295,00 € – 995,00 €
Product details
Synonyms = GP40; Leu9; p41; T-cell leukemia antigen; T-cell surface antigen Leu-9; Tp40; TP41
Antibody type = Recombinant Rabbit monoclonal / IgG
Clone = MSVA-007R
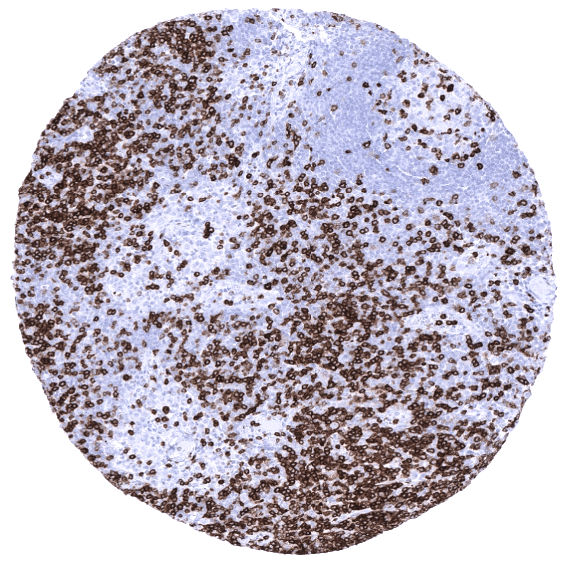
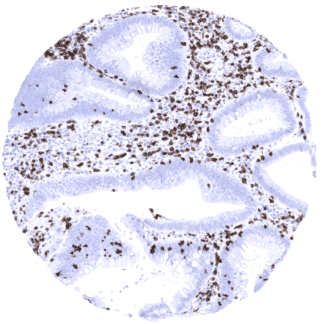
Positive control = Tonsil: A moderate to strong, predominantly membranous staining of T-cells in the interfollicular zones and the germinal centres should be seen. Colon: A moderate to strong staining of the intra-epithelial T-cells in the colon mucosa should be seen.
Negative control = Tonsil/colon: All epithelial structures should stain negative.
Cellular localization = Membranous
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100 – 1:200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
CD7 is expressed in early maturation stages of T-cells.
Biology Behind
CD7 is a transmembrane costimulatory glycoprotein and a member of the immunoglobulin supergene family. CD7 is one of the first cell surface proteins expressed during T‐cell maturation. CD7 is present on all thymocytes, most mature peripheral blood T cells, and on natural killer (NK) cells. The function of CD7 is not fully understood, but it may play a role in T-cell and T-cell/B-cell interactions during early lymphoid development. CD7 is also expressed in pluripotent bone marrow stem cells and CD7 expression occurs in about 30% of AML cases. These neoplasias are associated with poor prognosis. CD7 expression occasionally also occurs in solid cancers, the relevance of which is unclear. Only a small fraction of T-lymphocytes lack CD7. Loss of CD7 gene expression particularly occurs in a small subset of normal circulating T helper cells as well as in a majority of epidermal and dermal T cells of normal skin. These cells may represent the physiological counterpart of CD7 negative malignant T cells. Several studies indicate that the number of CD4+CD7- T cells increases with age and in diseases such as chronic inflammation and in T‐cell malignancies. The relevance of CD4+CD7- T cells in the microenvironment of cancers is unclear.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
Using antibody MSVA-007R, a strong staining is seen in a large subset of T-lymphocytes in lymphatic organs and all other tissues. Some cells in the bone marrow stain positive. In addition, basolateral membranes of the surface epithelium of the gallbladder can stain positive (1 of 8 cases).
These findings are largely comparable to the data described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression CD7)
Suggested positive tissue control: A moderate to strong, predominantly membranous staining of T-cells in the interfollicular T-zones, the germinal centres of the tonsil, and of the intra-epithelial T-cells in the colon mucosa should be seen.
Suggested negative tissue control: Virtually all normal epithelial structures should stain negative.
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
CD7 is almost always expressed in T-All, and usually present in mature T-cell lymphomas. However, in T-cell lymphoma of the skin, CD7 is often lost. CD7 is expressed in 30% of AML and can also be seen in CML as well as in other hematological neoplasias. It can – rarely – also be expressed in several solid tumor types including adenocarcinoma of the lung, liver cell carcinoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
The TCGA findings on CD7 RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Compatibility of Antibodies
No data available at the moment
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image galleries are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH9 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply MSVA-007R at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Agilent / Dako – Autostainer Link 48
Pretreatment in PT-Link for 30 minutes at 95°C (pH high); FLEX peroxidase blocking for 5 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-007R 1:150 for 20 minutes (room temperature), FLEX+ mouse/rabbit (LINKER) for 15 minutes (room temperature), horseradish peroxidase (HRP) for 20 minutes (room temperature), FLEX DAB+Sub-Chromo for 10 minutes (room temperature), FLEX hematoxylin for 5 minutes (room temperature).
These images reflect stainings by the protocol described above. It is of note that a comparable staining result can also be obtained by different protocols. In general, a longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, and a longer incubation time of FLEX+LINKER result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining. Modifications of the protocol with a strengthening effect on staining intensity in combination with changes of other parameters that result in lower staining intensity can result in a comparable result as shown above.
Leica – BOND RX
Dewax at 72°C for 30 seconds; Pretreatment in Bond Epitope Retrieval Solution (ER2 – EDTA pH9) for 20 minutes at 100°C; Peroxidase blocking for 5 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-007R 1:150 for 15 minutes (room temperature), Post primary (rabbit anti mouse) for 8 minutes (room temperature), Polymer (goat anti rabbit) for 8 minutes (room temperature), mixed DAB refine for 10 minutes (room temperature), hematoxylin for 5 minutes (room temperature).
These images reflect stainings by the protocol described above. It is of note that a comparable staining result can also be obtained by different protocols. In general, a longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, a higher temperature during incubation, and a longer incubation time of Post primary and or the Polymer result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining. Modifications of the protocol with a strengthening effect on staining intensity in combination with changes of other parameters that result in lower staining intensity can result in a comparable result as shown above.
Roche – Ventana Discovery ULTRA
Pretreatment for 64 minutes at 100°C (pH 8,4); CM peroxidase blocking for 12 minutes (room temperature), MSVA-007R 1:150 for 20 minutes at 36°C, secondary antibody (anti-rabbit HQ) for 12 minutes at 36°C, anti-HQ HRP for 12 minutes at room temperature, DAB at room temperature, hematoxylin II at room temperature for 8 minutes, bluing reagent at room temperature for 4 minutes.
These images depict staining results obtained by the protocol described above. It is of note, that the Ventana machines generally require higher antibody concentrations than other commonly used autostainers because the antibodies are automatically diluted during the procedure. Various other protocols can result in an identical result as shown above. A longer pretreatment, a longer incubation time of the primary antibody, a higher antibody concentration, a higher temperature during incubation, and a longer incubation time of secondary antibody and or the anti-HQ HRP result in stronger staining, potentially at the cost of more background staining.
Impact of pH
MSVA-007R results in strongest staining if pH9,0 is used for slide pretreatment. pH7,8 is acceptable but lower pH results in a significant reduction of sensitivity.
Potential pitfalls
Solid tumors can very rarely show strong mebranous CD7 positivity. This should not be mistaken for lymphoma.
Potential Research Applications
- The function of CD7 is not fully understood.
- The role of T-lymphocyte subpopulations (such as CD4, CD8) with loss of CD7 needs to be investigated.
- The prevalence of CD7 expression in hematological neoplasms should be further investigated.
- The clinical significance of CD7 expression in non-hematological neoplasms is unclear.
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
Specificity of MSVA-007R is documented by strong positive staining in cell types that are well documented to express CD7 such T-zone lymphocytes in combination with a virtual absence of staining in epithelial cells. Occasional epithelial staining has been confirmed by using other non-related antibodies. In addition, MSVA-007R did not show any staining of tissues notorious for non-specific IHC background such as kidney, colonic mucosa, and epidermis.