Product details
Synonyms = KI-67; Ki67; KI-67 Antigen (KIA); MKI67; Proliferation related Ki-67 antigen
Antibody type = mouse monoclonal / IgG1, kappa
Clone = MSVA-267M
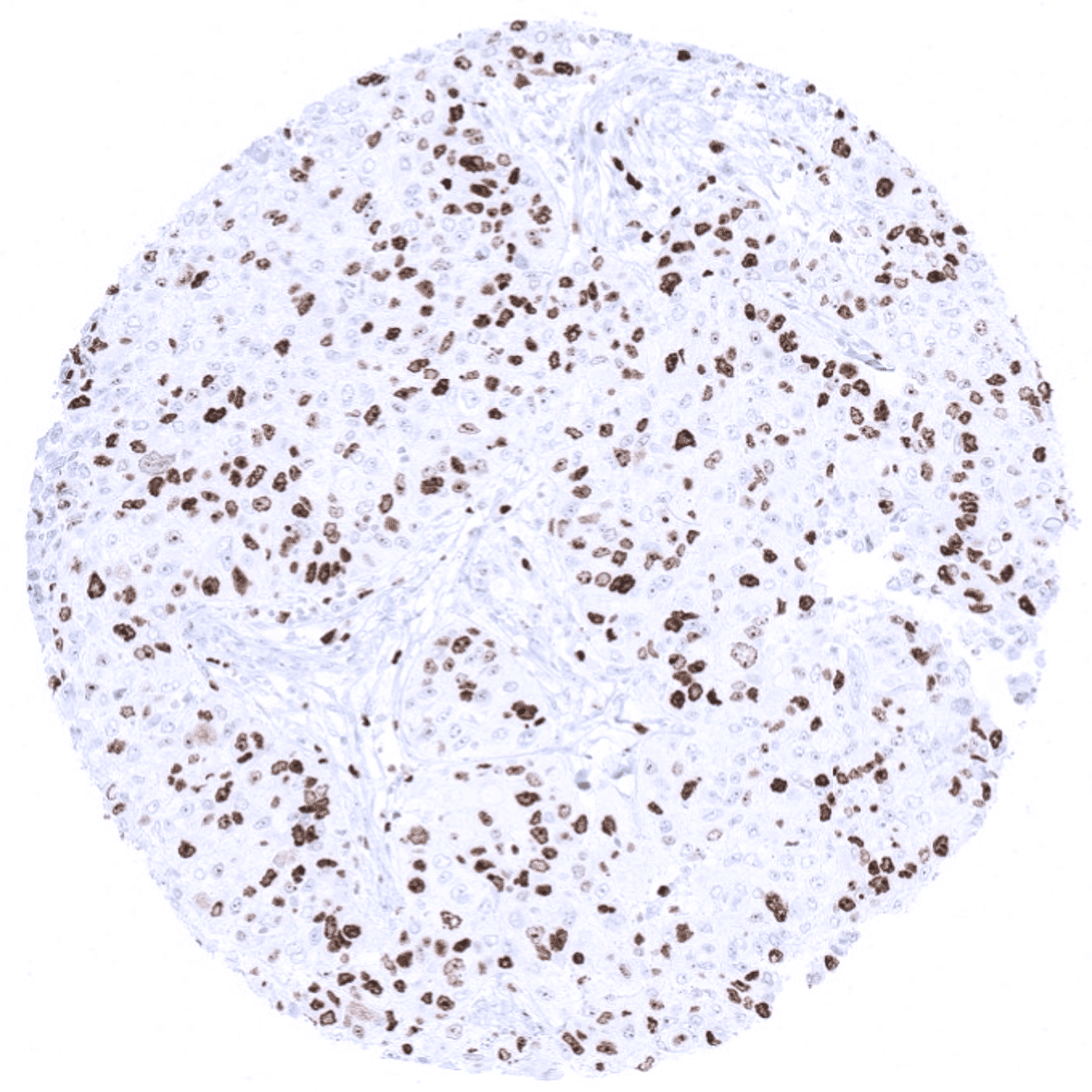
Positive control = tonsil (moderate to strong nuclear staining in 80-90% of the germinal centre B-cells and in the vast majority of the suprabasal squamous epithelial cells).
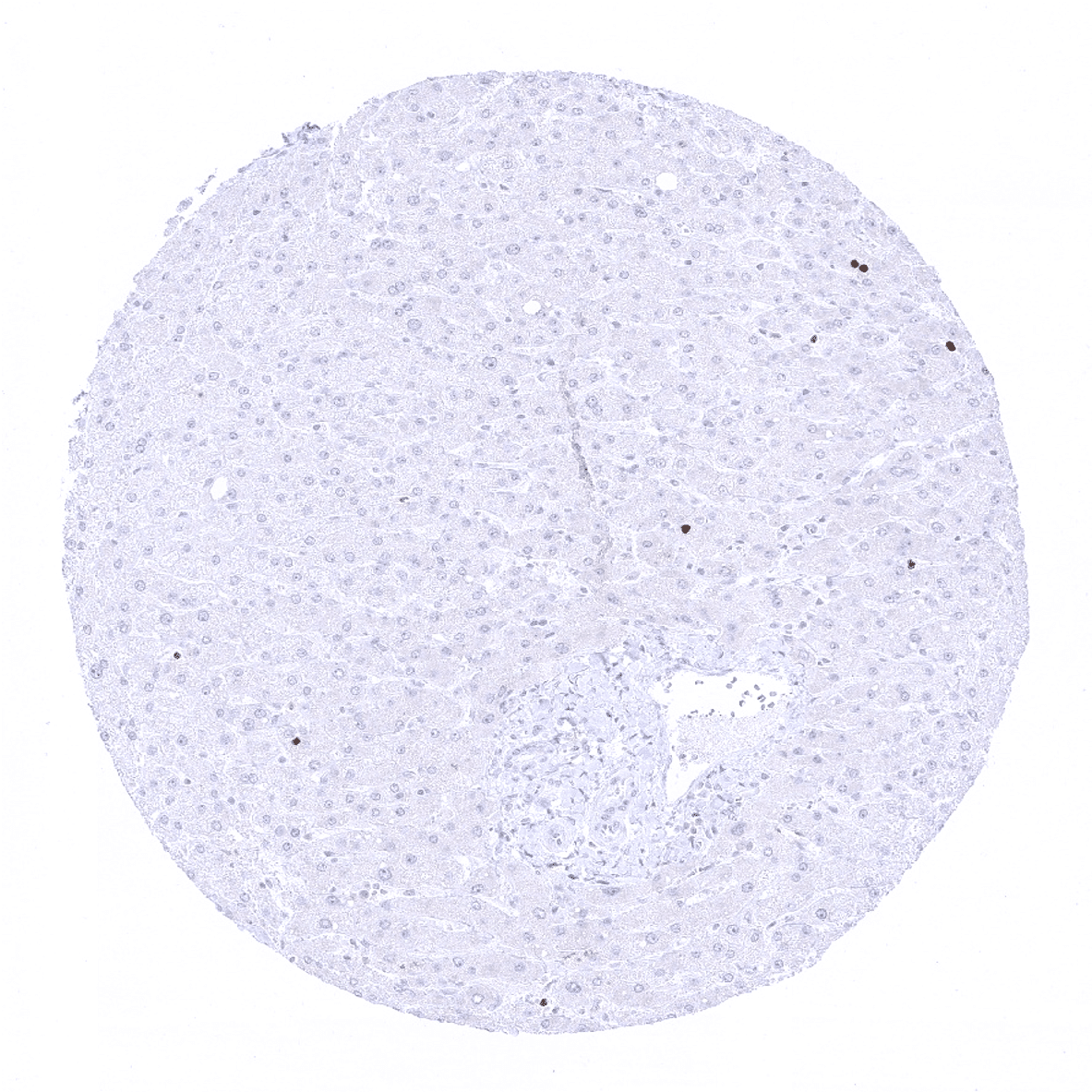
Negative control = liver (nuclear staining reaction only in scattered hepatocytes (<1%), cytoplasmic staining is absent or only weak)
Cellular localization = Nuclear
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100 – 1:200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
Biology Behind
The Ki67 protein is a labile, non-histone nuclear protein expressed in G1, S, G2 and M phases of the cell cycle, then rapidly catabolized at the end of M phase and not detectable in G0 and early G1 cells. When cells enter mitosis, chromosomes undergo chromosome condensation and are coated by a proteinaceous sheath termed the perichromosomal layer (PCL). The PCL comprises approximately one-third of the protein mass of mitotic chromosomes. Ki67 is one of the earliest proteins associated with the PCL and critical for its formation. Ki67 remains on the PCL until telophase. The percentage of Ki67 positive (tumor) cells – also called Ki-67 labeling index (Ki67 LI) – is widely used for quantification of tumor cell proliferation.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
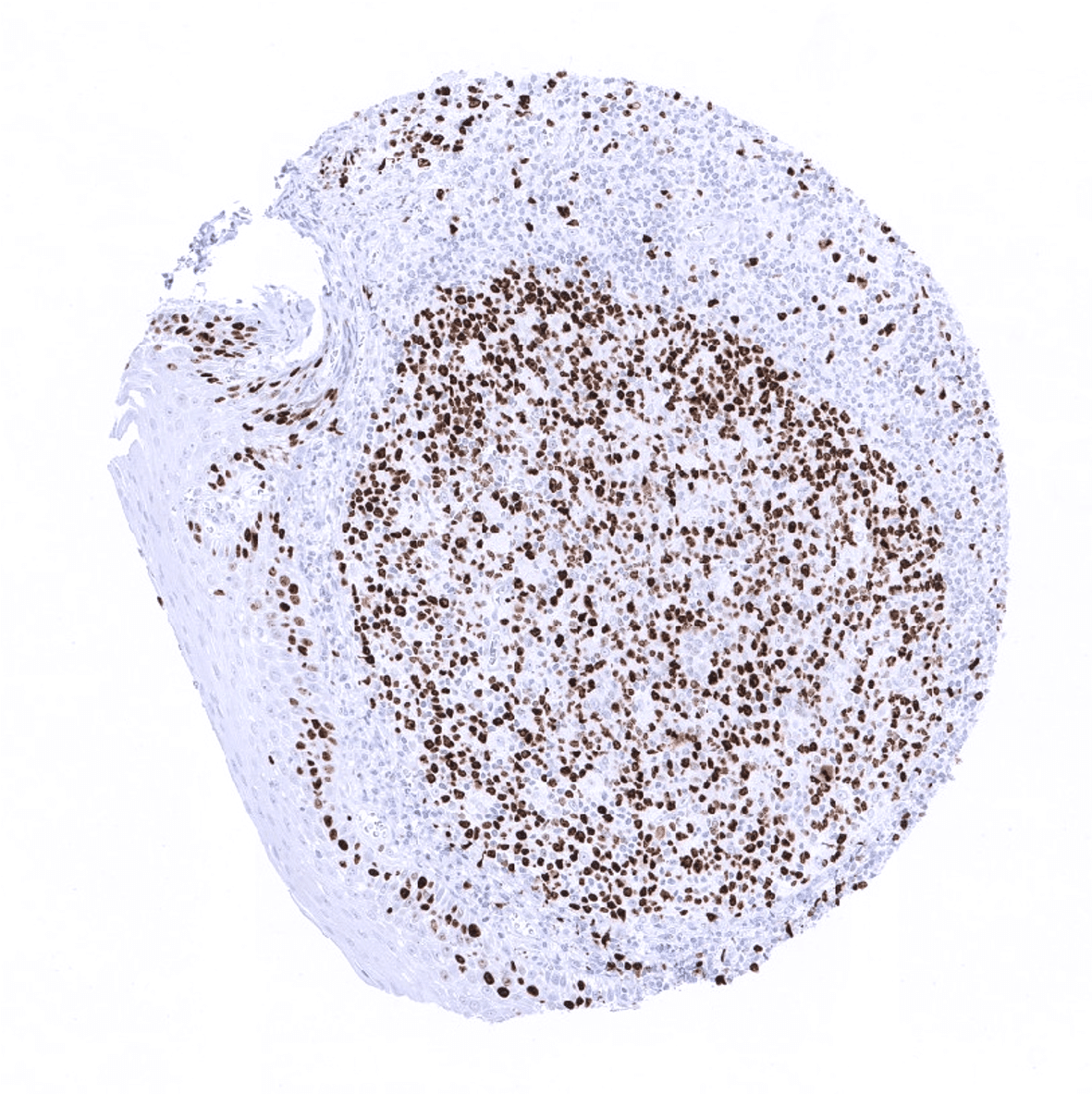
Using MSVA-267M, Ki67 positive cells can be seen in the vast majority of tissues. The number of Ki67 positive cells depends on the proliferative activity, which is particularly high in the thymus, germinal centres of lymphoid tissues, and in crypts of intestinal epithelium.
These findings obtained by MSVA-267M are largely similar as the protein data described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression Ki-67).
Suggested positive tissue control: tonsil (moderate to strong nuclear staining in 80-90% of the germinal centre B-cells and in the vast majority of the suprabasal squamous epithelial cells).
Suggested negative tissue control: liver (Nuclear staining reaction only in scattered hepatocytes (<1%), cytoplasmic staining is absent or only weak)
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
A variable fraction of Ki67 positive cells is seen in virtually every tumor. The percentage of positive tumors is highly variable both within and between tumor entities.
The TCGA findings on Ki-67 RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Compatibility of Antibodies
No data available at the moment
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in in our image galleries are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
Manual protocol
Freshly cut TMA sections are deparaffinized and exposed to heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 9 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Primary antibody specific against Ki67 protein (mouse monoclonal, MSVA-267M) is applied at 37°C for 60 minutes at a dilution of 1:150. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Agilent / Dako – Autostainer Link 48
Pretreatment in PT-Link for 30 minutes at 95°C (pH high); FLEX peroxidase blocking for 5 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-267M 1:150 for 20 minutes (room temperature), FLEX+ mouse/rabbit (LINKER) for 15 minutes (room temperature), horseradish peroxidase (HRP) for 20 minutes (room temperature), FLEX DAB+Sub-Chromo for 10 minutes (room temperature), FLEX hematoxylin for 5 minutes (room temperature).
These images reflect stainings by the protocol described above. It is of note that a comparable staining result can also be obtained by different protocols. In general, a longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, and a longer incubation time of FLEX+LINKER result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining. Modifications of the protocol with a strengthening effect on staining intensity in combination with changes of other parameters that result in lower staining intensity can result in a comparable result as shown above.
Leica – BOND RX
Dewax at 72°C for 30 seconds; Pretreatment in Bond Epitope Retrieval Solution (ER2 – EDTA pH9) for 20 minutes at 100°C; Peroxidase blocking for 5 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-267M 1:150 for 15 minutes (room temperature), Post primary (rabbit anti mouse) for 8 minutes (room temperature), Polymer (goat anti rabbit) for 8 minutes (room temperature), mixed DAB refine for 10 minutes (room temperature), hematoxylin for 5 minutes (room temperature).
These images reflect stainings by the protocol described above. It is of note that a comparable staining result can also be obtained by different protocols. In general, a longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, a higher temperature during incubation, and a longer incubation time of Post primary and or the Polymer result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining. Modifications of the protocol with a strengthening effect on staining intensity in combination with changes of other parameters that result in lower staining intensity can result in a comparable result as shown above.
Roche – Ventana Discovery ULTRA
Pretreatment for 64 minutes at 100°C (pH 8,4); CM peroxidase blocking for 12 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-267M 1:100 for 20 minutes at 36°C, secondary antibody (anti-mouse HQ) for 12 minutes at 36°C, anti-HQ HRP for 12 minutes at room temperature, DAB at room temperature, hematoxylin II at room temperature for 8 minutes, bluing reagent at room temperature for 4 minutes.
These images depict staining results obtained by the protocol described above. It is of note, that the Ventana machines generally require higher antibody concentrations than other commonly used autostainers because the antibodies are automatically diluted during the procedure. Various other protocols can result in an identical result as shown above. A longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, a higher temperature during incubation, and a longer incubation time of secondary antibody and or the anti-HQ HRP result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining.
Impact of pH
The strongest Ki67 staining by MSVA-267M is obtained at a pH 9,0. However, pH 7,8 results in only a slight reduction of the staining intensity as compared to pH9. We thus consider pH7,8 as optimal for manual staining because of the better tissue preservation at pH7,8 than at pH 9,0.
Potential Research Applications
- Ki67 is often used in studies employing multicolor-immunofluorescence.
- The prognostic role of Ki67 LI is established in many tumor types. Large-scale studies are still needed to exactly determine the practical clinical utility of KI67 measurement.
- Methods are needed for precise and automated Ki67 measurement in cancer tissues.
- The fraction of Ki67 positive lymphocyte subpopulations such as for example Ki67 positive CD8 positive cytotoxic T-lymphocytes is under intensive evaluation.
- The topographical distribution of Ki67 positive lymphocyte subtypes may be relevant.
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
Specificity of MSVA-267M is documented by strong positive nuclear staining in all mitoses and in a large fraction of cells in tissues known to proliferate rapidly. At the same time, staining is always absent in the cytoplasm and on membranes of any cells. The latter especially applies to tissues notorious for showing cytoplasmic background in IHC such as kidney, colonic mucosa, and epidermis.