295,00 € – 995,00 €
Product details
Synonyms = CAP, FSHRG4, HUNK1, HUNKI, MCAP
Antibody type = Recombinant Rabbit monoclonal / IgG
Clone = HMV4275
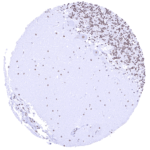
Positive control = Kidney: A moderate to strong BRD4 staining should be seen in all cell types.
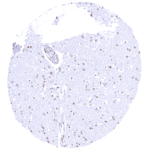
Negative control = Placenta (mature)*: BRD4 staining should be absent or only weak in nuclei of the syncytiotrophoblast but strong in other cell types.
Cellular localization = Nuclear
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100 – 1:200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
BRD4 is an epigenetic regulator and therapeutic target protein.
Biology Behind
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) is a multifunctional protein coded by the BRD4 gene on chromosome 19p13.12. BRD4 is a member of the BET (bromodomain and extra terminal domain) family, which also includes BRD2, BRD3, and BRDT. As all other BET family members, BRD4 contains two bromodomains – termed BD1 and BD2 – that recognize acetylated lysine residues of histones or other proteins in a central hydrophobic pocket. BD1 mainly binds to histone acetylated lysine residues, whereas BD2 mainly binds to other non-histone acetylated lysine residues, such as acetylated lysine residues of RelA which is a component of NFkB. BRD4 acts as a passive scaffolding factor that recruits several chromatin and transcriptional regulatory factors. Because of its additional enzymatic functions (kinase and HAT activity) it also modifies and thereby regulates its interacting partners one of it is cMYC. In line with its multifunctional capacity, BRD4 plays a role in various biological processes including DNA replication, transcription, as well as cell cycle and signaling during stress responses. BRD4 dysfunction has been associated with a broad range of disease types including cancer, kidney, lung, heart, and inflammatory diseases, organ fibrosis, neuro-degenerative disorders, and auto immune diseases. BRD4 is an actively researched drug target, partly due to its critical regulatory role for cMYC. Multiple clinical trials are currently ongoing.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
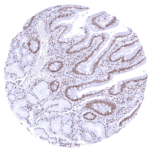
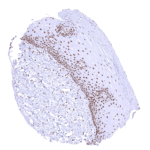
BRD4 is a nuclear protein which is ubiquitously expressed. Images describing the BRD4 staining pattern in normal tissues obtained by the antibody HMV4275 are shown in our “Normal Tissue Gallery”.
| Brain | Cerebrum | Nuclear BRD4 staining of glia cells while staining is low or absent in neuronal cells. |
| Cerebellum | Nuclear BRD4 staining of Purkinje cells, cells of the granule layer (variable intensity), and glia cells. | |
| Endocrine Tissues | Thyroid | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of epithelial cells. |
| Parathyroid | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of epithelial cells. | |
| Adrenal gland | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. | |
| Pituitary gland | Distinct nuclear staining of pituicytes and of epithelial cells. | |
| Respiratory system | Respiratory epithelium | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of respiratory epithelial cells. |
| Lung | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of pneumocytes. | |
| Gastrointestinal Tract | Salivary glands | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. Staining of glandular cells is somewhat weaker than of excretory duct cells. |
| Esophagus | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of squamous epithelial cells with a slight decrease of the staining intensity towards the most superficial cell layers. | |
| Stomach | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. Staining of surface epithelial cells is slightly more intense than in glandular cells. | |
| Duodenum | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. Staining of surface epithelial cells is markedly stronger than in Brunner glands. | |
| Small intestine | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. | |
| Appendix | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. | |
| Colon | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. Staining of surface epithelial cells is weaker than in crypts. | |
| Rectum | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. Staining of surface epithelial cells is weaker than in crypts. | |
| Liver | Nuclear BRD4 staining occurs in all cells. It is – by far – weakest in hepatocytes. | |
| Gallbladder | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. | |
| Pancreas | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. | |
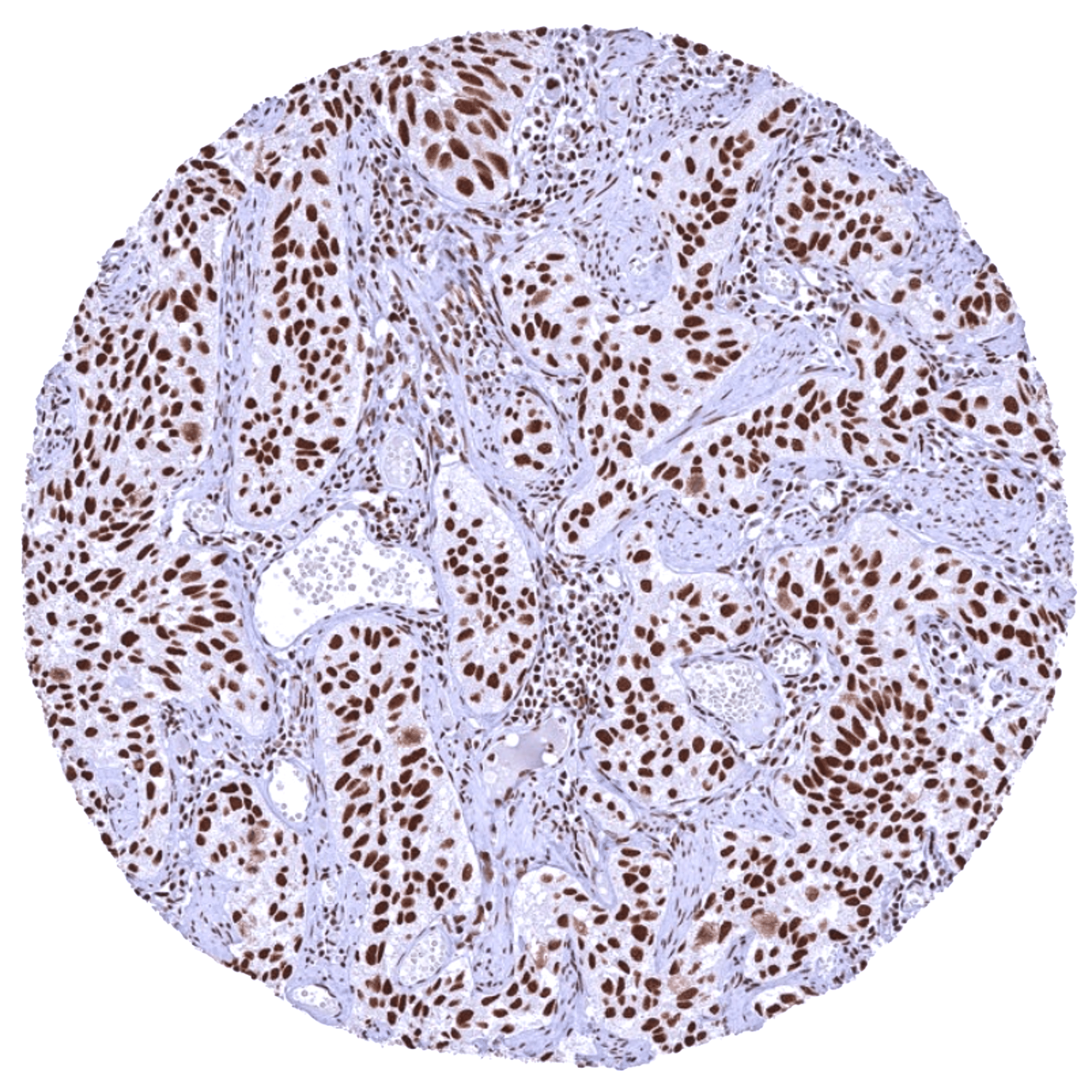
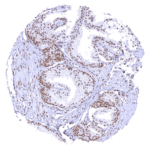
| Genitourinary | Kidney | Moderate to strong nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. |
| Urothelium | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of urothelial cells. | |
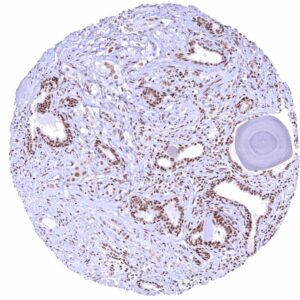
| Male genital | Prostate | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. Staining of basal cells is somewhat stronger than of acinar cells. |
| Seminal vesicles | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of epithelial cells. | |
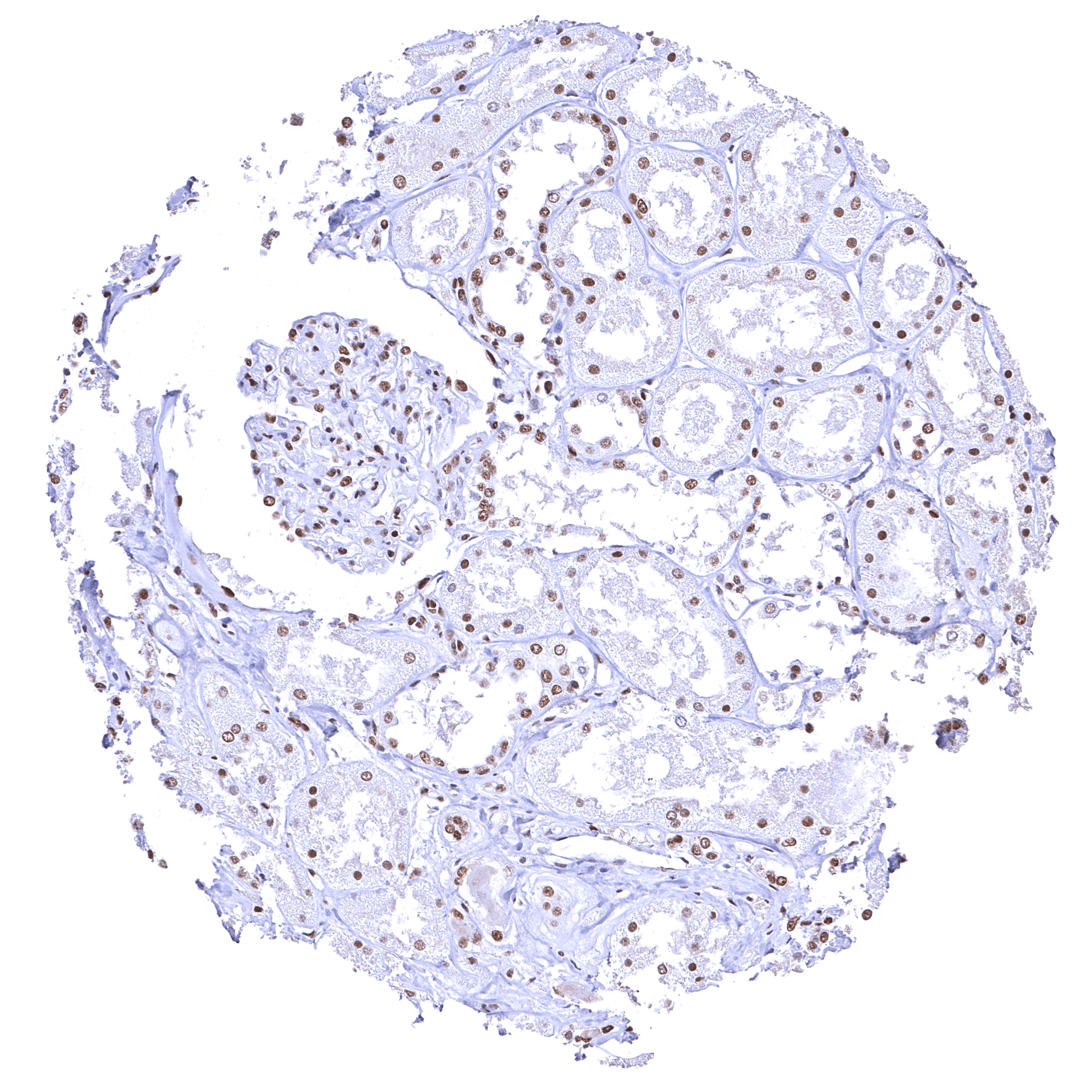
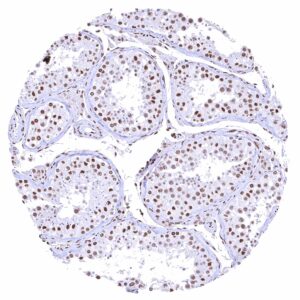
| Testis | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. The level of BRD4 staining decreases with maturation of germ cells. | |
| Epididymis | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. | |
| Female genital | Breast | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of epithelial cells. |
| Uterus, myometrium | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. | |
| Uterus, ectocervix | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of squamous epithelial cells with a slight decrease of the staining intensity towards the most superficial cell layers. | |
| Uterus endocervix | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of epithelial cells. | |
| Uterus, endometrium | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of epithelial and stromal cells. | |
| Fallopian Tube | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of epithelial cells. | |
| Ovary | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of stroma and corpus luteum cells. | |
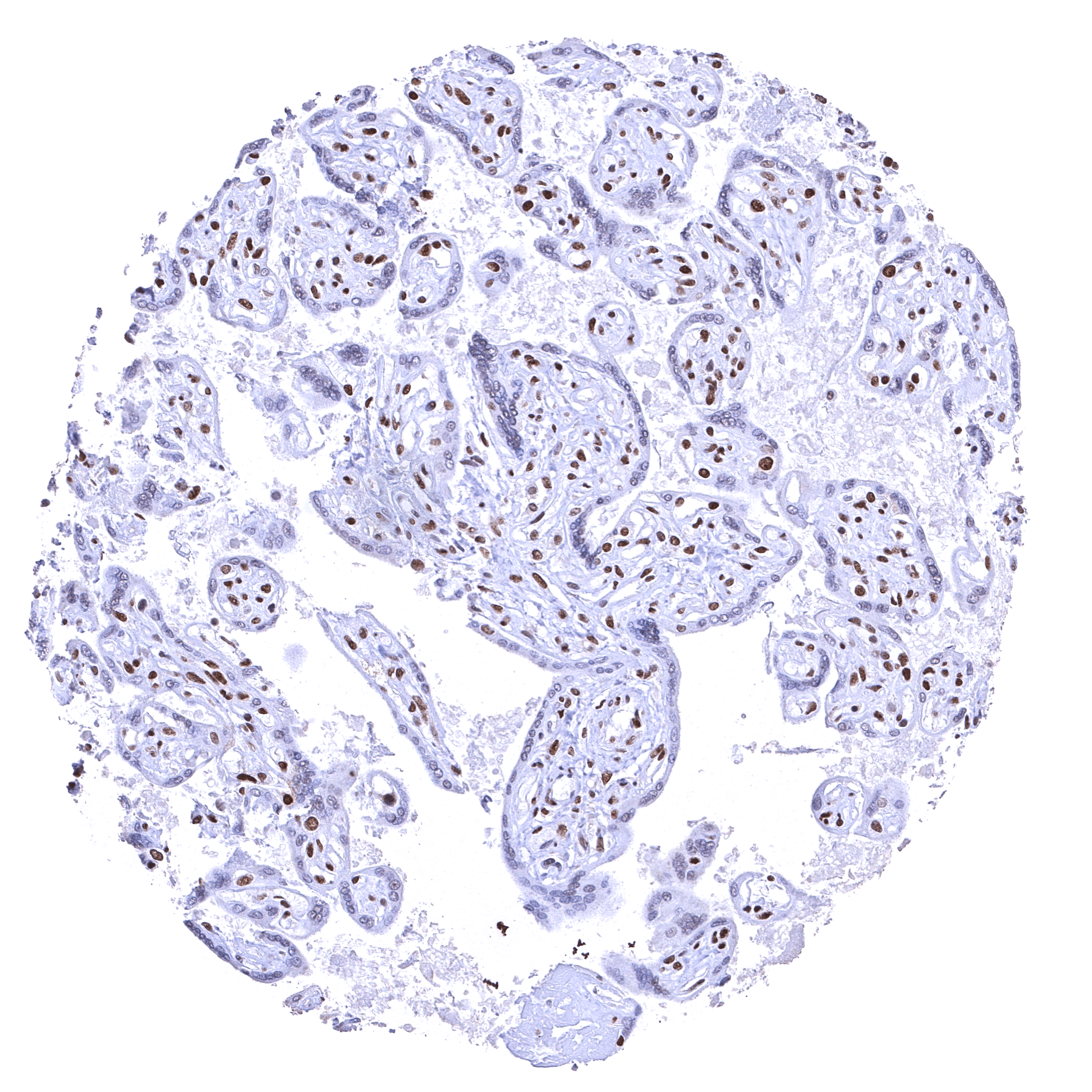
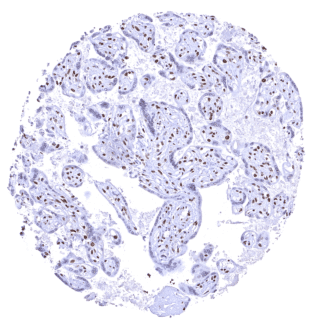
| Placenta early | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. Staining is particularly strong in trophoblast cells. | |
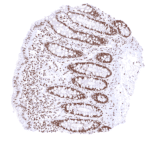
| Placenta mature | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of most cells but staining is either absent or massively reduced in the syncytiotrophoblast. | |
| Amnion | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of amnion cells. | |
| Chorion | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of chorion cells. | |
| Skin | Epidermis | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of squamous epithelial cells. |
| Sebaceous glands | Moderate to strong BRD4 staining of sebaceous gland cells. Nuclear BRD4 staining is somewhat stronger in associated hair follicle cells. | |
| Muscle/connective tissue | Heart muscle | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. An additional cytoplasmic staining of heart muscle cells in some cases may represent an antibody specific cross-reactivity. |
| Skeletal muscle | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. An additional cytoplasmic staining of skeletal muscle cells in some cases may represent an antibody specific cross-reactivity. | |
| Smooth muscle | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of smooth muscle cells. | |
| Vessel walls | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. | |
| Fat | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. | |
| Stroma | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. | |
| Endothelium | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of cells. | |
| Bone marrow/ lymphoid tissue | Bone marrow | Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. |
| Lymph node | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of all cell types. | |
| Spleen | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of all cell types. | |
| Thymus | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of all cell types. | |
| Tonsil | Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of squamous epithelial cells and of all immune cell types. | |
| Remarks | Nuclear BRD4 staining is seen in most tissues and in almost all cell types. |
The findings described above are thus consistent with the the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression BRD4). BRD4 staining is seen almost in all normal cell types although the staining intensity is variable. Staining is absent (or only minimal) in syncytiotrophoblast nuclei of the mature placenta and in the most mature cells of the spermatogenesis in the testis.
Positive control = Kidney: A moderate to strong BRD4 staining should be seen in all cell types.
Negative control = Placenta (mature)*: BRD4 staining should be absent or only weak in nuclei of the syncytiotrophoblast but strong in other cell types.
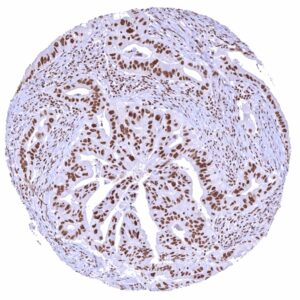
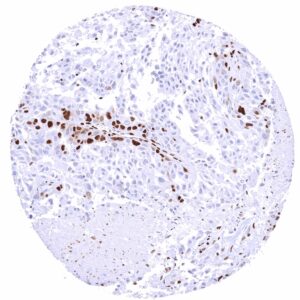
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
BRD4 expression occurs in cancers of all types. In rare cases, BRD4 expression can be lost in tumor cells.
The TCGA findings on BRD4 RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Compatibility of Antibodies
No data available at the moment
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image galleries are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 7,8 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply HMV4275 at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Potential Research Applications
- The mechanisms involving BRD4 in disease are not fully understood.
- The utility of BRD4 measurement in cancer needs to be evaluated.
- The utility of BRD4 as a biomarker is not clear.
- BRD4 is an intensively investigated therapeutic target.
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
There are two ways how the specificity of antibodies can be documented for immunohistochemistry on formalin fixed tissues. These are: 1. Comparison with a second independent method for target expression measurement across a large number of different tissue types (orthogonal strategy), and 2. Comparison with one or several independent antibodies for the same target and showing that all positive staining results are also seen with other antibodies for the same target (independent antibody strategy).
Orthogonal validation: For the antibody HMV4275 specificity is in line with data from three independent RNA screening studies, including the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) RNA-seq tissue dataset, the FANTOM5 project, and the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project, which are all compiled in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression BRD4). In agreement with HMV4275 immunostaining data, high RNA expression occurs in all normal tissues. However, it must be understood that orthogonal validation is not optimal for assessing ubiquitously expressed protein.
Comparison of antibodies: True expression of BRD4 in cell types with documented BRD4 immunostaining by HMV4275 is validated by largely identical staining patterns obtained by a second, independent commercially available BRD4 antibody, termed “validation antibody” for virtually all normal tissues. In particular, the use of the validation antibody confirmed characteristic variabilities of BRD4 staining in several tissue types. These included the absence or a significant reduction of BRD4 staining in syncytiotrophoblast nuclei of the mature placenta, and distinctive differences in the staining intensity between different cell types in non-keratinizing squamous epithelium, gastric mucosa, duodenum, colorectal mucosa, liver, salivary glands, prostate, testis, and in the grey matter of the cerebrum. That cerebral neurons were found BRD4 positive by the validation antibody and not by HMV4275 was interpreted as an antibody specific cross-reactivity of the validation antibody while a cytoplasmic staining of heart and skeletal muscle cells which was only seen by HMV4275 was considered an antibody specific cross-reactivity of HMV4275.