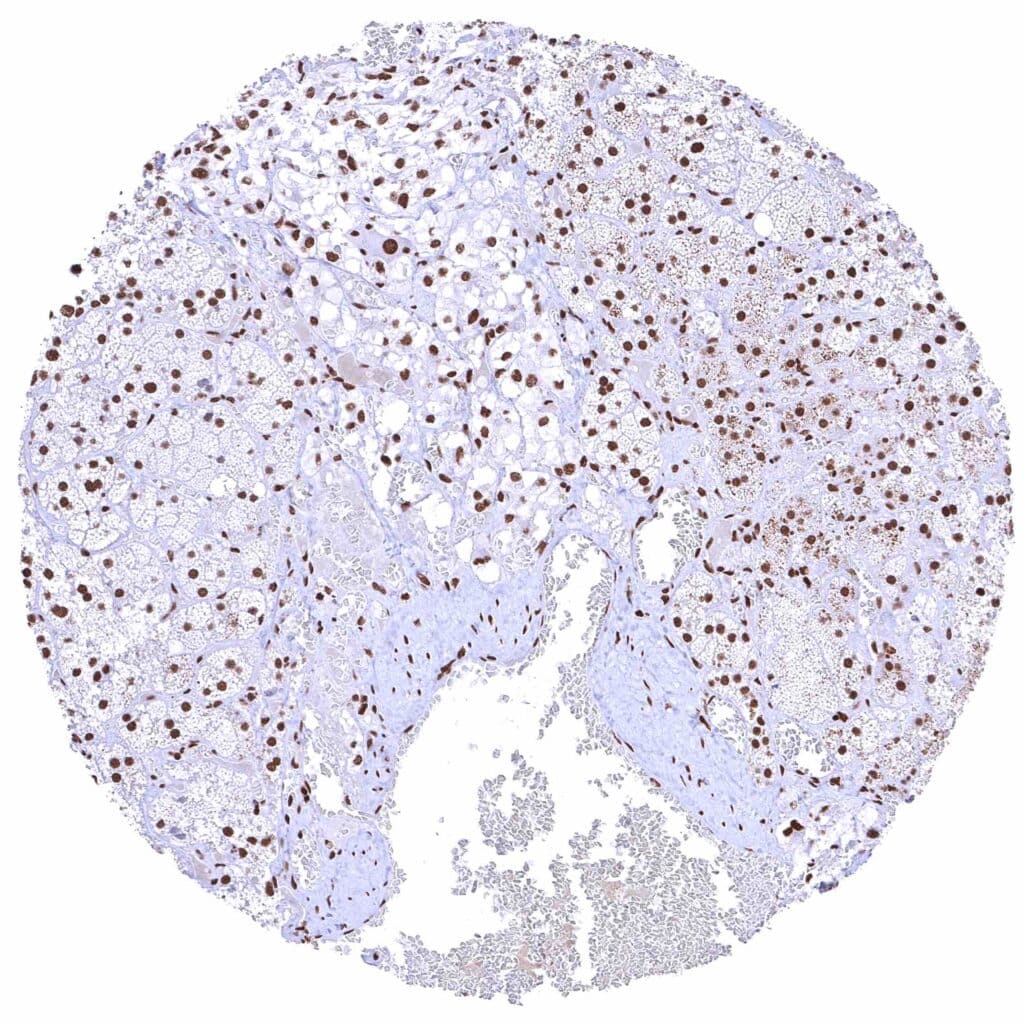
Adrenal gland – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of epithelial cells.
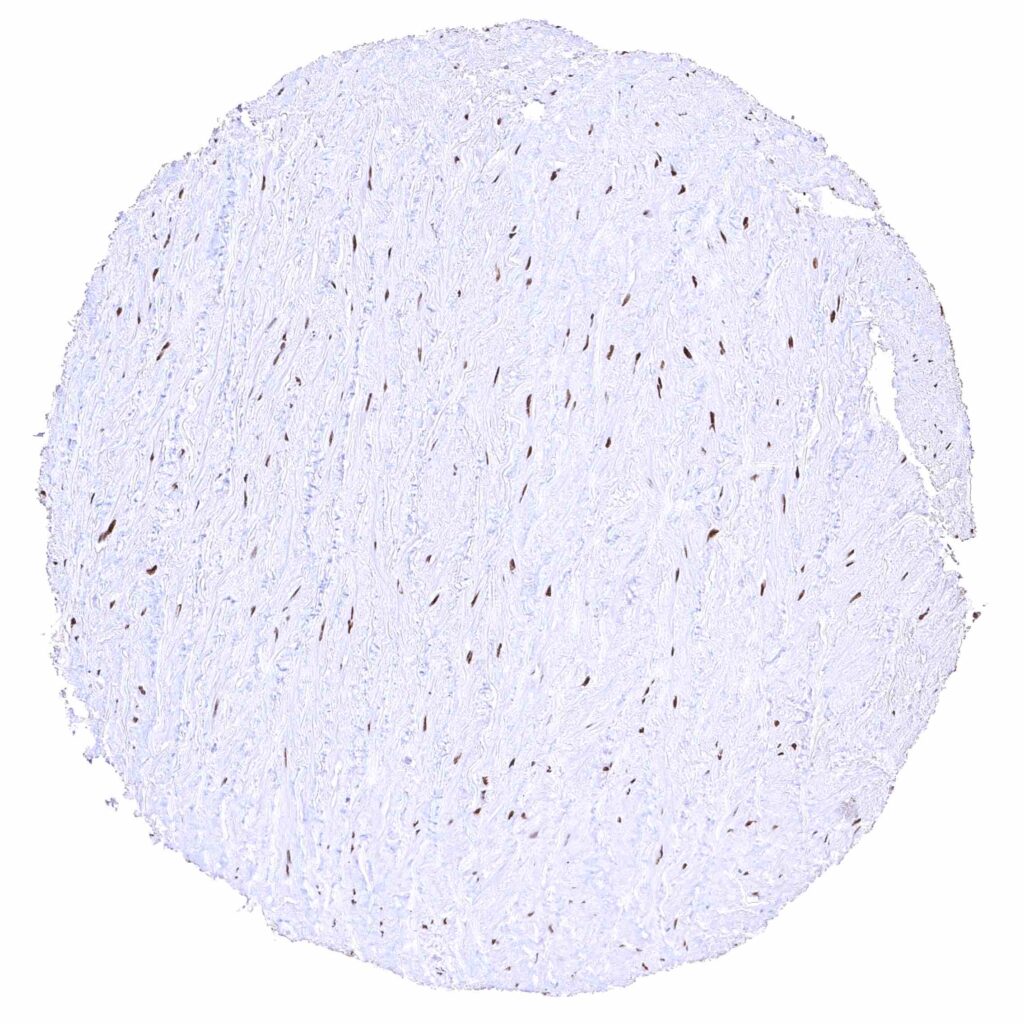
Aorta, media
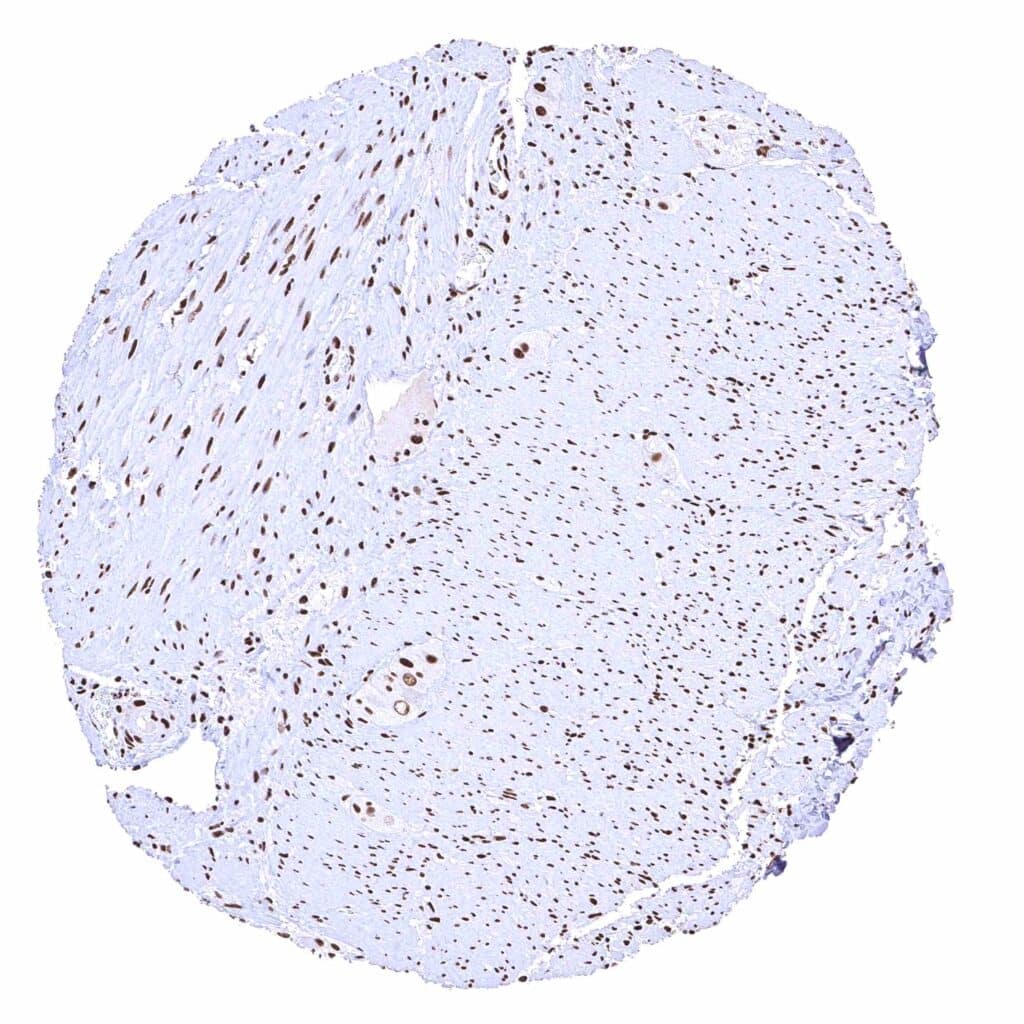
Appendix, muscular wall – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of smooth muscle and ganglion cells.
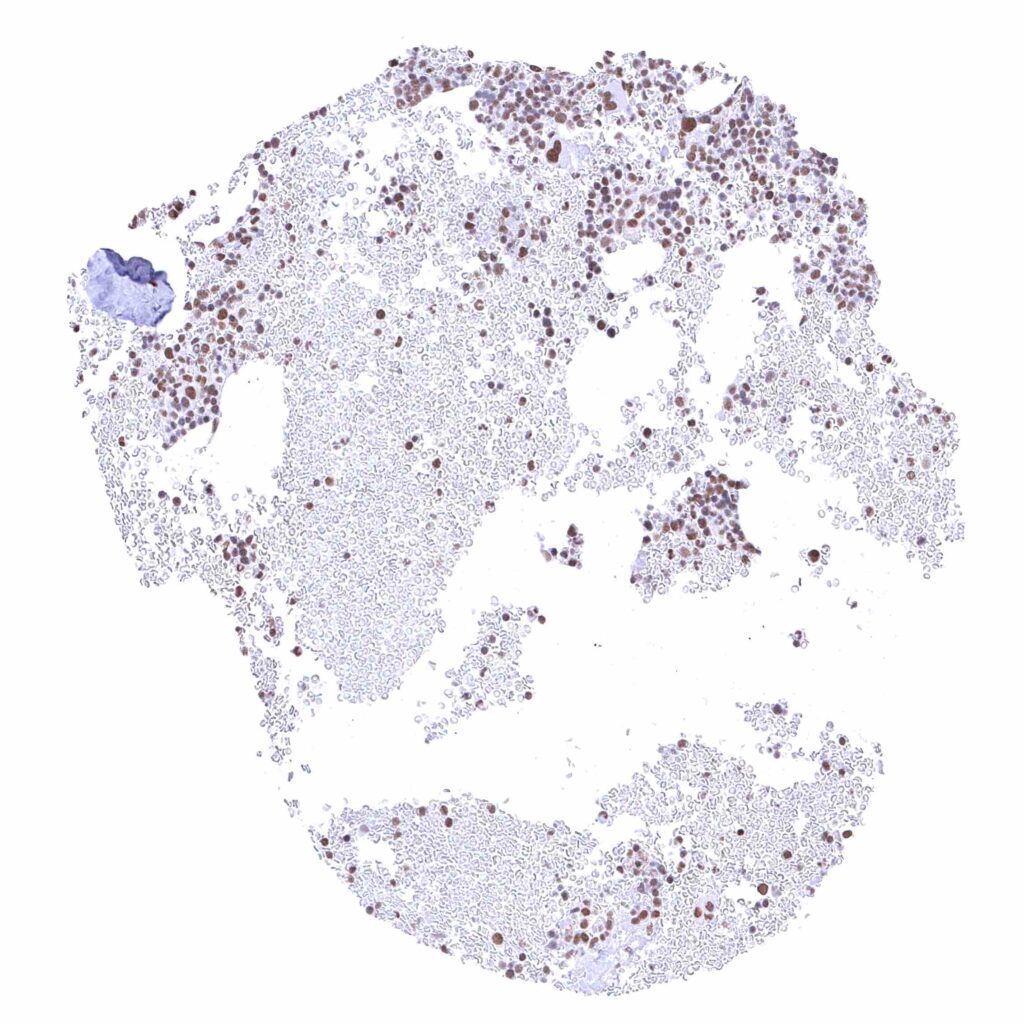
Bone marrow
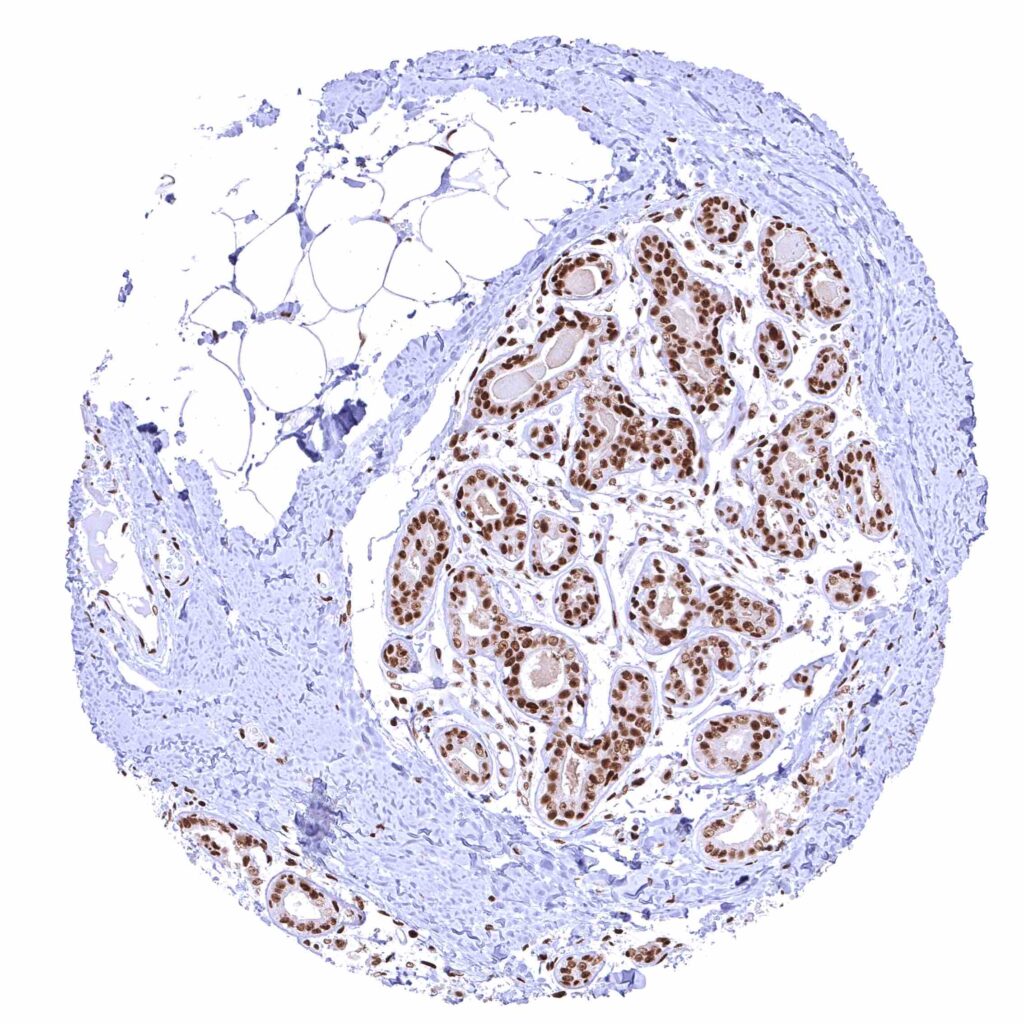
Breast – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of epithelial cells.
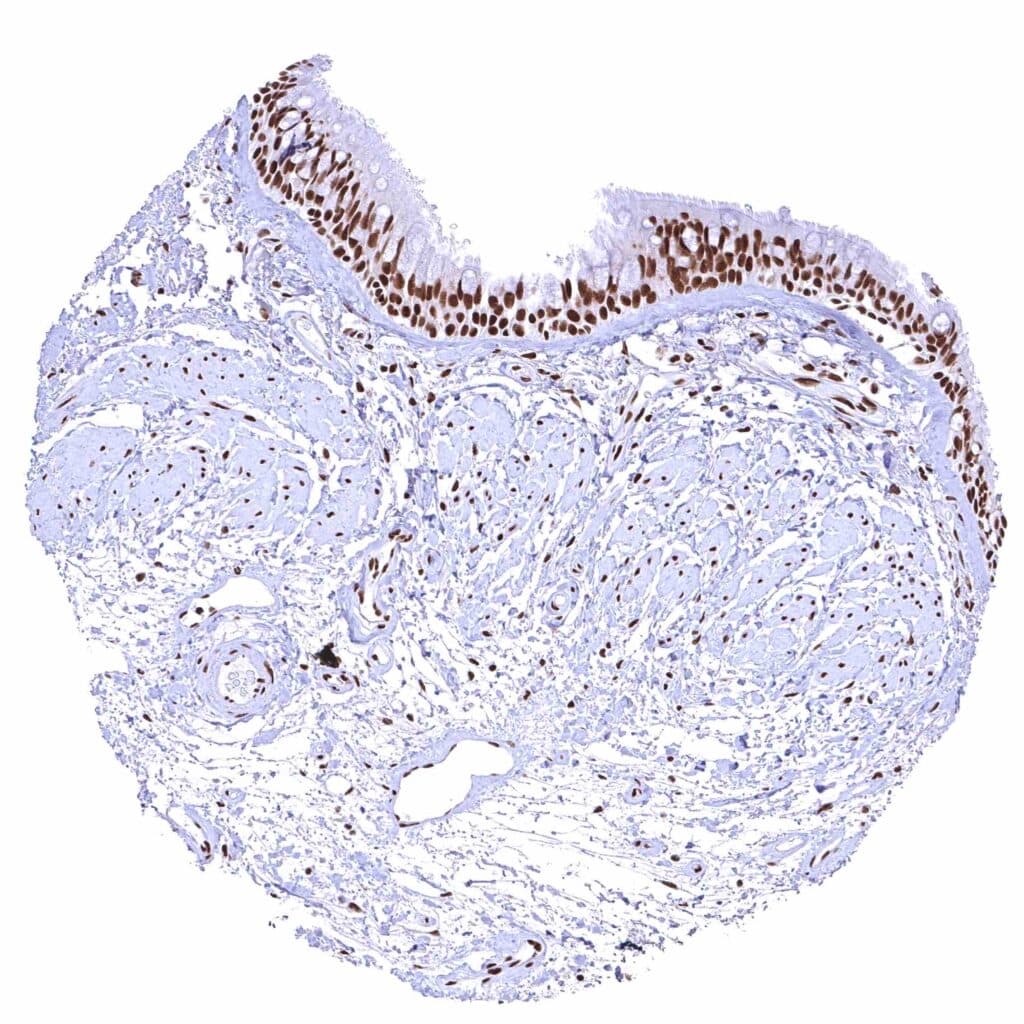
Bronchus, mucosa
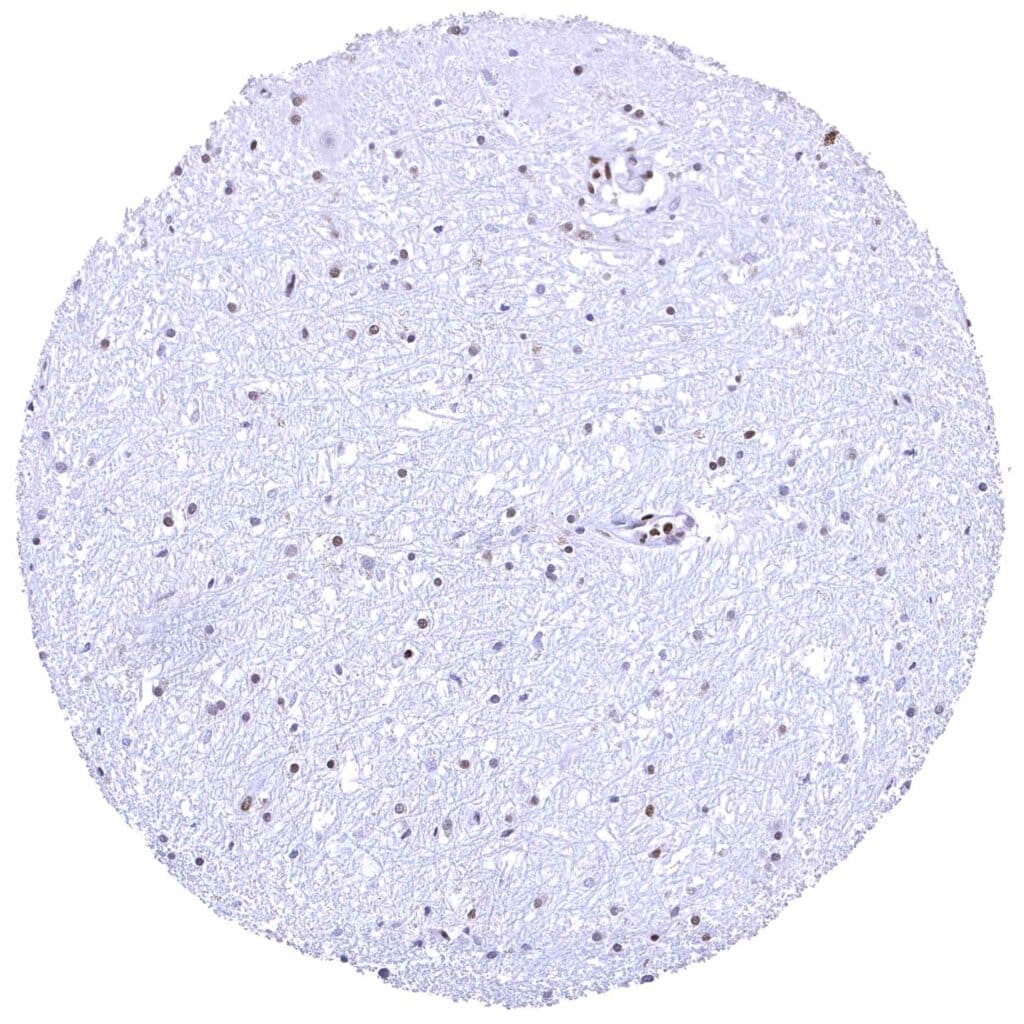
Cerebellum (white matter) – Nuclear BRD4 staining of glia cells.
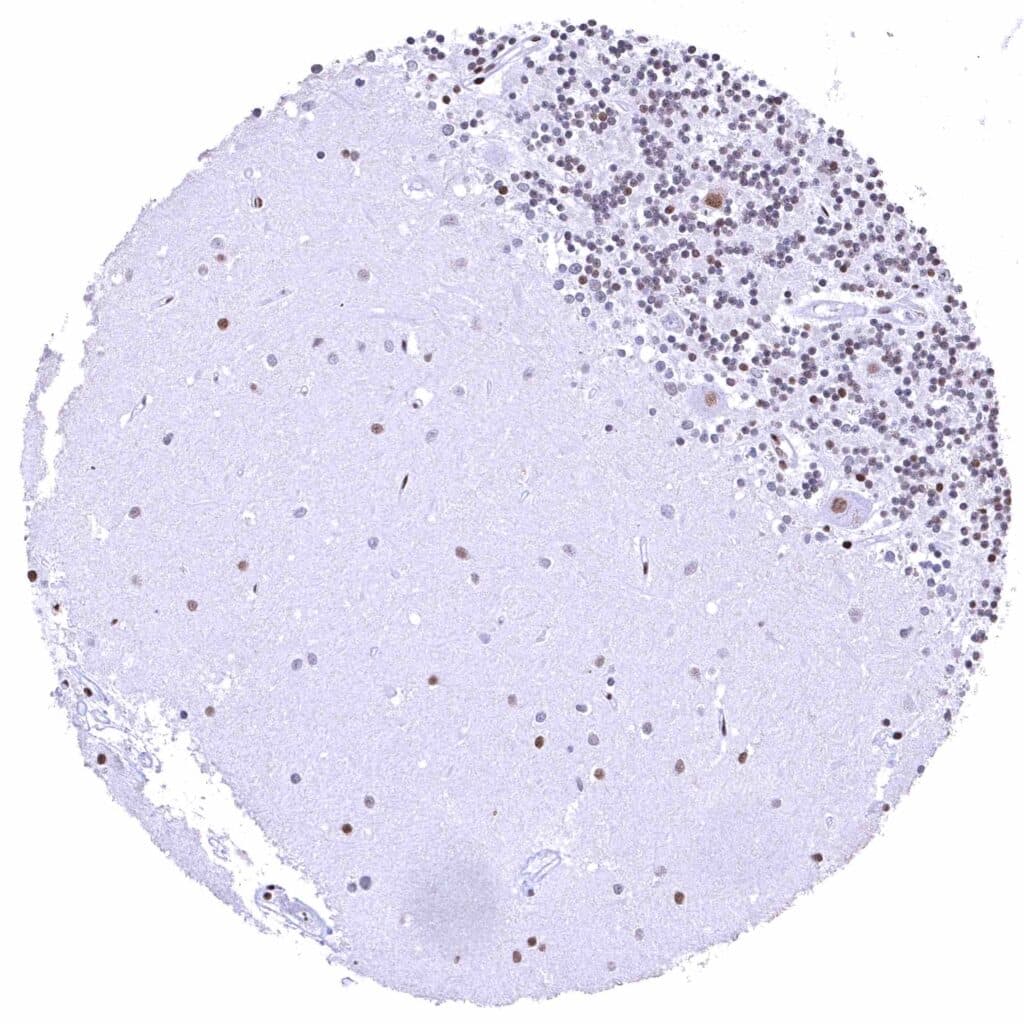
Cerebellum, cortex (molecular layer, Purkinje cell layer, granule cell layer) – Nuclear BRD4 staining of Purkinje cells, cells of the granule layer (variable intensity), and glia cells.
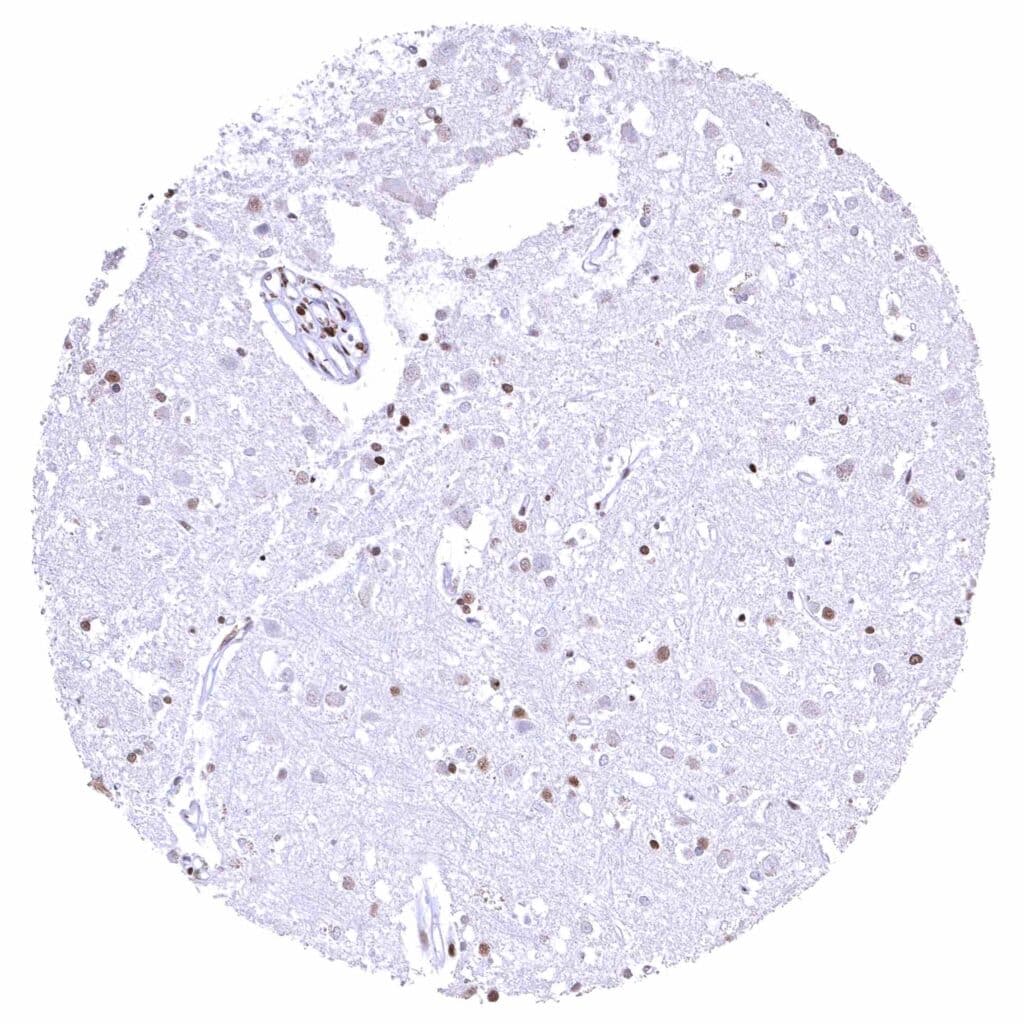
Cerebrum, grey matter – BRD4 staining is strong in glia cells but low or absent in neuronal cells.
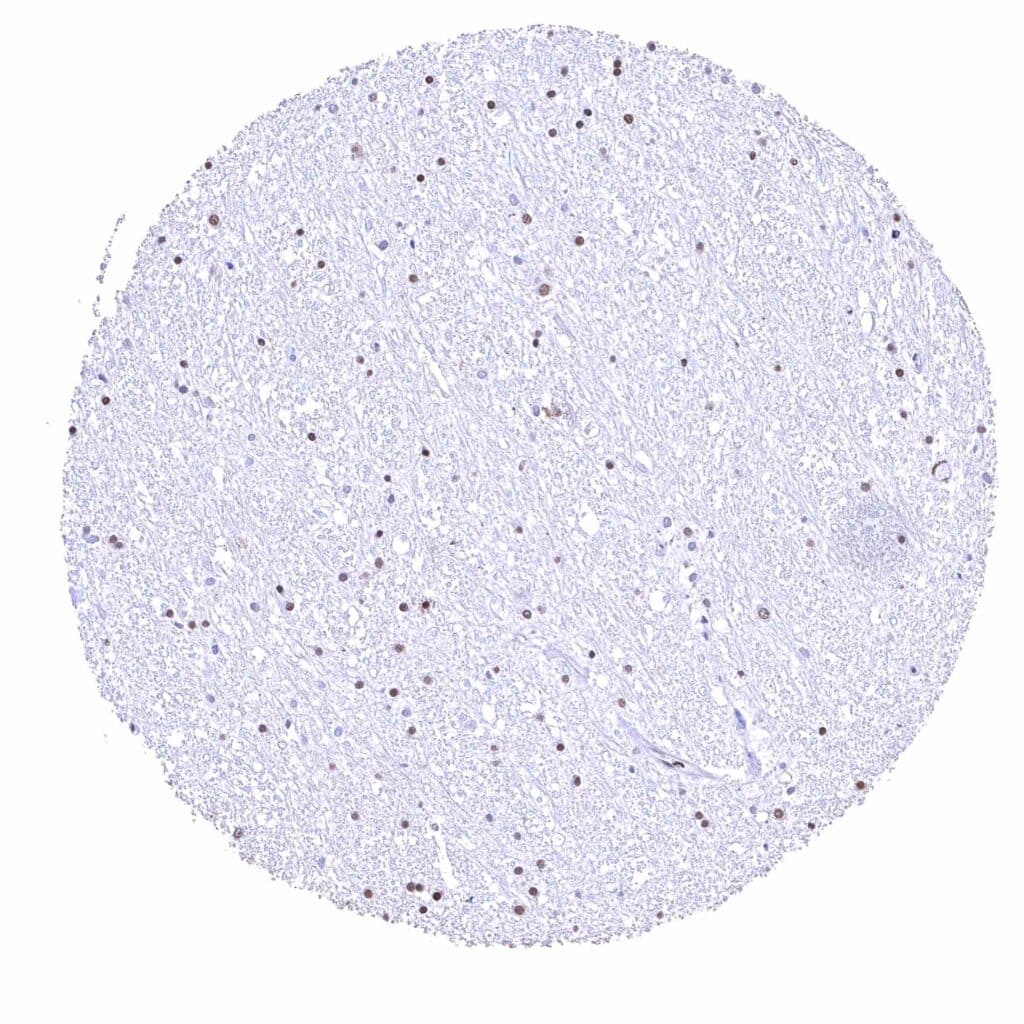
Cerebrum, white matter – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of glia cells.
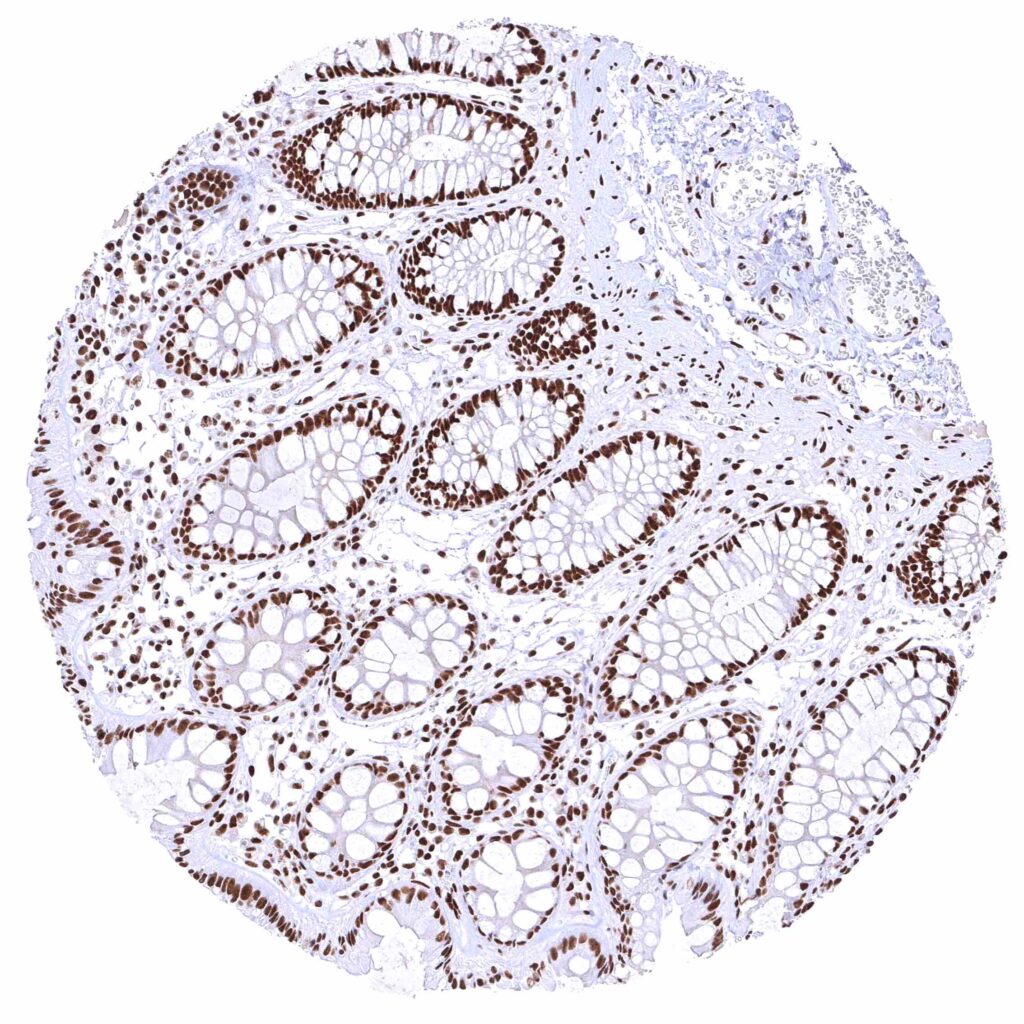
Colon descendens, mucosa – Nuclear BRD4 staining of surface epithelial cells is weaker than in crypts.
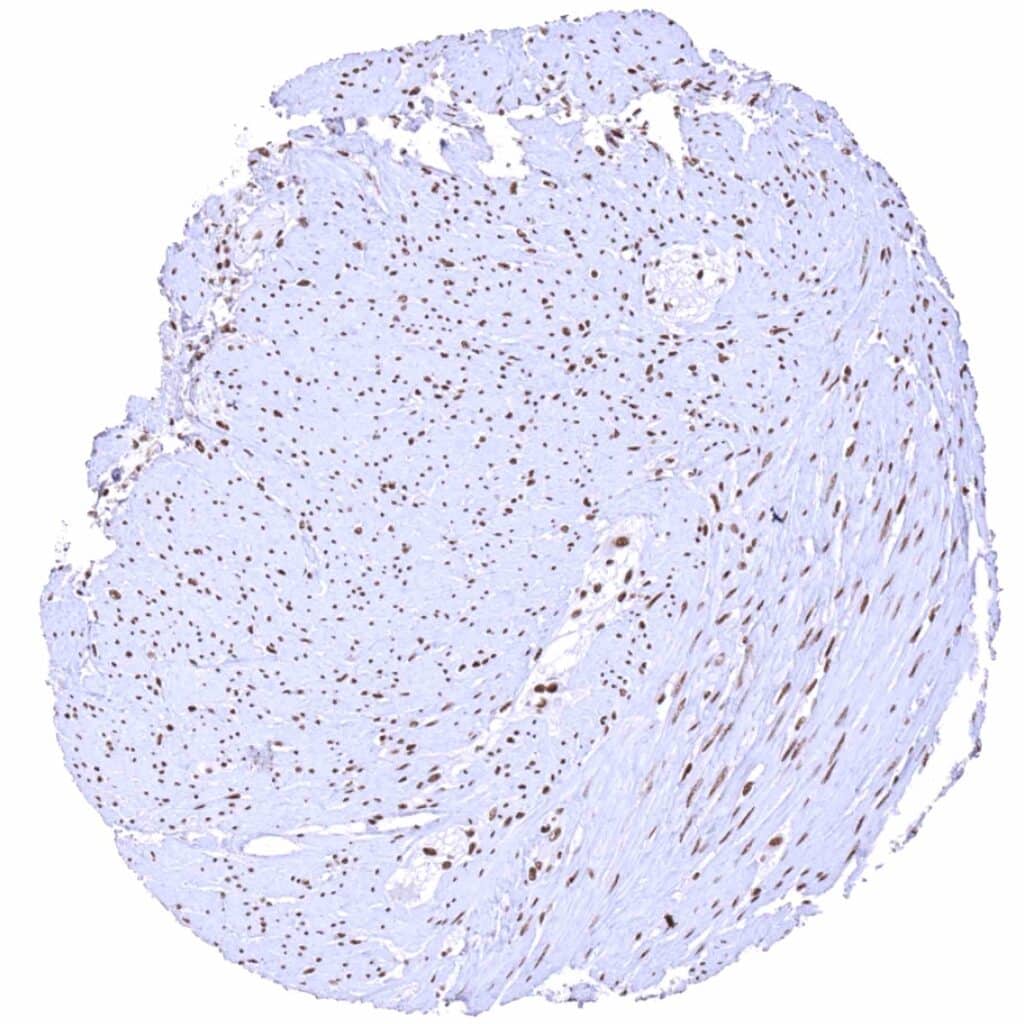
Colon descendens, muscular wall – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of smooth muscle and ganglion cells.
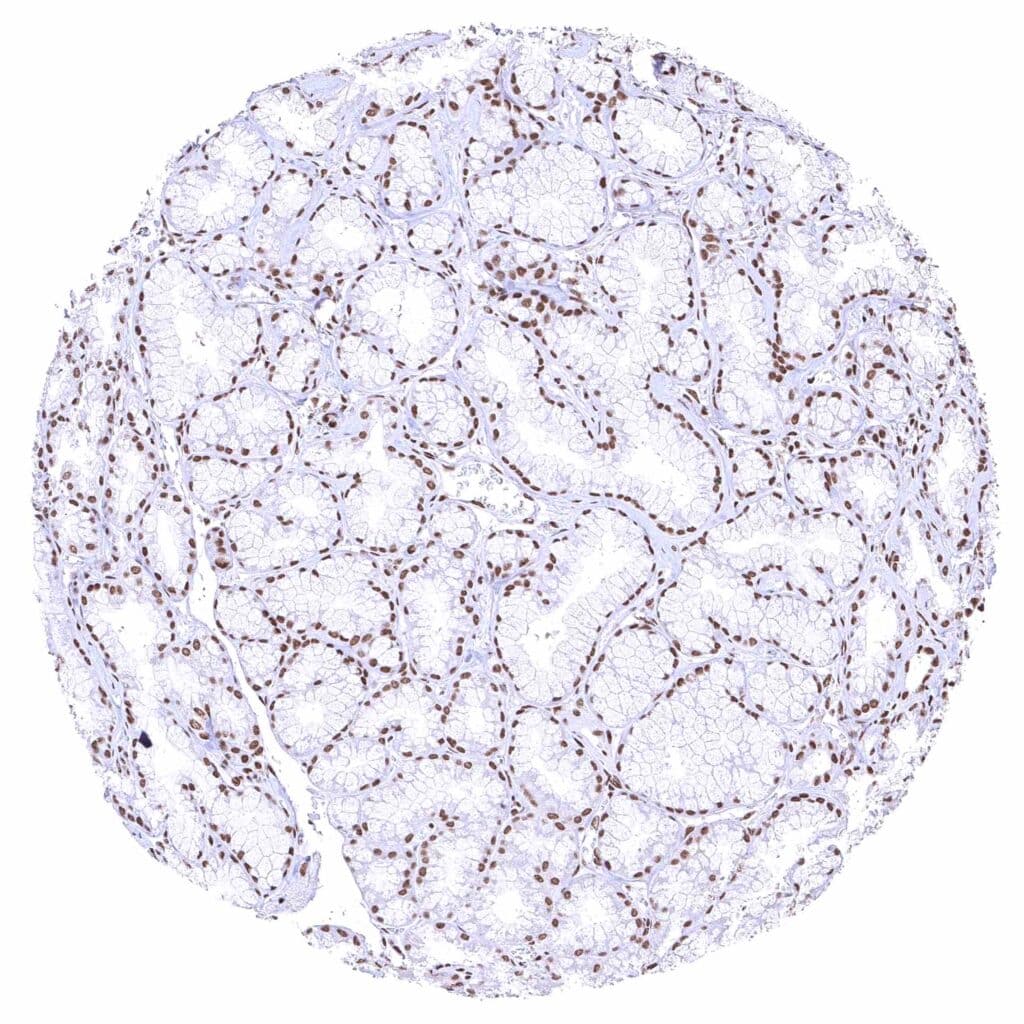
Duodenum, Brunner gland
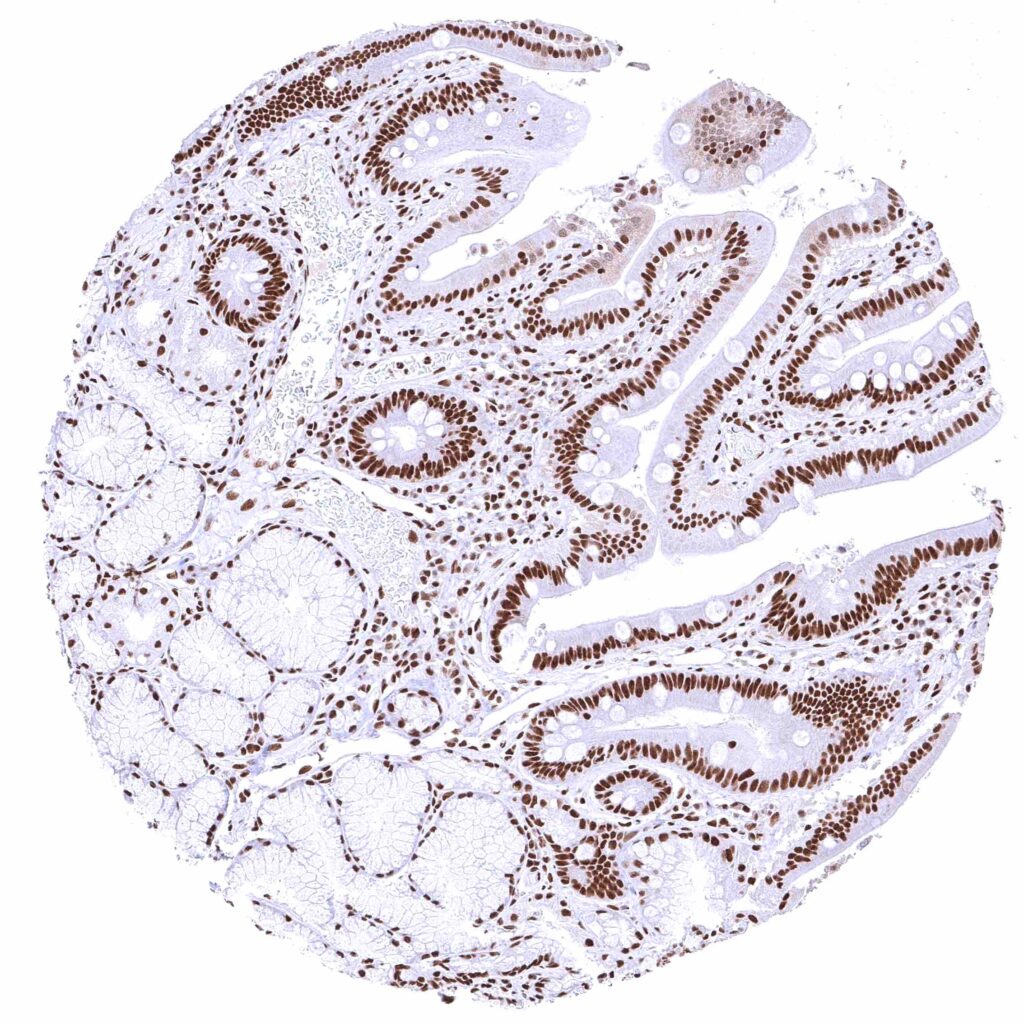
Duodenum, mucosa – BRD4 staining of surface epithelial cells is markedly stronger than in Brunner glands.
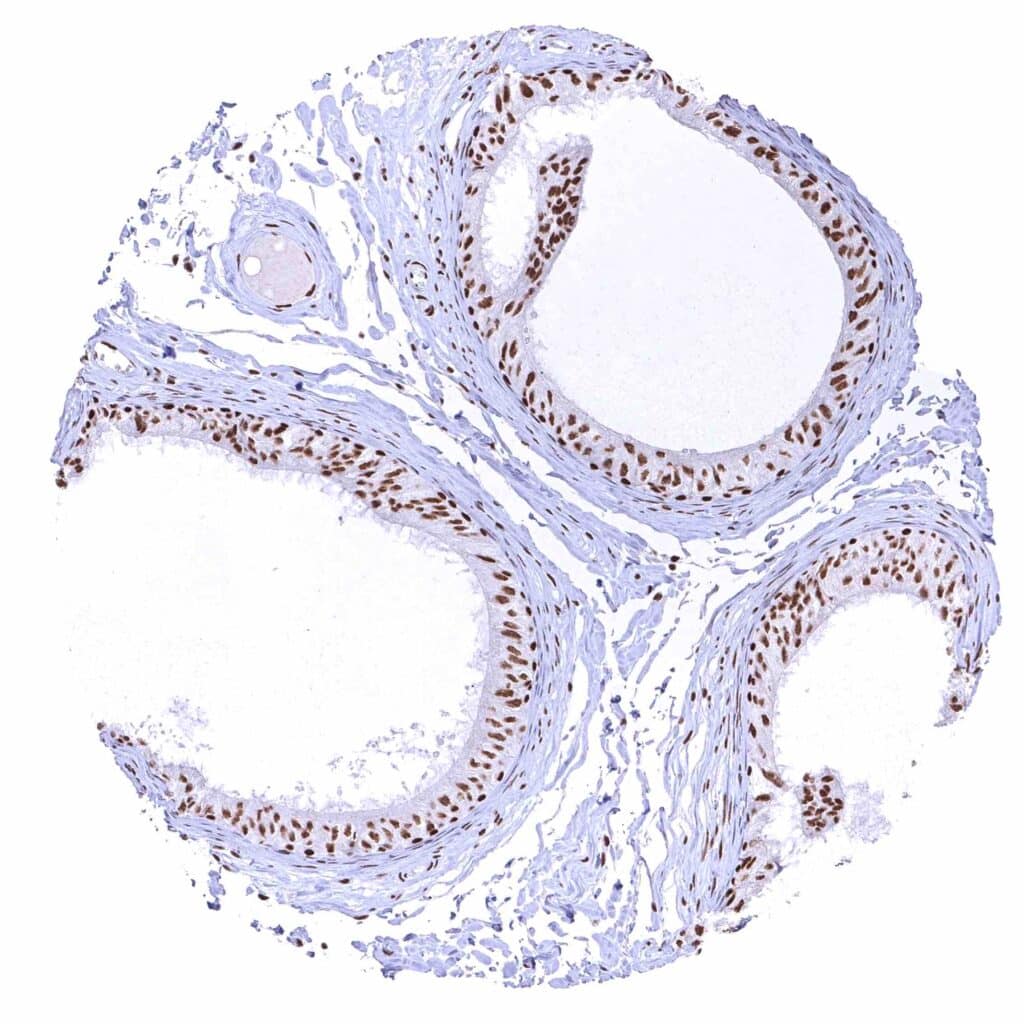
Epididymis (Caput)
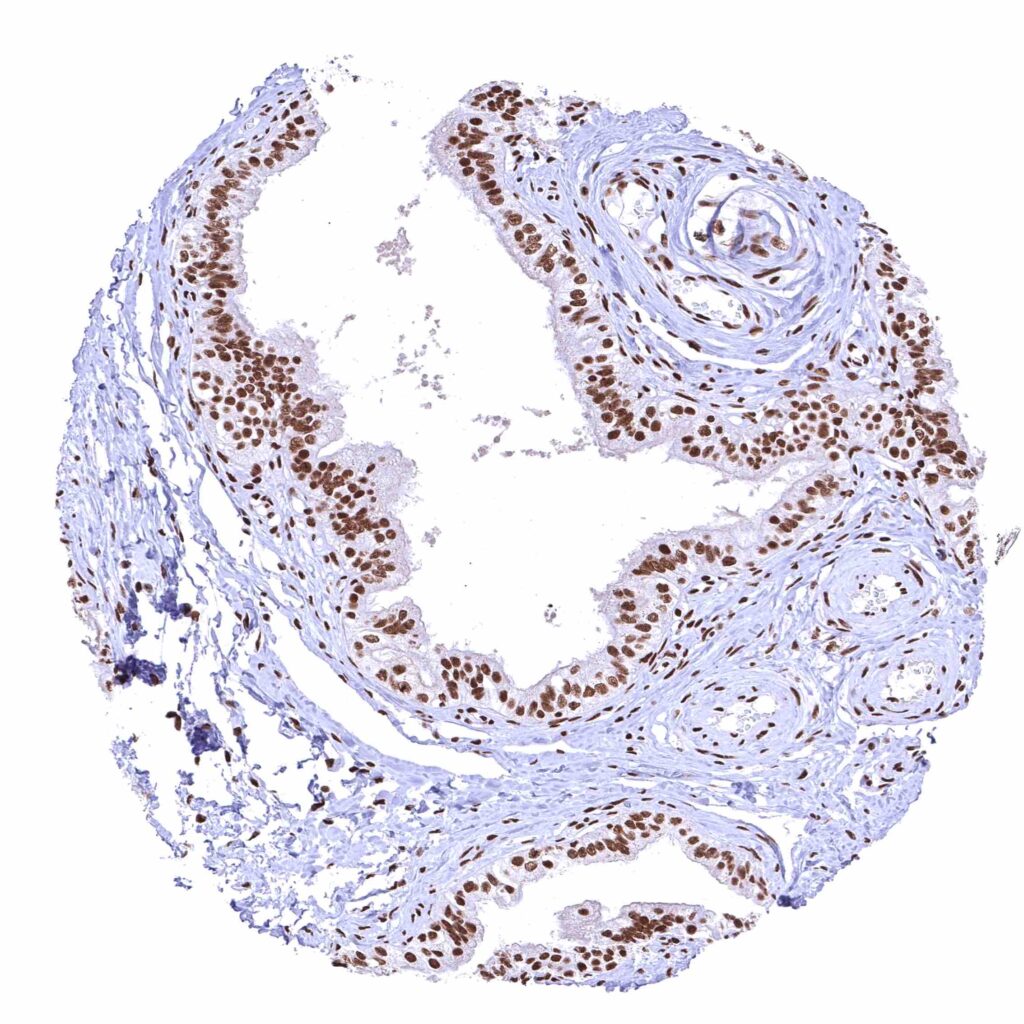
Epididymis (Cauda)
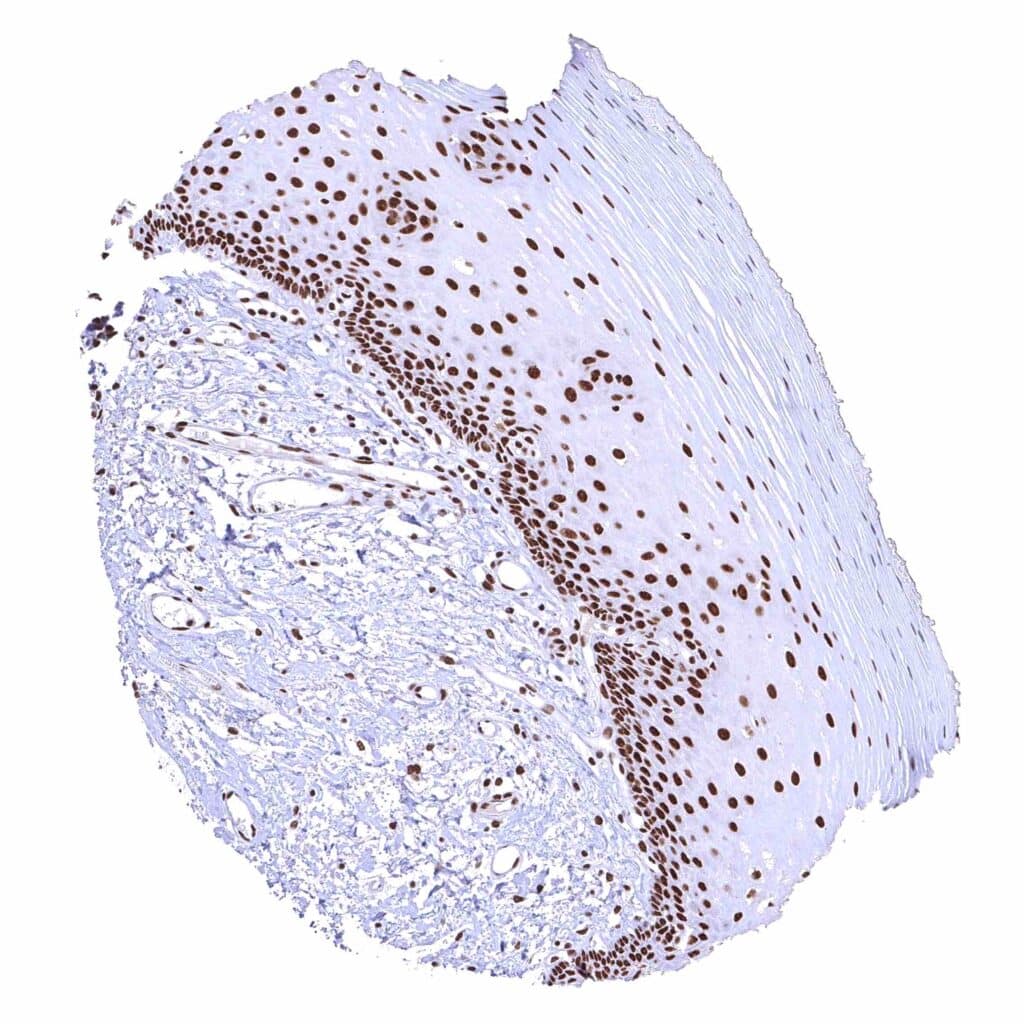
Esophagus, squamous epithelium – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of squamous epithelial cells with a slight decrease of the staining intensity towards the most superficial cell layers. .jpeg
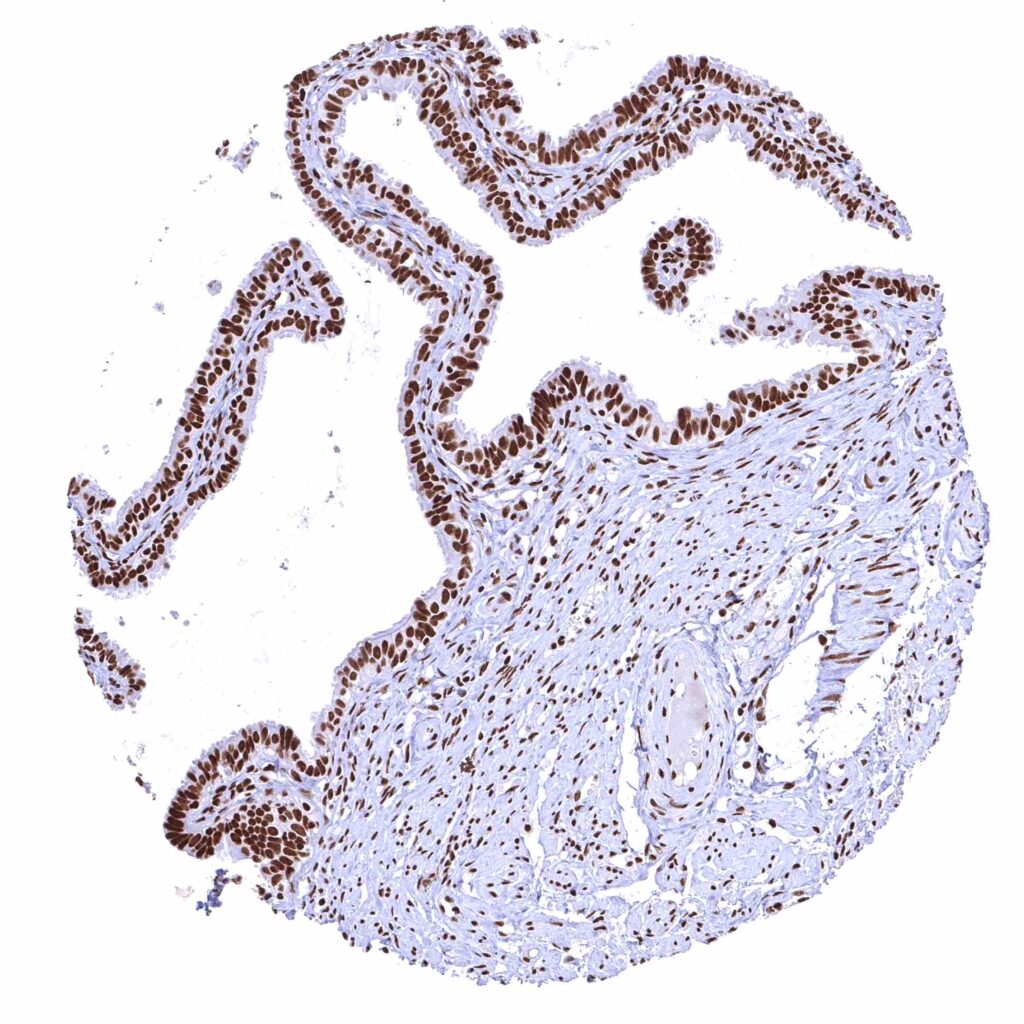
Fallopian tube, mucosa – Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of epithelial cells.
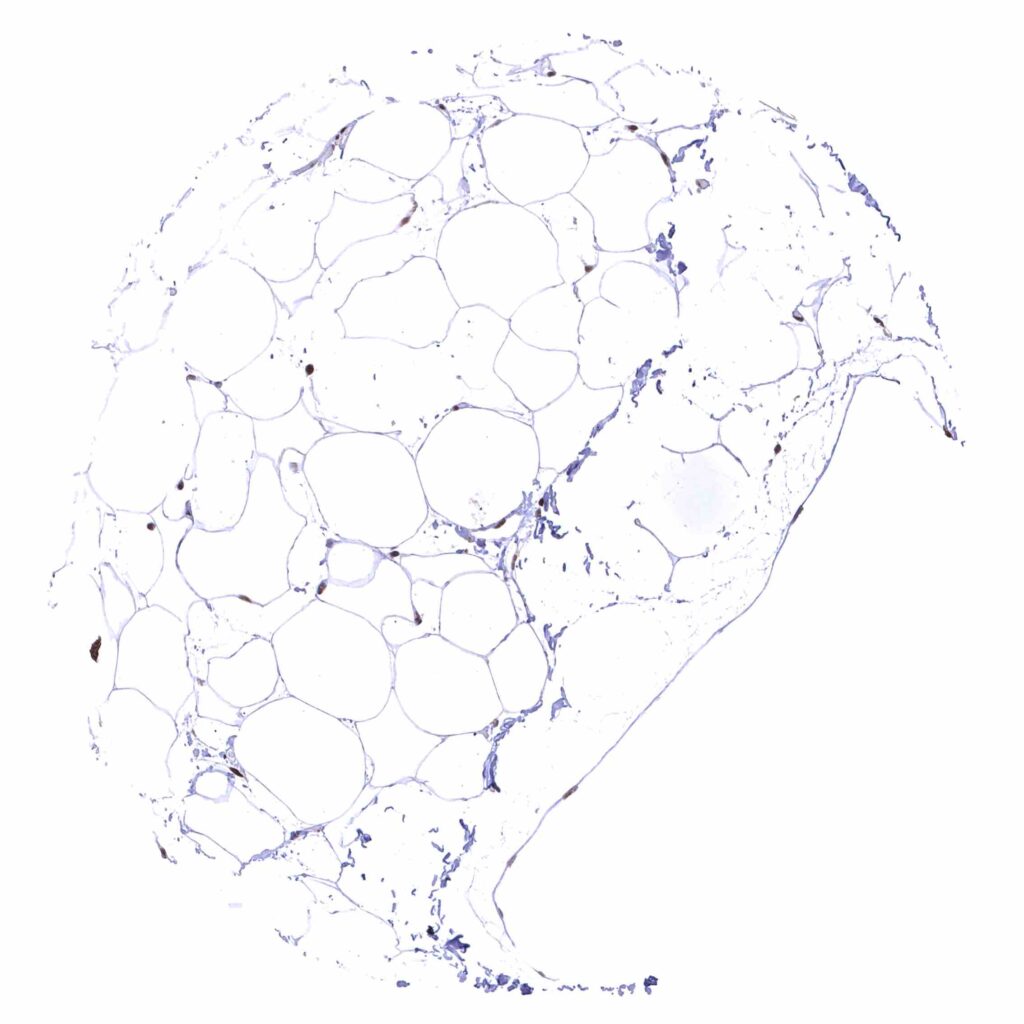
Fat – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of fat cells.
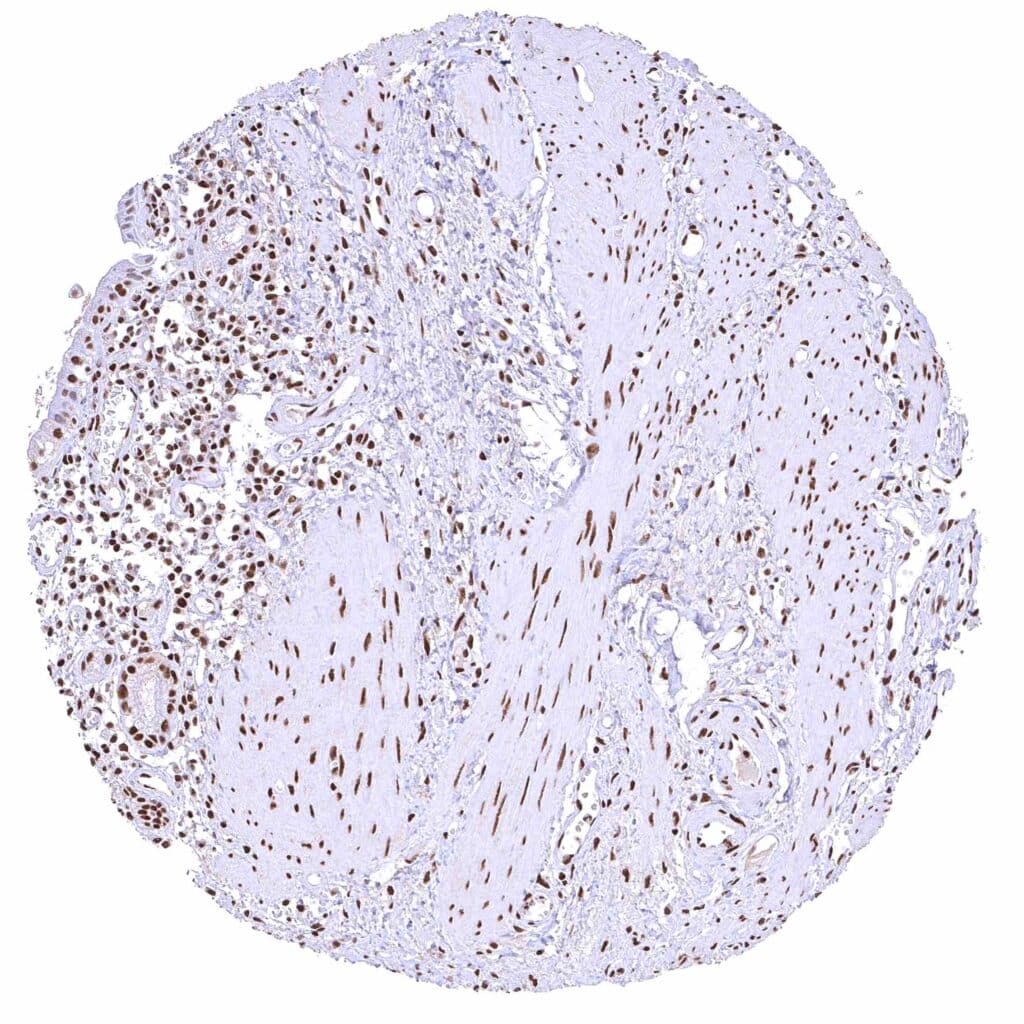
Gallbladder, epithelium
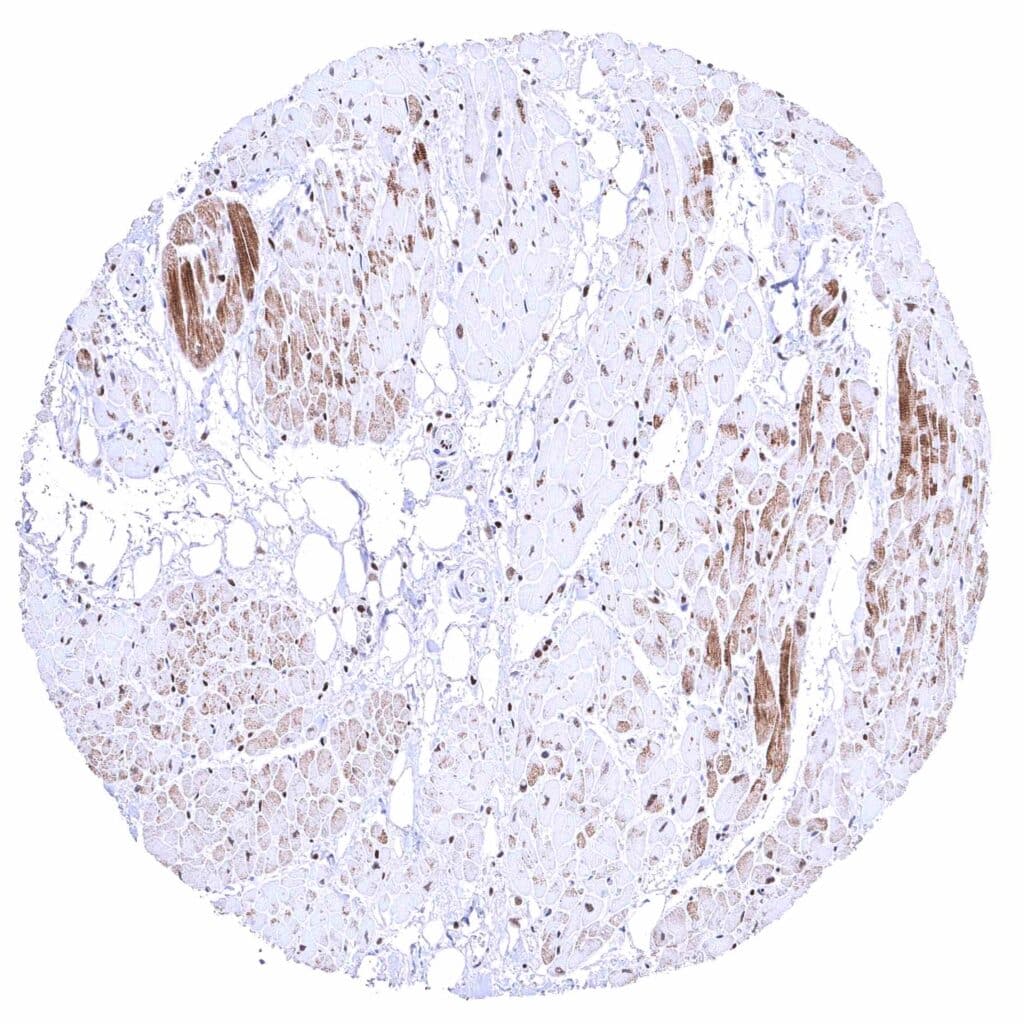
Heart muscle – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. The additional cytoplasmic staining of some muscle cells may represent an antibody specific cross-reactivity.
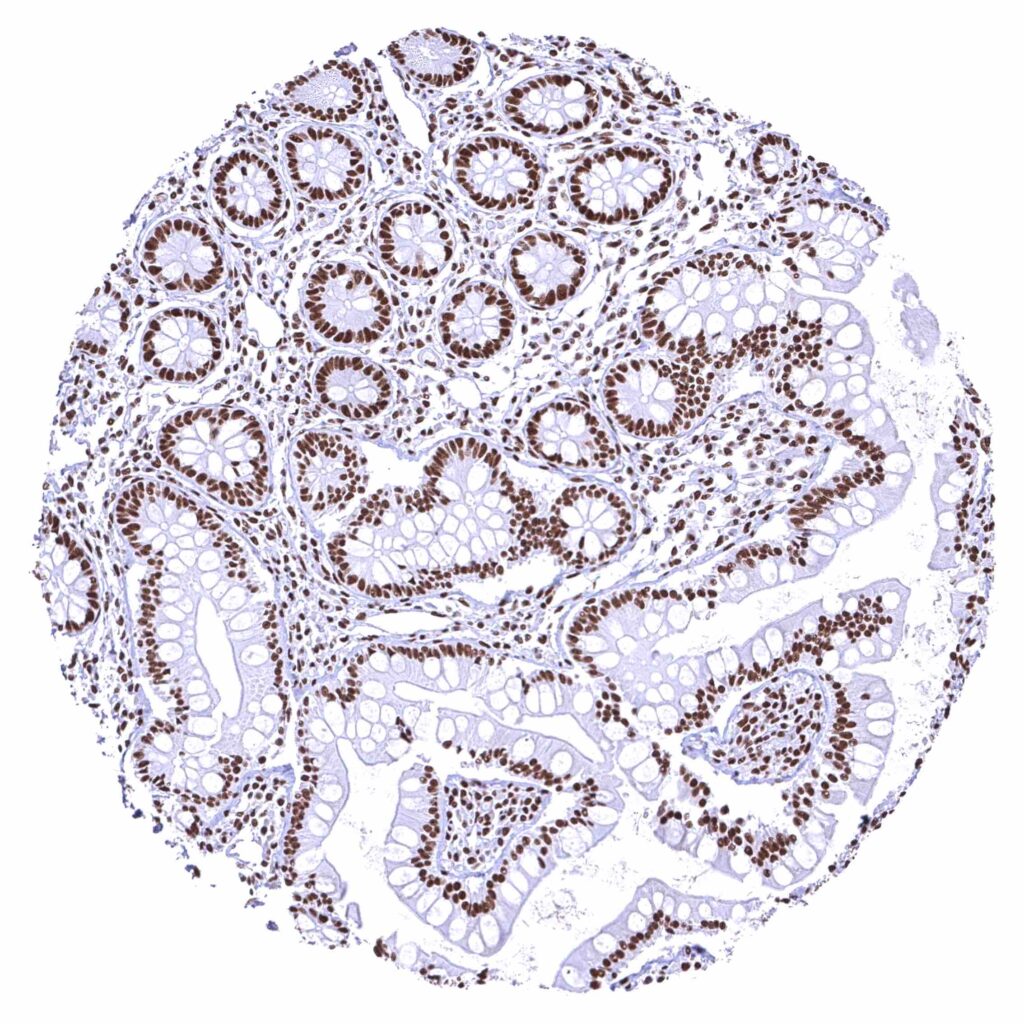
Ileum, mucosa
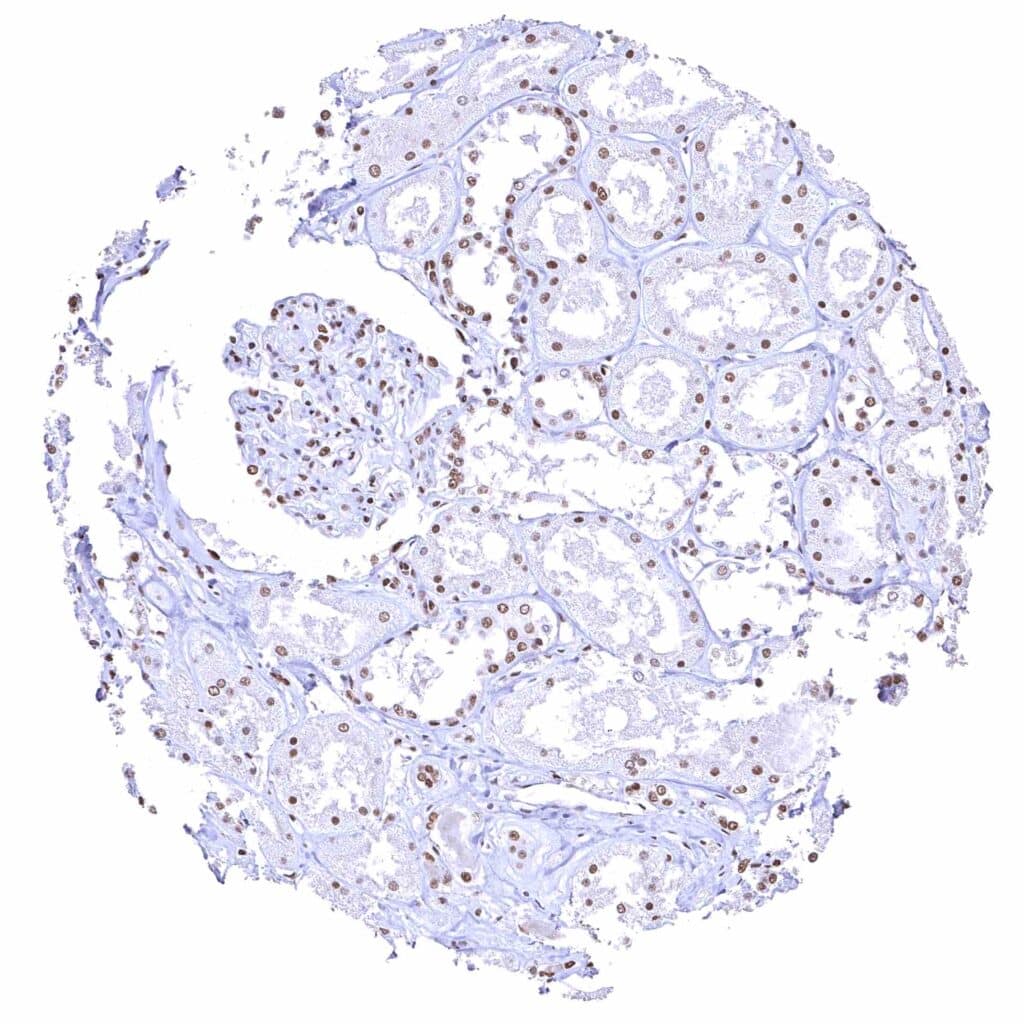
Kidney, cortex
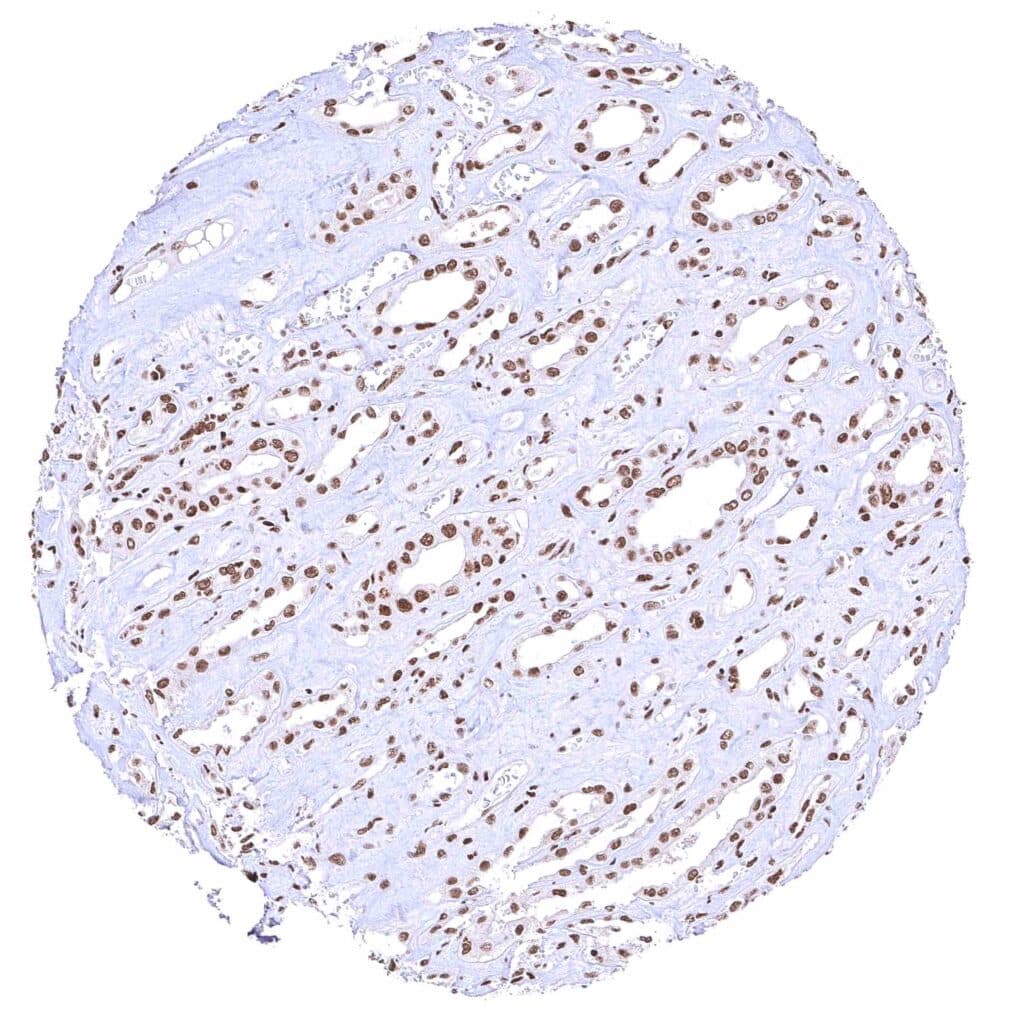
Kidney, medulla.jpeg
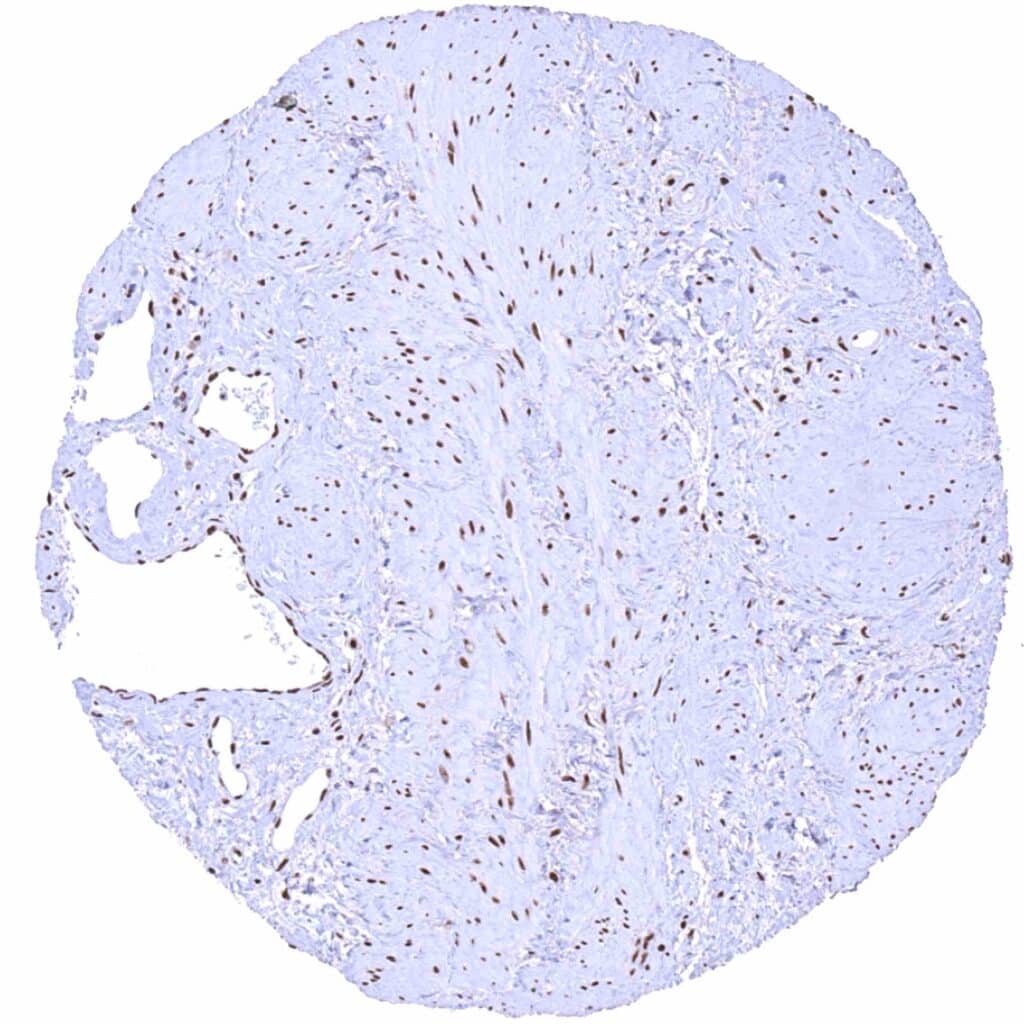
Kidney, pelvis, muscular wall
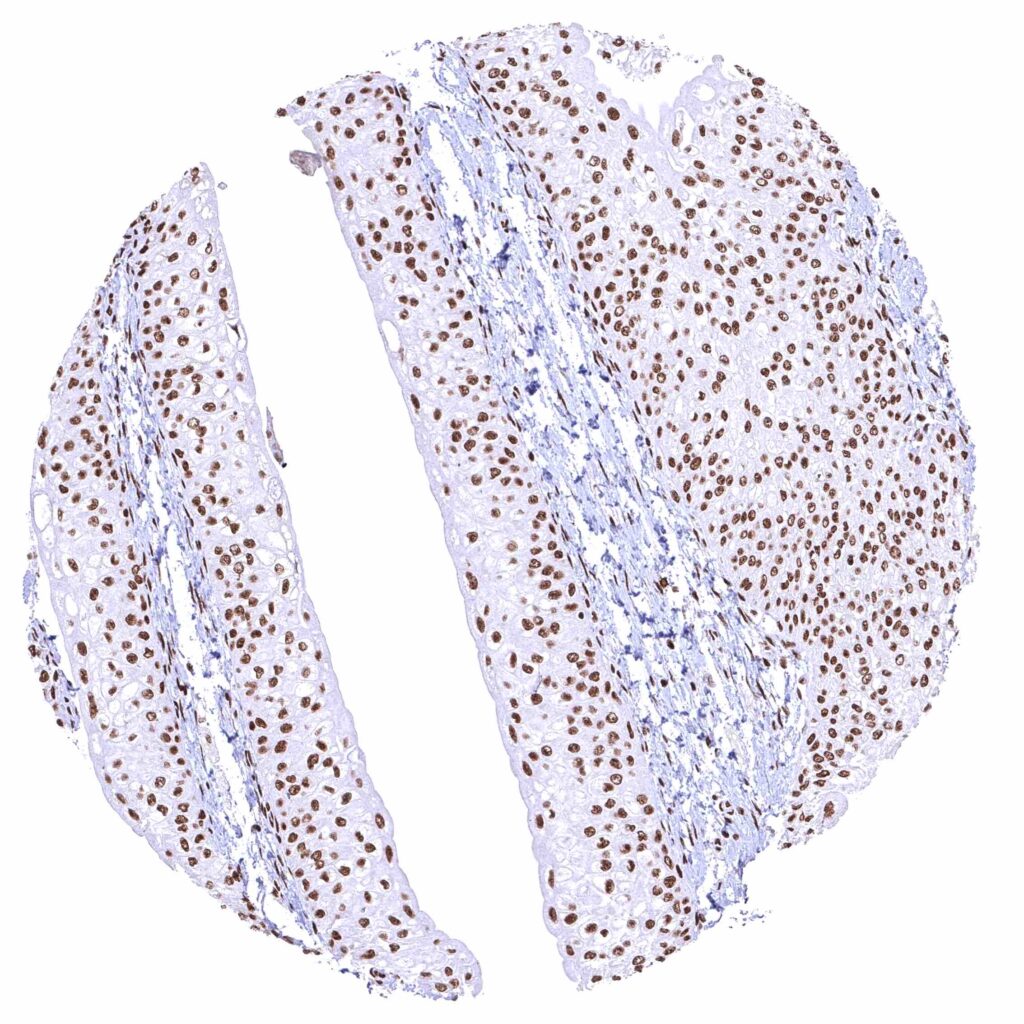
Kidney, pelvis, urothelium – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of urothelial cells.
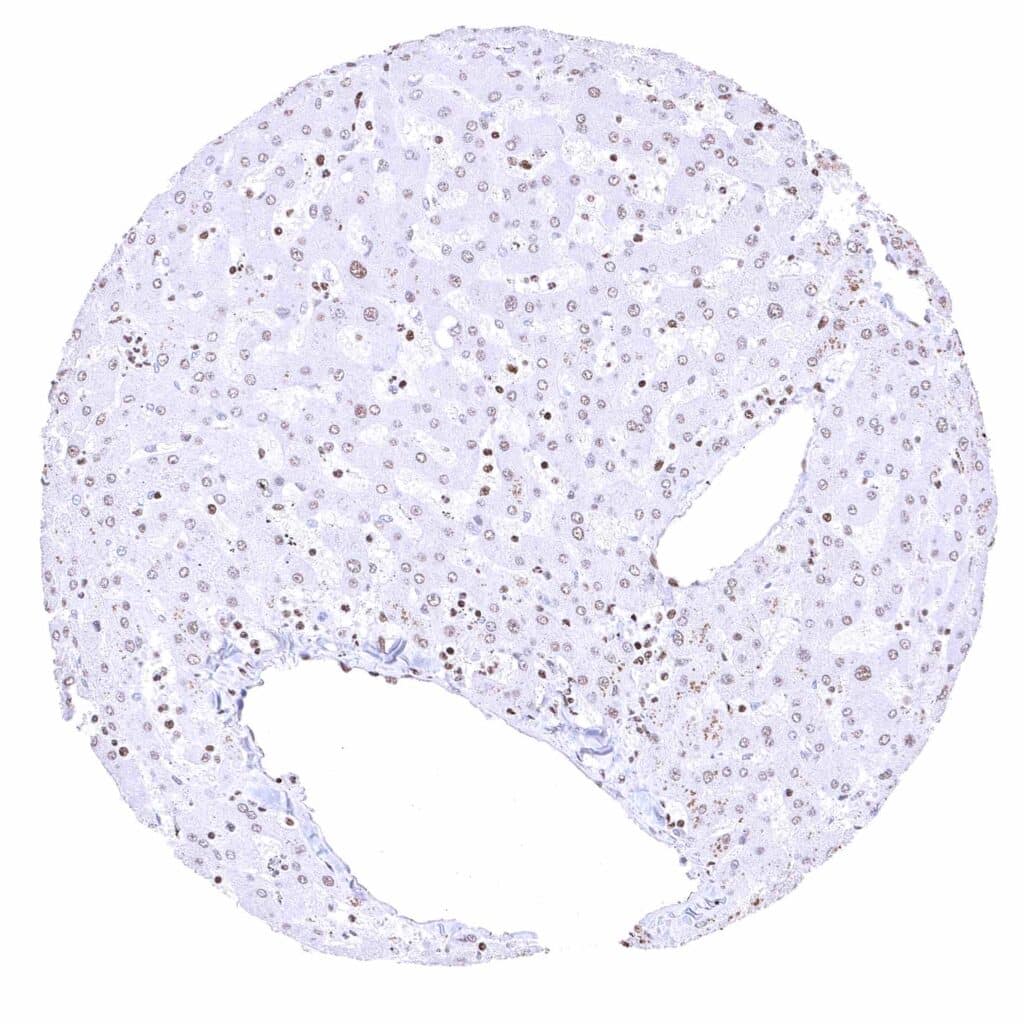
Liver – Nuclear BRD4 staining occurs in all cells, but is clearly weakest in hepatocytes.
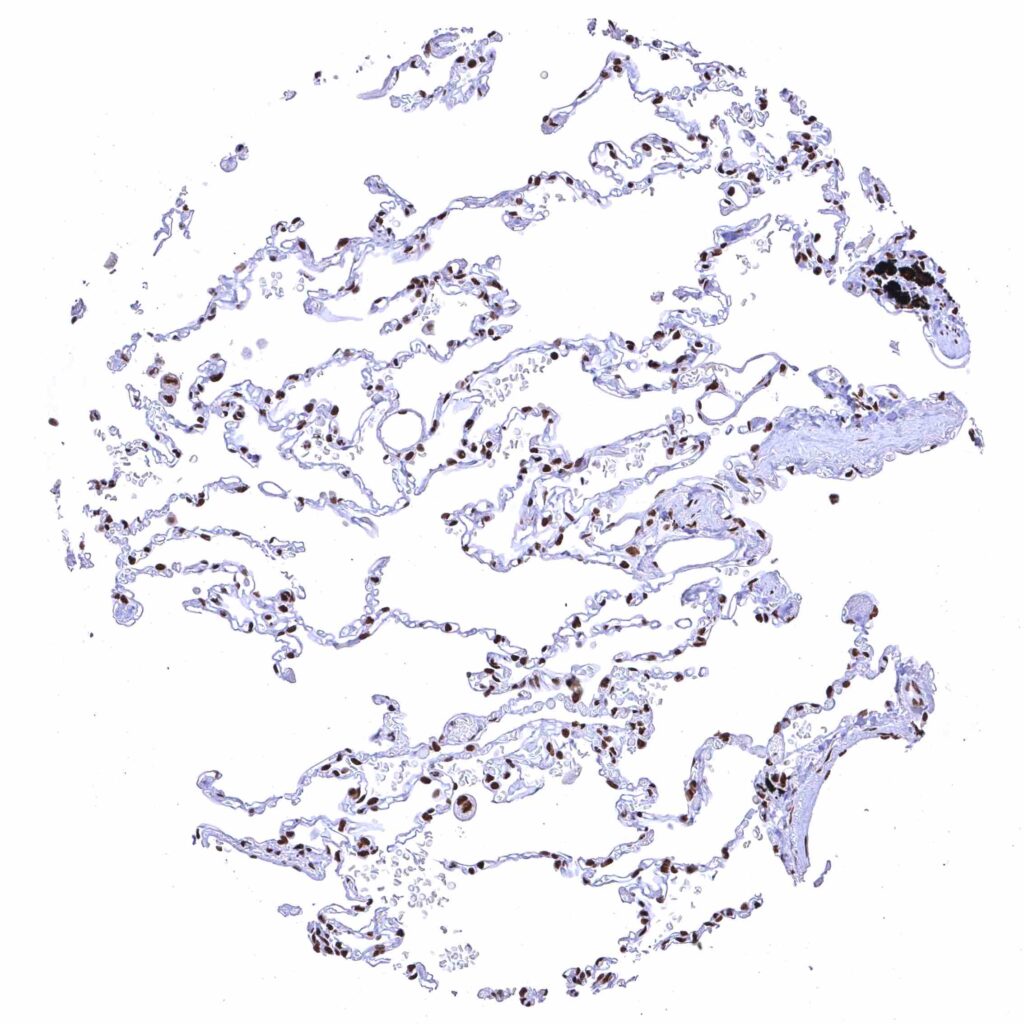
Lung
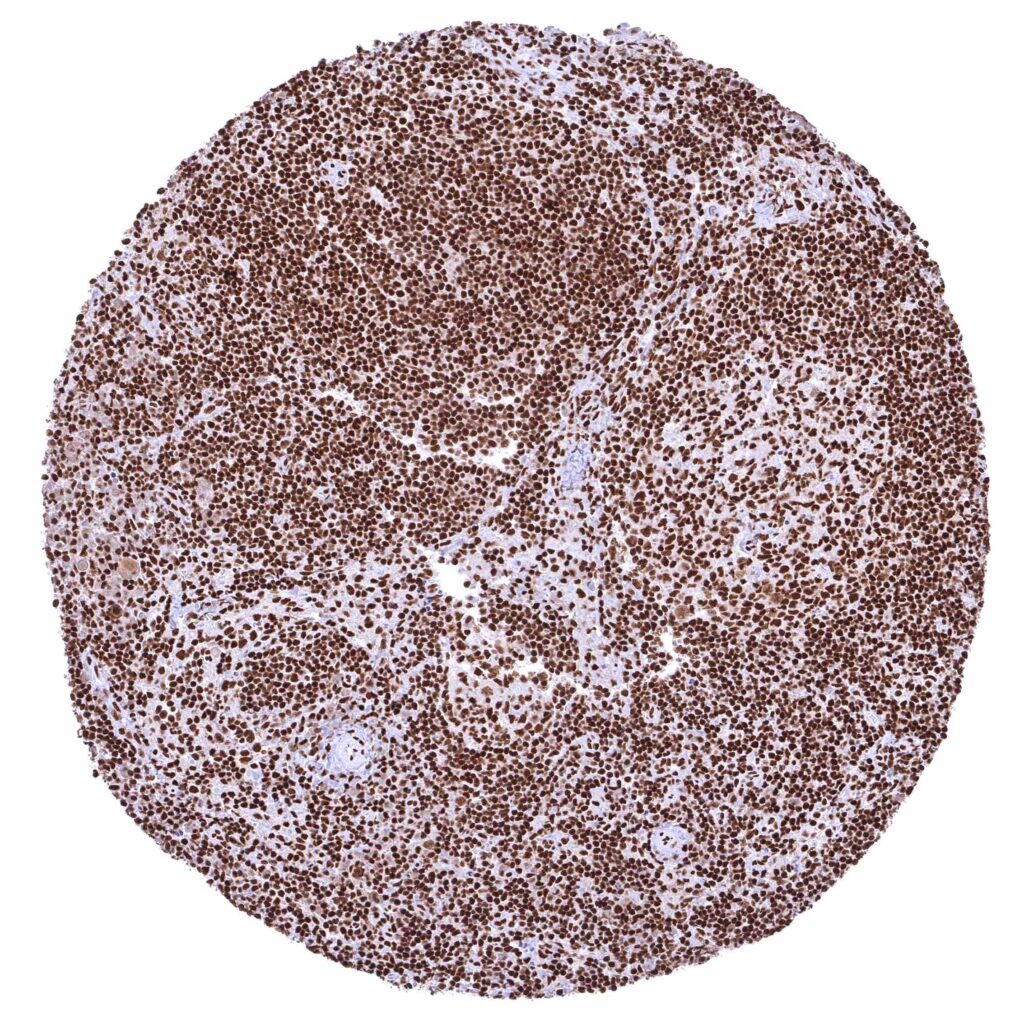
Lymph node – Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of all cell types.
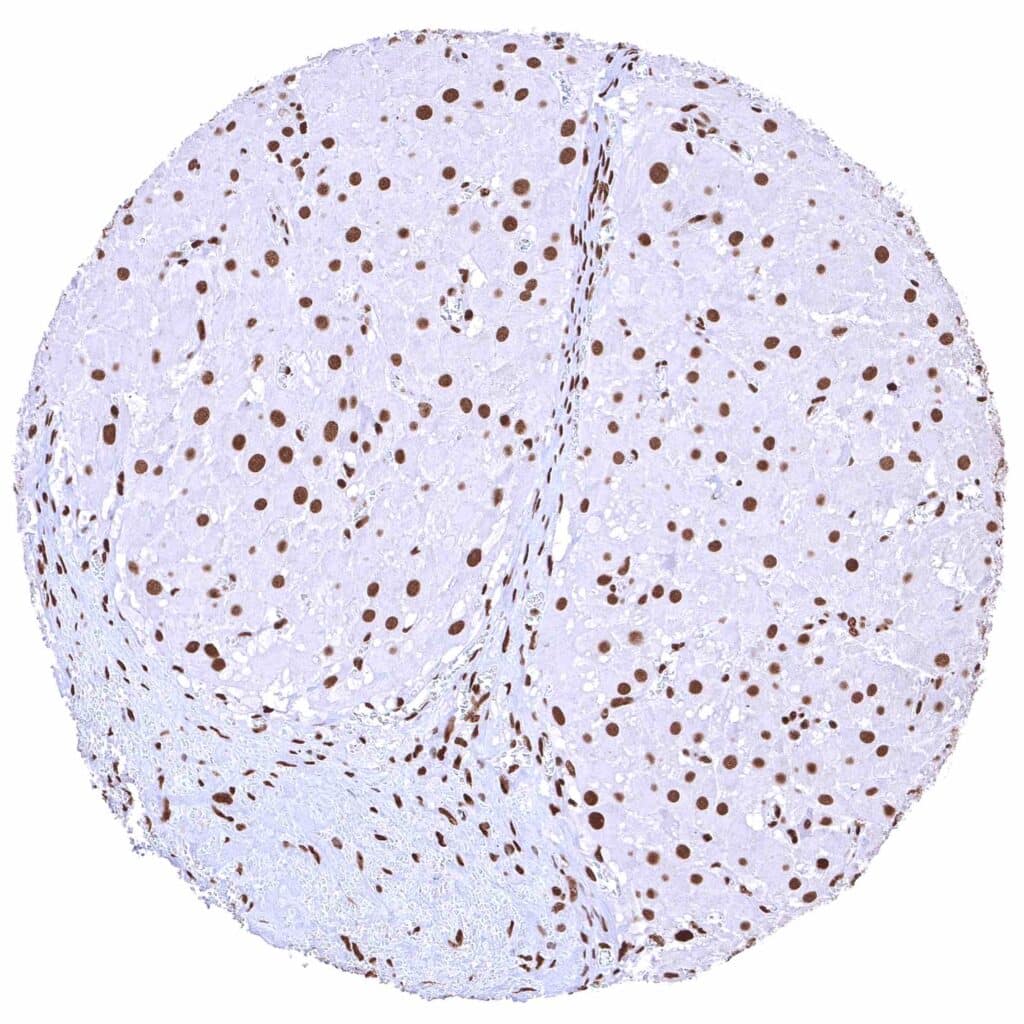
Ovary, corpus luteum – Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of corpus luteum cells.
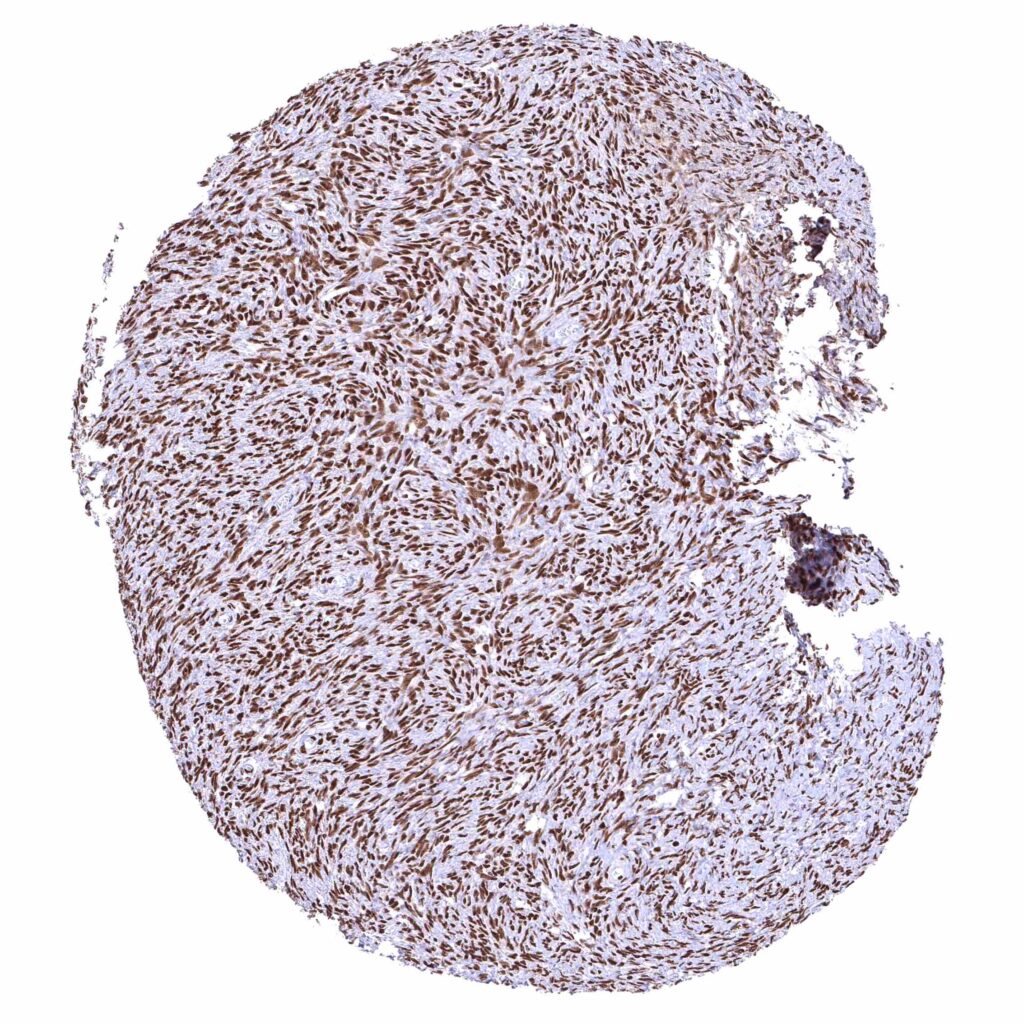
Ovary, stroma – Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of stroma cells.
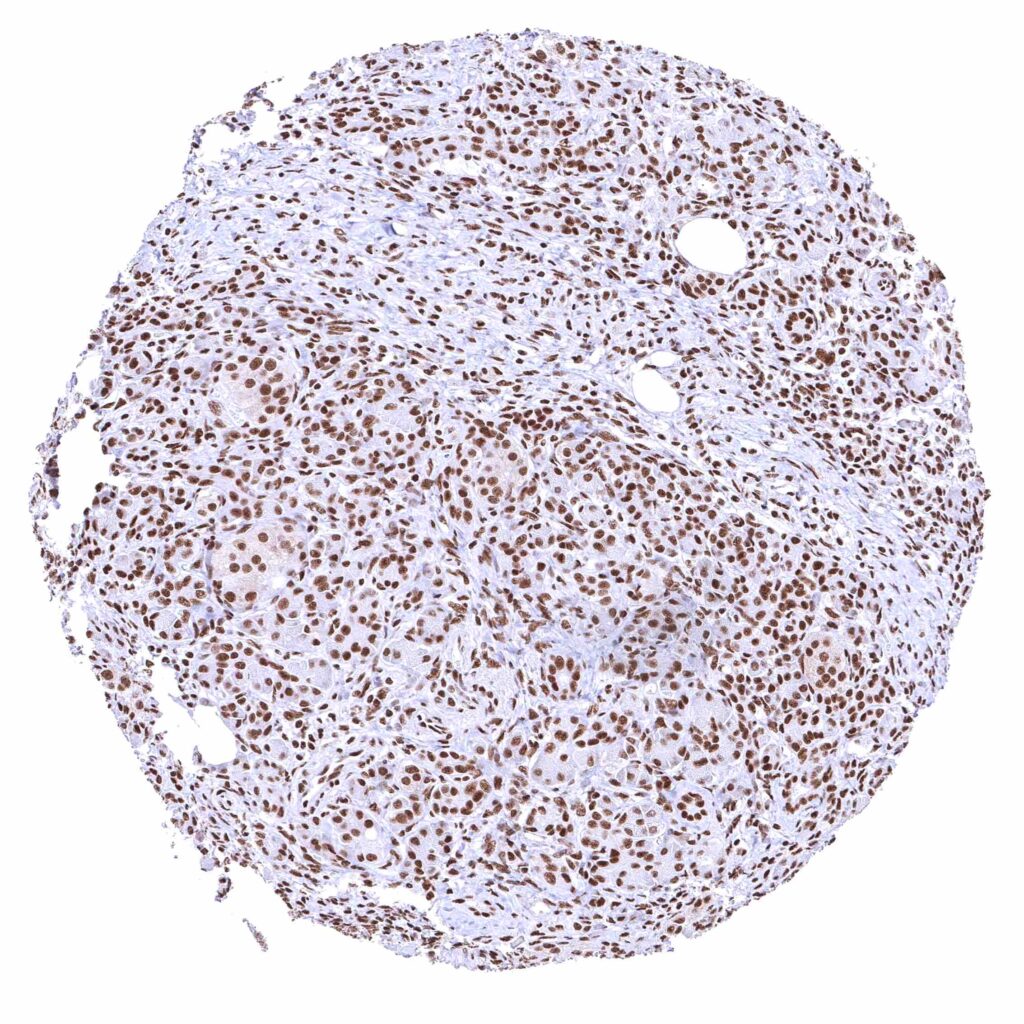
Pancreas
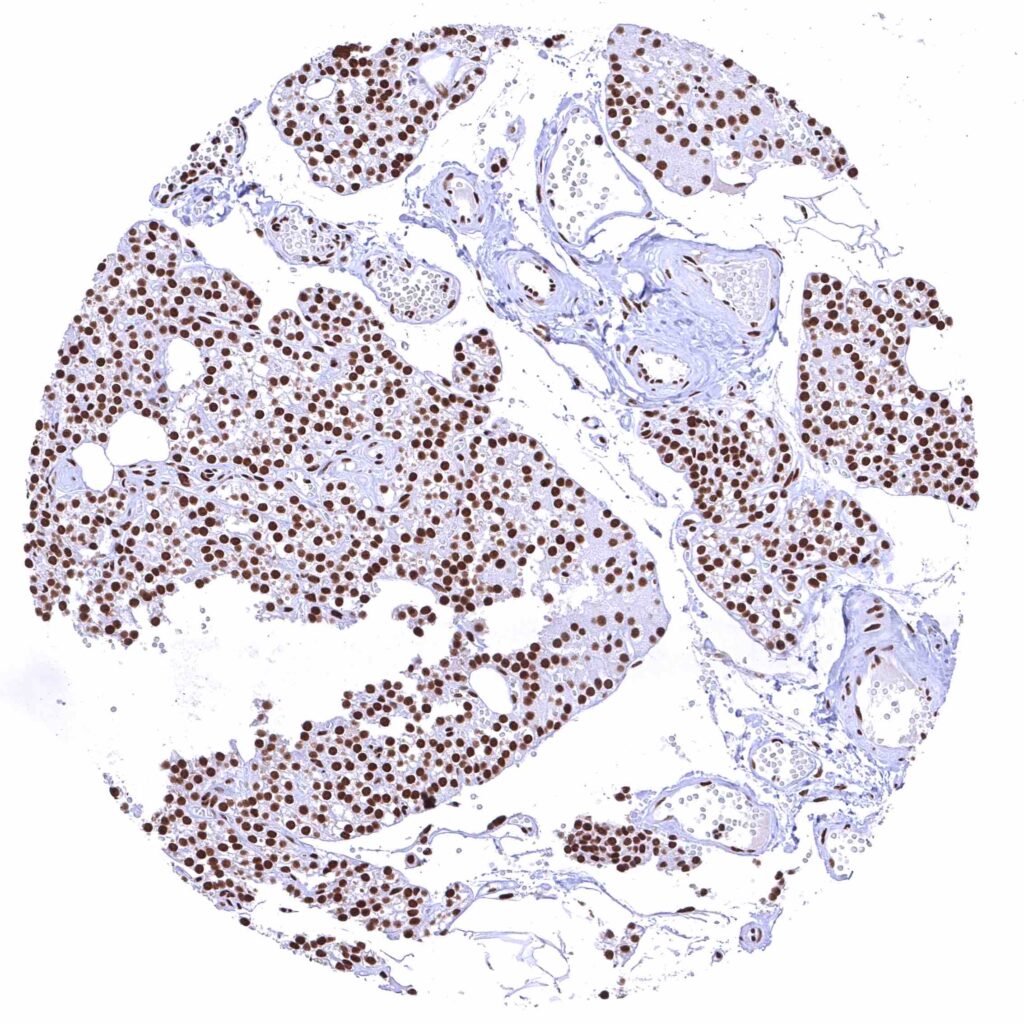
Parathyroid gland – Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of epithelial cells.
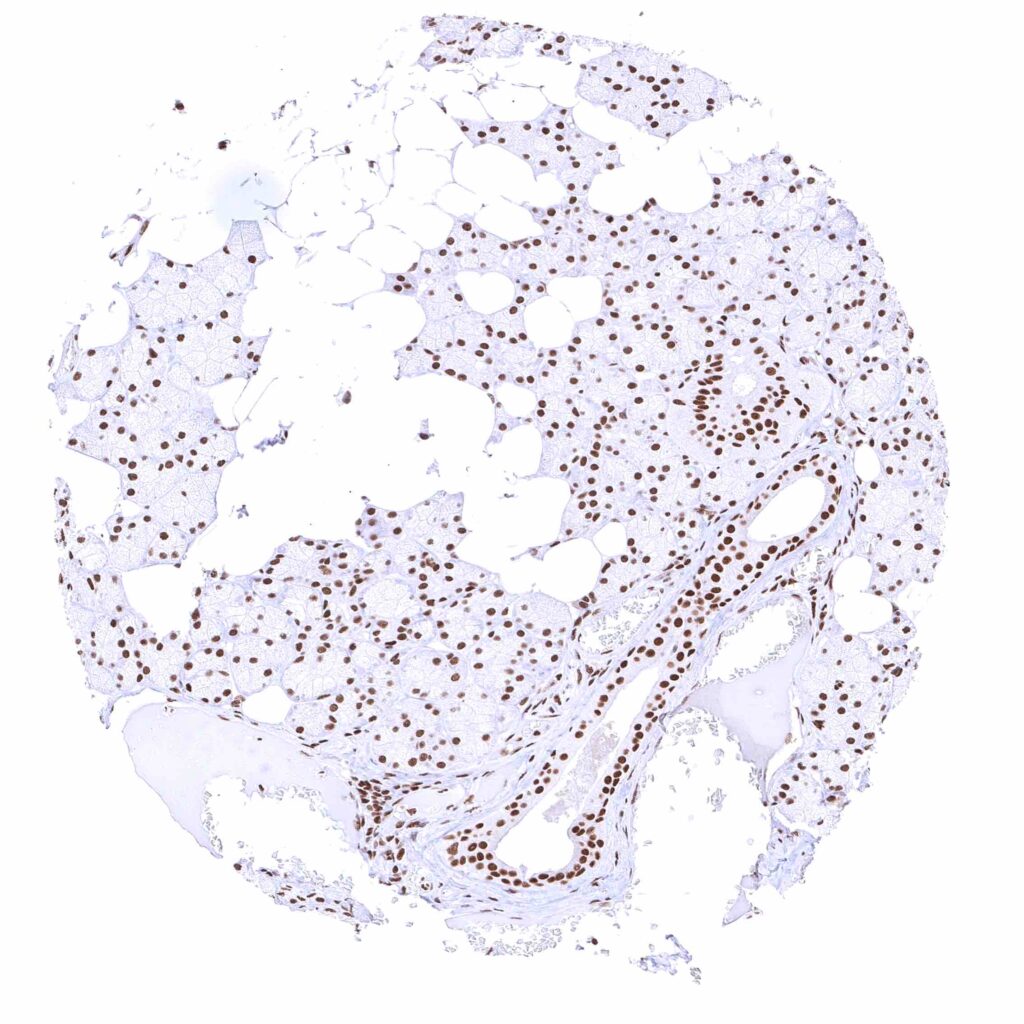
Parotid gland – BRD4 staining of glandular cells is somewhat weaker than of excretory duct cells.
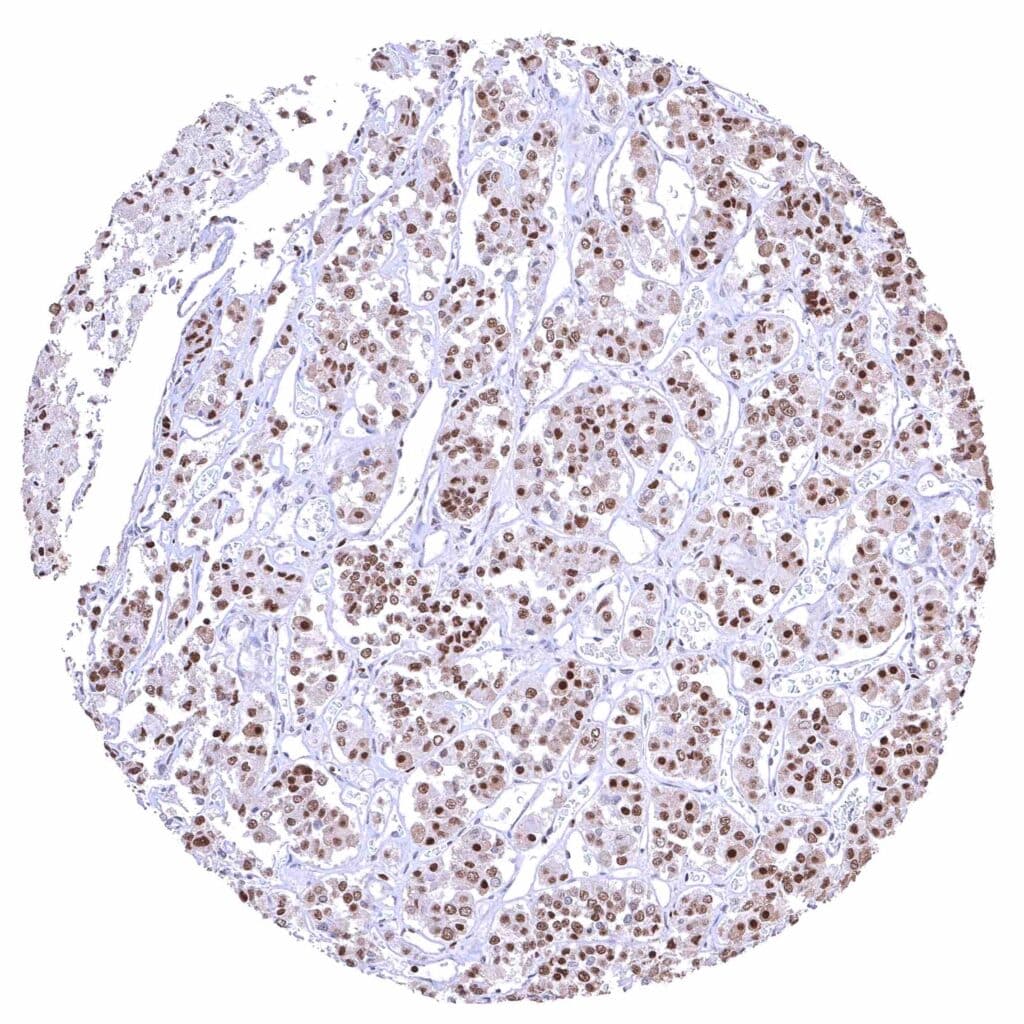
Pituitary gland, anterior lobe
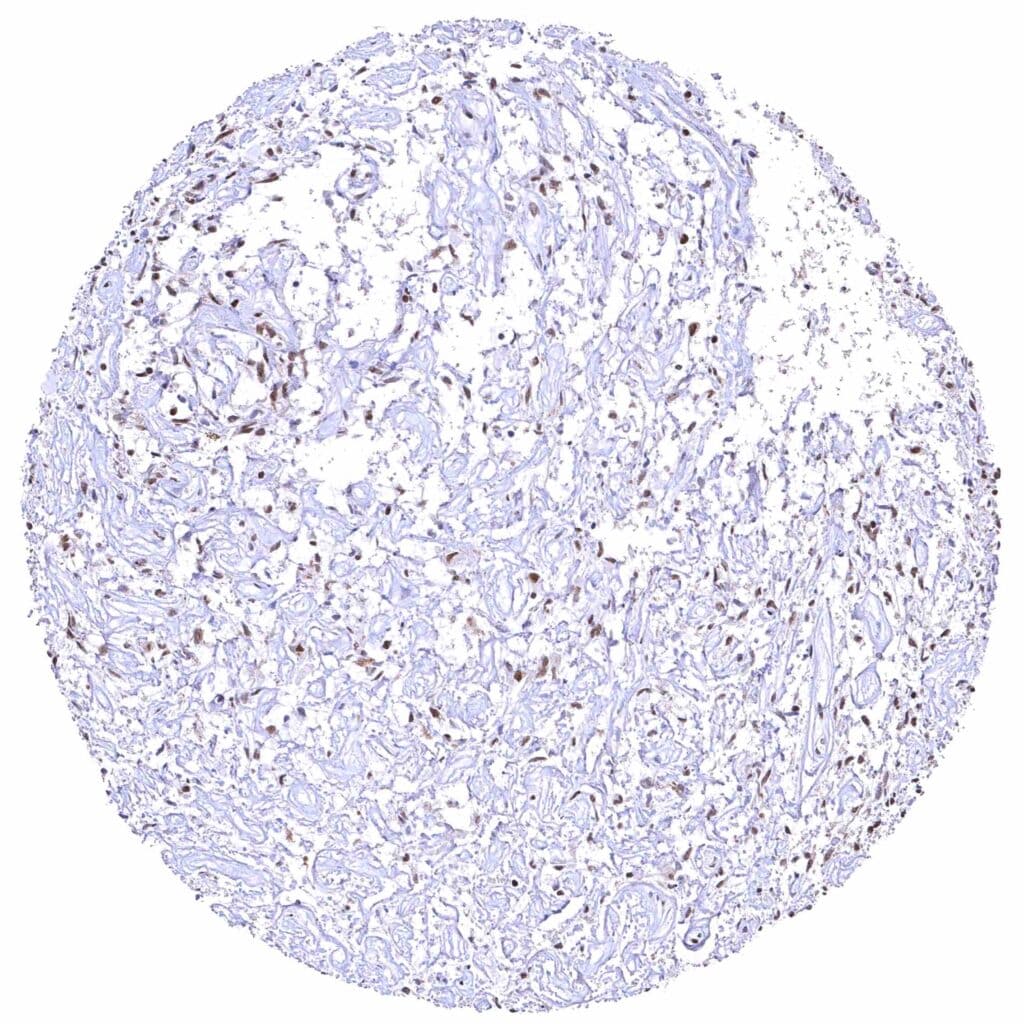
Pituitary gland, posterior lobe
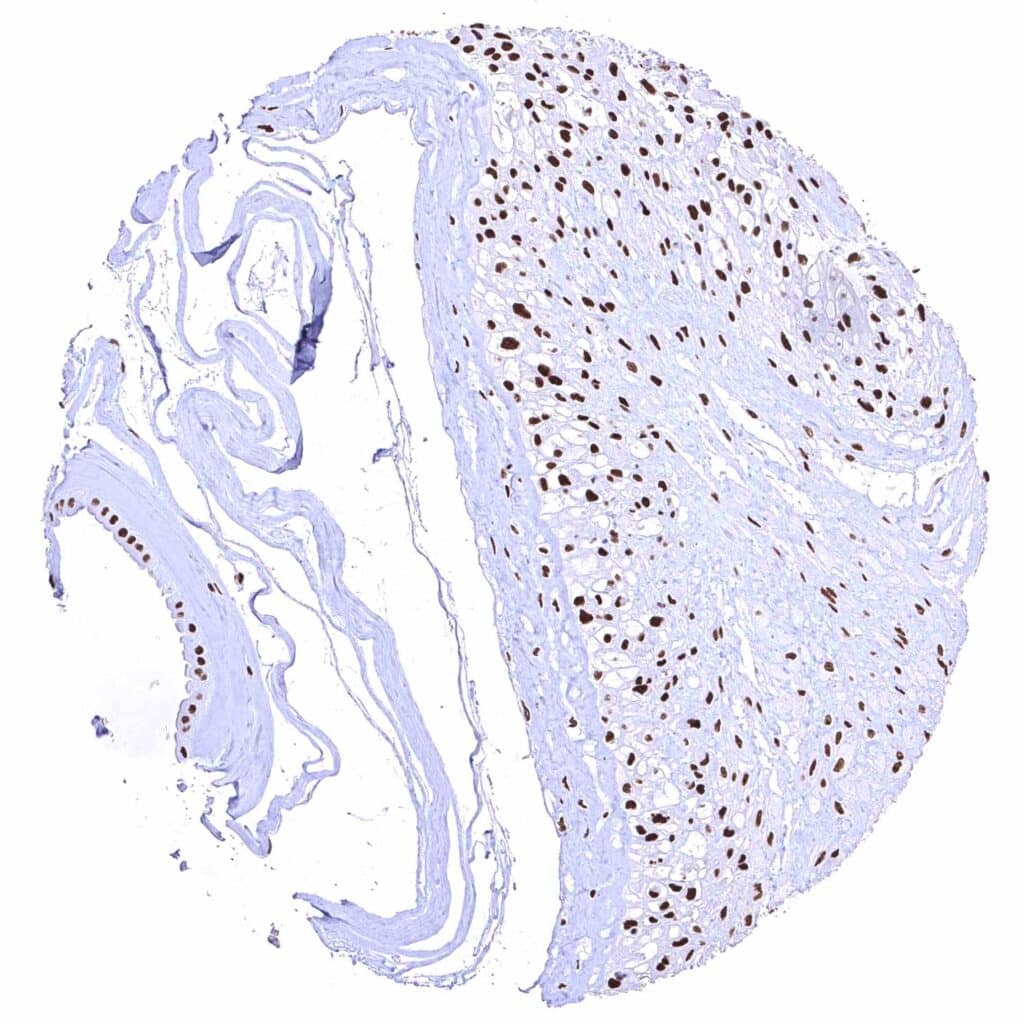
Placenta (amnion and chorion) – Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of both amnion and chorion cells.
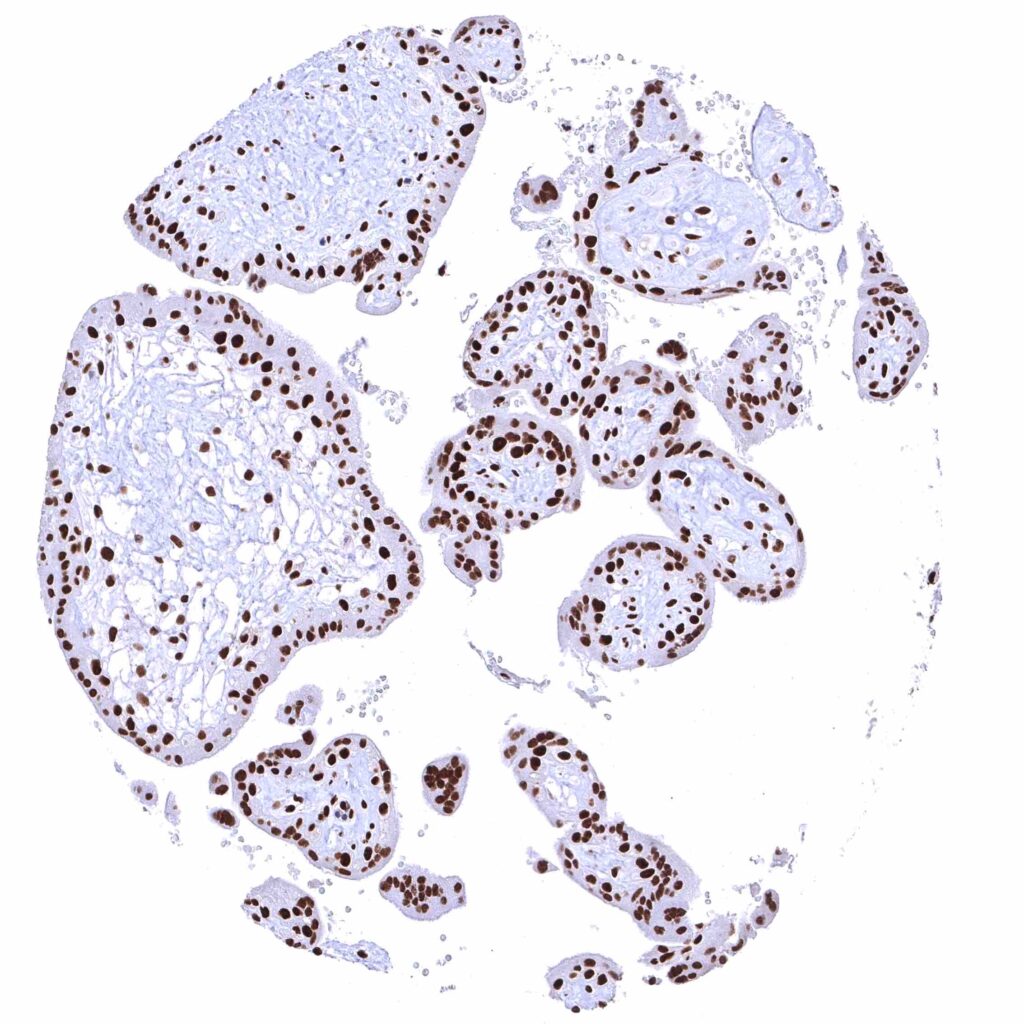
Placenta, early – Nuclear BRD4 staining is particularly strong in all trophoblast cells.
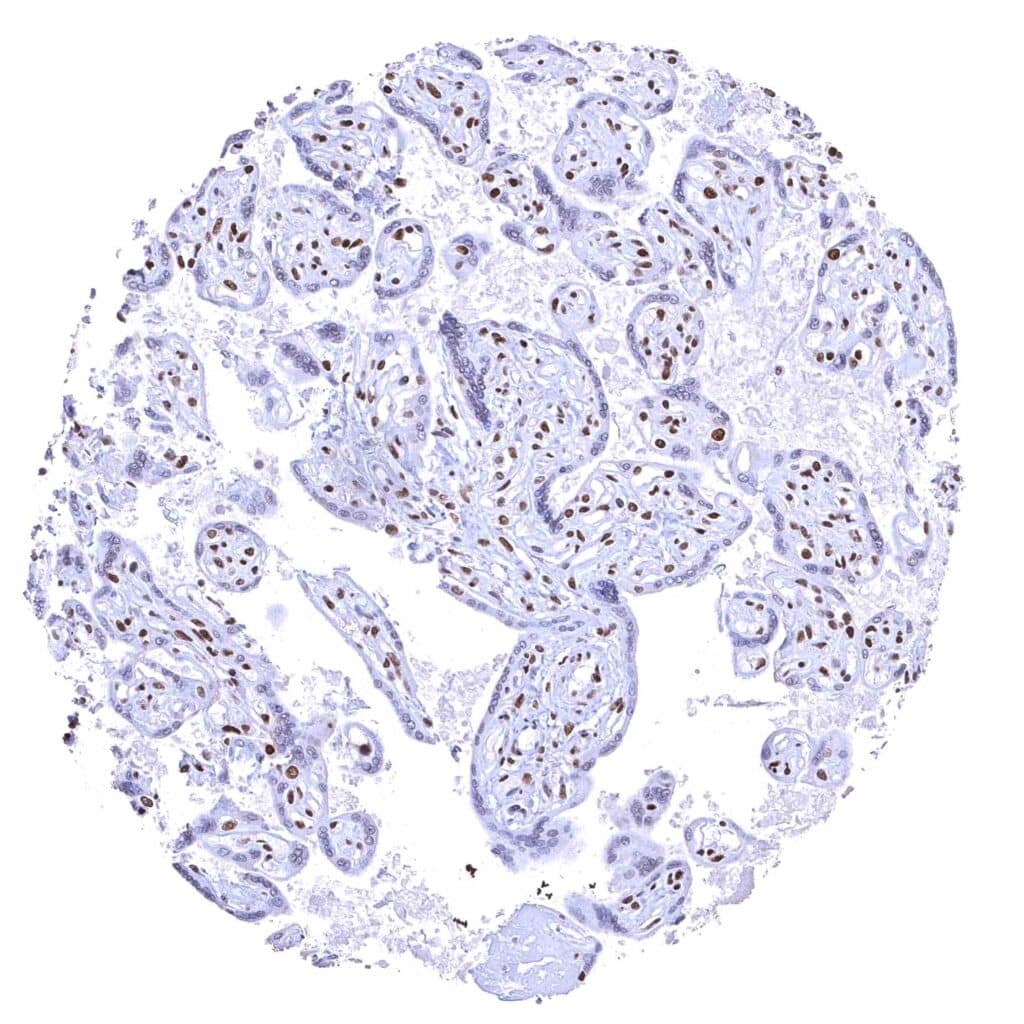
Placenta, mature – BRD4 staining is either absent or massively reduced in the syncytiotrophoblast.
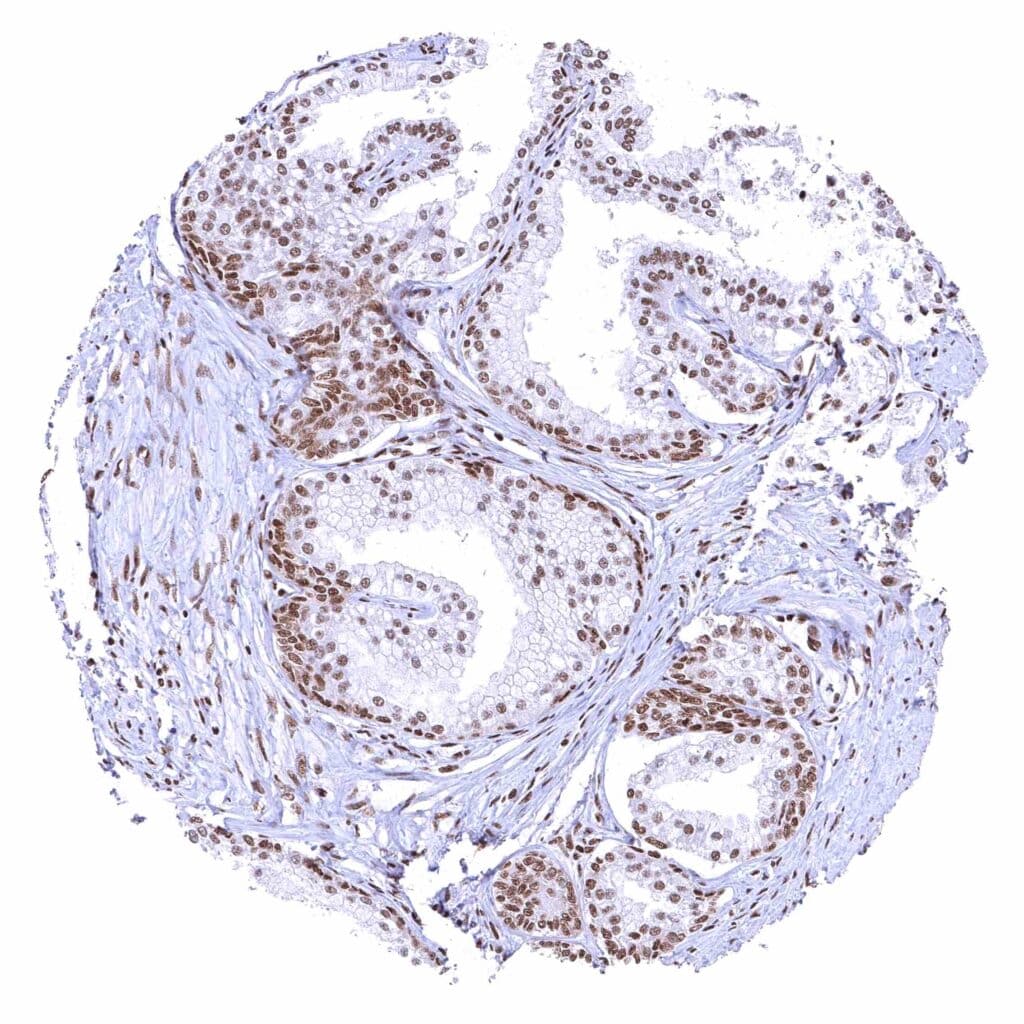
Prostate – BRD4 staining of basal cells is somewhat stronger than of acinar cells.
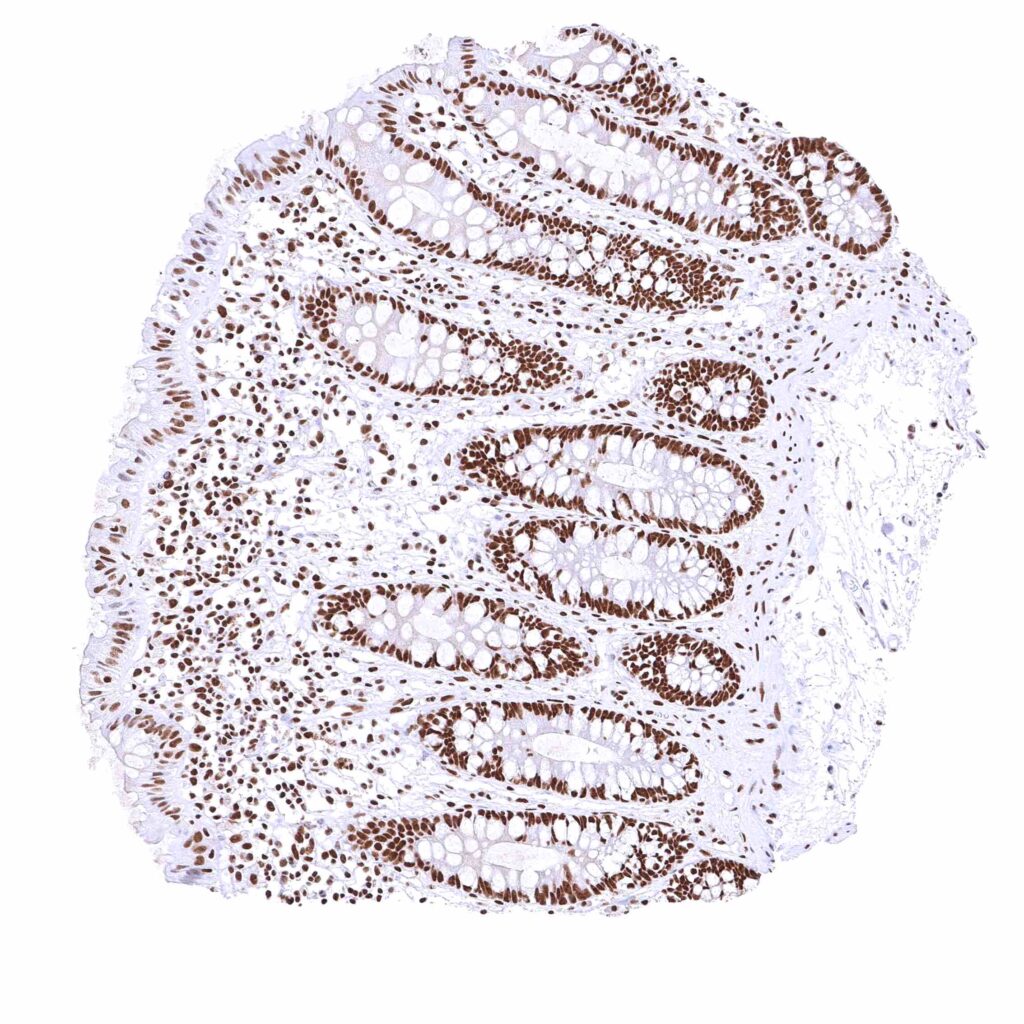
Rectum, mucosa – Nuclear BRD4 staining of surface epithelial cells is weaker than in crypts. .jpeg
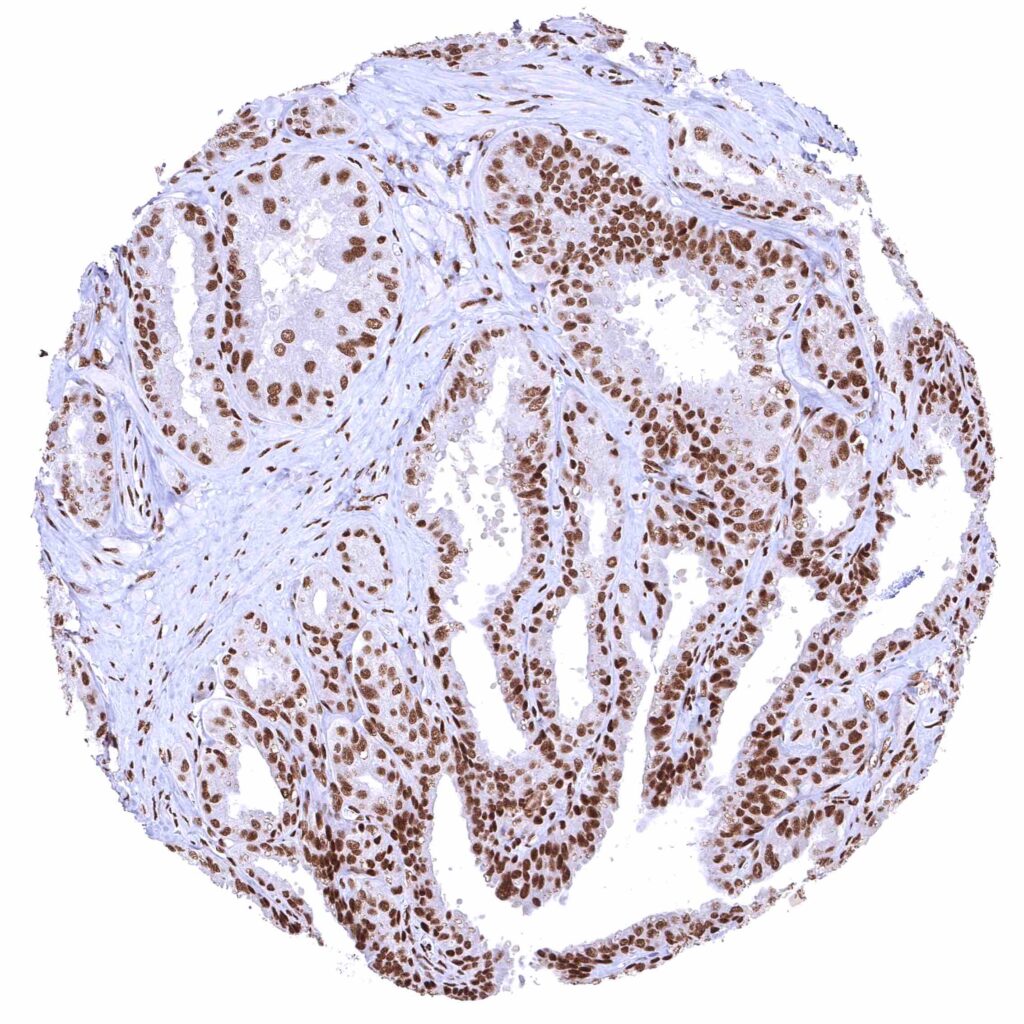
Seminal vesicle.jpeg
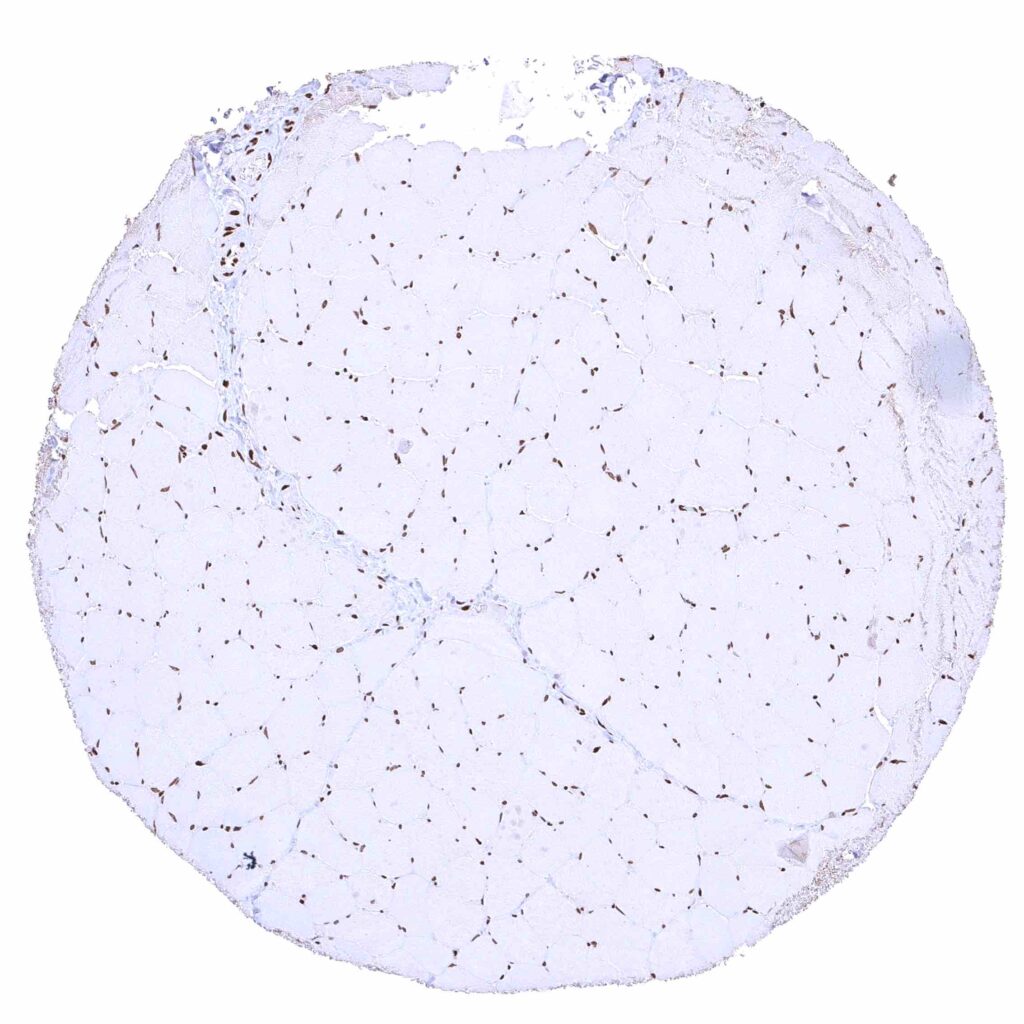
Skeletal muscle – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. A cytoplasmic staining of muscle cells is not seen in this sample.
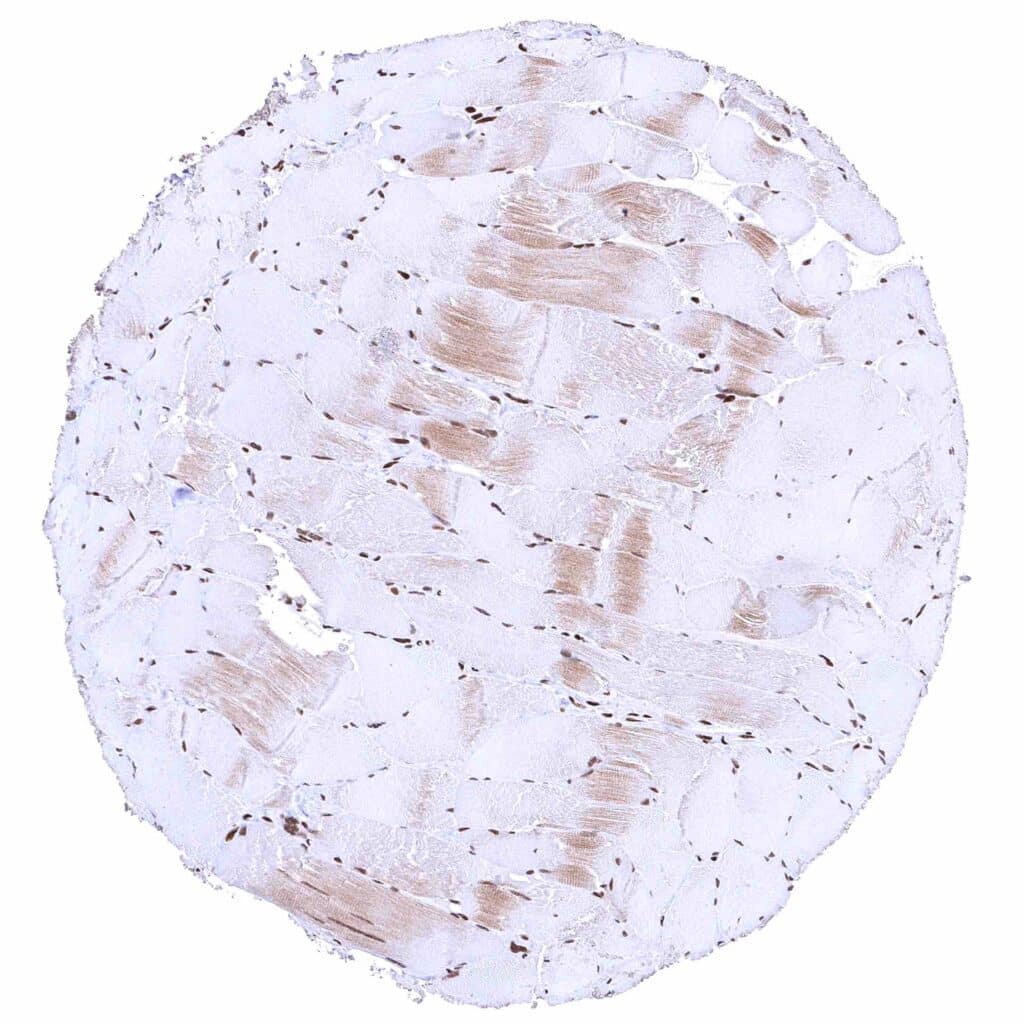
Skeletal muscle – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all cells. The additional cytoplasmic staining of some muscle cells may represent an antibody specific cross-reactivity.
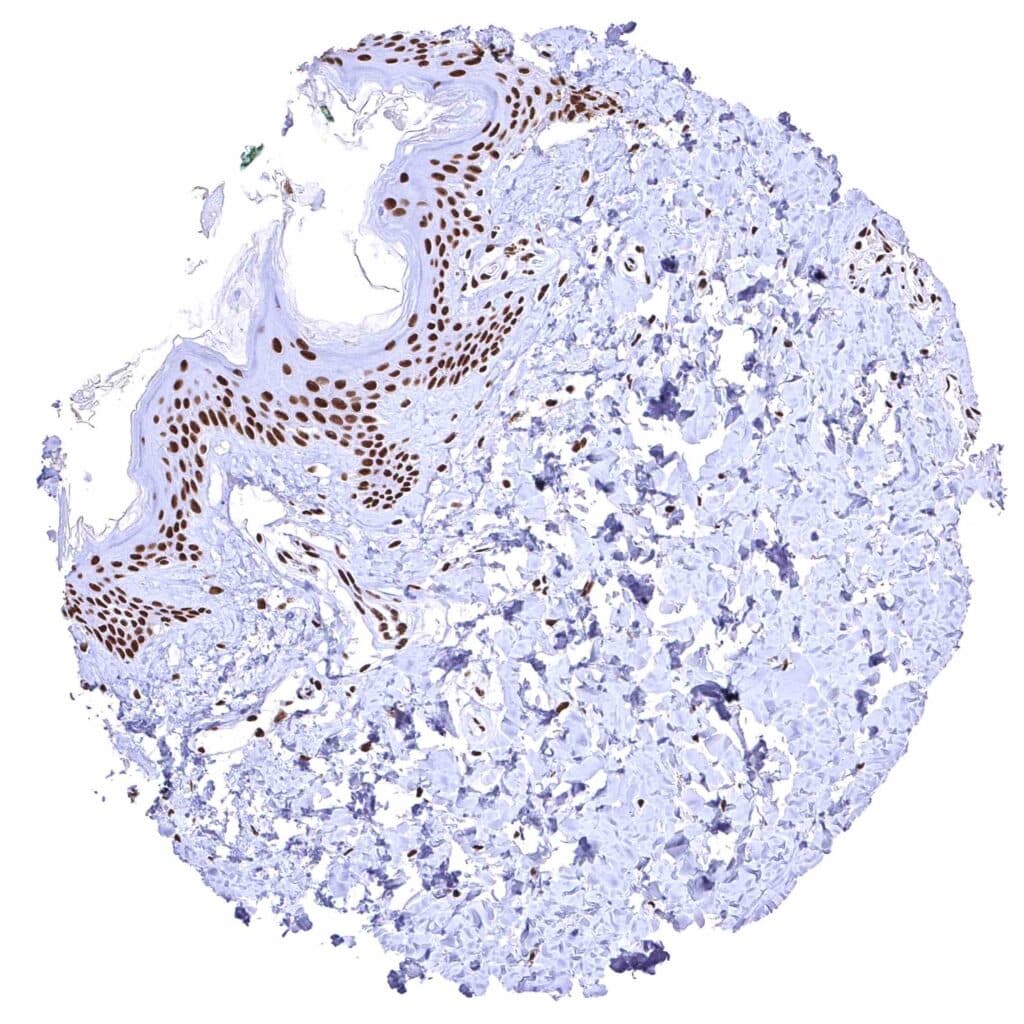
Skin – Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of squamous epithelial cells.
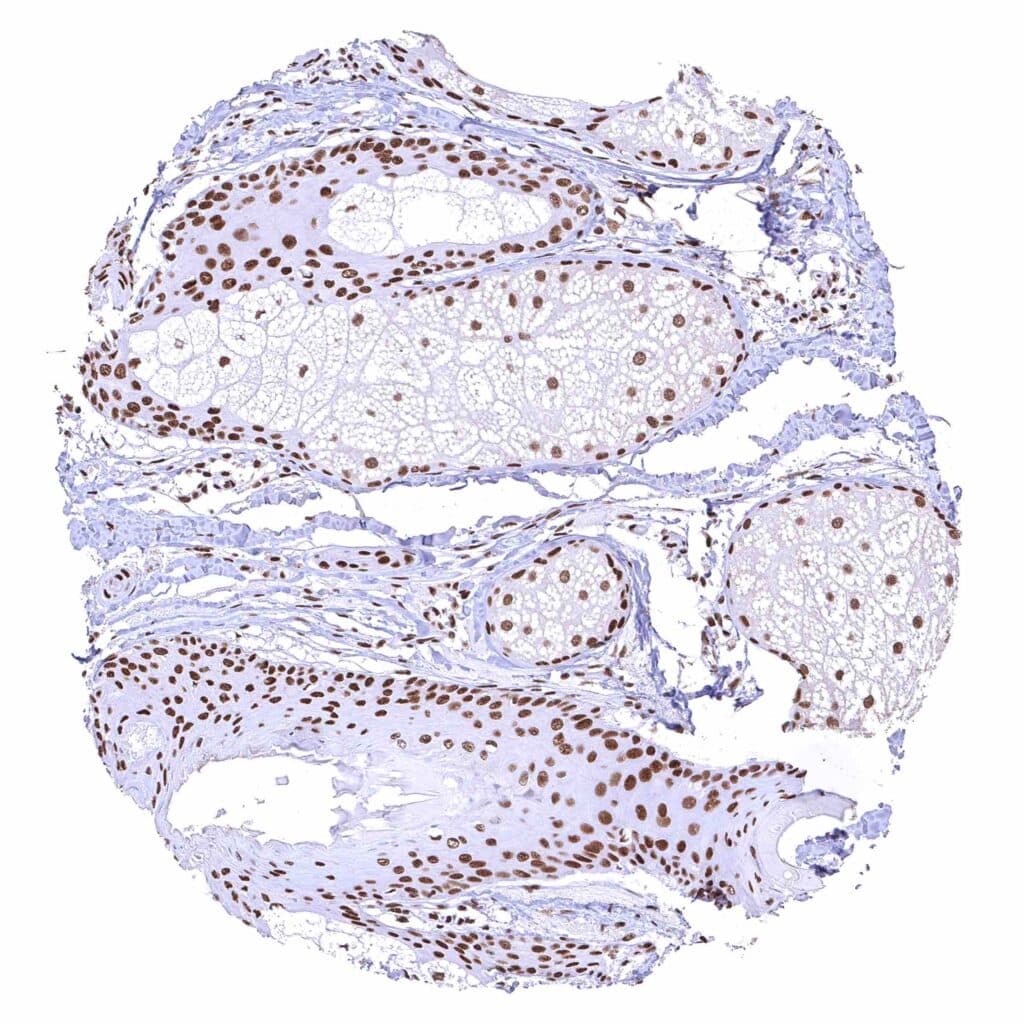
Skin, hairfollicel and sebaceous glands – Moderate to strong BRD4 staining of sebaceous gland cells. Nuclear BRD4 staining is somewhat stronger in associated hair follicles cells.
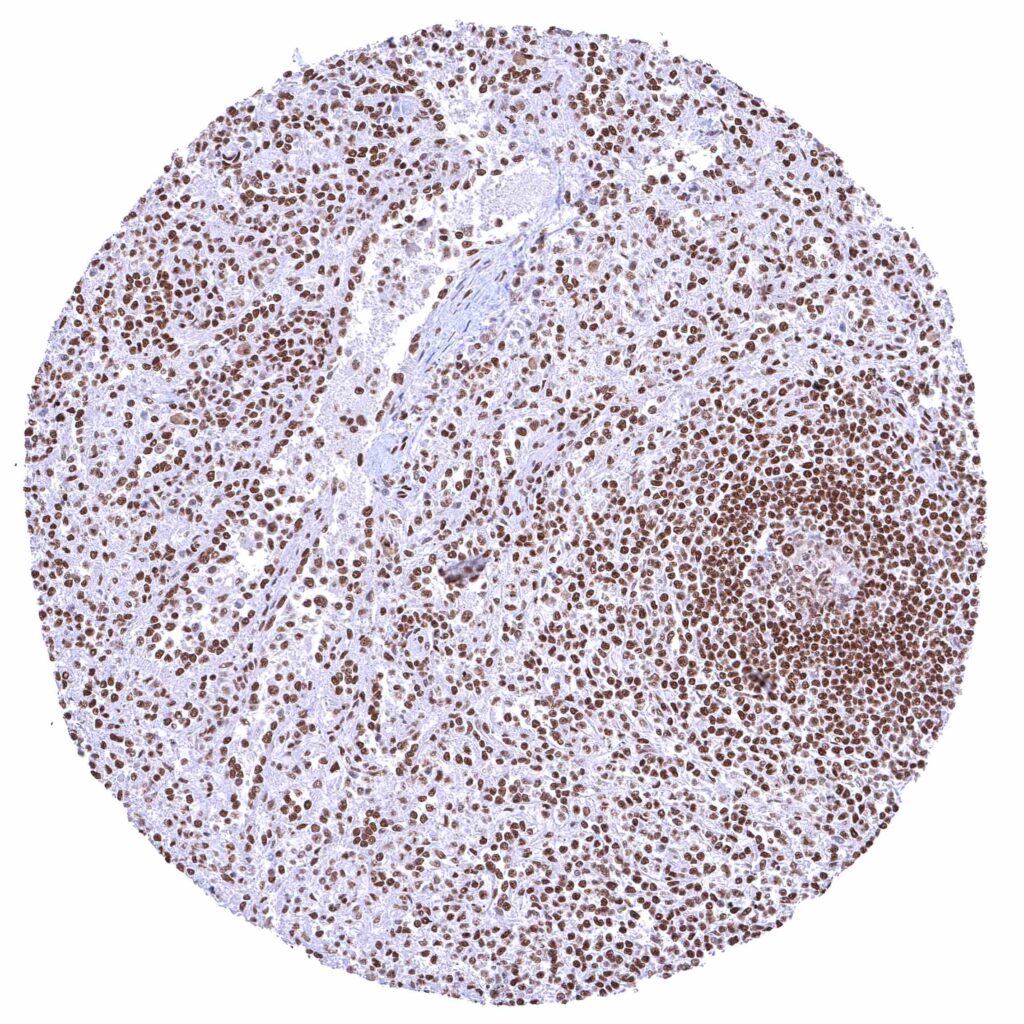
Spleen – Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of all cell types.
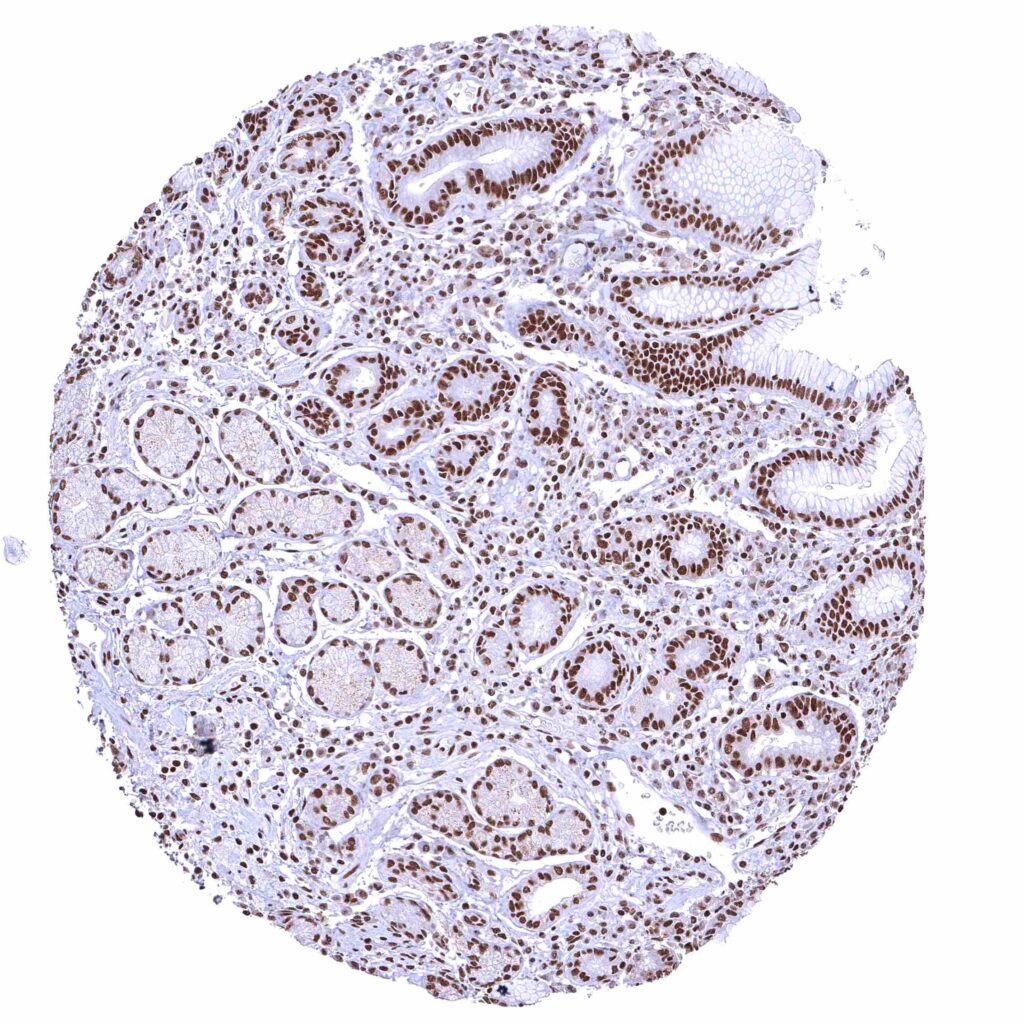
Stomach, antrum – BRD4 staining of surface epithelial cells is slightly more intense than in glandular cells.
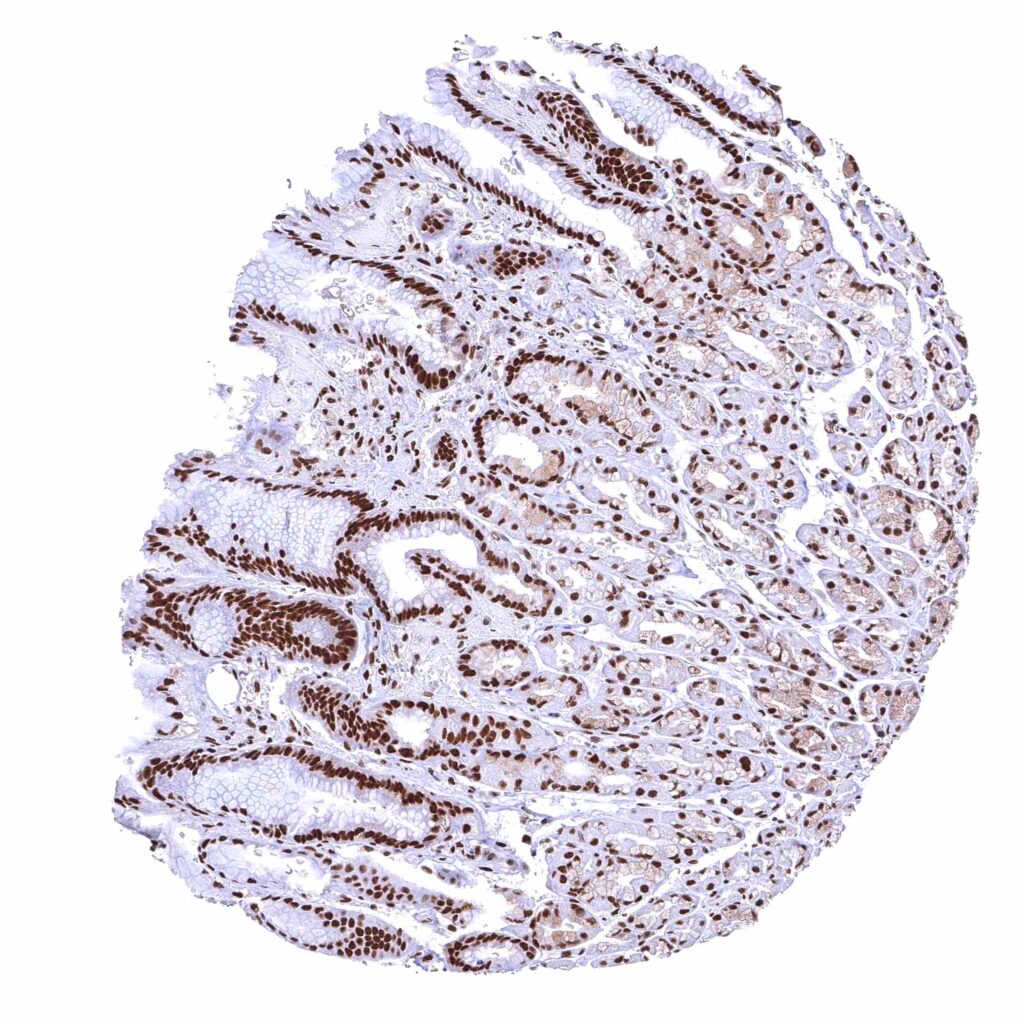
Stomach, corpus – BRD4 staining of surface epithelial cells is slightly more intense than in glandular cells.
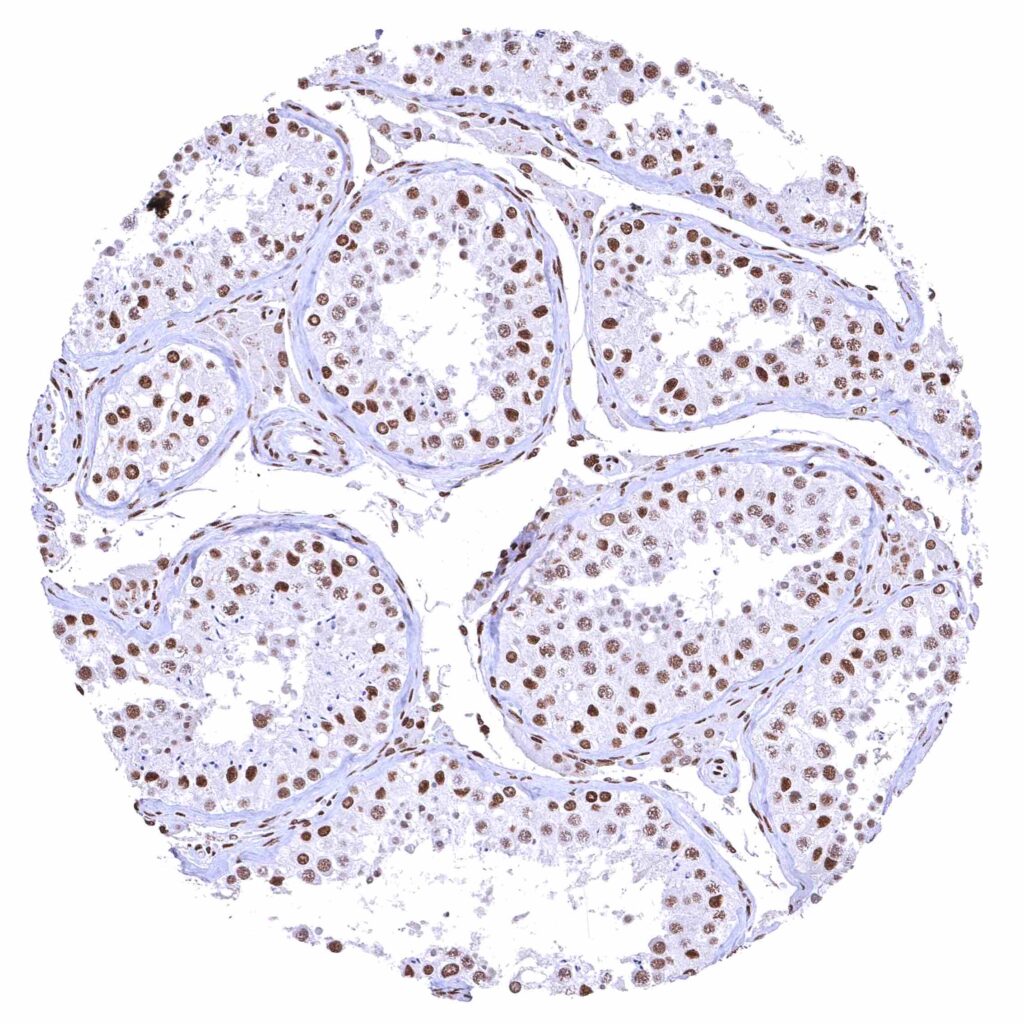
Testis – The level of nuclear BRD4 staining decreases with maturation of germ cells. .jpeg
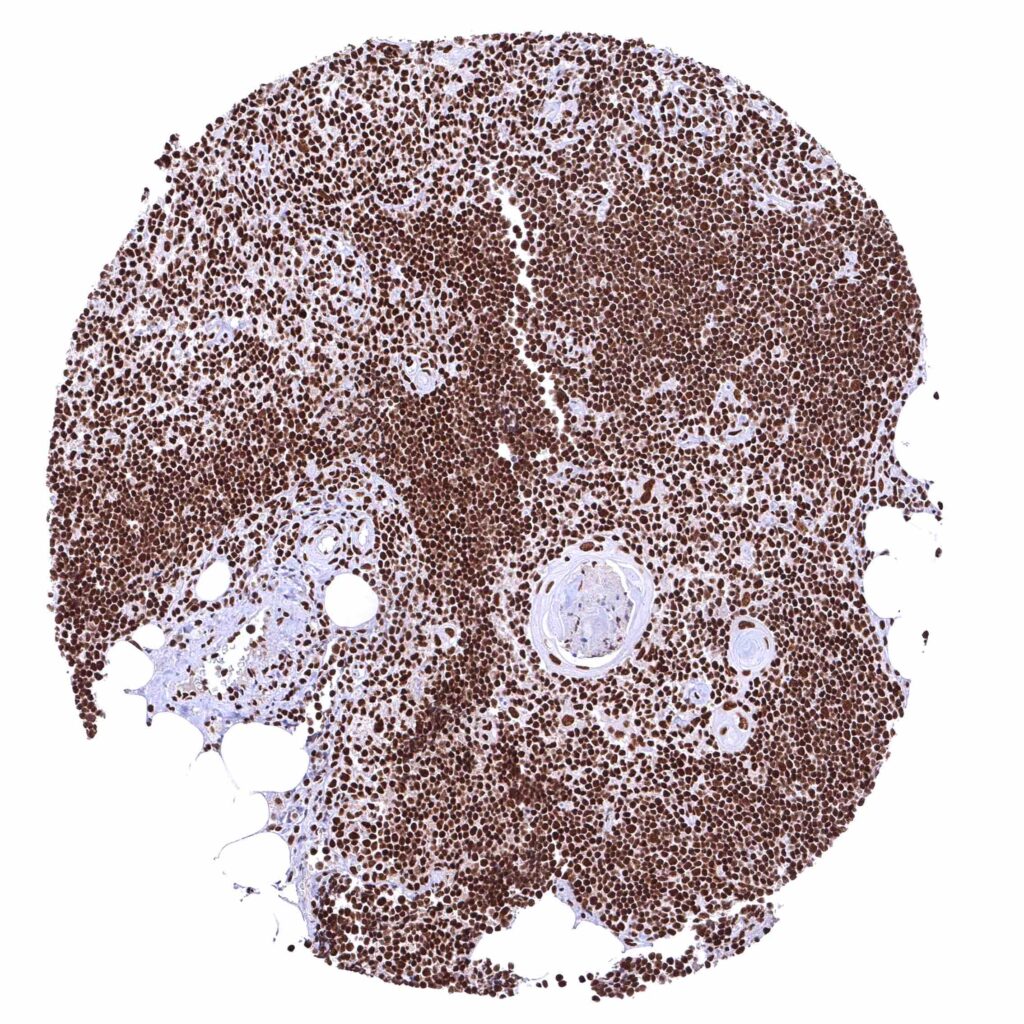
Thymus – Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of all cell types.
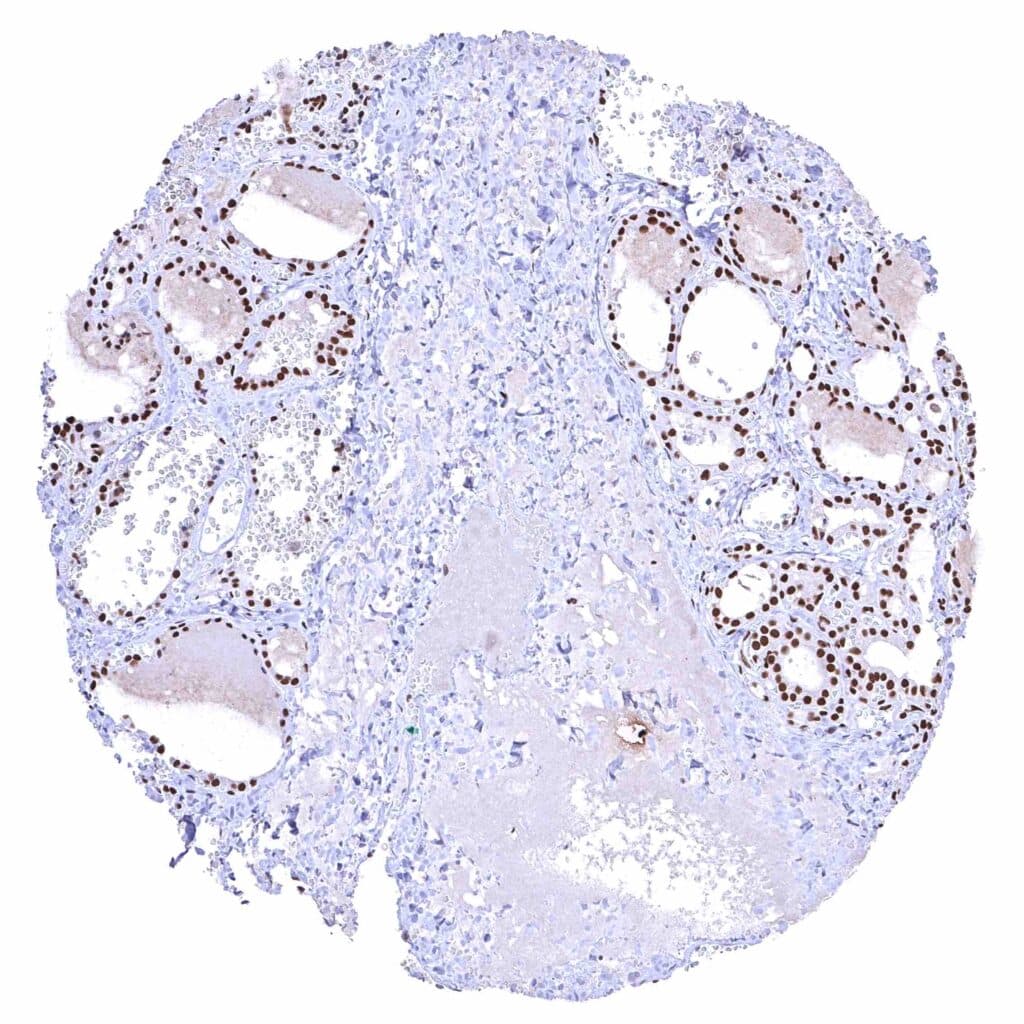
Thyroid gland – Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of epithelial cells. .jpeg
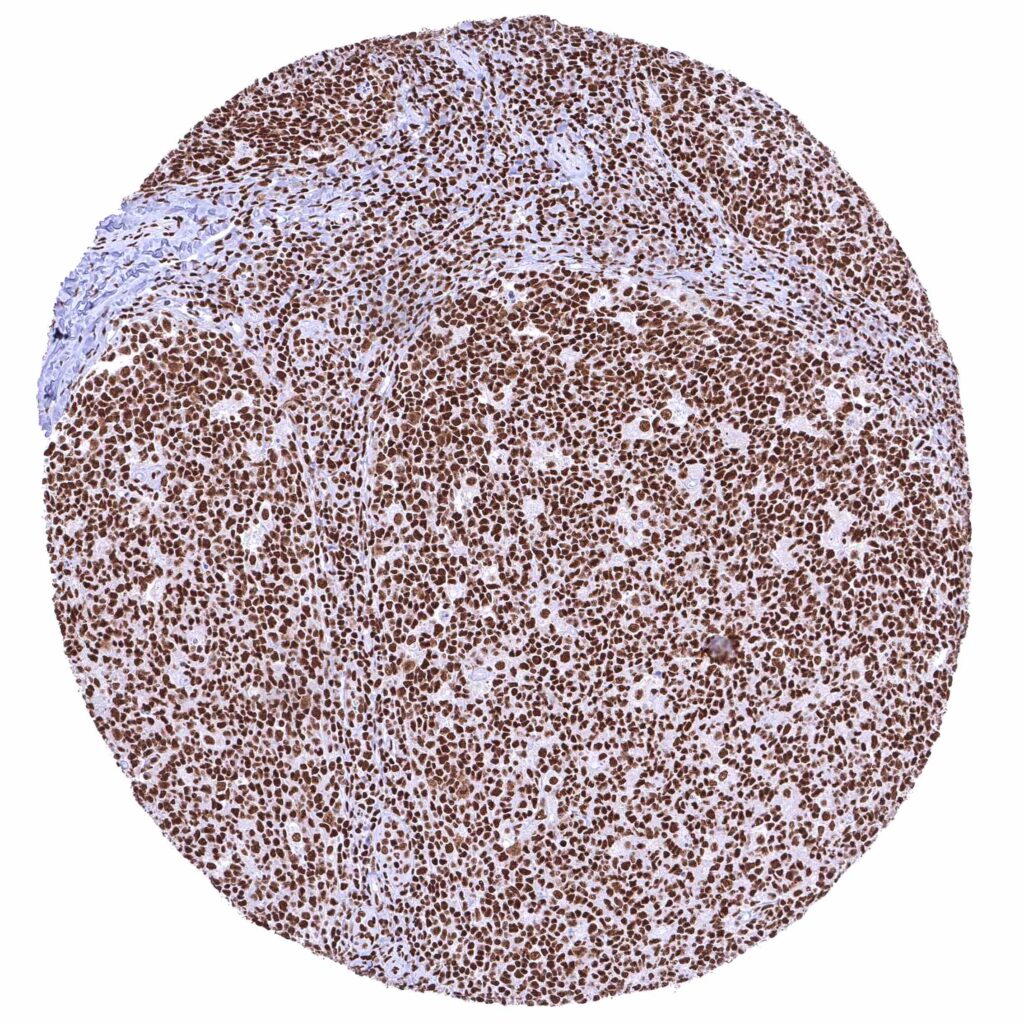
Tonsil – Strong nuclear BRD4 staining of all cell types. .jpeg
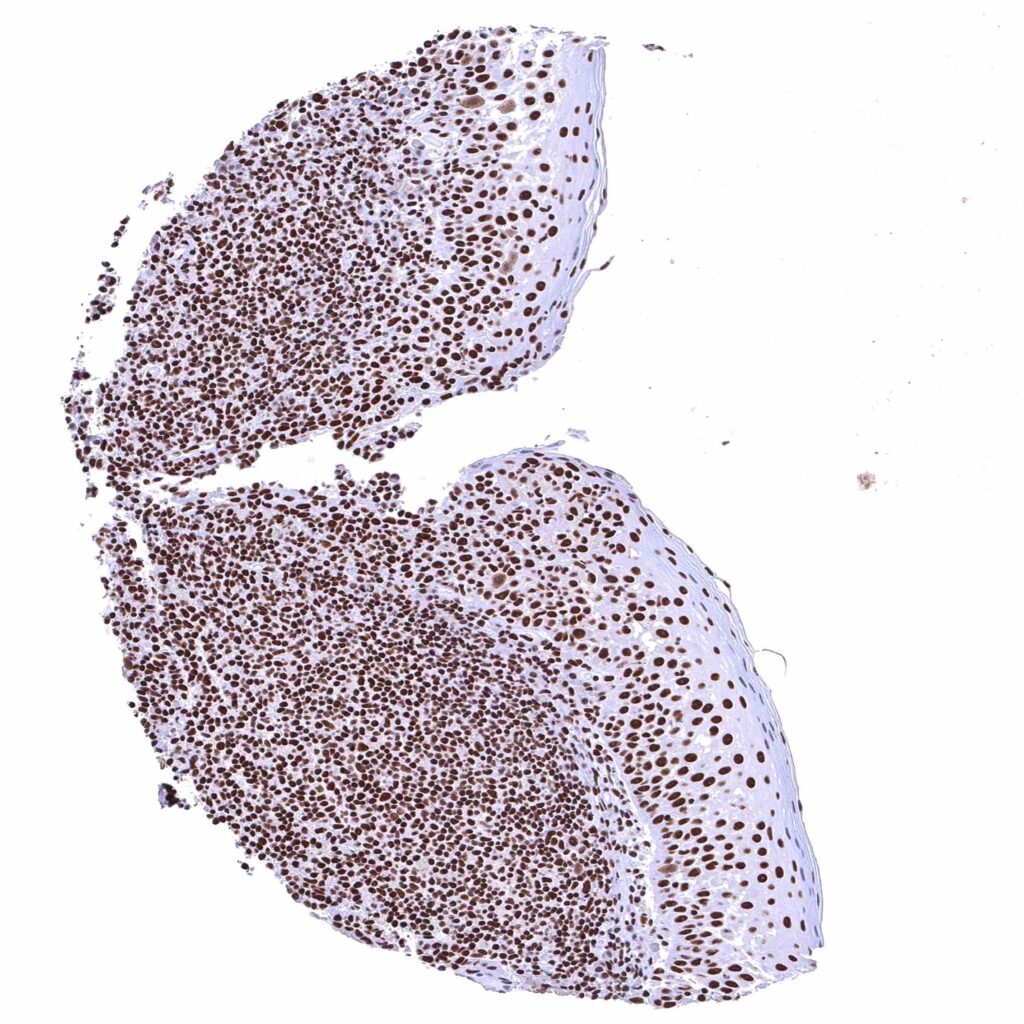
Tonsil, surface epithelium
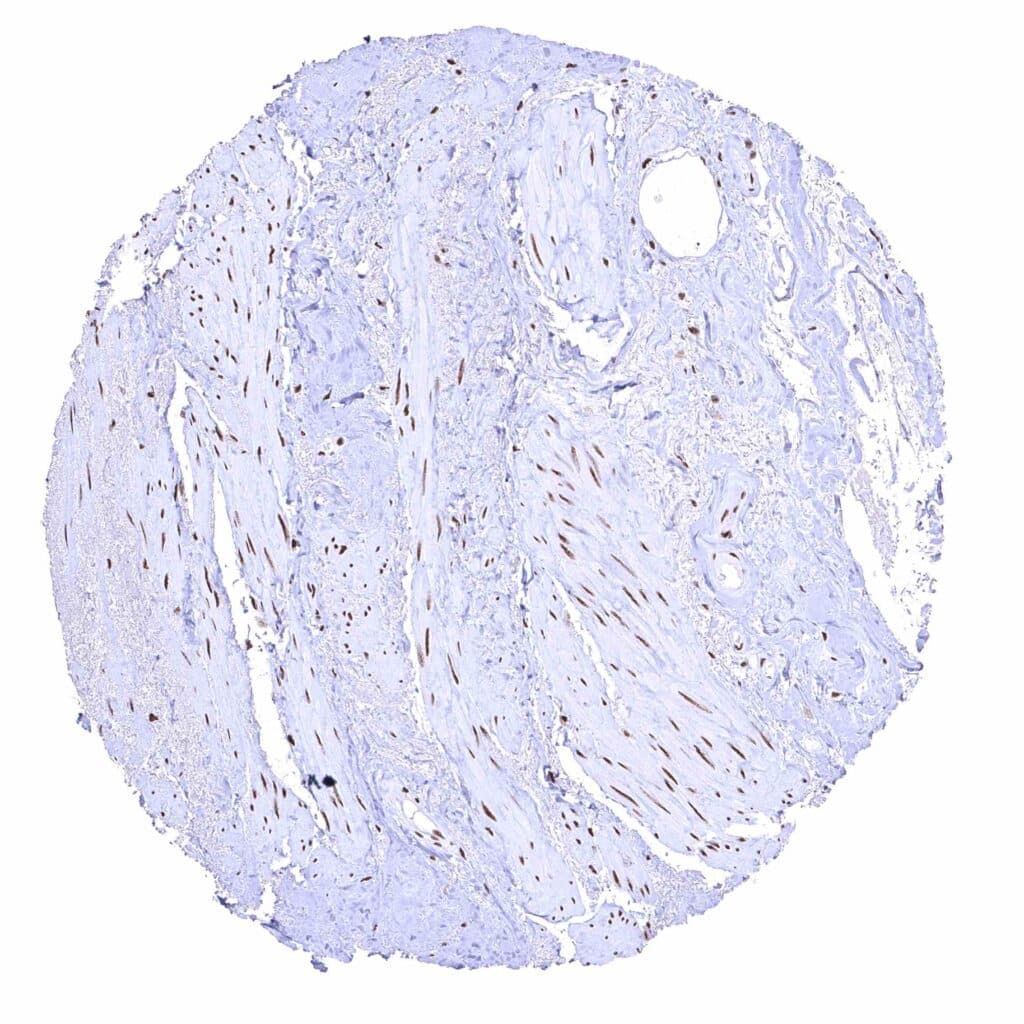
Urinary bladder, muscular wall
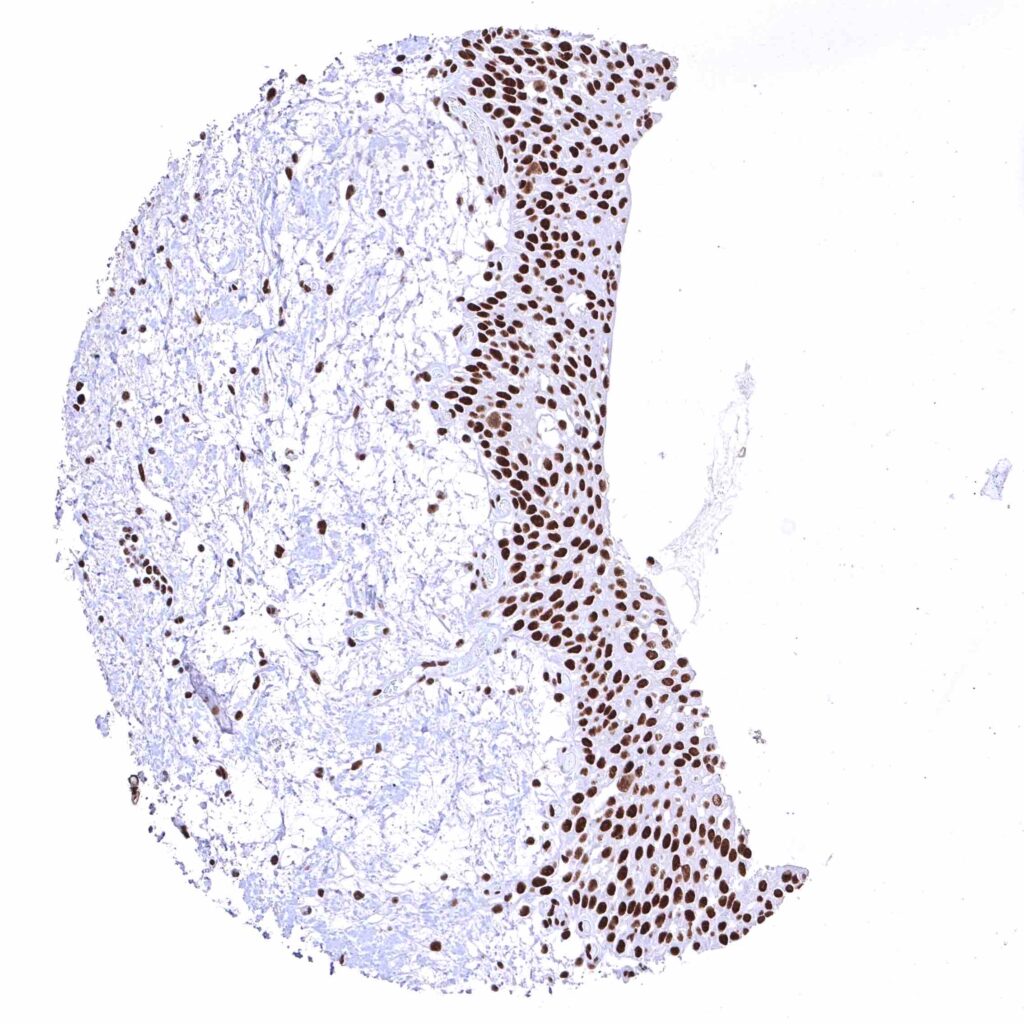
Urinary bladder, urothelium – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of urothelial cells.
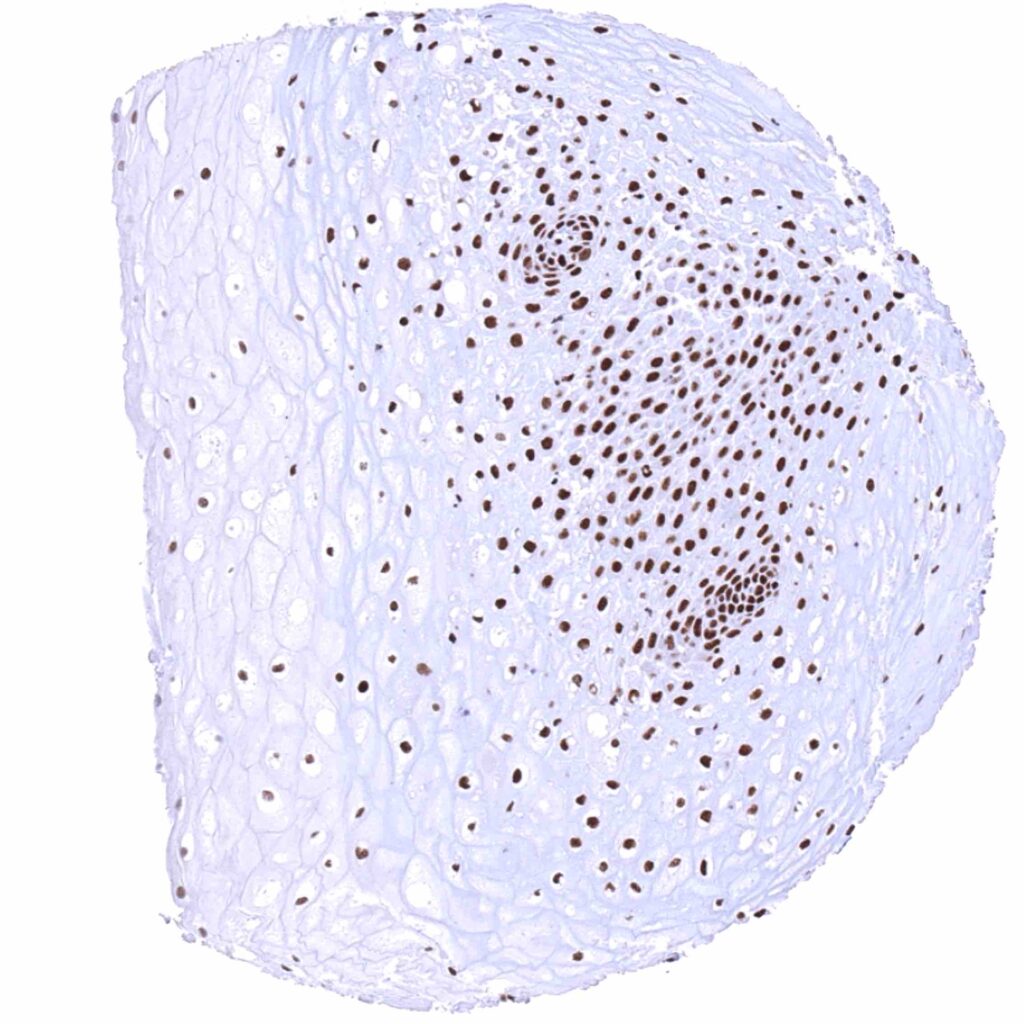
Uterus, ectocervix – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of squamous epithelial cells with a slight decrease of the staining intensity towards the most superficial cell layers. .jpeg
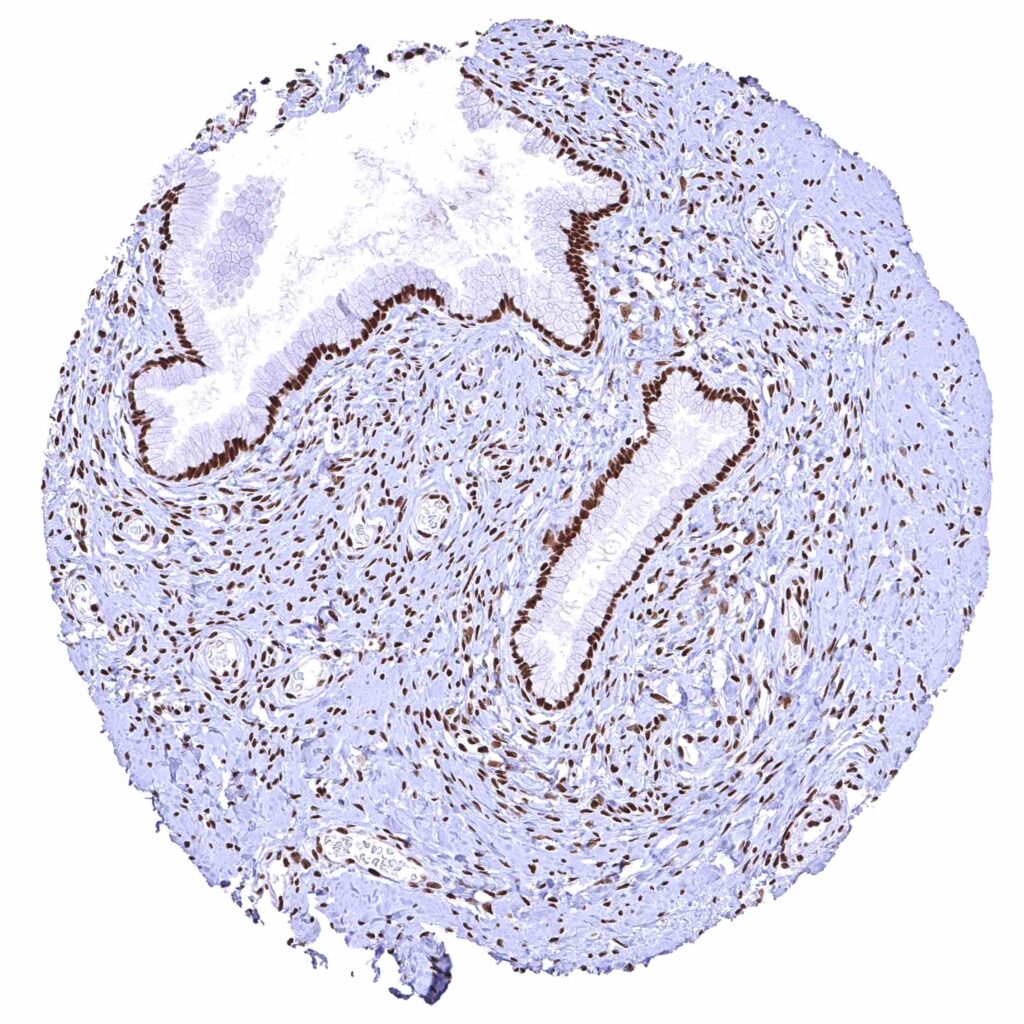
Uterus, endocervix
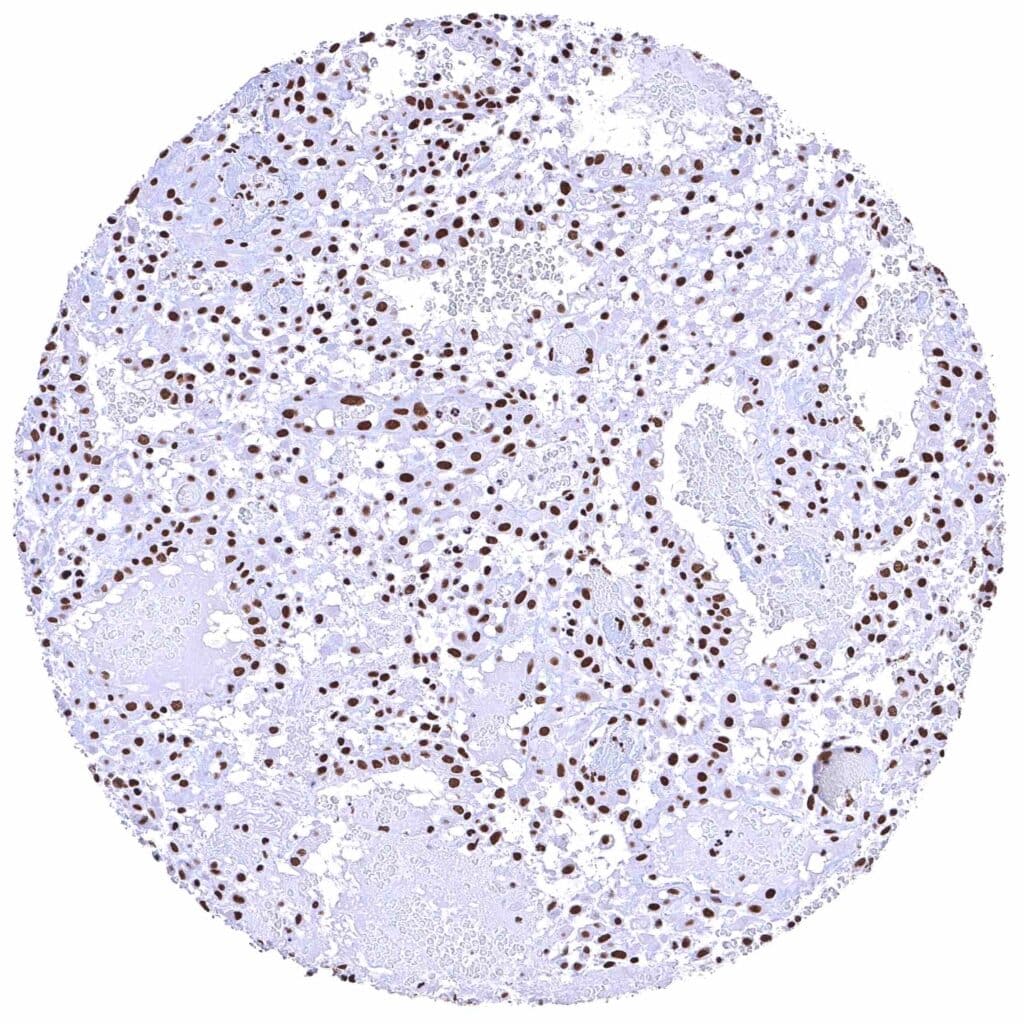
Uterus, endometrium (pregnancy)
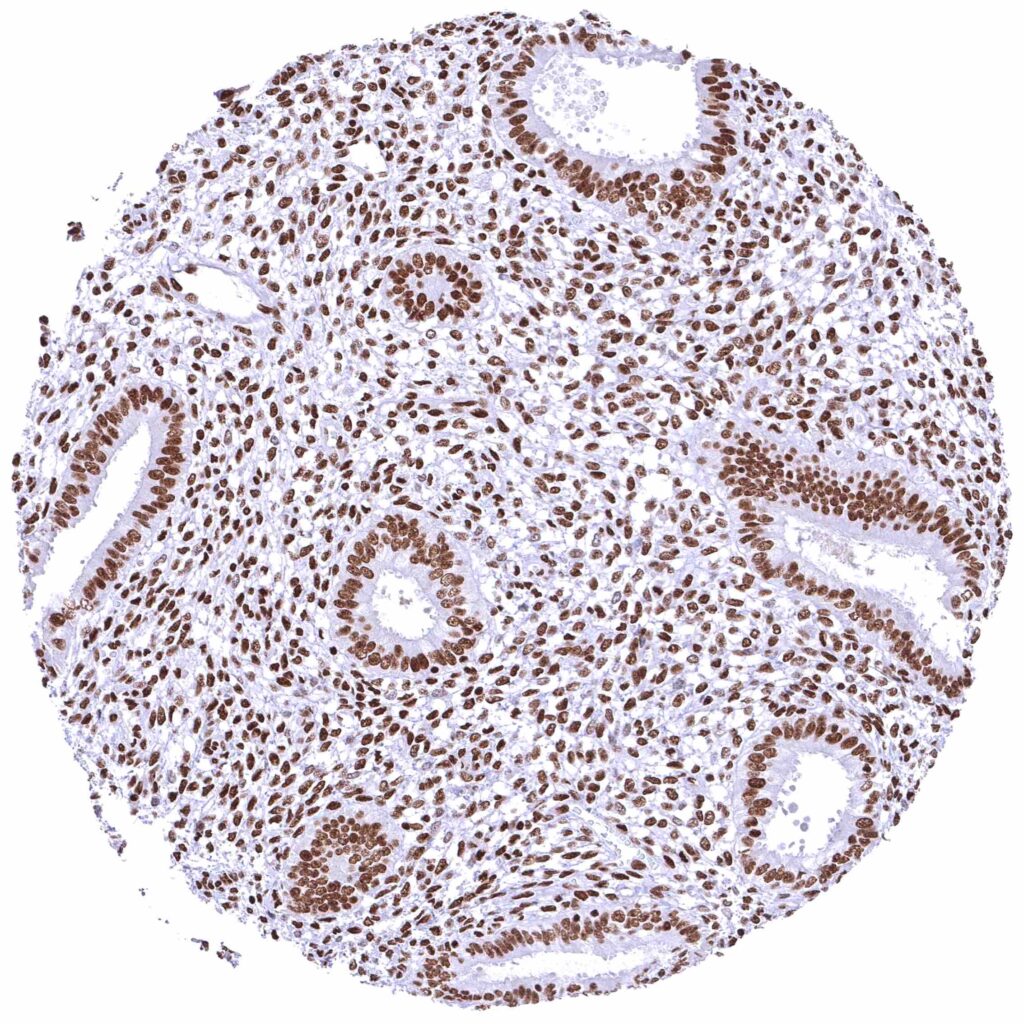
Uterus, endometrium (proliferation)
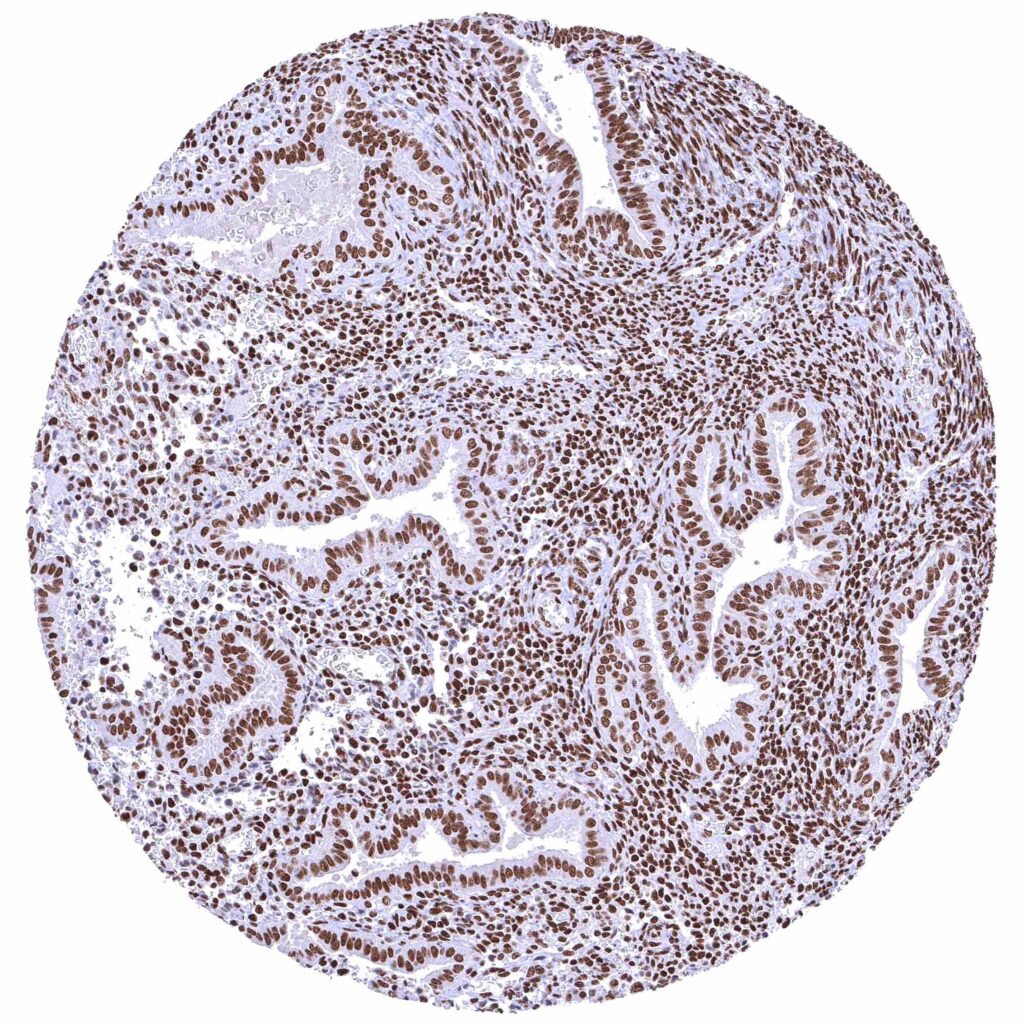
Uterus, endometrium (secretion)
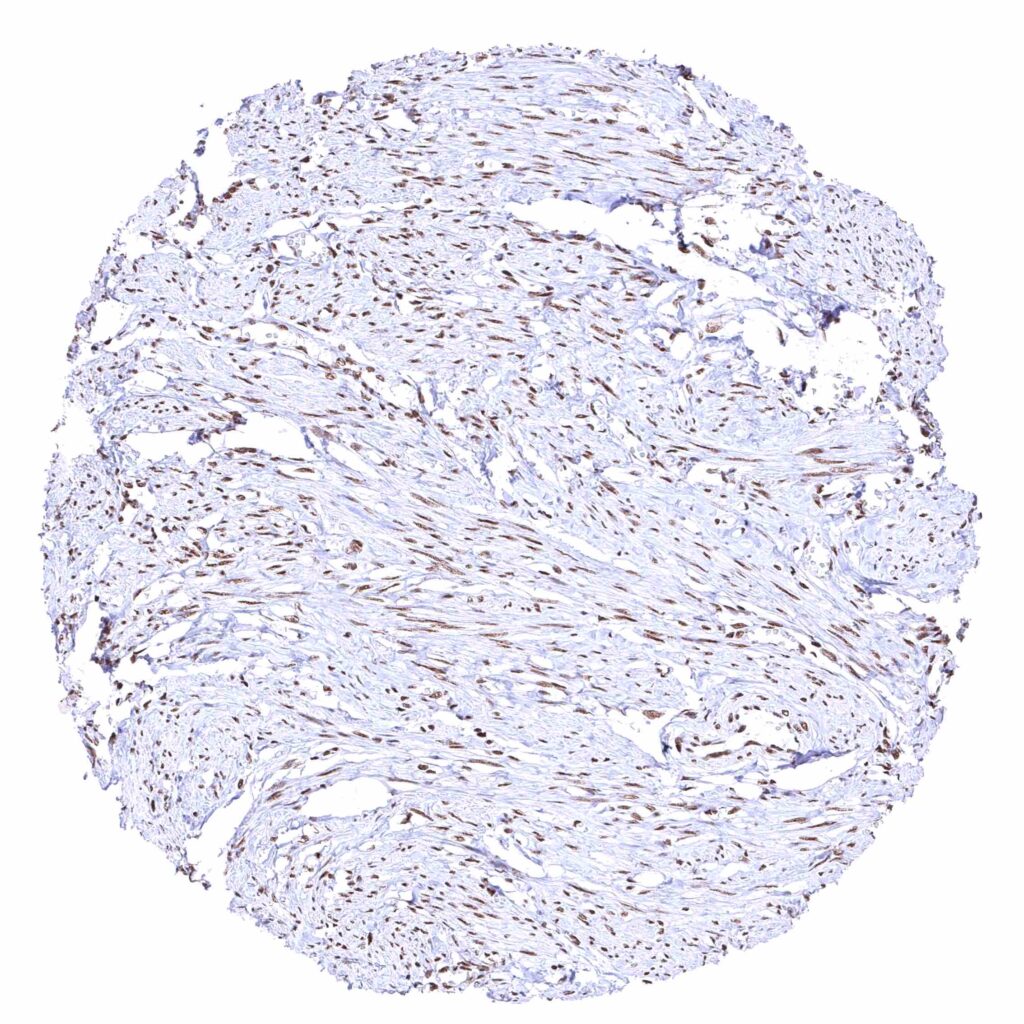
Uterus, myometrium – Distinct nuclear BRD4 staining of all muscle cells.
