295,00 € – 995,00 €
Product details
Synonyms = CAAF1, CAGC, CGRP, ENRAGE, MRP6, p6
Antibody type = Mouse monoclonal / IgG
Clone = MSVA-812M
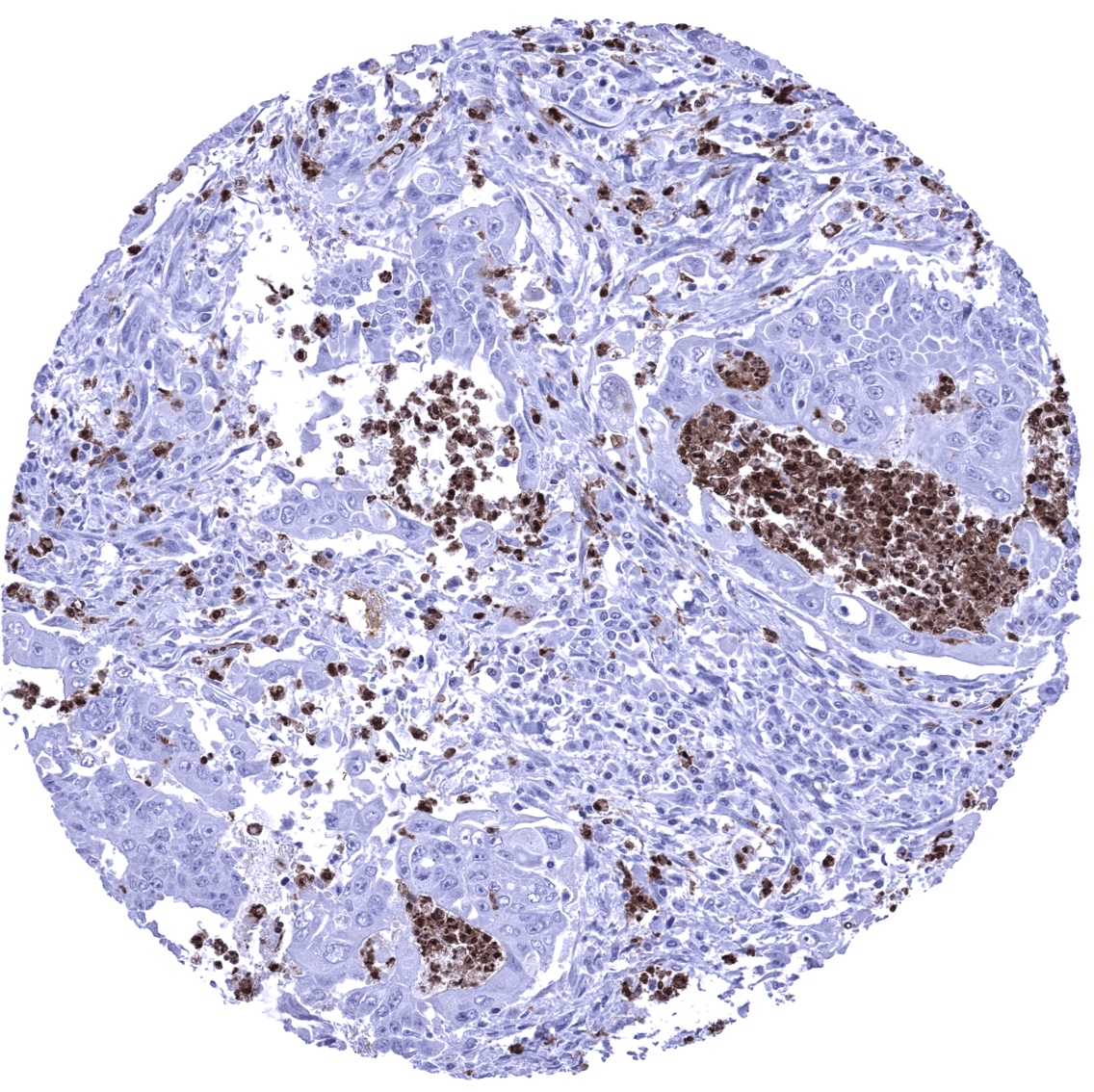
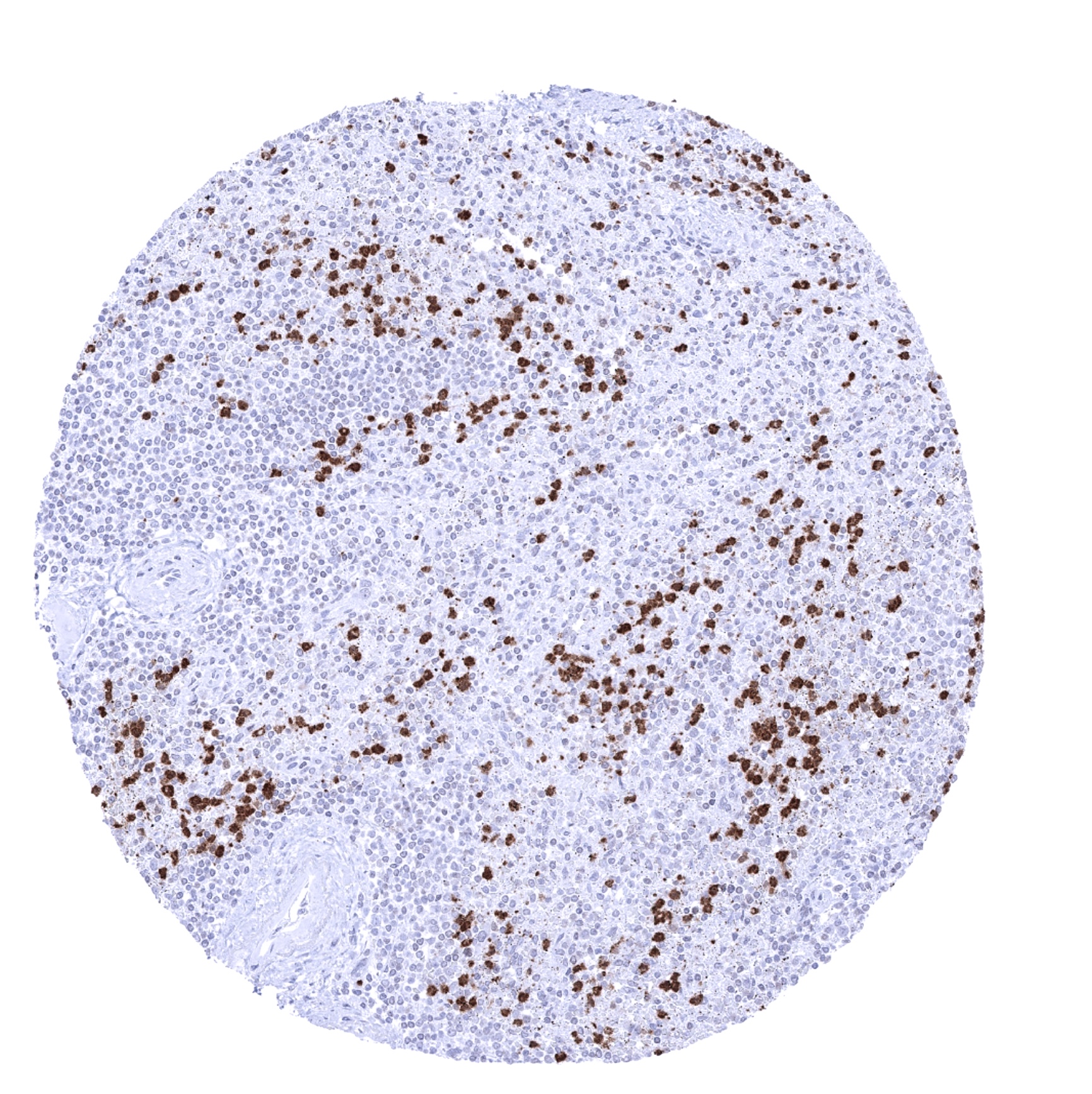
Positive control = Spleen: A significant number of inflammatory cells should show a strong S100A12 immunostaining while the majority of cells remain completely negative.
Negative control = Colon: All epithelial and muscular cells must not show any S100A12 immunostaining. Few scattered S100A12 positive inflammatory cells can occur (mostly within blood vessels)
Cellular localization = Intracellular, Secreted
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100 – 1:200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
S100A12 is a Marker for granulocytes and other “non-lymphocytic” inflammatory cells.
Biology Behind
S100A12 is a 10,5 kDa protein which is coded by the S100A12 gene at chromosome 1q21. Within granulocytes, S100A12 is co-expressed with S100A8 and S100A9 which jointly form the calprotectin heterodimer. S100A12 and S100A8/A9 proteins are all coded by neighboring genes and appear to be coregulated, to have functional similarities, and to interact with each other. S100A12 is constitutively expressed in neutrophils but can be induced in other cell types including epithelial cells. S100A12 acts as a damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) protein. These are molecules released by stressed cells undergoing necrosis and act as endogenous signals to promote a proinflammatory response. Accordingly, S100A12 promotes upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β. S100A12 is also a ligand for the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) on monocytes or epithelial cells.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
S100A12 immunostaining is primarily seen in granulocytes and their precursor cells in the bone marrow. Although it cannot be excluded, that at a fraction of histiocytes/monocytes are also S100A12 positive, (at least) most of these cells do not exhibit a S100A12 immunostaining in non-inflamed normal tissues. All other normal cell types including all epithelial cells, mesenchymal tissues, and the brain also do not show S100A12 immunostaining.
The findings described above are this consistent with the RNA data described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression S100A12)
Positive control = Spleen: A significant number of inflammatory cells should show a strong S100A12 immunostaining while the majority of cells remain completely negative.
Negative control = Colon: All epithelial and muscular cells must not show any S100A12 immunostaining. Few scattered S100A12 positive inflammatory cells can occur (mostly within blood vessels)
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
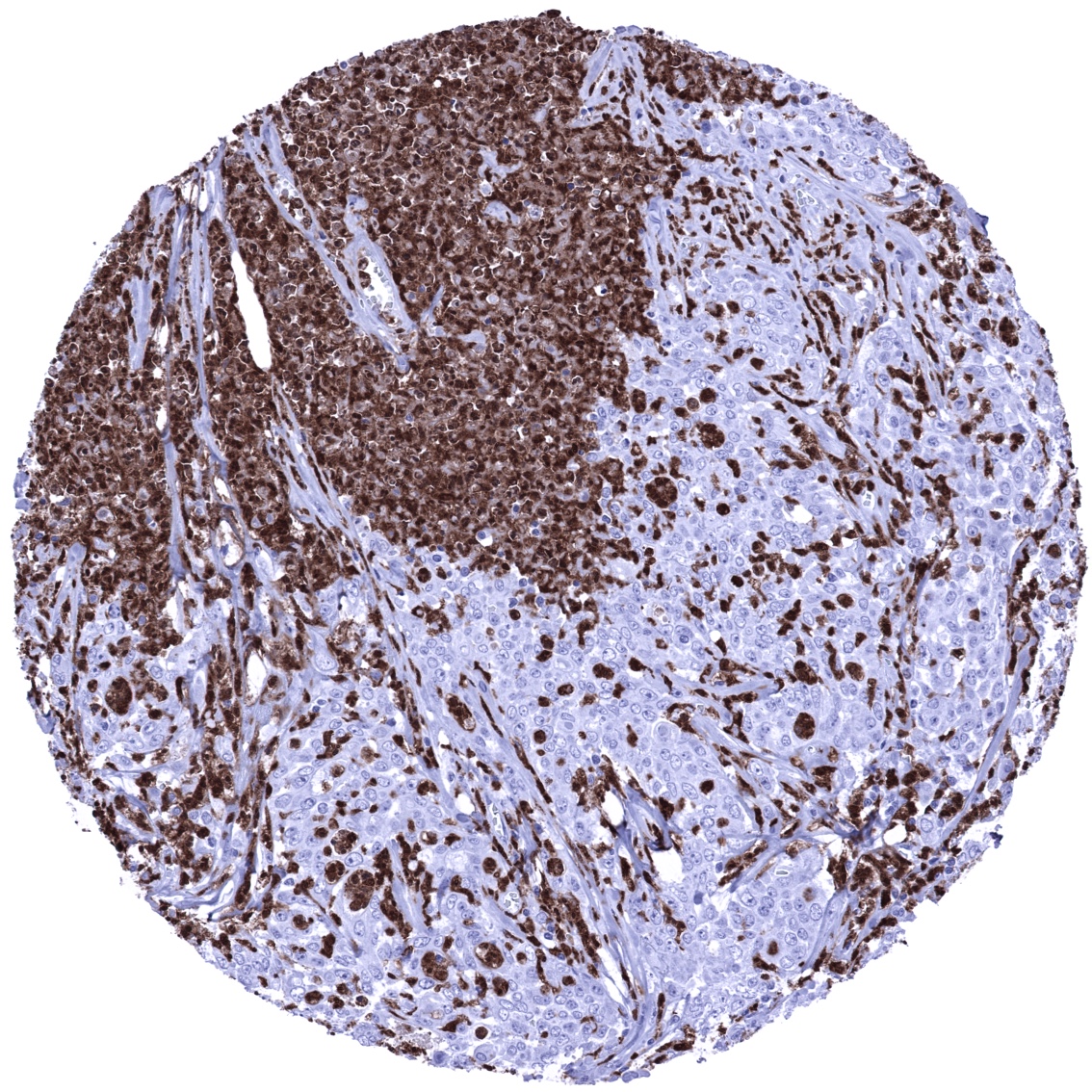
S100A12 immunostaining is regularly seen in a fraction of inflammatory cells within tumors.
The TCGA findings on S100A12 RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas. These data suggest the occurrence of S100A12 expression in head and neck, urothelial, lung, cervical, stomach, and renal cancer.
Compatibility of Antibodies
No data available at the moment
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image galleries are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
-Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 7,8 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply MSVA-812M at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Potential Research Applications
- A prognostic relevance of intratumoral S100A12 expression levels has been suggested for multiple tumor entities.
- Different S100A12 expression levels depending on the subtypes of chronic inflammatory disease have been proposed.
- The specific role of S100A12 in inflammatory disease needs to be further elucidated.
- The clinical role of the quantity of intratumoral S10A12 positive inflammatory cells is unclear.
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
There are two ways how the specificity of antibodies can be documented for immunohistochemistry on formalin fixed tissues. These are: 1. Comparison with a second independent method for target expression measurement across a large number of different tissue types (orthogonal strategy), and 2. Comparison with one or several independent antibodies for the same target and showing that all positive staining results are also seen with other antibodies for the same target (independent antibody strategy).
Orthogonal validation: For the antibody MSVA-812M specificity is suggested by the strong concordance of the immunostaining data with data from three independent RNA screening studies, including the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) RNA-seq tissue dataset, the FANTOM5 project, and the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project, which are all summarized in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression S100A12). Immunostaining by using MSVA-812M was almost exclusively detected in organs with documented RNA expression such as in lymphoid tissues, bone marrow and blood cells. RNA expression was further described to occur in lung, vagina, and heart muscle which was not observed by MSVA-812M. Considering also that S100A12 RNA expression in the lung was not seen in the HPA data set and that S100A12 RNA expression in the heart was not observed in the HPA and GTEx data sets, it is possible that documented RNA expression in these tissues may be due to a blood contamination of some specimen.
Comparison of antibodies: True expression of S100A12 detected by MSVA-812M is also corroborated by similar staining patterns obtained by the antibodies CAB025872 and HPA002881 which were both used for tissue analyses shown in the protein atlas. Both antibodies show a predominant staining of a. fraction of inflammatory cells in the spleen and lack tissue expression in the vagina , heart and lung. In these organs S100A12 immunostaining by all antibodies is largely limited to intravascular inflammatory cells.