295,00 € – 995,00 €
Product details
Synonyms = Angiotensin I converting enzyme 2
Antibody type = Recombinant Rabbit monoclonal / IgG
Clone = MSVA-919R
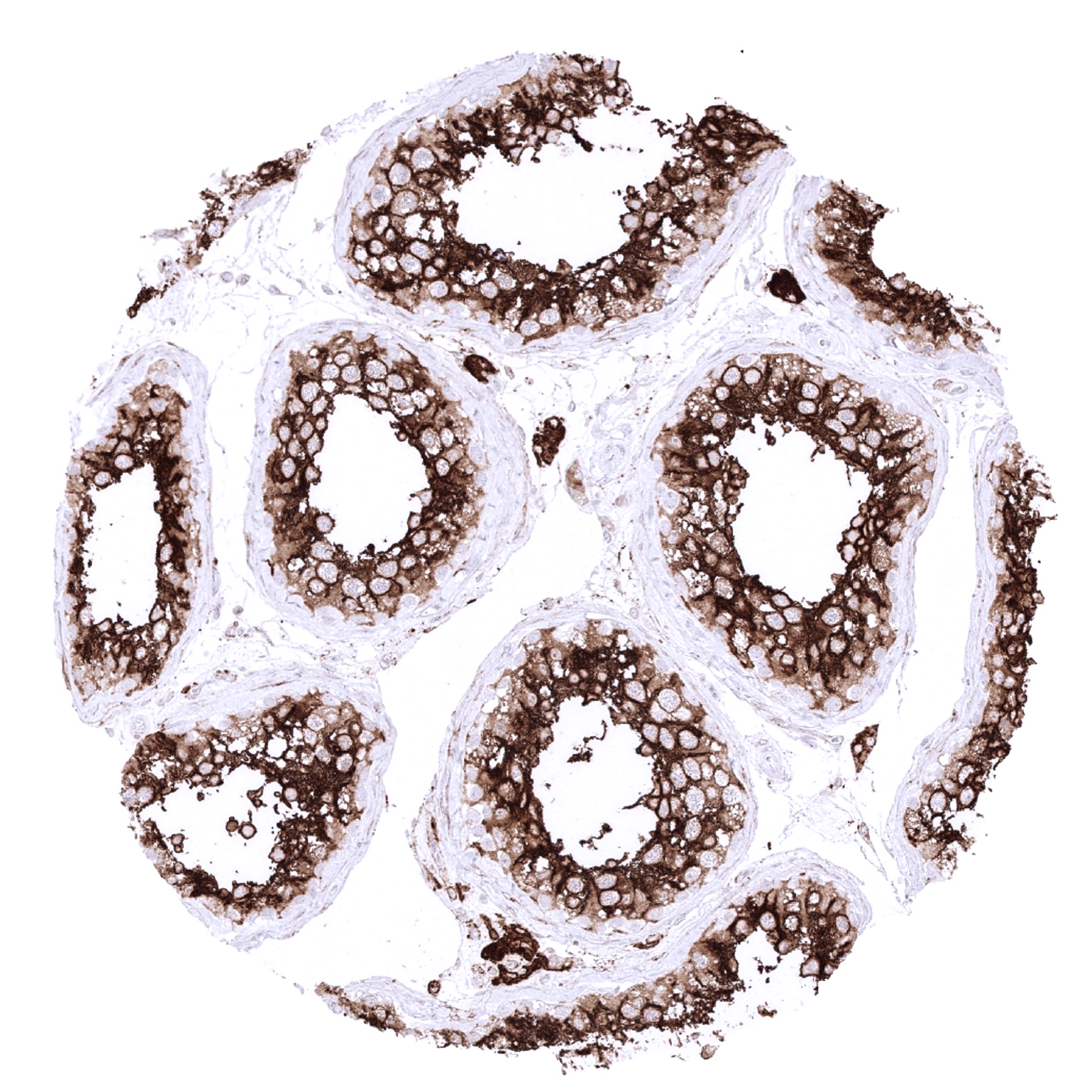
Positive control = Kidney: Cells of proximal tubuli should show a moderate to strong ACE2 immunostaining with accentuation of the staining at the apical membrane.
Negative control = Kidney: Cells of distal tubuli and glomeruli should not show ACE2 immunostaining.
Cellular localization = Cytoplasmic
Reactivity = Human
Application = Immunohistochemistry
Dilution = 1:100 – 1:200
Intended Use = Research Use Only
Relevance of Antibody
ACE2 detects a relevant entry port for the coronavirus causing COVID-19.
Biology Behind
The Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 gene (ACE2) is located on Xp22.2 and codes for a dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase located at the surface of endothelial and other cells. The primary function of ACE2 is to counterbalance the Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). ACE cleaves the angiotensin I hormone into the vasoconstricting angiotensin II. ACE2, in turn, cleaves the carboxyl-terminal amino acid phenylalanine from angiotensin II and hydrolyses it into the vasodilator angiotensin. ACE2 can also cleave numerous other peptides such as bradykinin, apelin, neurotensin, dynorphin A, and ghrelin. ACE2 is also involved in the regulation of membrane trafficking of proteins and it acts as the entry point into cells for several coronaviruses. As such, ACE2 is a key host cell receptor for the spike glycoprotein of the coronavirus HCoV-NL63 causing the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The binding of the spike S1 protein of SARS-CoV-2 to the enzymatic domain of ACE2 on the surface of cells results in endocytosis and translocation of both the virus and the enzyme into endosomes located within cells.
Staining Pattern in Normal Tissues
ACE2 staining pattern in Normal Tissues with antibody MSVA-919R (images are shown in our “Normal Tissue Gallery”)
| Brain | Cerebrum | Negative. |
| Cerebellum | Negative. | |
| Endocrine Tissues | Thyroid | Negative. |
| Parathyroid | Negative. | |
| Adrenal gland | Granular cytoplasmic staining (may represent tolerable cross-reactivity) | |
| Pituitary gland | Negative. | |
| Respiratory system | Respiratory epithelium | Negative. |
| Lung | Negative. | |
| Gastrointestinal Tract | Salivary glands | Negative. |
| Esophagus | Negative. | |
| Stomach | Weak to moderate focal staining of few epithelial cells. | |
| Duodenum | Strong staining of the surface epithelium. | |
| Small intestine | Strong staining of the surface epithelium. | |
| Appendix | Weak to moderate focal staining of epithelial cells. | |
| Colon | Weak to moderate focal staining of epithelial cells. | |
| Rectum | Weak to moderate focal staining of epithelial cells. | |
| Liver | Negative. | |
| Gallbladder | Strong staining of the surface epithelium. | |
| Pancreas | Negative. | |
| Genitourinary | Kidney | Strong staining of proximal tubuli. Weak to moderate of the parietal layer of the Bowman capsule. |
| Urothelium | Negative. | |
| Male genital | Prostate | Negative. |
| Seminal vesicles | Strong membranous, predominantly apical staining of a fraction of epithelial cells. | |
| Testis | Strong staining of Leydig cells and spermatocytes. | |
| Epididymis | A weak to moderate apical membrane staining can occur. | |
| Female genital | Breast | Negative. |
| Uterus, myometrium | Negative. | |
| Uterus, ectocervix | Negative. | |
| Uterus endocervix | Negative. | |
| Uterus, endometrium | Negative. | |
| Fallopian Tube | Moderate positivity of apical membranes of few epithelial cells. | |
| Ovary | Strong staining of corpus luteum. | |
| Placenta early | Weak to moderate membranous staining of syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast. | |
| Placenta mature | Weak to moderate membranous staining of syncytiotrophoblast, cytotrophoblast, and some decidua cells (rather cytoplasmic). | |
| Amnion | Negative. | |
| Chorion | Weak to moderate membranous staining of a fraction of chorion cells. | |
| Skin | Epidermis | Negative. |
| Sebaceous glands | Weak to moderate staining. | |
| Muscle/connective tissue | Heart muscle | Weak to moderate staining of some heart muscle cells. |
| Skeletal muscle | Negative. | |
| Smooth muscle | Negative. | |
| Vessel walls | Negative. | |
| Fat | Negative. | |
| Stroma | Negative. | |
| Endothelium | Variable ACE2 staining intensity varying between organs. Expression is high in the heart and possibly in endocrine tissues. | |
| Bone marrow/lymphoid tissue | Bone marrow | Negative. |
| Lymph node | Negative. | |
| Spleen | Negative. | |
| Thymus | Negative. | |
| Tonsil | Negative. | |
| Remarks | Because of a variable ACE2 staining in endothelial cells, some “ACE2 positivity” is also seen in tissues designated as “negative”. |
The findings described above are this consistent with the RNA data described in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression ACE2)
Immunostaining by using MSVA-919R was detected in all organs/tissues containing epithelial cells (except the adrenal gland).
Positive control = Kidney: Cells of proximal tubuli should show a moderate to strong ACE2 immunostaining with accentuation of the staining at the apical membrane.
Negative control = Kidney: Cells of distal tubuli and glomeruli should not show ACE2 immunostaining.
Staining Pattern in Relevant Tumor Types
ACE2 immunostaining is most commonly seen in papillary and clear cell renal cell carcinoma (>90%), colorectal adenocarcinoma (>75%) and also occurs at a relevant frequency in gastric and pancreatic adenocarcinoma. ACE2 expression can also be found – often at lower levels – in a large variety of other tumor entities.
The TCGA findings on ACE2 RNA expression in different tumor categories have been summarized in the Human Protein Atlas.
Compatibility of Antibodies
ACE2 (MSVA-919R) publication summary
Relevant publication: Meiners et al. “Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Protein Is Overexpressed in a Wide Range of Human Tumour Types: A Systematic Tissue Microarray Study on >15,000 Tumours” published in Biomedicines, December 3th 2021
A total of 12,644 tumors were analyzed from 119 different tumor categories by using the following protocol: Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH7,8 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. MSVA-919R at a dilution of 1:60 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent). This protocol was also used for all stainings depicted in our tumor and normal tissue galleries.
At least one case with a positive ACE2 immunostaining was seen in 83 (69.7%) and at least one case with a strong ACE2 immunostaining was seen in 37 (31.1%) of 119 tumor categories. The distribution of positive staining results is shown “organ-systematic” and in a “ranking order” figure below (images based on data from Meiners et al). Results on possible associations with histopathological and clinical parameters of tumor aggressiveness are also summarized below (table based on data from Meiners et al).
Authors conclusions on diagnostic utility with respect to the distinction of benign versus malignant (Meiners et al):
- Not applicable.
Authors conclusions on diagnostic utility with respect to the distinction of different tumor entities (Meiners et al):
- The exceptional low rate of ACE2 positivity in chromophobe renal cell cancers (4%) as compared to clear cell (86%) or papillary (94%) renal cell cancers suggests that ACE2 immunohistochemistry may be helpful for the distinction of renal cell cancer subtypes.
Authors conclusions on prognostic/predictive role of ACE2 expression.
- ACE expression is linked to poor grade, loss of ER/PR, HER2 positivity as well as “triple negativity” in breast cancer (p<0,0001 each).
- In colorectal cancer, reduced ACE expression is linked to advanced stage, microsatellite instability, RAS and BRAF mutations as well as tumor localization in the right colon.
- In clear cell renal cell carcinoma, reduced ACE expression is linked to high grade.
Data from the publication: “Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Protein Is Overexpressed in a Wide Range of Human Tumour Types: A Systematic Tissue Microarray Study on >15,000 Tumours” Published by Meiners et al. in Biomedicines, December 3th 2021. Summarized in own graphics:
Figure 1: Organ-systematic distribution of ACE2 staining in human tumors with antibody MSVA-919R.
Figure 2: Ranking order of ACE2 positivity in human tumors antibody MSVA-919R.
Protocol Recommendations
IHC users have different preferences on how the stains should look like. Some prefer high staining intensity of the target stain and even accept some background. Others favor absolute specificity and lighter target stains. Factors that invariably lead to more intense staining include higher concentration of the antibody and visualization tools, longer incubation time, higher temperature during incubation, higher temperature and longer duration of the heat induced epitope retrieval (slide pretreatment). The impact of the pH during slide pretreatment has variable effects and depends on the antibody and the target protein.
All images and data shown here and in our image galleries are obtained by the manual protocol described below. Other protocols resulting in equivalent staining are described as well.
Manual protocol
Freshly cut sections should be used (less than 10 days between cutting and staining). Heat-induced antigen retrieval for 5 minutes in an autoclave at 121°C in pH 7,8 Target Retrieval Solution buffer. Apply MSVA-919R at a dilution of 1:150 at 37°C for 60 minutes. Visualization of bound antibody by the EnVision Kit (Dako, Agilent) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Potential Research Applications
- ACE2 is a key host cell receptor for the spike glycoprotein of the coronavirus HCoV-NL63 causing the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). As such, ACE2 immunostaining is a valuable tool for studies aiming at a better understanding of COVID-19.
- The clinical significance of ACE2 expression in cancers of various types is unknown.
Evidence for Antibody Specificity in IHC
There are two ways how the specificity of antibodies can be documented for immunohistochemistry on formalin fixed tissues. These are: 1. comparison with a second independent method for target expression measurement across a large number of different tissue types (orthogonal strategy), and 2. Comparison with one or several independent antibodies for the same target and showing that all positive staining results are also seen with other antibodies for the same target (independent antibody strategy).
Orthogonal validation: For the antibody MSVA-919R specificity is suggested by the strong concordance of the immunostaining data with data from three independent RNA screening studies, including the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) RNA-seq tissue dataset, the FANTOM5 project, and the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project, which are all summarized in the Human Protein Atlas (Tissue expression ACE2). Immunostaining by using MSVA-919R was almost exclusively detected in organs with documented RNA expression such as kidney, testis, small intestine, duodenum, colorectum, gallbladder, and seminal vesicle. Further sites of ACE2 immunostaining such as in sebaceous glands of the skin, syncytiotrophoblast, cytotrophoblast, and chorion cells of the placenta, decidua cells, fallopian tube, the caput epididymis, adrenocortical cells, apical cell membranes of few alveolar pneumocytes, a small subset of respiratory epithelial cells as well as in endothelial cells of various organs is not mirrored by RNA data. Most of these structures constitute small subsets of the total amount of cells in these organs and may have been largely underrepresented in RNA analyses.
Comparison of antibodies: True expression of ACE2 in respiratory epithelium and stomach glands is suggested by similar findings obtained by the use of the antibody HPA000288. The respective images are depicted in the protein atlas for respiratory epithelium and stomach glands.
The only ACE2 findings obtained by MSVA-919R and not confirmed by HPA000288 include corpus luteum and adrenal cortex staining. Based on published images, corpus luteum was probably not analyzed by HPA000288. Based on studies describing a role of ACE2 in corpus luteum, it is likely that ACE2 is expressed in this organ (PMID: 22046052, PMID: 26679819). As neither RNA expression nor HPA000288 staining occurred in the adrenal cortex, this staining by MSVA-919R is considered a (tolerable) cross-reactivity.