295,00 € – 995,00 €
Product details
Synonyms = A2m Marker; Ig alpha 1 Chain C Region; Ig alpha 2 Chain C Region; IGHA1; IGHA2; Immunoglobulin Am1; Immunoglobulin Am2; Immunoglobulin Heavy Constant Alpha 1; Immunoglobulin Heavy Constant Alpha 2
Antibody type = Recombinant Rabbit monoclonal / Rabbit IgG
Clone = MSVA-700R
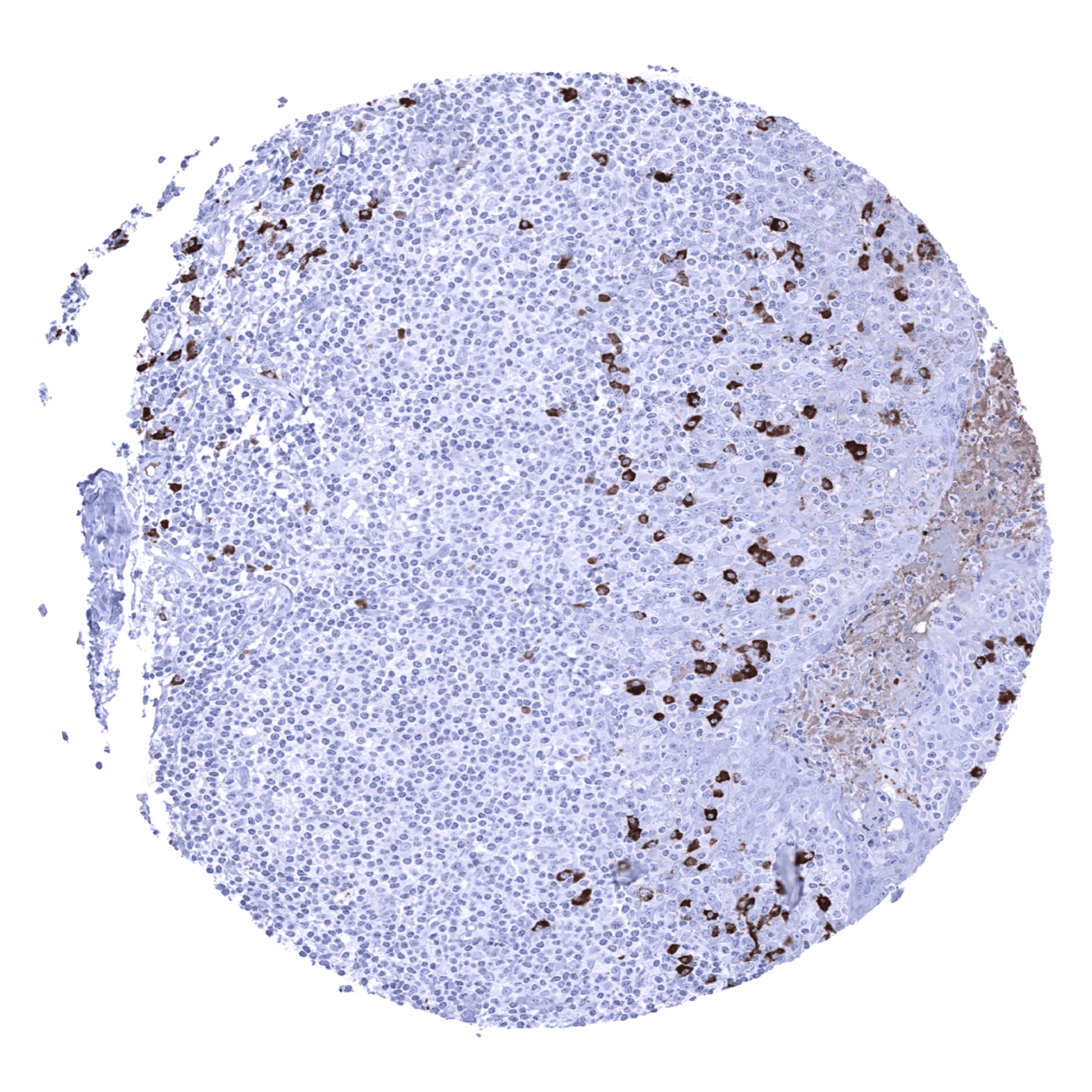
Positive control = Tonsil: A strong staining should be seen in a fraction of plasma cells.
Negative control = Tonsil: Lymphocytes should not stain for IgA.
Cellular localization = Cytoplasm, cell surface and secreted.
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100 – 1:200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
IgA is a pivotal molecule in the immune function of mucous membranes.
Biology Behind
IgA (Immunoglobulin A) has two subclasses (IgA1 and IgA2) which are both heavily glycosylated proteins. IgA1 and IgA2 can occur as monomers or dimers. The IgA dimeric form is secreted and represents an important component of body fluids such as tears, saliva, sweat, colostrum and secretions from the genitourinary tract, gastrointestinal tract, prostate and respiratory epithelium. Accordingly, IgA plays an important role in the immune function of mucous membranes. Most likely, IgA antigen binding helps to prevent passage of foreign structures into the circulatory system. The amount of IgA produced in association with mucosal membranes is substantial. For example, 3-5 grams of IgA are secreted into the intestinal lumen each day. This quantity makes up for up to 15% of total daily immunoglobulin production. The high prevalence of IgA in the mucus is a result of a cooperation between IgA producing plasma cells and mucosal epithelial cells that express polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR). IgA binds to the pIgR on the basolateral surface of epithelial cells, and is taken up into the cell via endocytosis. The receptor-IgA complex passes through the cellular compartments before being secreted on the luminal surface of the epithelial cells.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
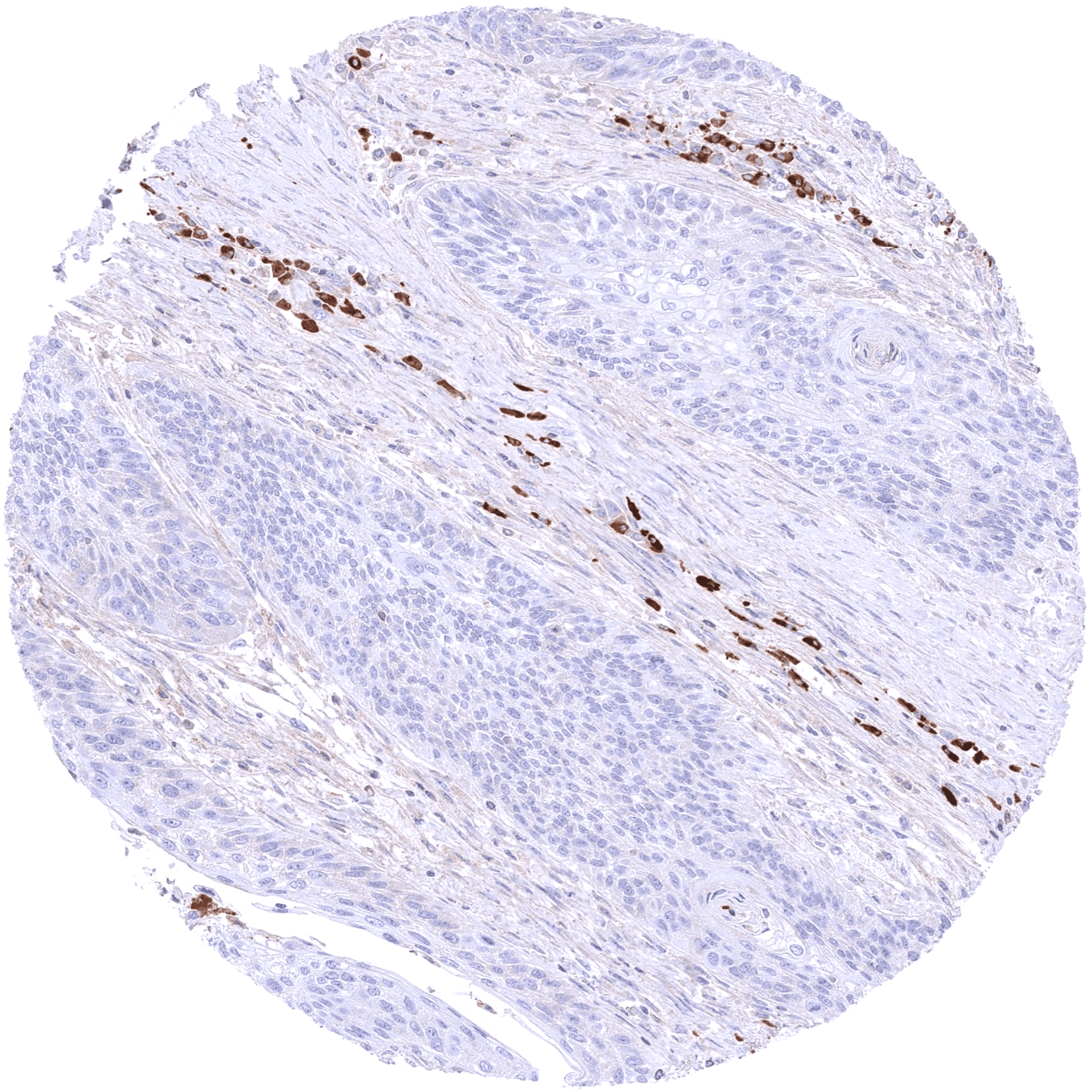
A strong cytoplasmic IgA immunostaining occurs in a fraction of plasma cells. The percentage of IgA positive plasma cells varies between tissues and is particularly high in the mucosa of diverse organs. In gastrointestinal and other epithelia, a cytoplasmic IgA staining is sometimes seen which often predominates in the basolateral compartment of the cells. In addition, a diffuse IgA staining is sometimes seen in mucus, blood vessels or in the stroma of areas of inflammation. This staining pattern represents soluble IgA derived from serum or body fluids.
RNA and protein expression data of IgA findings are also described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression IGHA1)
Suggested Positive control = Tonsil: A strong staining should be seen in a fraction of plasma cells.
Suggested Negative control = Tonsil: Lymphocytes should not stain for IgA.
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
A positive IgA immunostaining can be seen in few lymphomas and in a small fraction of plasmacytomas.
The TCGA findings on IGHA1 RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image galleries are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 7,8 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply MSVA-700R at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Potential Research Applications
- IgA plays a pivotal role in the immune function of mucous membranes.
- The role of IgA antibodies in various diseases awaits further investigation.
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
There are two ways how the specificity of antibodies can be documented for immunohistochemistry on formalin fixed tissues. These are: 1. Comparison with a second independent method for target expression measurement across a large number of different tissue types (orthogonal strategy), and 2. Comparison with one or several independent antibodies for the same target and showing that all positive staining results are also seen with other antibodies for the same target (independent antibody strategy).
Orthogonal validation: Orthogonal validation is not well applicable for IgA antibodies because of the ubiquitous presence of IgA expressing plasma cells in virtually all organs. Moreover, IgA expression data in normal tissues are unavailable in public databases.
Comparison of antibodies: A specific IgA staining of MSVA-700R in a subset of plasma cells, various epithelial cell types, mucus, blood vessels or in the stroma of areas of inflammation is corroborated by comparison with a commercially available independent second antibody (termed “validation antibody”). In this comparison, all stainings obtained by MSVA-700R were matched by the “validation antibody”. It is of note that the “validation antibody” – an IVDR RTU – shows an oversensitive staining in this analysis.