295,00 € – 995,00 €
Product details
Synonyms = Claudin-6, CLDN6
Antibody type = Recombinant Rabbit monoclonal
Clone = MSVA-916R
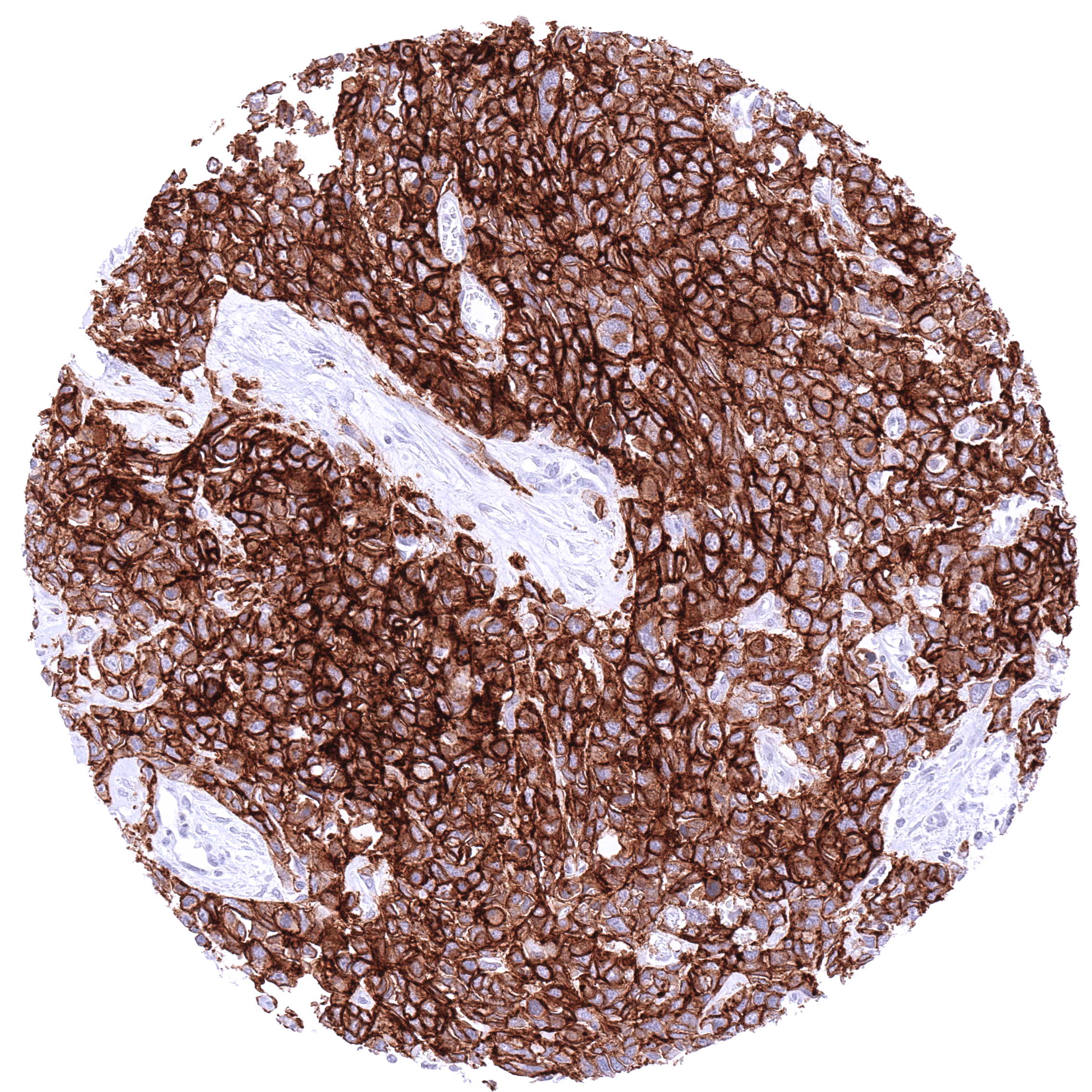
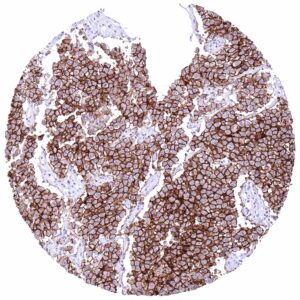
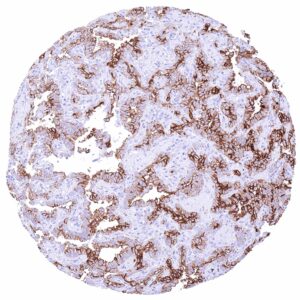
Positive control = Placenta (first trimester): A strong membranous CLDN6 staining should be seen in cytotrophoblast cells while other cell types remain CLDN6 negative.
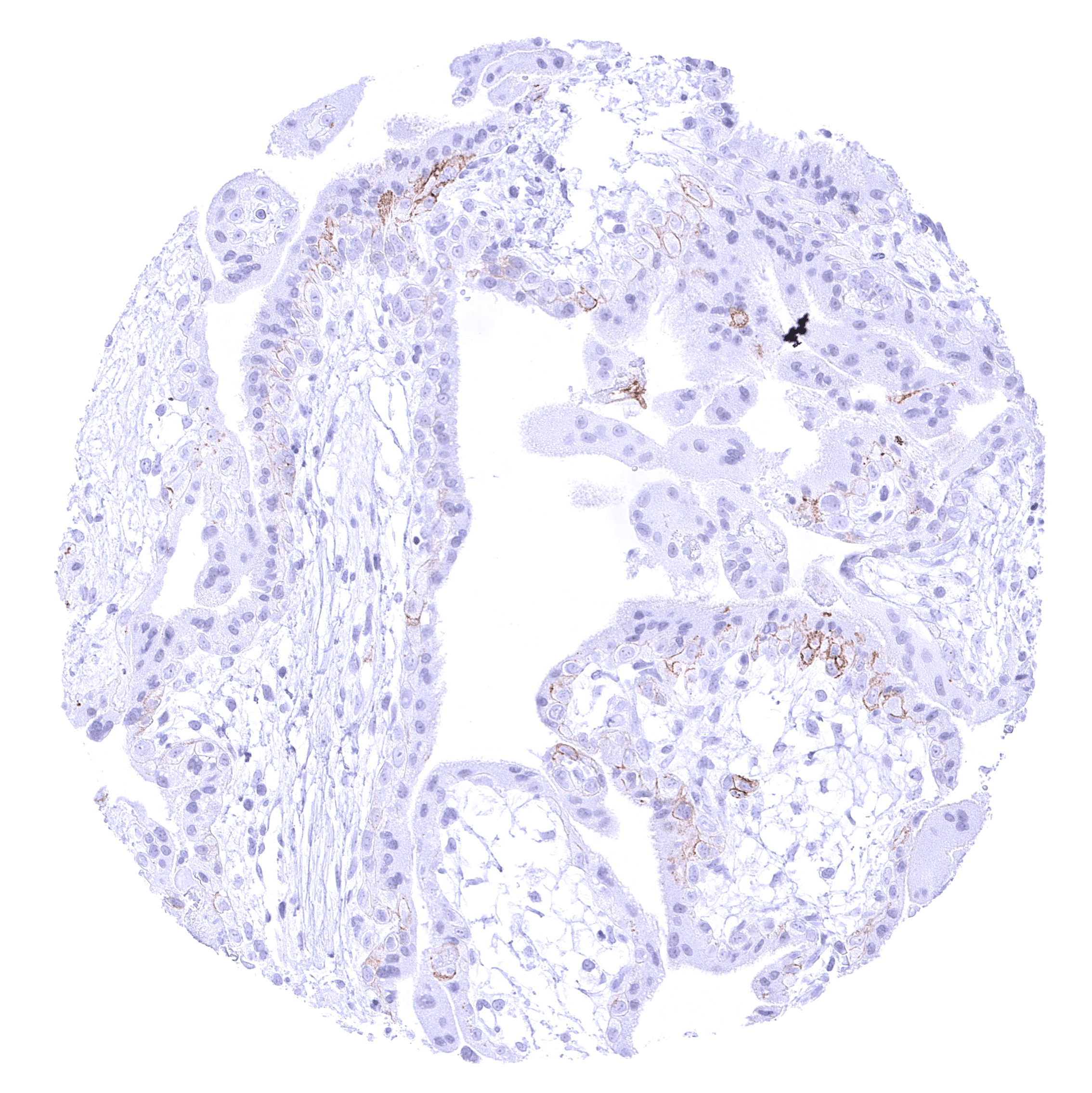
Negative control =Tonsil: Epithelial and inflammatory cells must not show any CLDN6 staining.
Cellular localization = Membranous
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100 – 1:200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
Claudin-6 is a therapeutic target protein.
Biology Behind
Claudin-6 (CLDN6) is one of 26 members of the claudin family of membrane proteins that are crucial components of tight junctions, regulating paracellular permeability and maintaining cell polarity. Claudin-6 is coded by the CLDN6 gene on chromosome 16p13.3. Its molecular weight is approximately 23 kDa. CLDN6 is one of the earliest proteins expressed in embryonic stem cells. It is expressed in specific fetal tissues such as the kidney, lung, pancreas, and the stomach, but it is not expressed in the corresponding adult tissues. That knockout mice lacking mouse homolog CLDN6 do not exhibit an aberrant phenotype indicates that CLDN6 is dispensable for normal development and tissue homeostasis. While CLDN6 expression is largely lacking on normal tissues, it is highly expressed in several cancers. Therefore, CLDN6 is considered a potential therapeutic target. Studies evaluating CLDN6 as a target for monoclonal antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates, bispecific antibodies, and CAR-T cells are underway.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
CLDN6 staining in normal tissues is rare. It is strongest in cytotrophoblast cells of the first trimester placenta. A weak to moderate membranous CLDN6 can also occur in few chorion cells, few intercalated ducts and/or acinar cells of the pancreas, few epithelial cells of the adenohypophysis, and in few tubular or collecting duct cells of the kidney.
Images describing the Claudin-6 staining pattern in normal tissues obtained by the antibody MSVA-916R are shown in our “Normal Tissue Gallery”.
| Brain | Cerebrum | Negative. |
| Cerebellum | Negative. | |
| Endocrine Tissues | Thyroid | Negative. |
| Parathyroid | Negative. | |
| Adrenal gland | Negative. | |
| Pituitary gland | Faint CLDN6 staining some membranes of few epithelial cells of the anterior gland. | |
| Respiratory system | Bronchus, Respiratory epithelium | Negative. |
| Lung | Negative. | |
| Gastrointestinal Tract | Salivary glands | Negative. |
| Esophagus | Negative. | |
| Stomach | Negative. | |
| Duodenum | Negative. | |
| Small intestine | Negative. | |
| Appendix | Negative. | |
| Colon | Negative. | |
| Rectum | Negative. | |
| Liver | Negative. | |
| Gallbladder | Negative. | |
| Pancreas | Weak to moderate membranous CLDN6 staining of a small fraction of intercalated ducts and/or acinar cells. | |
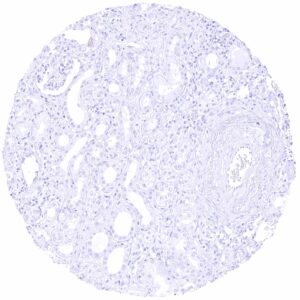
| Genitourinary | Kidney | Weak to moderate membranous CLDN6 staining of few tubular cells (distal tubulus or collection duct); not in all samples. |
| Urothelium | Negative. | |
| Male genital | Prostate | Negative. |
| Seminal vesicles | Negative. | |
| Testis | Negative. | |
| Epididymis | Negative. | |
| Female genital | Breast | Faint CLDN6 staining of apical membranes of luminal epithelial cells of breast glands (not in all samples; cross-reactive). |
| Uterus, myometrium | Negative. | |
| Uterus, ectocervix | Negative. | |
| Uterus endocervix | Negative. | |
| Uterus, endometrium | Negative. | |
| Fallopian Tube | Negative. | |
| Ovary | Negative. | |
| Placenta early | Moderate membranous CLDN6 staining of cytotrophoblast cells. | |
| Placenta mature | Negative. | |
| Amnion | Negative. | |
| Chorion | Weak membranous CLDN6 staining of few chorion cells in some samples. | |
| Skin | Epidermis | Negative. |
| Sebaceous glands | Negative. | |
| Muscle/connective tissue | Heart muscle | Weak to moderate cytoplasmic CLDN6 staining of some muscle fibers in some samples (cross-reactive). |
| Skeletal muscle | Weak to moderate cytoplasmic CLDN6 staining of some muscle fibers in some samples (cross-reactive). | |
| Smooth muscle | Negative. | |
| Vessel walls | Negative. | |
| Fat | Negative. | |
| Stroma | Negative. | |
| Endothelium | Negative. | |
| Bone marrow/ lymphoid tissue | Bone marrow | Negative. |
| Lymph node | Negative. | |
| Spleen | Negative. | |
| Thymus | Negative. | |
| Tonsil | Negative. | |
| Remarks |
These findings are largely consistent with the RNA data described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression Claudin-6).
Positive control = Placenta (first trimester): A strong membranous CLDN6 staining should be seen in cytotrophoblast cells while other cell types remain CLDN6 negative.
Negative control =Tonsil: Epithelial and inflammatory cells must not show any CLDN6 staining.
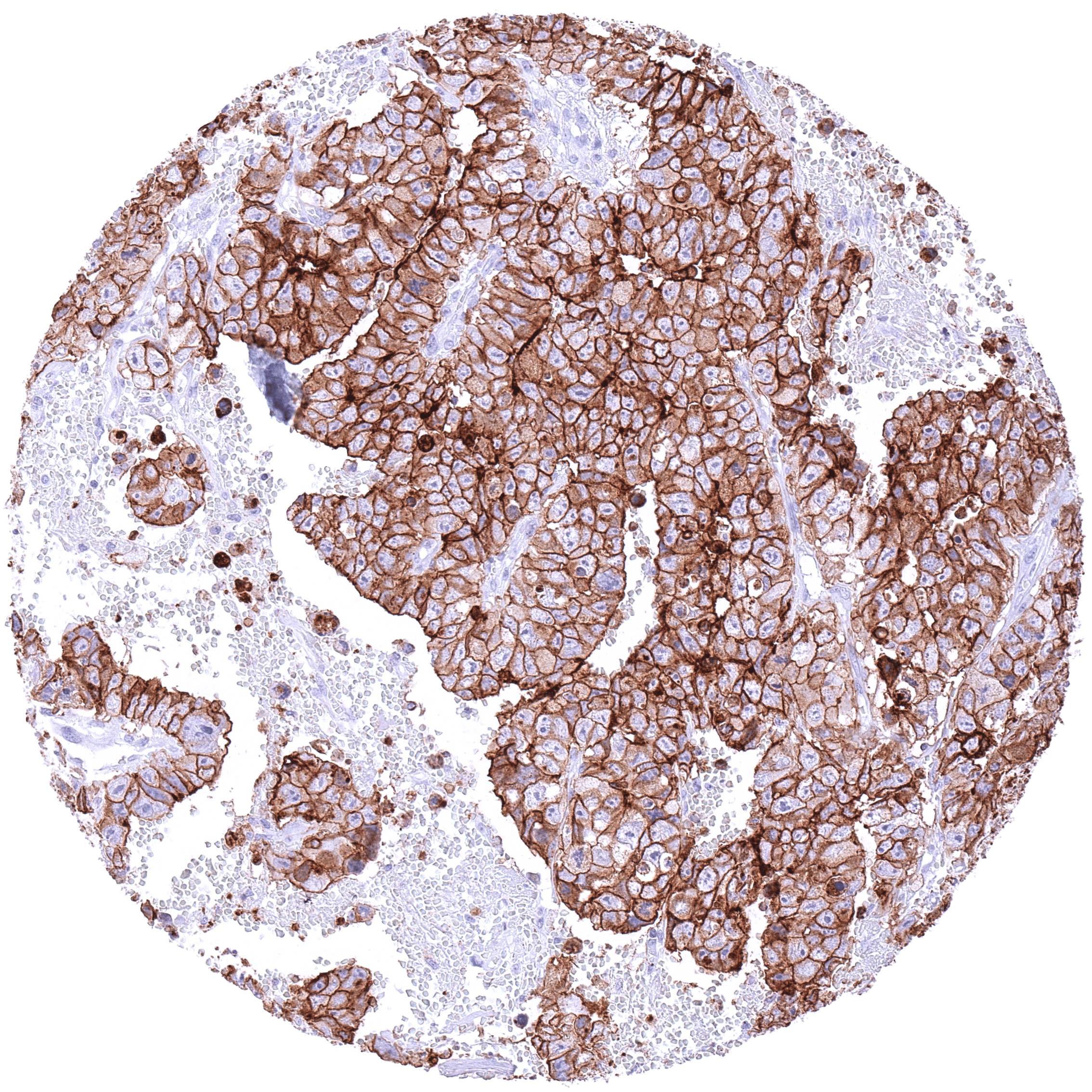
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
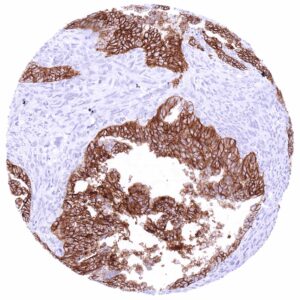
CLDN6 expression is particularly frequent in testicular germ cell tumors as well as in ovarian and endometrial cancer but it also occurs in various other tumor entities.
The TCGA findings on Claudin-6 RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Compatibility of Antibodies
No data available at the moment
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image galleries are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 7,8 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply MSVA-916R at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Potential Research Applications
- How does aberrant CLDN6 expression contribute to tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis across different cancer types?
- What is the prevalence of CLDN6 expression in different tumor entities?
- What are the most effective strategies for targeting CLDN6 in cancer therapy?
- Determine the specificity and sensitivity of CLDN6 detection methods, such as IHC for the identification of tumors responding to anti-CLDN6 therapies.
- What are potential resistance mechanisms for CLDN6-targeted therapies?
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
There are two ways how the specificity of antibodies can be documented for immunohistochemistry on formalin fixed tissues. These are: 1. Comparison with a second independent method for target expression measurement across a large number of different tissue types (orthogonal strategy), and 2. Comparison with one or several independent antibodies for the same target and showing that all positive staining results are also seen with other antibodies for the same target (independent antibody strategy).
Orthogonal validation: For the antibody MSVA-916R a high specificity is supported by the good concordance of the immunostaining data with data from three independent RNA screening studies, including the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) RNA-seq tissue dataset, the FANTOM5 project, and the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project, which are all summarized in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression Claudin-6). CLDN6 immunostaining by using MSVA-916R was only detected in the placenta, kidney, pancreas, and the adenohypophysis which are all organs that also showed detectable RNA expression. Of note, other RNA findings such as CLDN6 expression in testis, cerebrum, and the adrenal gland were not confirmed by IHC data. In case of testis, CLDN6 RNA expression could have been caused by an admixture of neoplastic cells which are often CLDN6 positive. Membranous breast gland positivity (apical membranes) and a weak to moderate cytoplasmic staining of few skeletal and heart muscle fibers were the only stainings seen by MSVA-916R which were not corroborated by RNA expression data.
Comparison of antibodies: True expression of CLDN6 in placenta, kidney, pancreas, and the adenohypophysis was validated by identical IHC staining patterns obtained by a second, independent CLDN6 antibody, termed “validation antibody”. Because the CLDN6 staining of apical membranes of luminal breast gland cells and weak to moderate cytoplasmic staining of few skeletal and heart muscle fibers was not confirmed by the validation antibody, these stainings are considered to represent an antibody specific cross-reactivity of MSVA-916R. Additional cytoplasmic staining in adenohypophysis, testis, bone marrow, ovary, breast, fallopian tube, and several other tissues which were only seen by using the validation antibody were considered antibody specific cross-reactivities of the validation antibody.