145,00 € – 595,00 €
Product details
Synonyms = Elastin; ELN; SVAS; Tropoelastin; WBS; WS
Antibody type = Recombinant Rabbit monoclonal / IgG
Clone = MSVA-648R
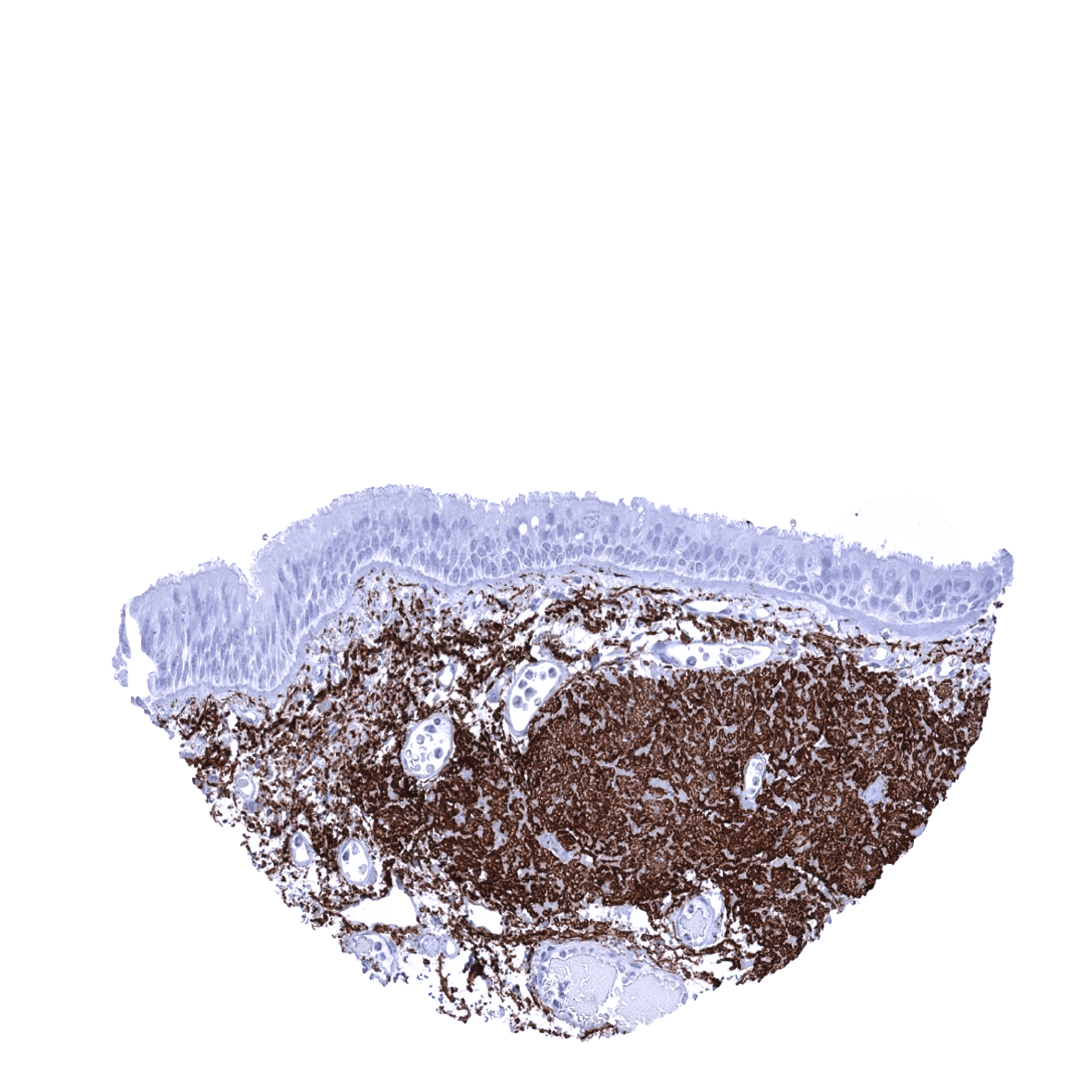
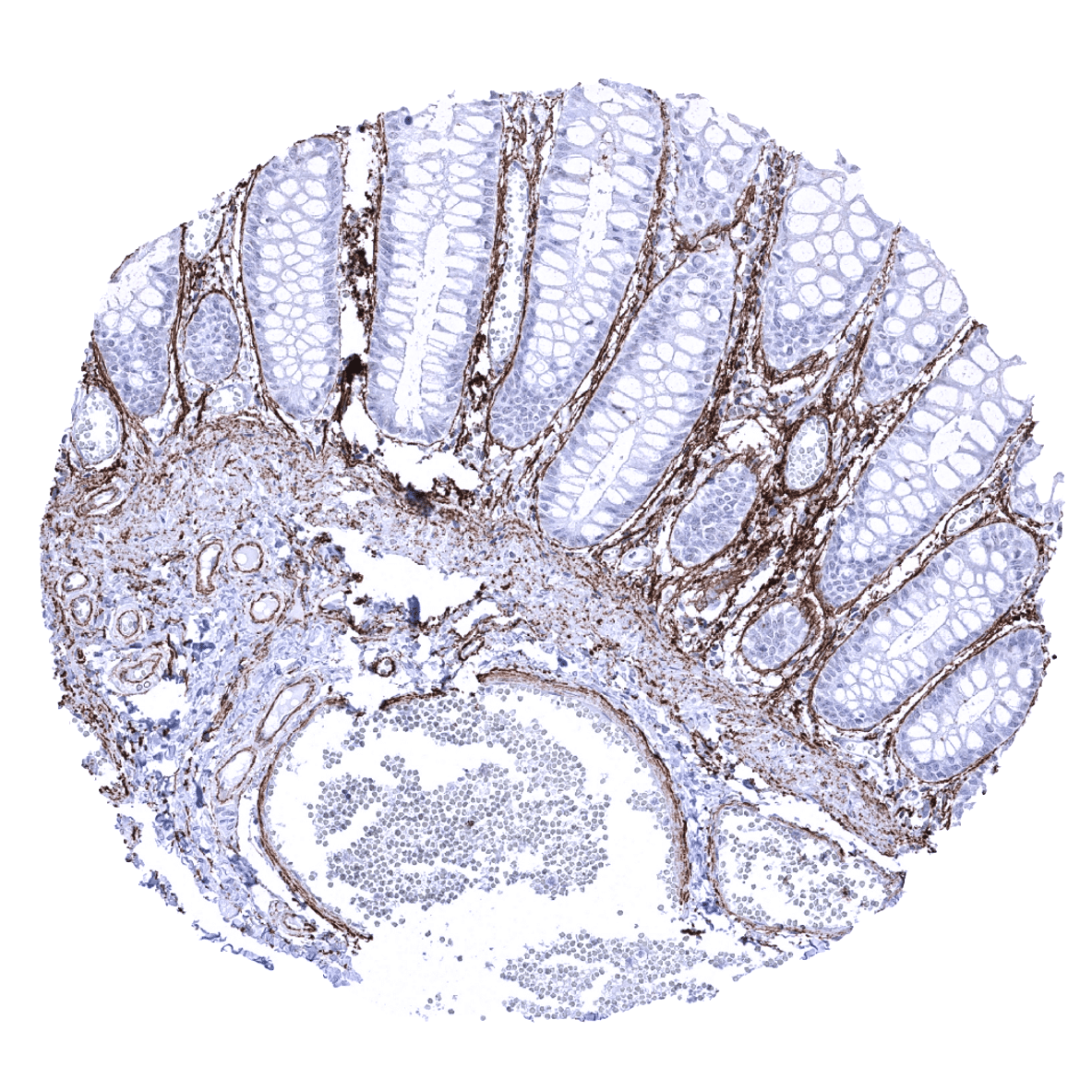
Positive control = Colon: A moderate to strong elastin immunostaining should be seen of fibres in the lamina propria, around smooth muscle cells of the muscularis mucosae, and in blood vessels (subendothelial).
Negative control = Colon: Elastin immunostaining should be absent in all epithelial cells.
Cellular localization = Extracellular.
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100 – 1:200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
Elastin is expressed in extracellular matrix and blood vessels.
Biology Behind
Elastin protein consists of a wide range of elastic peptide and protein sequences that exist in different lengths and with different compositions. Elastin is a pivotal element of the extracellular matrix. As elastin is about 1000 times more flexible than collagens, this protein assures tissue elasticity and provides resilience to tissues and organs. Elastin is the dominant extracellular matrix protein in extensible tissues. Related to the tissues dry weight, it constitutes for 50% of blood vessels, 70% of elastic ligaments, 30% of lungs, and 2–4% of the skin. Tropoelastin, the precursor of elastin, is derived from fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, chondrocytes, or endothelial cells before it is processed to elastin by cleavage of its signal peptide. Deletions and mutations in this gene are associated with supravalvular aortic stenosis (SVAS), the autosomal dominant cutis laxa, and the Williams–Beuren syndrome.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
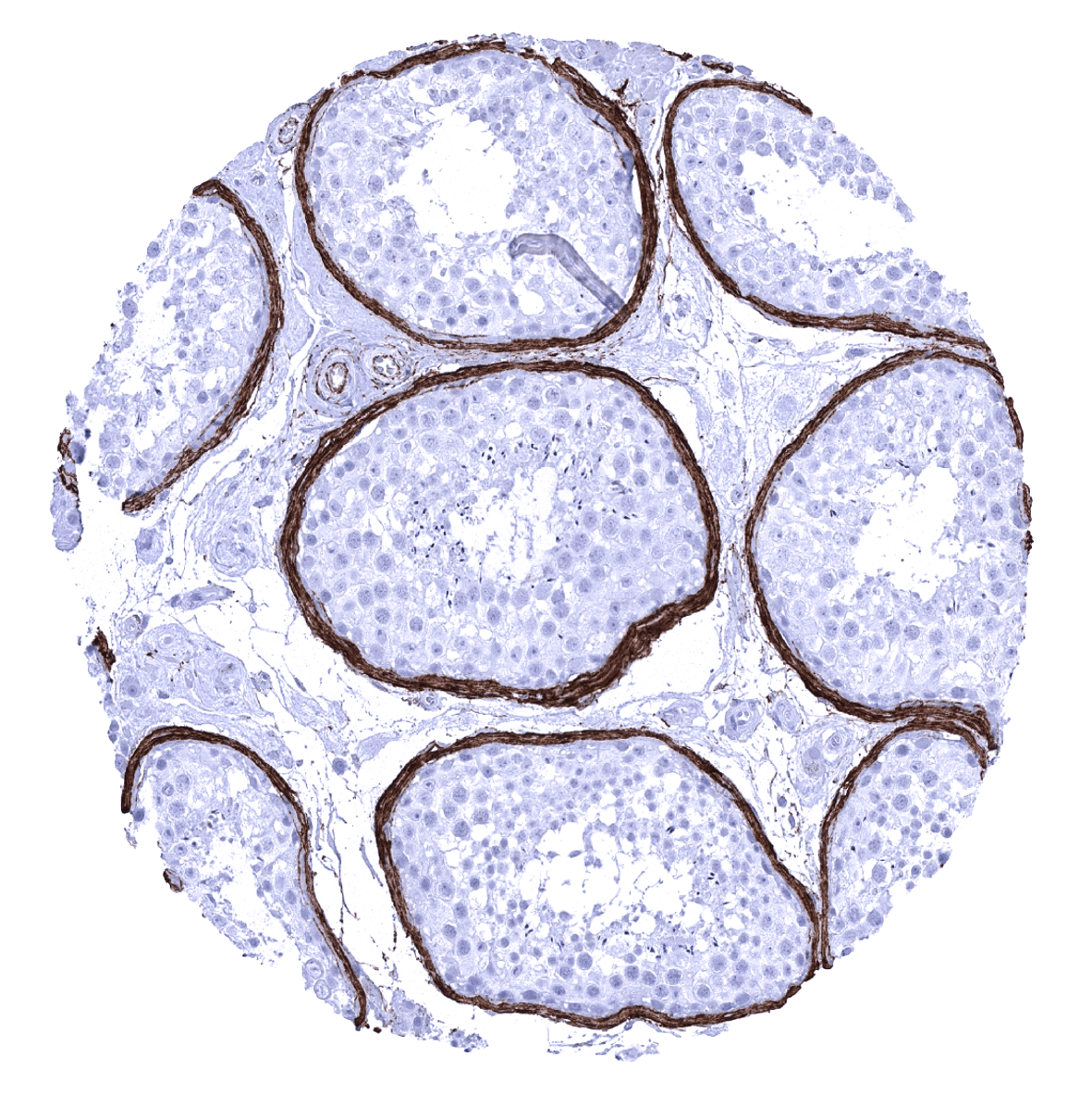
Elastin immunostaining is – to a variable extent – seen in the vast majority of tissues. Most abundantly it occurs in the media of the aorta and in vessels of the elastic type. A subendothelial band is seen in muscular type arteries and in veins. Elastin fibres typically surround muscle cells of all types including the myometrium. Organs with particular high elastin levels include lung, epididymis, and the gallbladder. Organs with particularly low levels of elastin include fat, placenta, kidney (except vessels), parathyroid gland, and the brain. In the liver, elastin only occurs around central veins and in portal fields.
These findings are largely consistent with the RNA and protein data described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression Elastin)
Positive control: Colon: A moderate to strong elastin immunostaining should be seen of fibres in the lamina propria, around smooth muscle cells of the muscularis mucosae, and in blood vessels (subendothelial).
Negative control: Colon: Elastin immunostaining should be absent in all epithelial cells.
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
In tumors, elastin immunostaining is preferentially seen in remnants of structures invaded by cancer and around vessels. Less commonly, newly formed elastin can be observed in the tumor stroma (stroma elastosis).
The TCGA findings on Elastin RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Compatibility of Antibodies
No data available at the moment
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image galleries are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
-Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 7,8 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply MSVA-648R at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Potential Research Applications
- Elastin is an abundant component of the extracellular matrix but never expressed in epithelial tissues. Elastin immunostaining may thus be used for tissue characterization in multicolor immunohistochemistry together with other markers.
- The role of stromal elastosis in cancer is unknown.
- The role of immunohistochemical assessment of elastin in heart disease, degenerative disorders and other diseases has not been extensively studied.
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
There are two ways how the specificity of antibodies can be documented for immunohistochemistry on formalin fixed tissues. These are: 1. comparison with a second independent method for target expression measurement across a large number of different tissue types (orthogonal strategy), and 2. Comparison with one or several independent antibodies for the same target and showing that all positive staining results are also seen with other antibodies for the same target (independent antibody strategy).
Orthogonal validation: is not suited for validation of targets such as extracellular matrix markers that are expressed in every organ.
Comparison of antibodies: Specific elastin staining by MSVA-648R was suggested by a complete absence of elastin immunostaining in epithelial cells and the fact, that all structures identified by a MSVA-648R were also stained by the antibody HPA018111 which was employed for analyses within the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression Elastin).