Product details
Synonyms = CD8 antigen, alpha polypeptide (p32), T8/Leu-2 T-lymphocyte differentiation antigen, Ly3, LYT3, MAL, T-cell surface glycoprotein CD8 alpha chain
Antibody type = Recombinant Rabbit monoclonal / IgG
Clone = MSVA-008R
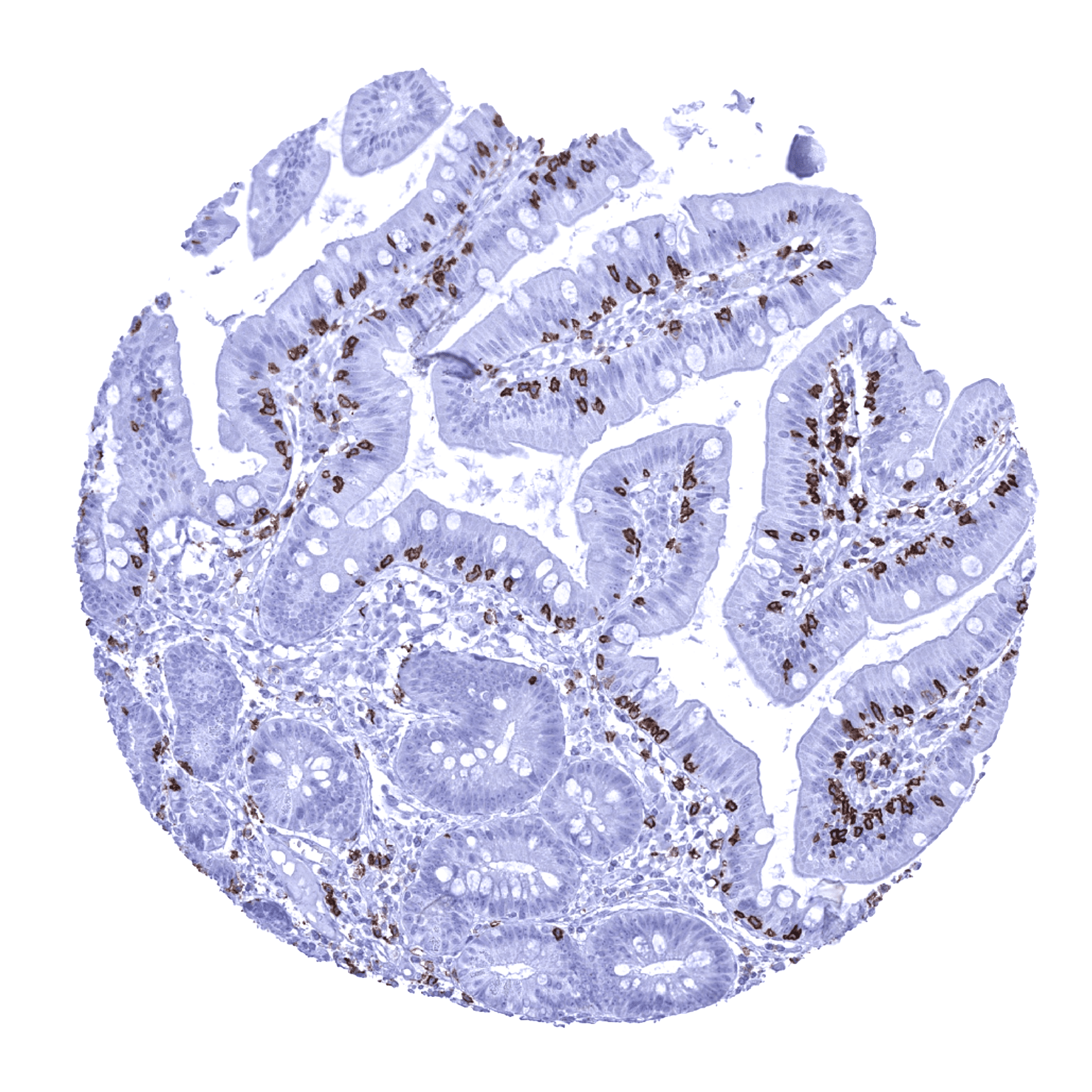
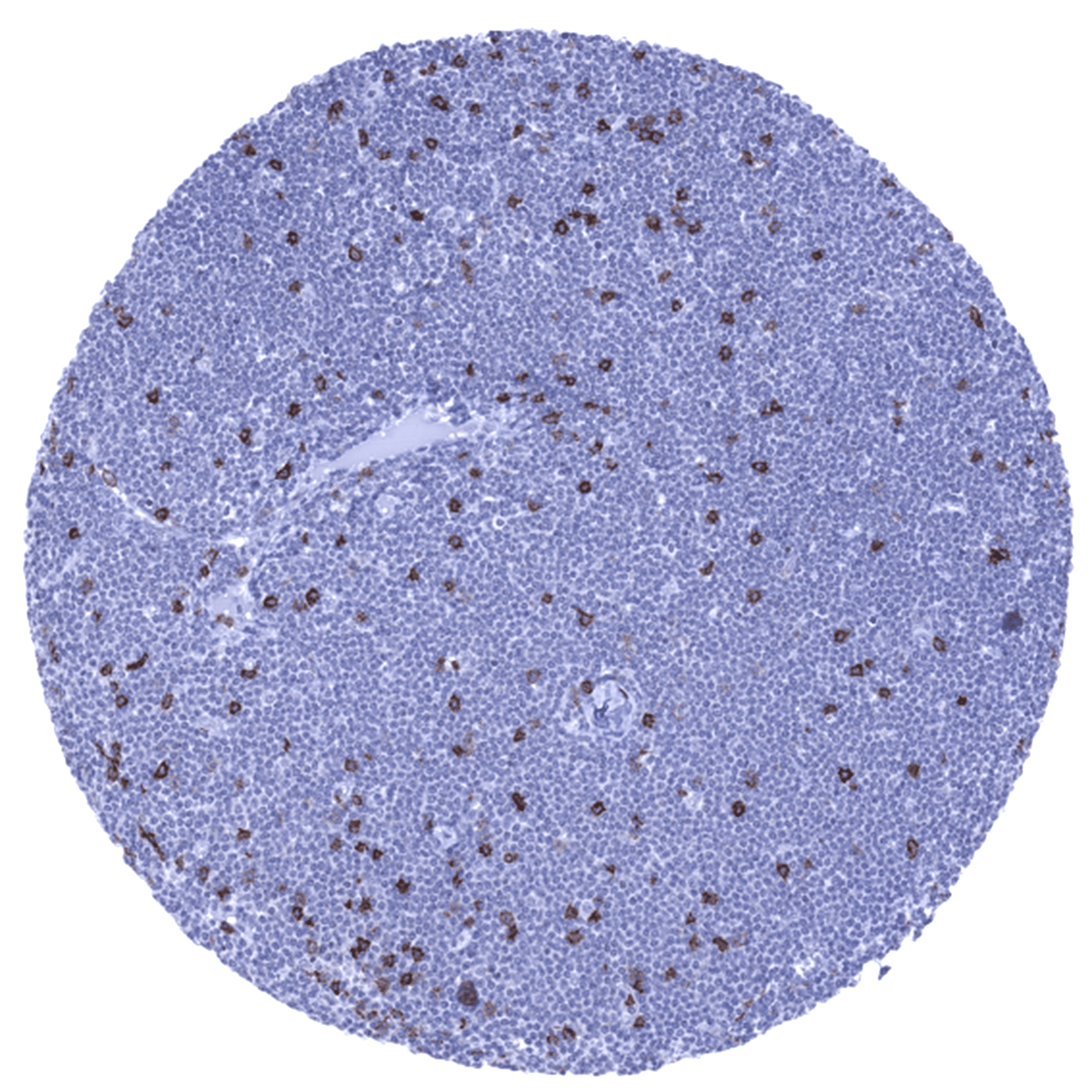
Positive control = Tonsil (interfollicular areas)
Negative control = Epithelial tissues, majority of cells in germinal centres of lymphatic organs
Cellular localization = Cell surface
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100 – 1:200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
CD8 is expressed on cytotoxic T-lymphocytes.
Biology Behind
CD8 (cluster of differentiation 8) is a transmembrane glycoprotein co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR) with a pivotal role in T cell signaling and cytotoxic T cell antigen interactions. To exert its function, CD8 forms a dimer, consisting of a pair of CD8 chains. The CD8 chains exist in multiple isoforms which are members of the immunoglobulin superfamily and contain an immunoglobulin variable (IgV)-like extracellular domain. The extracellular IgV-like domain of CD8-α interacts with the Class I MHC molecule. This keeps the cytotoxic T cell and antigen presenting cell closely together during antigen-specific activation. The CD8 co-receptor is predominantly expressed on the surface of cytotoxic T cells, but can also be found on natural killer cells, and cortical thymocytes. For practical purposes, the CD8 molecule is considered a marker for cytotoxic T cell population as this cell type predominates strongly among CD8 positive cells.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
The staining of CD8 positive cells in normal tissues reflects the physiologic distribution of cytotoxic T cells (about 30% of peripheral T-cells), natural killer cells, and cortical thymocytes. Accordingly, CD8 positive cells are most prominently seen in the thymus and lymphatic organs. In addition, venous sinuses in the spleen are CD8 positive.
These findings are largely consistent with the RNA and protein data described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression CD8)
Positive control = Tonsil (interfollicular areas)
Negative control = Epithelial tissues, majority of cells in germinal centres of lymphatic organs
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
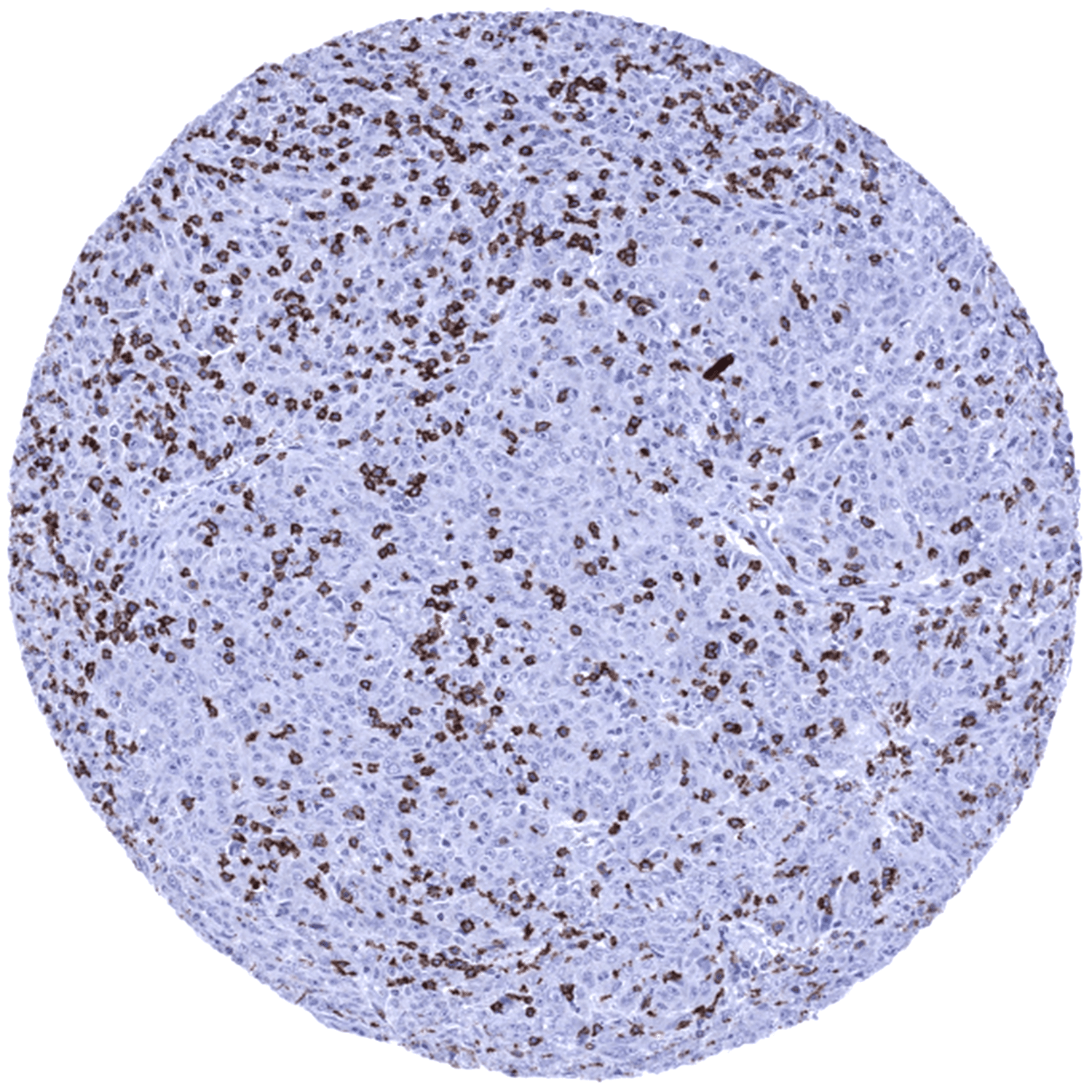
CD8 immunostaining is seen in a fraction of T-cell lymphomas. In rare cases, B-cell lymphomas can also express CD8, however. A variable number of tumor infiltrating CD8 positive lymphocytes is regularly seen in all kinds of neoplasms.
The TCGA findings on CD8 RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Compatibility of Antibodies
No data available at the moment
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image galleries are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
-Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 9 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply MSVA-008R at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Potential Research Applications
- The clinical significance of the number of intratumoral CD8 positive lymphocytes is under intensive research.
- CD8 is a key component of multicolor assays analyzing the role of lymphocyte subsets in cancers and other diseases.
- The prevalence of a positive CD8 immunostaining in hematological and non-hematological neoplasms should be further evaluated.
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
There are two ways, how the specificity of antibodies can be documented for immunohistochemistry on formalin fixed tissues. These are:
1. Comparison with a second independent method for measuring target expression across a large number of different tissue types (orthogonal strategy), and
2. Comparison with one or several independent antibodies for the same target and showing that all positive staining results are also seen with other antibodies for the same target (independent antibody strategy).
As a standard orthogonal validation process for MSVA antibodies, RNA data summarized in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression CD8) are used for comparison. However, this procedure has limited validity for proteins that are expressed in significant subsets of lymphocytes because these cells occur in virtually all organs.
The preferential CD8 RNA expression in the thymus and other lymphatic tissues such as the spleen and lymph nodes fits with the staining pattern observed by MSVA-008R in normal tissues. The validation of MSVA-008R is, however, preferentially based on a comparison with a second independent, CD8 antibody (termed “Validation-antibody”). This comparison of antibodies revealed identical staining patterns for MSVA-008R and the “Validation-antibody” in lymphatic tissues with identical subsets of lymphocytes staining. It is also of note, that the staining pattern of MSVA-008R matches the expectations as lymphocytes are preferable staining that occur at locations where cytotoxic T-lymphocytes are known to predominate such as in the thymus, interfollicular areas of lymph node and the tonsil as well as in mucosa associated tissues.
Antibody Comparison: MSVA-008R vs another independent CD8 antibody called “Validation Antibody”