
Adrenal gland – Strong nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells.
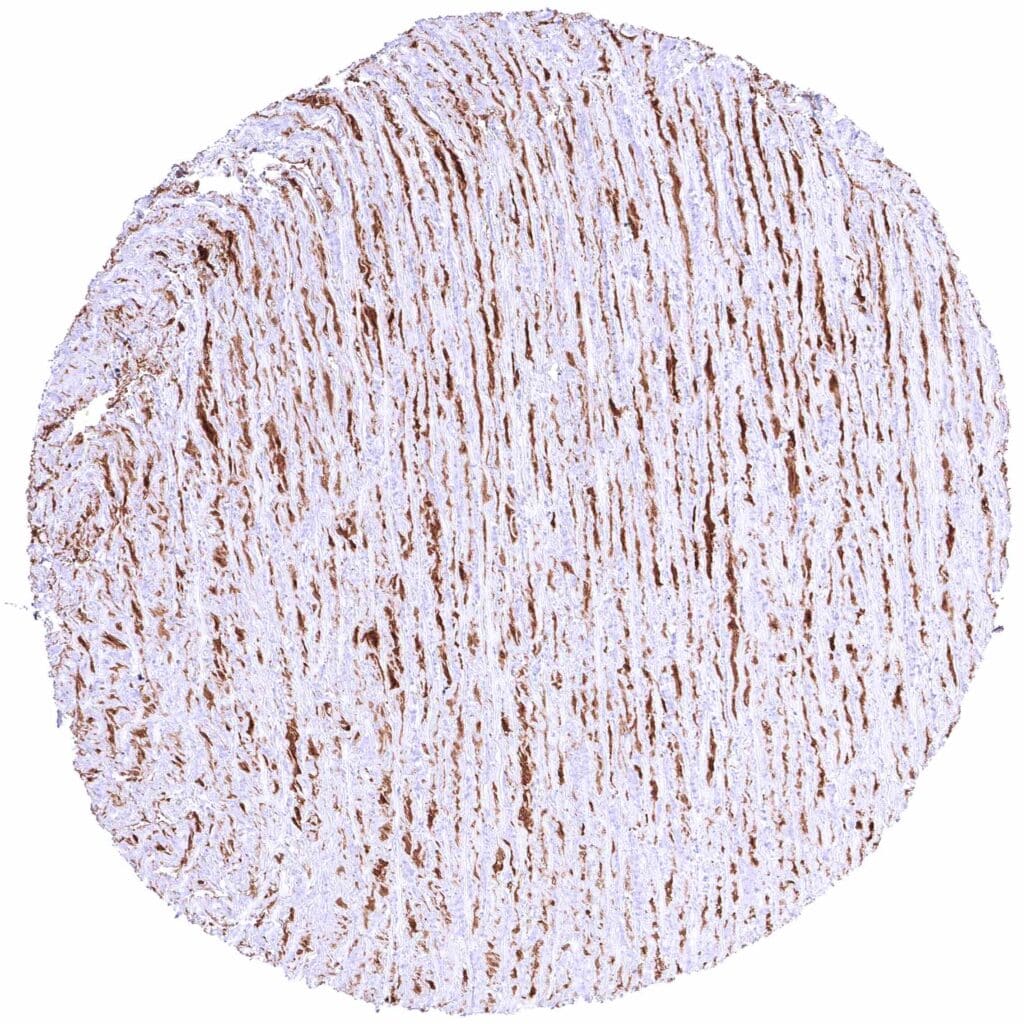
Aorta, endothelium
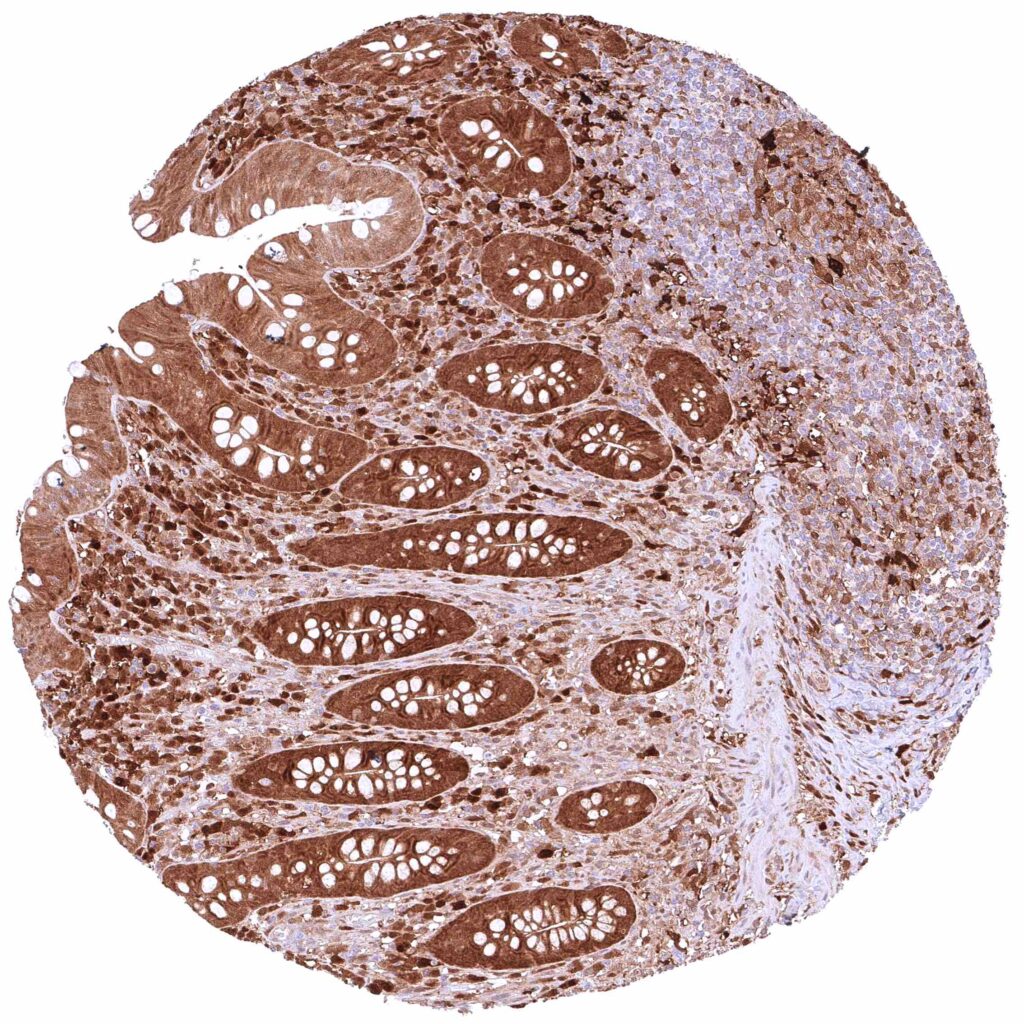
Appendix, mucosa – Strong, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells. Staining is most intense at the base of crypts and decreases slightly towards the surface epithelium.

Appendix, muscular wall – Weak cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of smooth muscle cells.

Bone marrow – Moderate to strong, nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 staining of most cell populations although some cell types (erythropoiesis_) remain GSTP1 negative

Breast – Moderate to strong, nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of most luminal epithelial cells, although some of them remain negative in this sample. Staining is less intensive in basal-myoepithelial cells than in luminal cells

Bronchus, mucosa – Strong nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of respiratory epithelial cells.

Cerebellum (molecular layer, Purkinje cell layer, granule cell layer) – Moderateto strong GSTP1 staining of Purkinje cells and fibers in the molecular layer. Weak to moderate positivity of a small subset of cells of the granule cell layer and of endothelial cells.

Cerebellum (white matter) – Moderate to strong GSTP1 staining of glia cells. Weak to moderate positivity of endothelial cells.

Cerebrum (grey matter) – Distinct GSTP1 positivity of fibres and of all cell types except neurons.

Cerebrum (white matter) – Distinct GSTP1 positivity of fibres and of glial cells.

Colon descendens, muscular wall – Weak cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of smooth muscle cells.

Colon descendens, mucosa – Moderate, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells. Staining is most intense at the base of crypts and decreases slightly towards the surface epithelium

Duodenum, Brunner gland – Brunner glands are largely GSTP1 negative if cells are distant enough from the mucosa layer.

Duodenum, mucosa – Strong predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells.

Epididymis (Caput) – Intense, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 staining of epithelial cells.

Epididymis (Cauda) – Intense, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 staining of epithelial cells.

Esophagus, muscular wall – Faint cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of smooth muscle cells.

Esophagus, squamous epithelium – Strong cytoplasmic and nuclear GSTP1 positivity of squamous epithelial cells. Staining intensity is highest in the basal and suprabasal cell layers and decreases slightly towards the surface

Fallopian tube, mucosa – Intense nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells.

Fat

Gallbladder, epithelium – Strong nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells.

Heart muscle – Most GSTP1 staining occurs around small capillaries while the muscle cells are GSTP1 negative.

Ileum, mucosa – Moderate to strong cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells. Staining is most intense at the base of crypts and decreases slightly towards the surface epithelium.

Ileum, muscular wall – Weak cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of smooth muscle cells.

Kidney, cortex – GSTP1 staining is intense in distal tubuli, collecting ducts, and in the parietal layer of the capsule of Bowman but “only” moderate in proximal tubuli in this sample.

Kidney, cortex – GSTP1 staining is strong in distal tubuli, collecting ducts, and in the parietal layer of the capsule of Bowman but weak or absent in proximal tubuli in this sample.

Kidney, medulla – Strong GSTP1 staining in collecting ducts.

Kidney, pelvis, muscular wall – Weak cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of few smooth muscle cells.

Kidney, pelvis, urothelium – Strong, nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of most urothelial cells but the staining is only weak in a subset of umbrella cells.

Liver – Weak to moderate, cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of sinus endothelial cells while staining is stronger in Kupffer cells. Hepatocytes are GSTP1 negative.

Lung – Moderate, predominantly cytoplasmic positivity of alveolar endothelial cells. Strong, nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of at least a significant subset of alveolar cells.

Lymph node – At least a weak cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity occurs in all cells of this sample.

Lymph node – Nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity is limited to a small subset of cells in this sample.

Ovary, corpus luteum – Weak to moderate, cytoplasmic GSTP1 of corpus luteum cells.

Ovary, follicular cyst – Moderate to strong nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 staining of granulosa cells.

Ovary, stroma – Intense, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of stroma cells.

Pancreas – Weak to moderate, nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of acinar cells. Strong GSTP1 staining of intercalated and excretory ducts. Weak GSTP1 positivity of only a subset of islet cells

Parathyroid gland – Strong nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells.

Parotid gland – Weak to moderate, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 staining of glandular cells. GSTP1 staining is markedly stronger in intercalated and excretory ducts.

Pituitary gland, posterior lobe – Distinct GSTP1 positivity of fibres and probably also of pituicytes.

Pituitary gland, anterior lobe – All cells are GSTP1 positive in the adenohypophysis, but the intensity varies sharply from moderate to intense (mosaic pattern).

Placenta (amnion and chorion) – Moderate to strong, nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of chorion and amnion cells.

Placenta, early – Intense, nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast cells in this sample.

Placenta, early – Weak, nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast cells in this sample.

Placenta, mature – Intense, nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast cells in this sample.

Prostate – Intense nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 staining of basal cells while staining is faint or absent in acinar cells

Prostate – Intense nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 staining of basal cells while staining is faint or absent in acinar cells

Prostate – Intense nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 staining of basal cells while staining is faint, weak or even absent in acinar cells

Rectum, mucosa – Strong, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells. Staining is most intense at the base of crypts and decreases slightly towards the surface epithelium.

Seminal vesicle – Intense, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 staining of epithelial cells.

Sinus paranasales – Moderate nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of respiratory epithelial cells.

Skeletal muscle – Most GSTP1 staining occurs around small capillaries while the muscle cells are GSTP1 negative.

Skin – Strong nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of all squamous epithelial cells.

Skin, ekkrine glands – Strong GSTP1 positivity of eccrine glands.

Skin, hairfollicle and sebaceous glands – Strong GSTP1 positivity of hair follicles and peripheral germinative cells of sebaceous glands while sebaceous cells remain GSTP1 negative.

Spleen – At least a weak cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity occurs in all cells of this sample.

Spleen – Nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity is limited to a small subset of cells in this sample. .jpeg

Stomach, antrum – Strong, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of gastric surface epithelium and most cell types of antrum glands.

Stomach, corpus – Strong, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of gastric surface epithelium and specific glandular cells (parietal cells are GSTP1 negative).

Stomach, muscular wall – Weak cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of smooth muscle cells.

Sublingual gland – Weak to moderate, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 staining of glandular cells, more intense in mucinous than in serous glands. Staining is markedly stronger in excretory ducts.

Submandibular gland – Weak to moderate, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 staining of glandular cells. Staining is markedly stronger in intercalated and excretory ducts.

Testis – Faint cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of spermatogonia while maturing germ cells and Sertoli cells are GSTP1 negative. Strong GSTP1 positivity of Leydig cells.

Testis – Very faint cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of spermatogonia while maturing germ cells and Sertoli cells are GSTP1 negative. Moderate GSTP1 positivity of Leydig cells.

Thymus – At least a weak cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity occurs in all cells of this sample.

Thymus – Nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity is limited to a small subset of cells in this sample. Many GSTP1 positive cells are thymic epithelial cells.

Thymus – Nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of a subset of cells including thymic epithelial cells and corpuscles of Hassall’s.

Thyroid gland – Strong nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells.

Tonsil – At least a weak cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity occurs in all cells of this sample.

Tonsil – GSTP1 positivity is most prominent in a subset of germinal centre cells (dendritic cells_) in this sample.

Tonsil – GSTP1 positivity is most prominent in squamous epithelial cells and a subset of germinal centre cells in this sample.

Tonsil, surface epithelium – Strong nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of all squamous epithelial cells. Variable, often weak, staining of lymphatic cells.

Urinary bladder, urothelium – Moderate to strong, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of urothelial cells.

Urinary bladder, urothelium – Moderate to strong, predominantly nuclear GSTP1 positivity of urothelial cells.

Urinary bladder, muscular wall – Weak cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of smooth muscle cells.

Uterus, ectocervix – Cytoplasmic and nuclear GSTP1 positivity of variable intensity of squamous epithelial cells. Staining intensity is highest in the basal and suprabasal cell layers and decreases towards the surface

Uterus, endocervix – Strong, nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells.

Uterus, endometrium (pregnancy) – Intense GSTP1 positivity of endometrial epithelial cells. Weak to moderate, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 staining of decidua cells.

Uterus, endometrium (proliferation) – Strong, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells. However, Staining is only faint or absent in certain distinct cell groups

Uterus, endometrium (secretion) – Strong, predominantly cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of epithelial cells.

Uterus, myometrium – Distinct, nuclear and cytoplasmic GSTP1 positivity of muscle cells.
