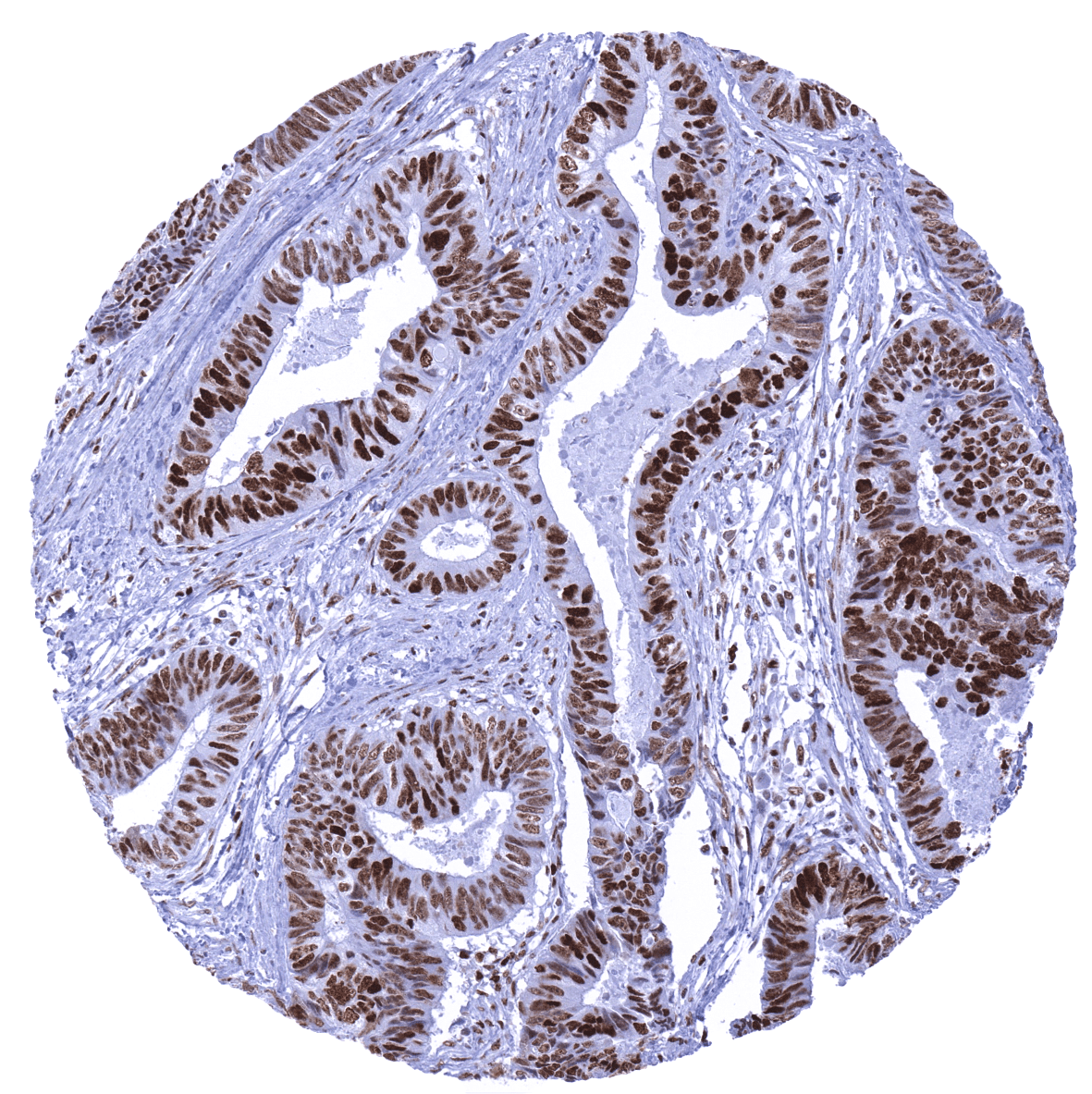
Positive control = Tonsil: Virtually all mantle zone B-cells must show an at least weak to moderate nuclear staining. A moderate to strong nuclear staining must be seen in the germinal centre B-cells.
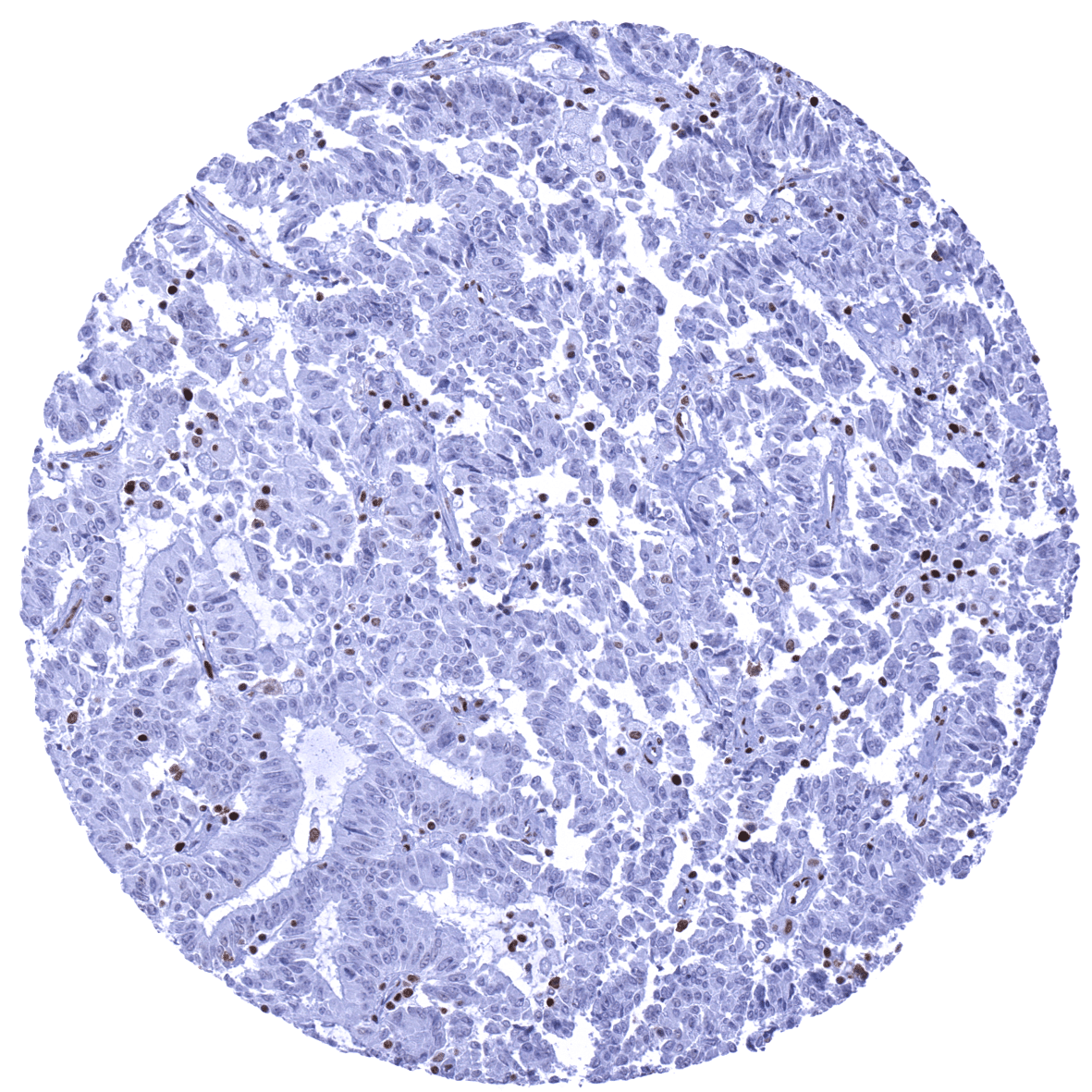
Negative control = Colon adenocarcinoma with previously documented loss of MSH6 expression: Nuclear staining should be absent in cancer cells, while a nuclear staining must be seen in stromal and inflammatory cells.
Cellular localization = Nuclear
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
MSH6 is a pivotal protein for DNA mismatch repair.
Biology Behind
MSH6 is a 160 kDa protein coded by the MSH6 gene at 2p16.3 The MSH6 protein belongs to the Mutator S (MutS) family of proteins that play a key role in DNA damage repair. DNA mismatches commonly occur as a result of DNA replication errors, genetic recombination, or other chemical and physical factors. Recognizing those mismatches and repairing them is extremely important for cells and a failure to do so results in microsatellite instability. MSH6 combines with MSH2 to form the active protein complex, hMutS alpha. MSH6 only functions when bound to the MSH2 protein as a heterodimer, although MSH2 itself can function as a homomultimer or as a heterodimer with MSH3. When a G/T mismatch is recognized, hMutS alpha complex binds and exchanges ADP for ATP. This leads to a conformational change which helps trigger downstream events to repair the damaged DNA. In contrast to other mismatch repair genes, mutations in hMSH6 cause only a modest mutator phenotype. Defects in hMSH6 are associated with atypical hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer not fulfilling the Amsterdam criteria for HNPCC.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
A nuclear MSH6 immunostaining is seen in virtually all cells. The highest levels of MSH6 expression are seen in lymphocytes of the cortex of the thymus. In the gastrointestinal tract, surface epithelial cells and the stomach glands show the lowest staining levels. MSH6 immunostaining is largely absent in the brain. Here only glial cells and vessels may show a rather weak staining.
These findings are largely comparable to the RNA and protein data described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression MSH6)
Suggested positive tissue control: Tonsil: Virtually all mantle zone B-cells must show an at least weak to moderate nuclear staining. A moderate to strong nuclear staining must be seen in the germinal centre B-cells.
Suggested negative tissue control: Colon adenocarcinoma with previously documented loss of MSH6 expression: Nuclear staining should be absent in cancer cells, while a nuclear staining must be seen in stromal and inflammatory cells.
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
Most tumors show a nuclear MSH6 immunostaining of variable intensity. A loss of MSH6 indicating a mismatch repair deficiency can occur in many different tumor types. A loss of MSH6 most commonly occurs in combination with a loss of MSH2. Colorectal adenocarcinoma, gastric adenocarcinoma, and endometroid carcinomas of the uterus and the ovary show the highest rates of mismatch repair deficiency (5-15%). Mismatch repair deficiency can also occur in virtually all other tumor entities, typically at a frequency of 0,5-2%.
The TCGA findings on MSH6 RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Compatibility of Antibodies
No data available at the moment
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image gallery are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 7,8 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply MSVA-906R at a dilution of 1:100 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Agilent / Dako – Autostainer Link 48
Pretreatment in PT-Link for 30 minutes at 95°C (pH high); FLEX peroxidase blocking for 5 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-906R 1:50 for 20 minutes (room temperature), FLEX+ mouse/rabbit (LINKER) for 15 minutes (room temperature), horseradish peroxidase (HRP) for 20 minutes (room temperature), FLEX DAB+Sub-Chromo for 10 minutes (room temperature), FLEX hematoxylin for 5 minutes (room temperature).
These images reflect stainings by the protocol described above. It is of note that a comparable staining result can also be obtained by different protocols. In general, a longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, and a longer incubation time of FLEX+LINKER result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining. Modifications of the protocol with a strengthening effect on staining intensity in combination with changes of other parameters that result in lower staining intensity can result in a comparable result as shown above.
Leica – BOND RX
Dewax at 72°C for 30 seconds; Pretreatment in Bond Epitope Retrieval Solution (ER2 – EDTA pH9) for 20 minutes at 100°C; Peroxidase blocking for 5 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-906R 1:50 for 15 minutes (room temperature), Post primary (rabbit anti mouse) for 8 minutes (room temperature), Polymer (goat anti rabbit) for 8 minutes (room temperature), mixed DAB refine for 10 minutes (room temperature), hematoxylin for 5 minutes (room temperature).
These images reflect stainings by the protocol described above. It is of note that a comparable staining result can also be obtained by different protocols. In general, a longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, a higher temperature during incubation, and a longer incubation time of Post primary and or the Polymer result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining. Modifications of the protocol with a strengthening effect on staining intensity in combination with changes of other parameters that result in lower staining intensity can result in a comparable result as shown above.
Potential Research Applications
- The clinical relevance of MSH6 expression levels in cancer is not clear. Particularly high levels of MSH6 have been suggested to be linked with poor prognosis in certain cancers.
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
There are two ways, how the specificity of antibodies can be documented for immunohistochemistry on formalin fixed tissues. These are: 1. comparison with a second independent method for target expression measurement across a large number of different tissue types (orthogonal strategy), and 2. Comparison with one or several independent antibodies for the same target and showing that all positive staining results are also seen with other antibodies for the same target (independent antibody strategy).
Orthogonal validation: The staining pattern the antibody MSVA-906R is consistent with the RNA expression data derived from the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) RNA-seq tissue dataset, the FANTOM5 project, and the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project which are all summarized in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression MSH6). However, since virtually all tissues were found positive by both methods, this concordance of data per se not very ascertaining.
Comparison of antibodies: The patterns of immunostaining obtained by using MSVA-906R was largely identical with findings obtained by CAB070870, an antibody used for MSH6 protein analysis in the human protein atlas.