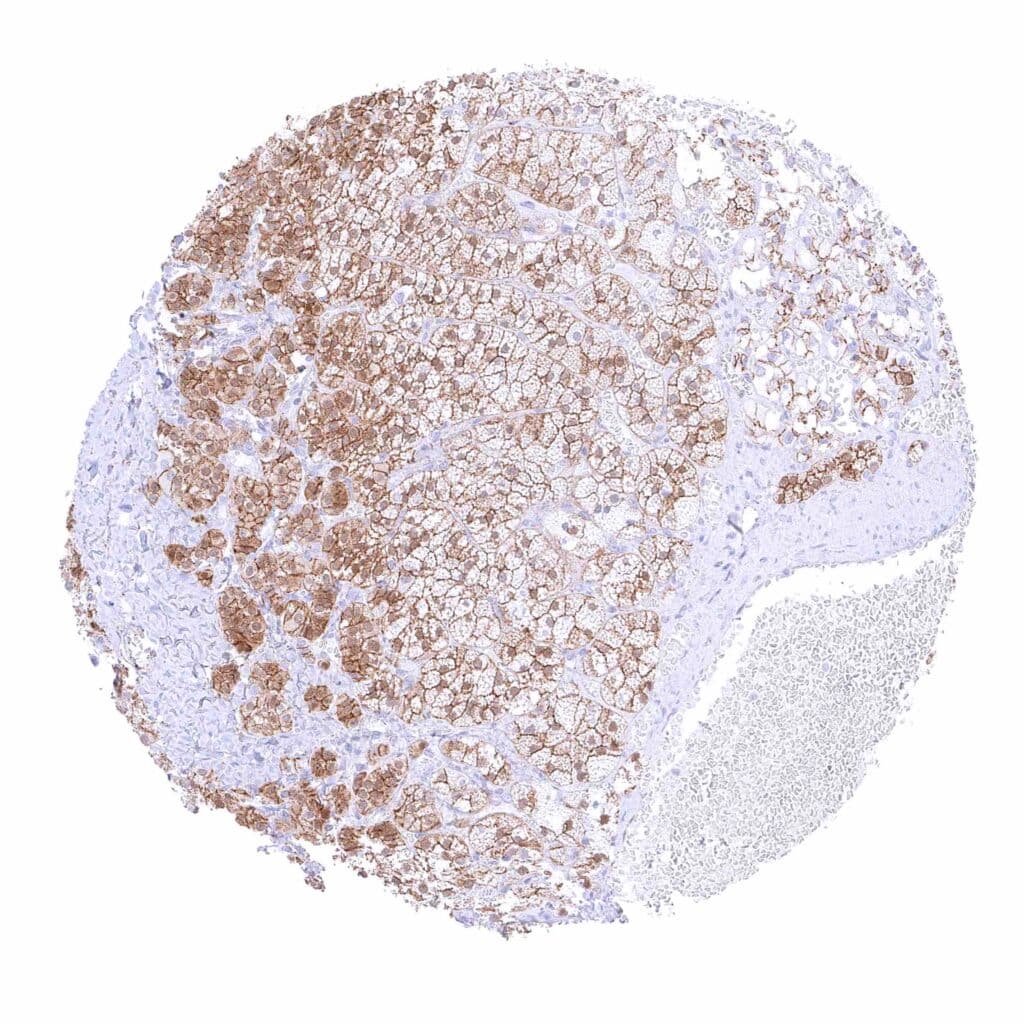
Adrenal gland – Moderate membranous beta catenin staining of adrenocortical cells, in a fraction of cells accompanied by a nuclear and cytoplasmic positivity.
Aorta, media
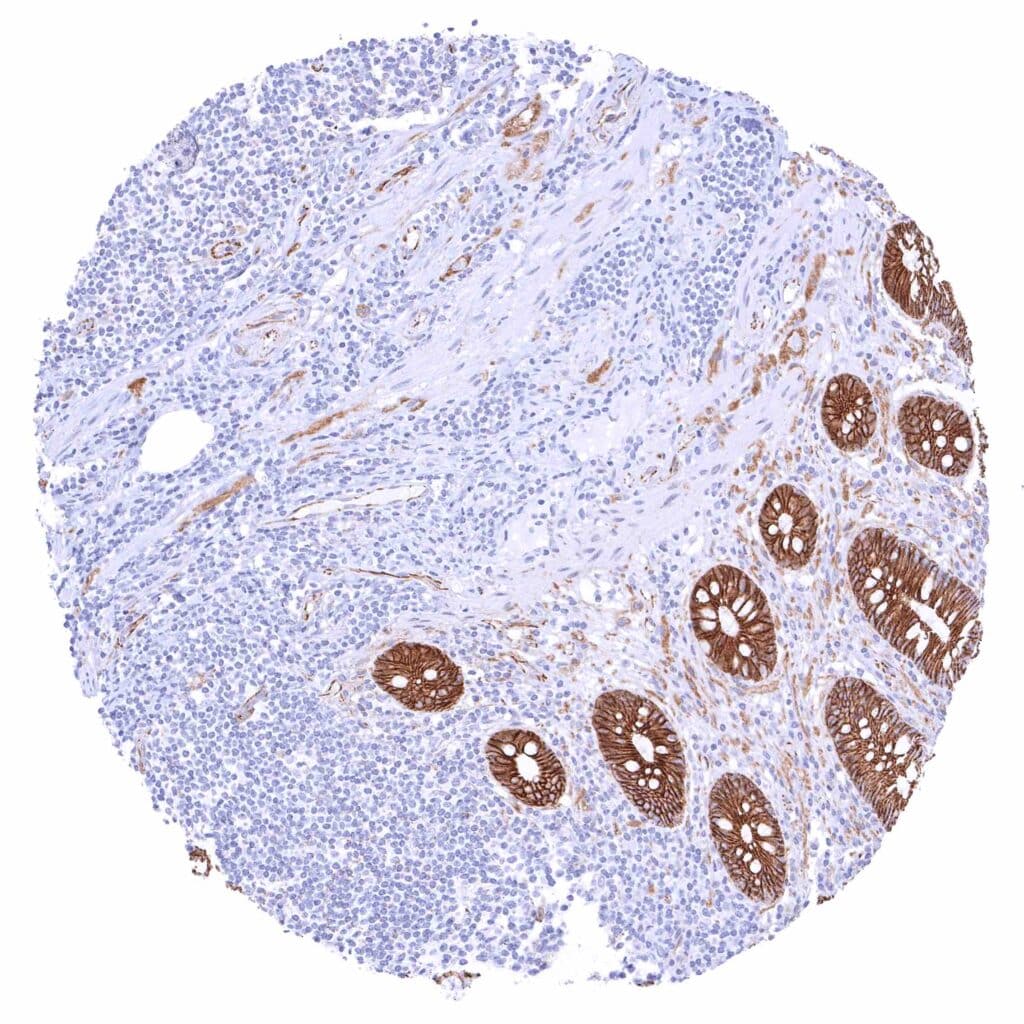
Appendix, mucosa – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of all epithelial cells while staining is weak to moderate in endothelial cells.
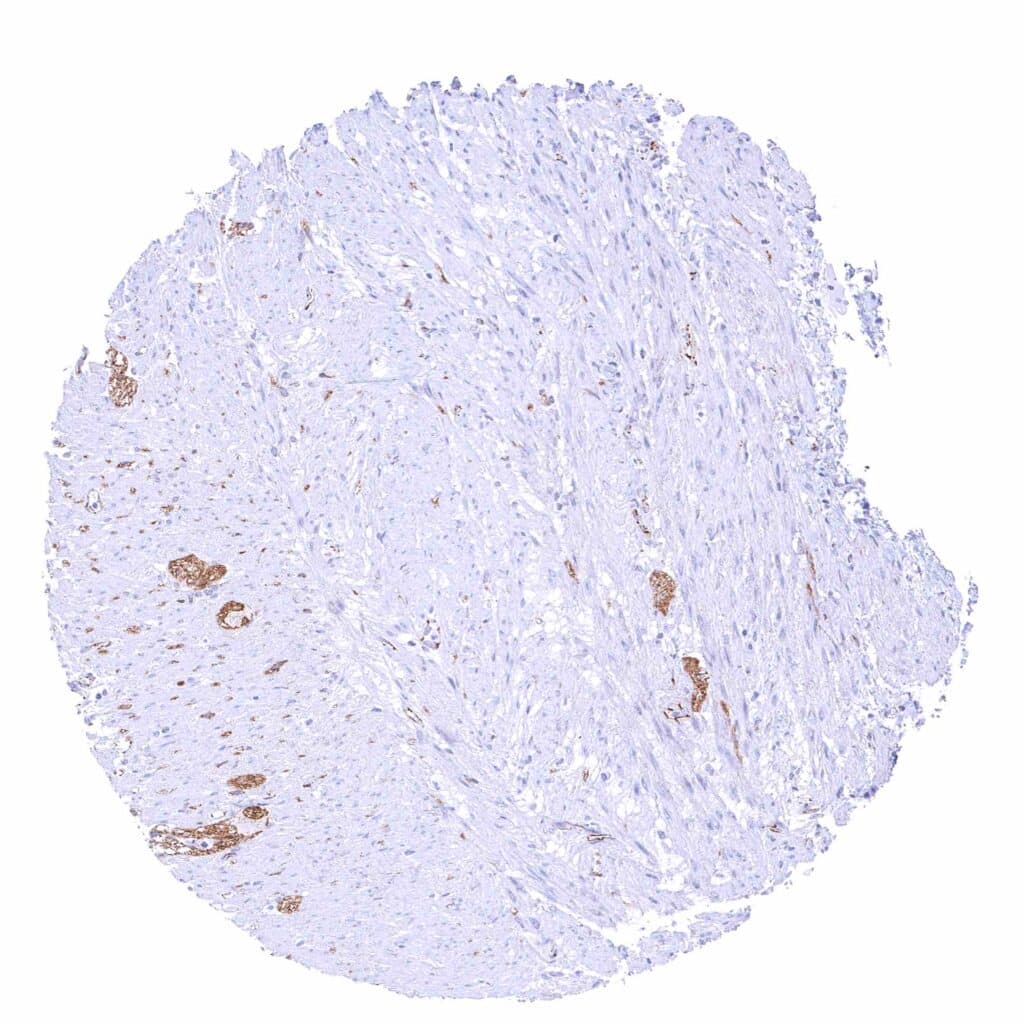
Appendix, muscular wall – Strong beta catenin staining of nerves.
Bone marrow
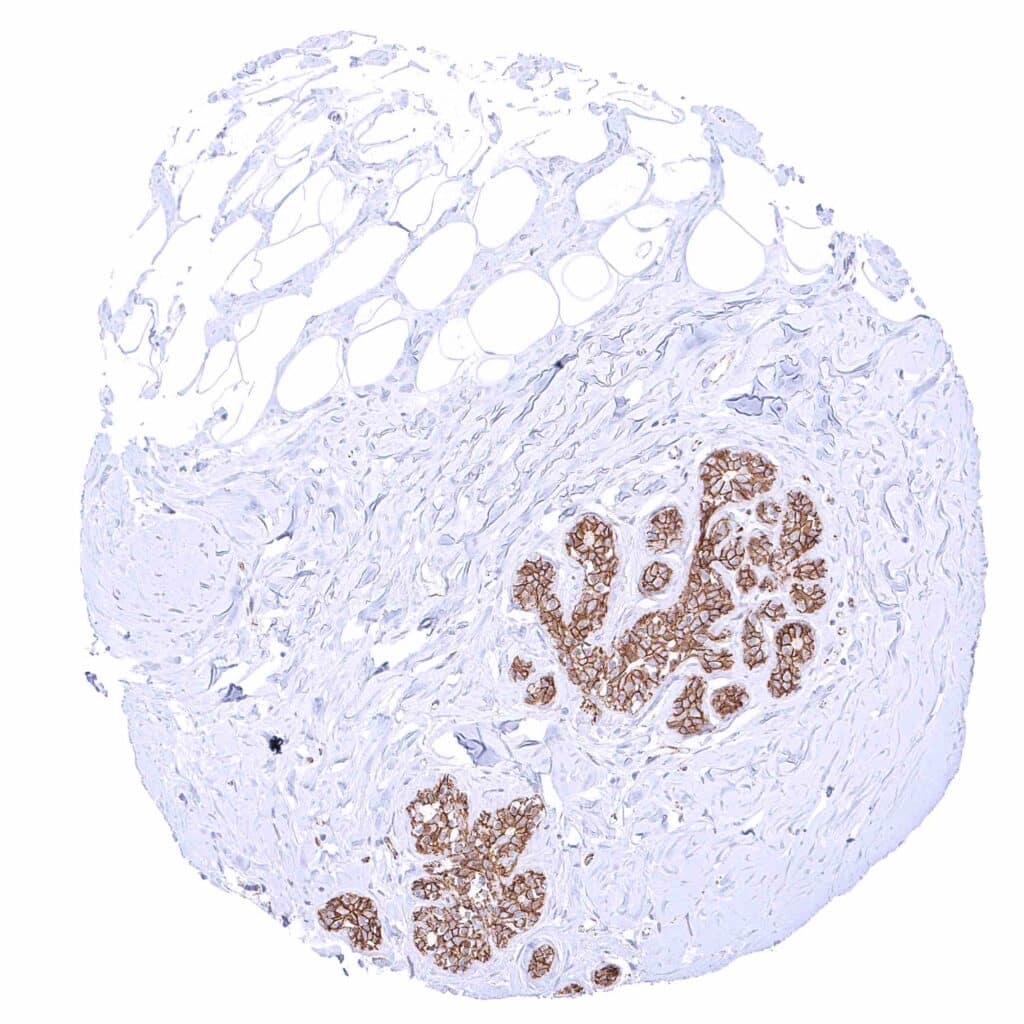
Breast – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells.
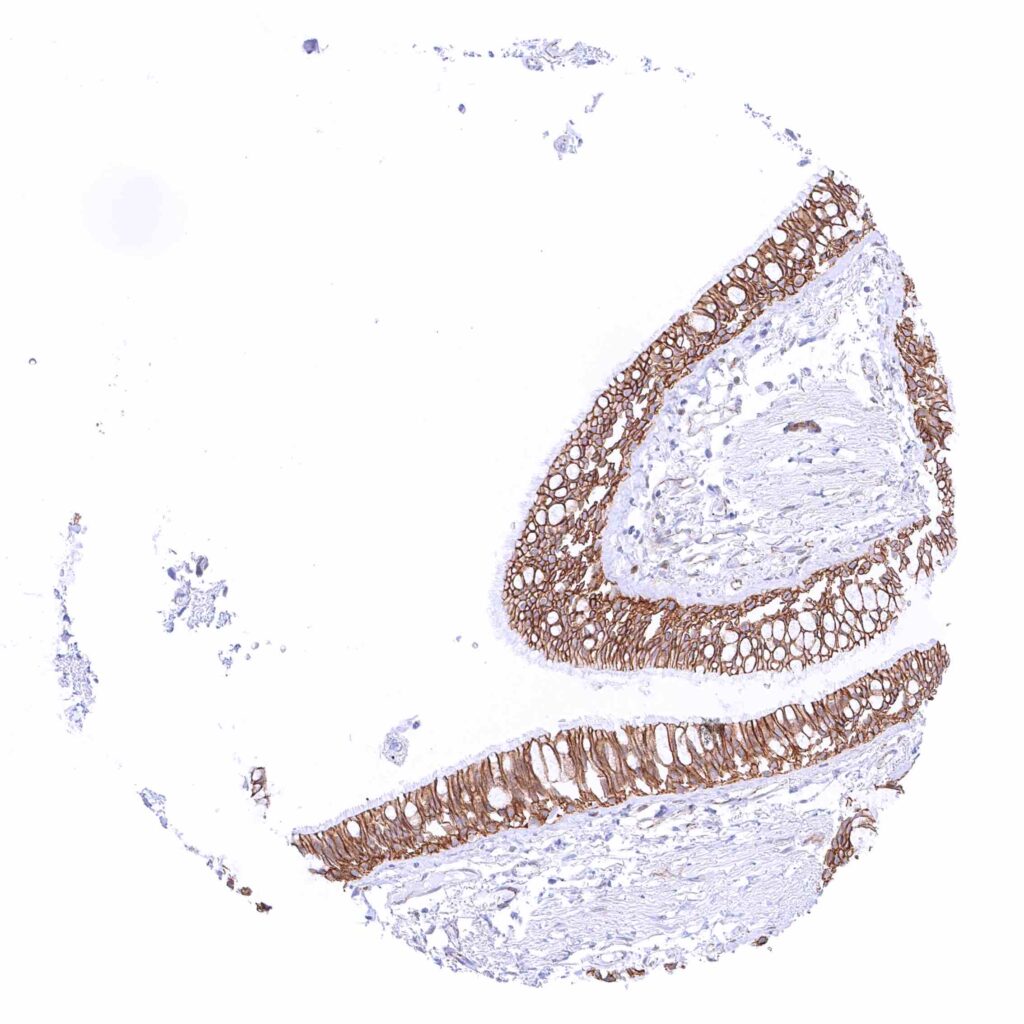
Bronchus, mucosa – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of respiratory epithelial cells. Ciliae are beta catenin negative.
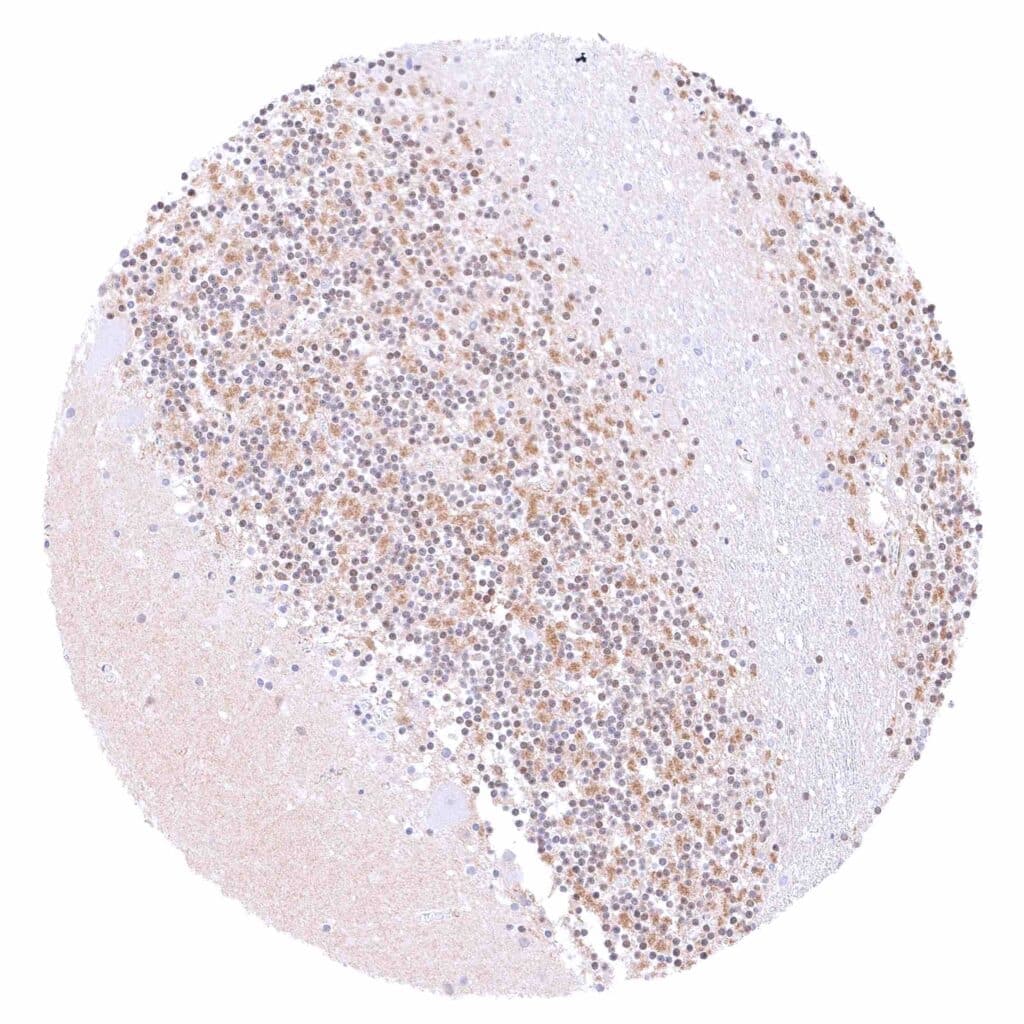
Cerebellum (molecular layer, Purkinje cell layer, granule cell layer, white matter) – Moderate to strong beta catenin staining of cerebellar glomeruli (post-synaptic granule cell dendrites and pre-synaptic terminals of mossy fibers).
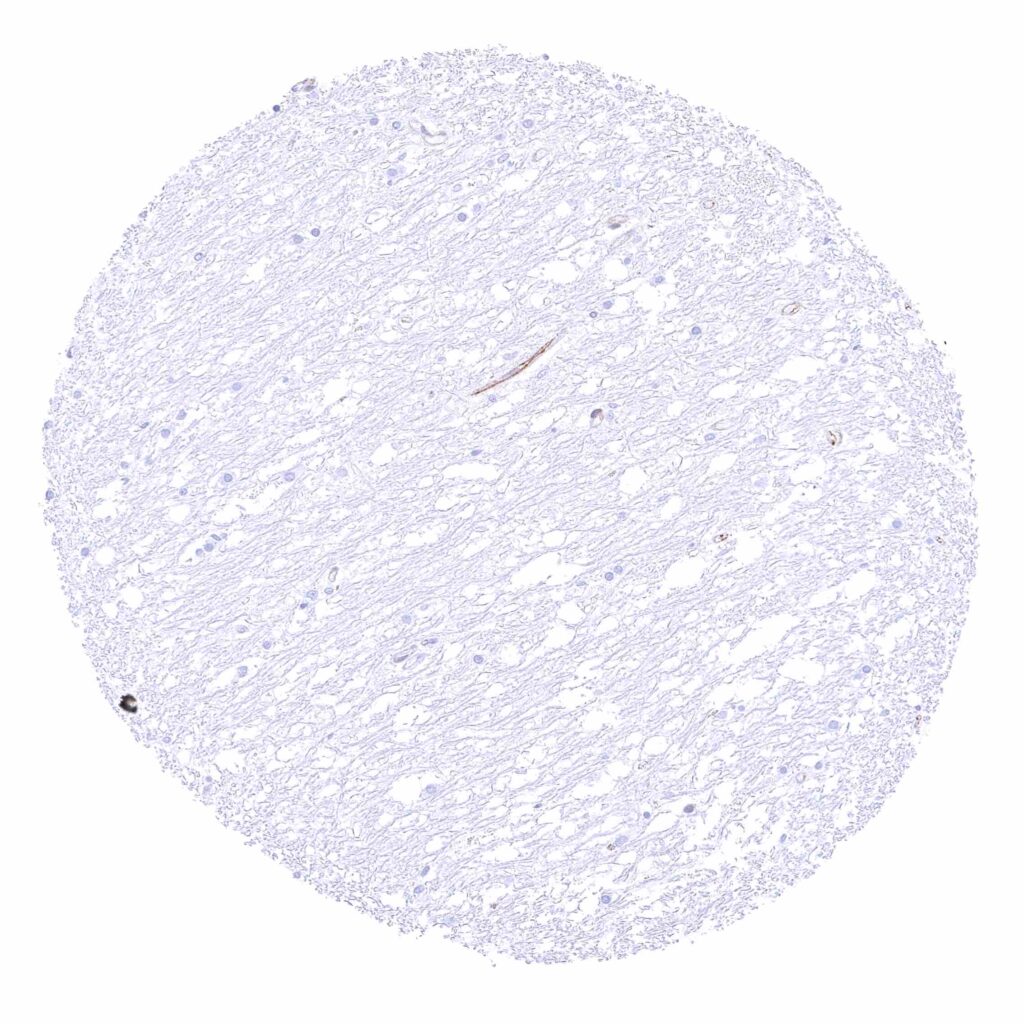
Cerebellum (white matter)
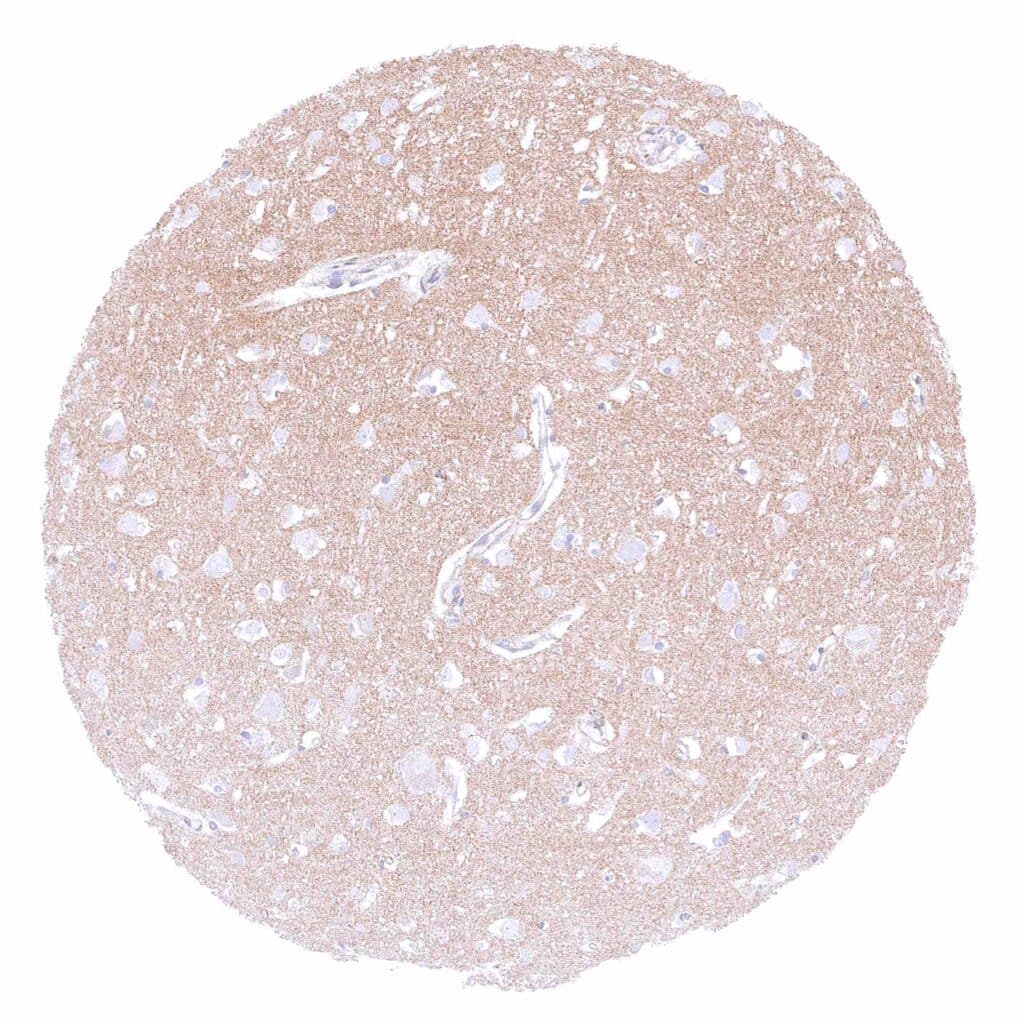
Cerebrum, grey – Moderate beta catenin staining of nerve fibers in the grey matter of the cerebrum.
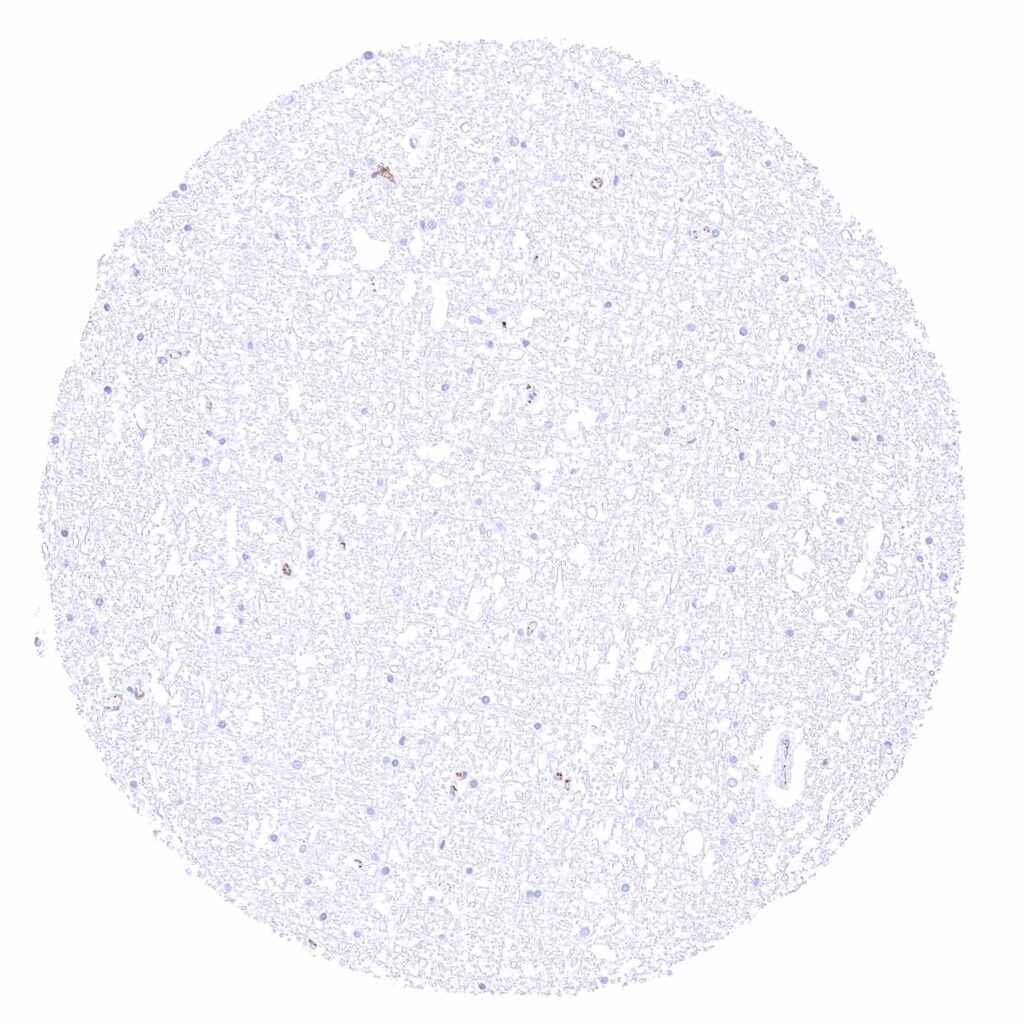
Cerebrum, white
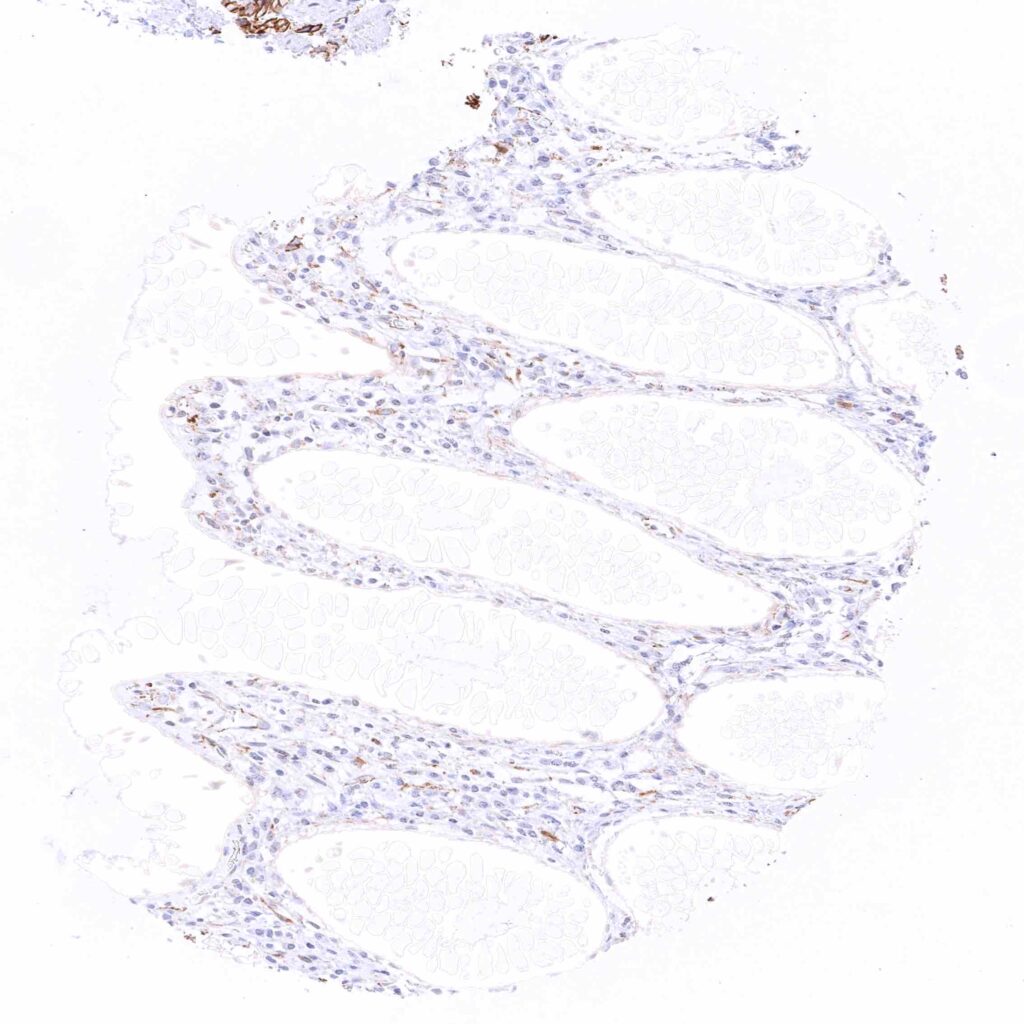
Colon descendens, mucosa
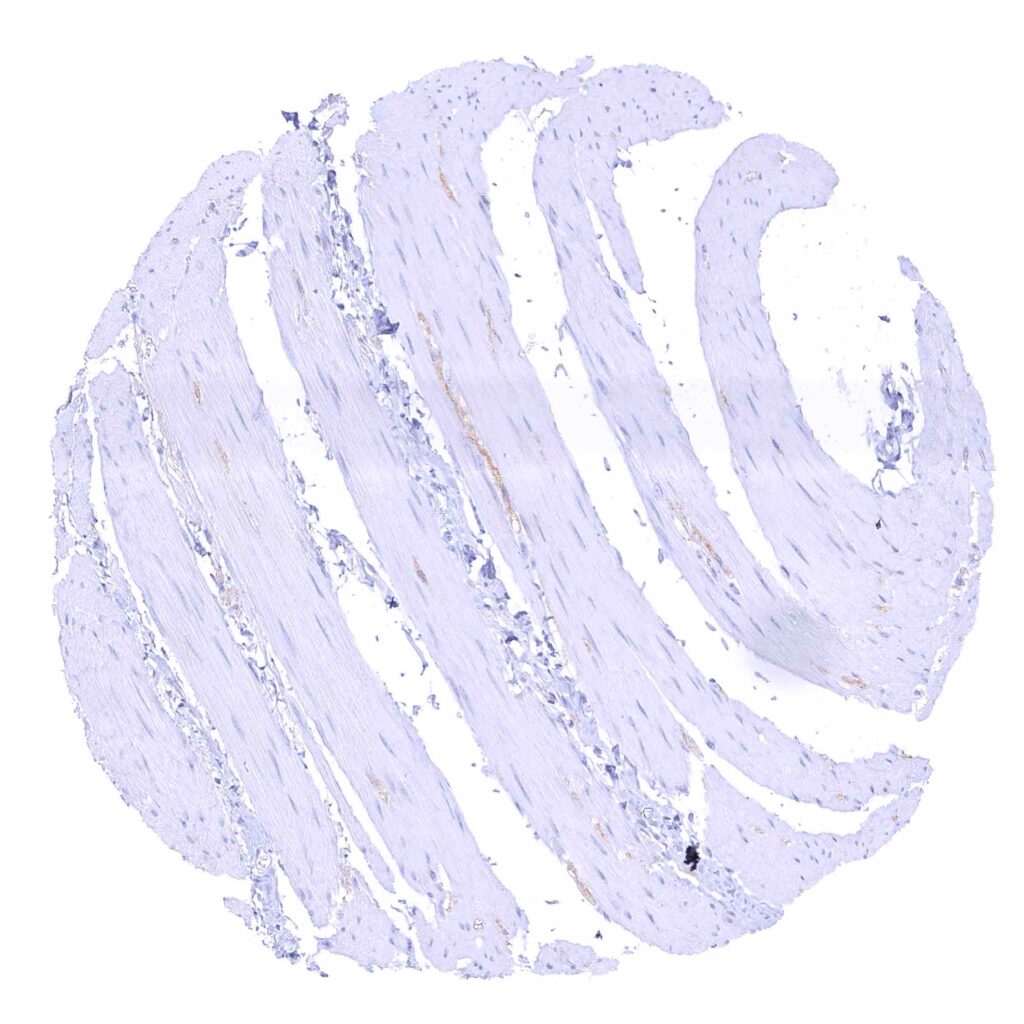
Colon descendens, muscular wall
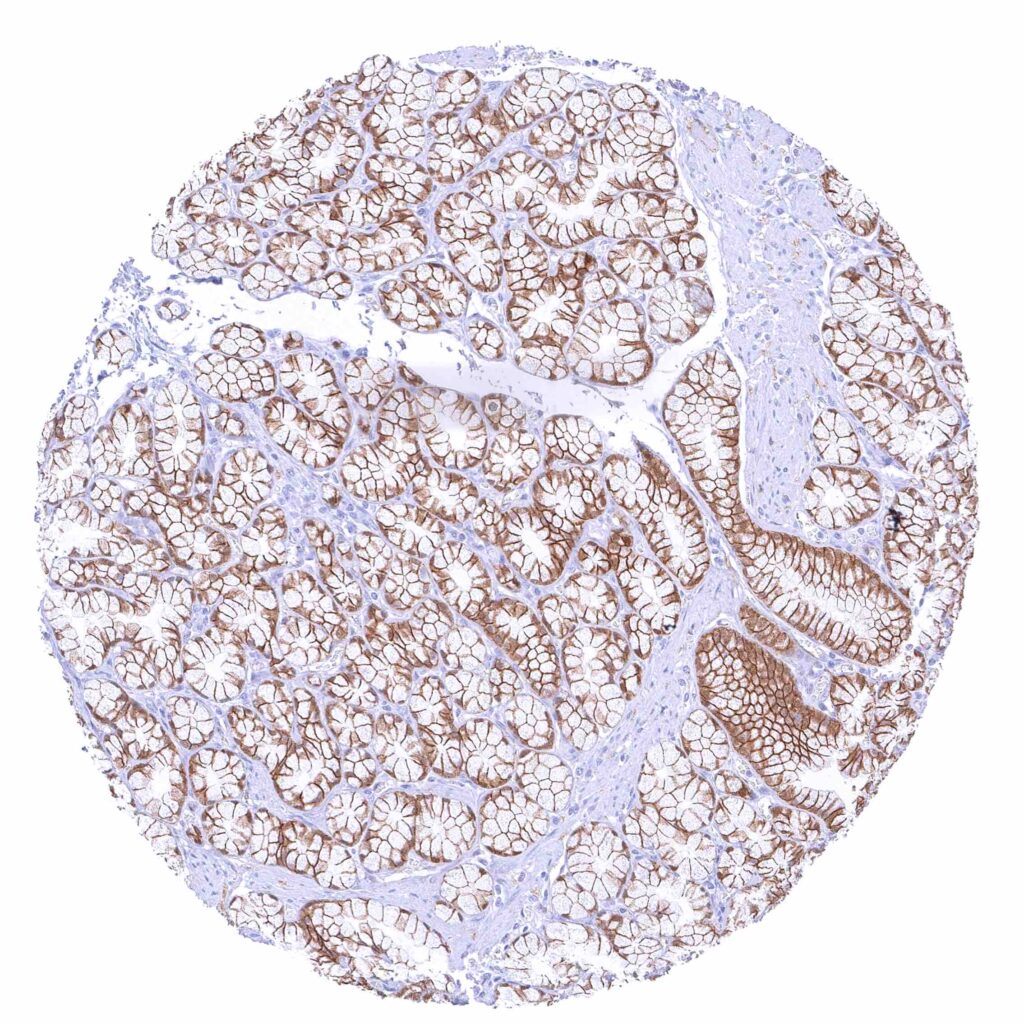
Duodenum, Brunner gland – Distinct membranous beta catenin staining of glandular cells .jpeg
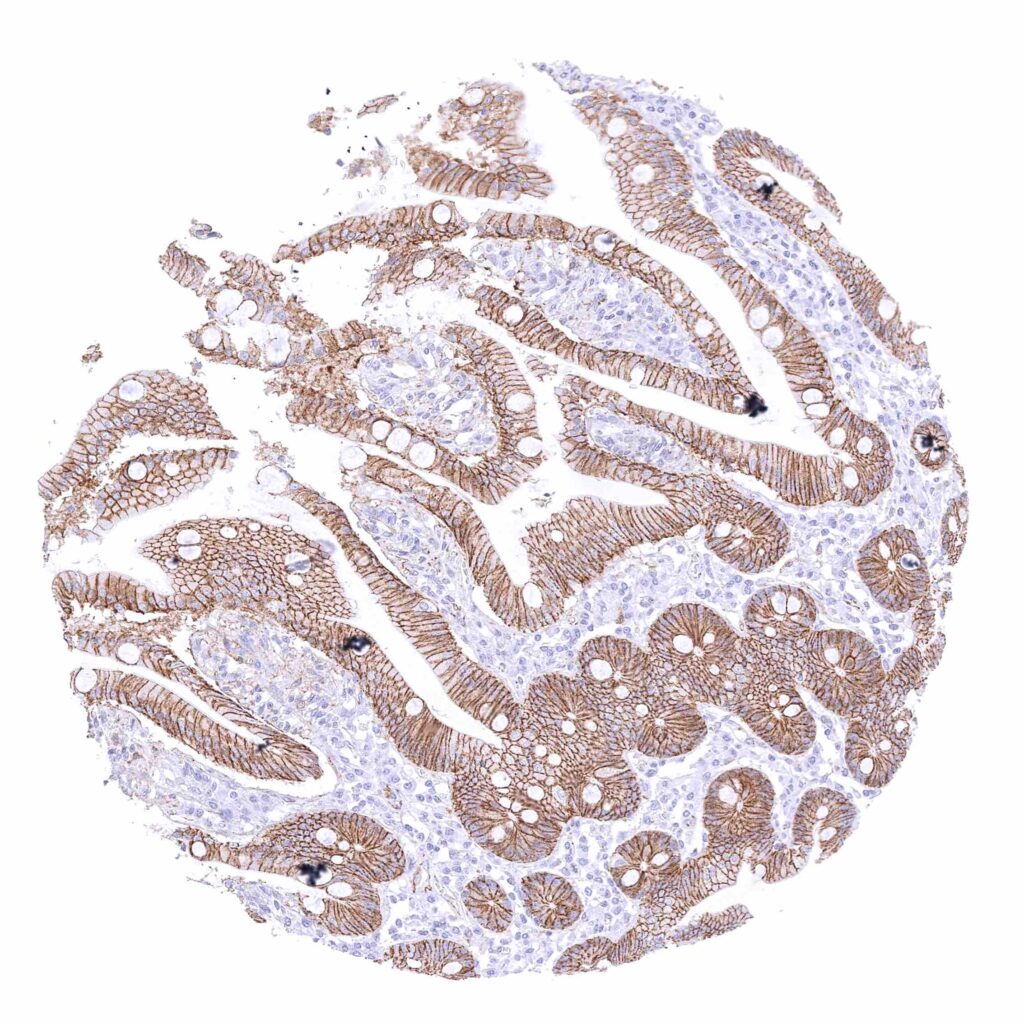
Duodenum, mucosa – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of all epithelial cells.
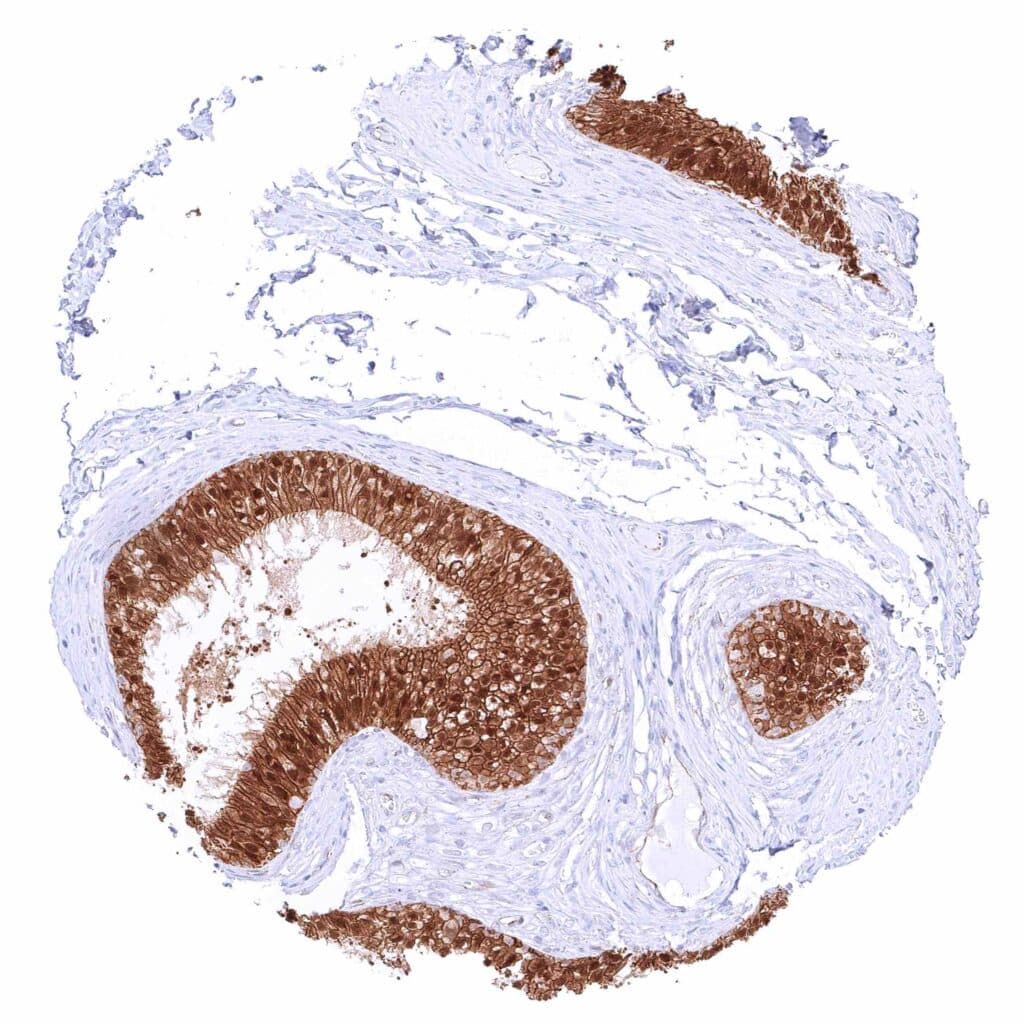
Epididymis (Caput) – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of all epithelial cells with an additional strong nuclear staining in the tall columnar cells of the caput.
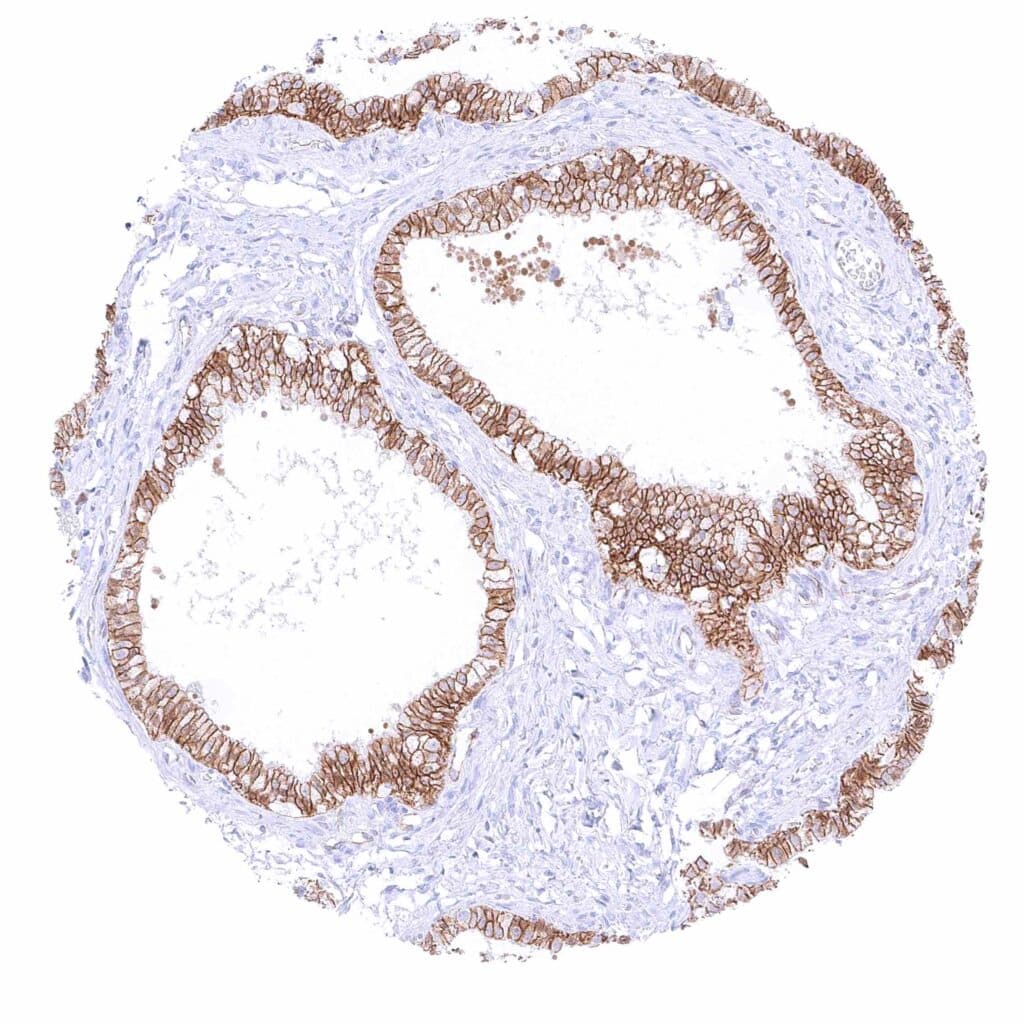
Epididymis (Cauda) – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of all epithelial cells.
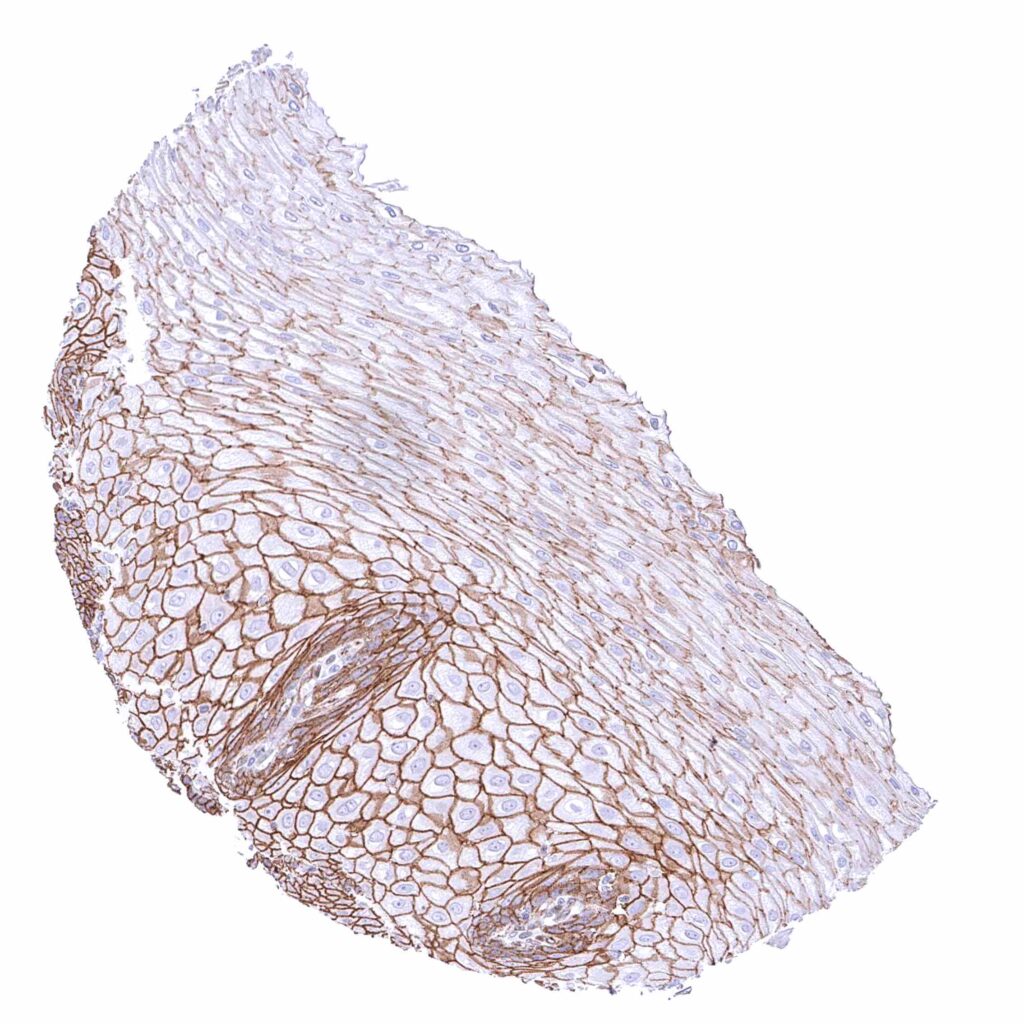

Esophagus, squamous epithelium – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of squamous epithelial cells with decreasing staining intensity from basal towards superficial cell layers.
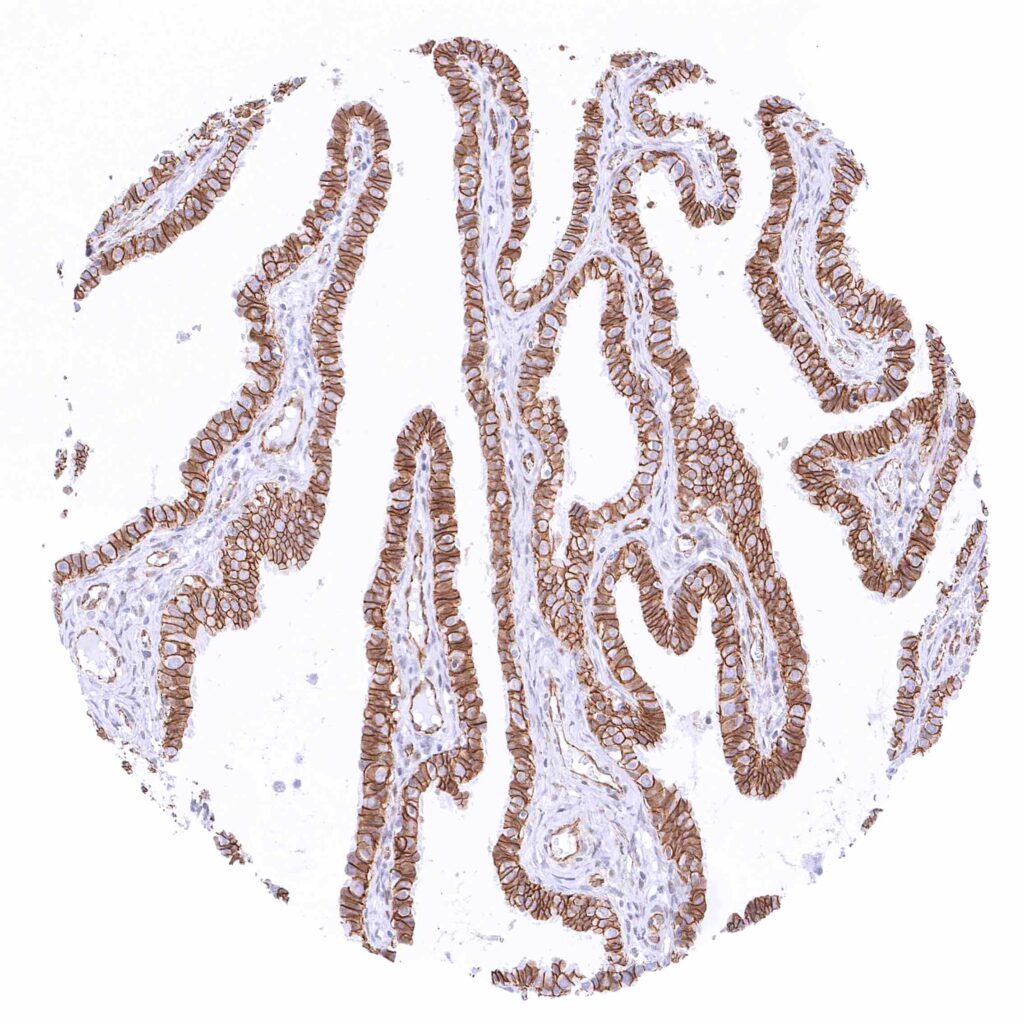
Fallopian tube, mucosa – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells.
Fat
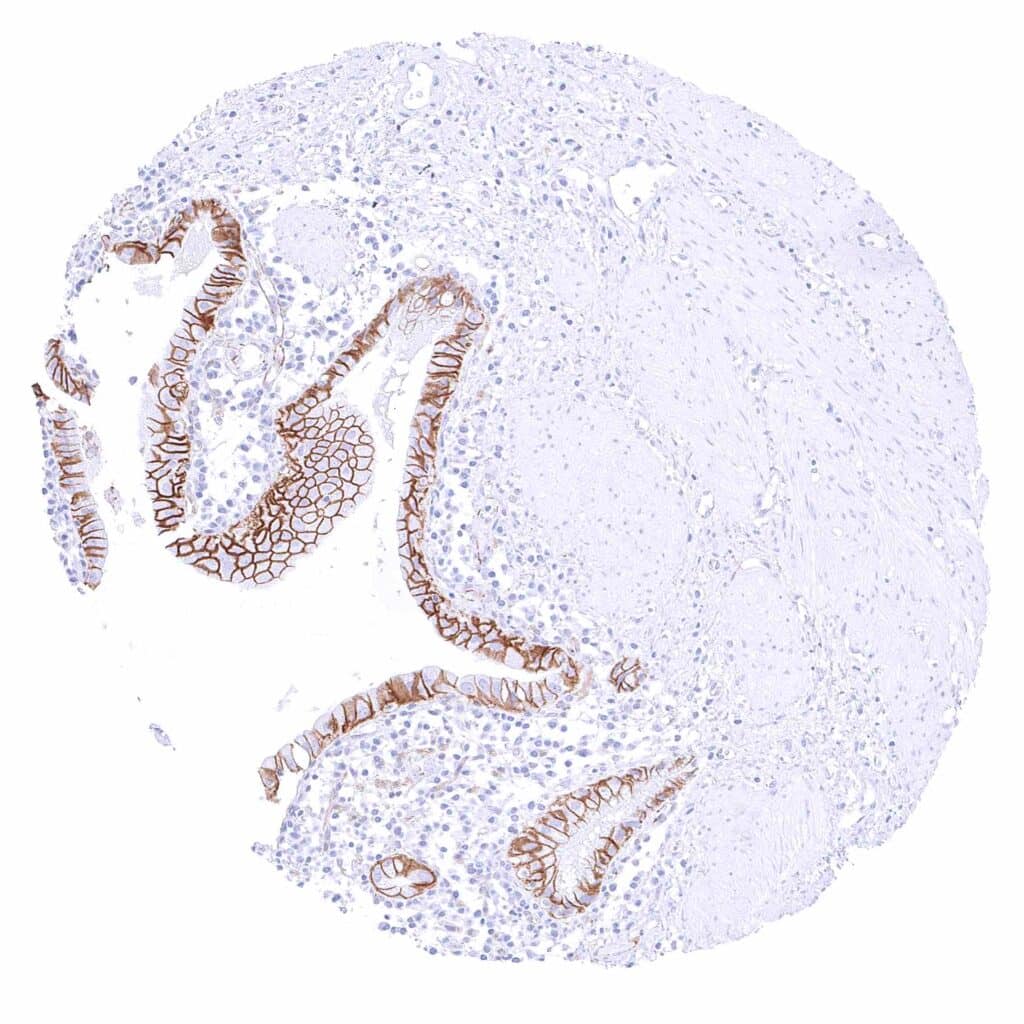
Gallbladder, epithelium – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells.
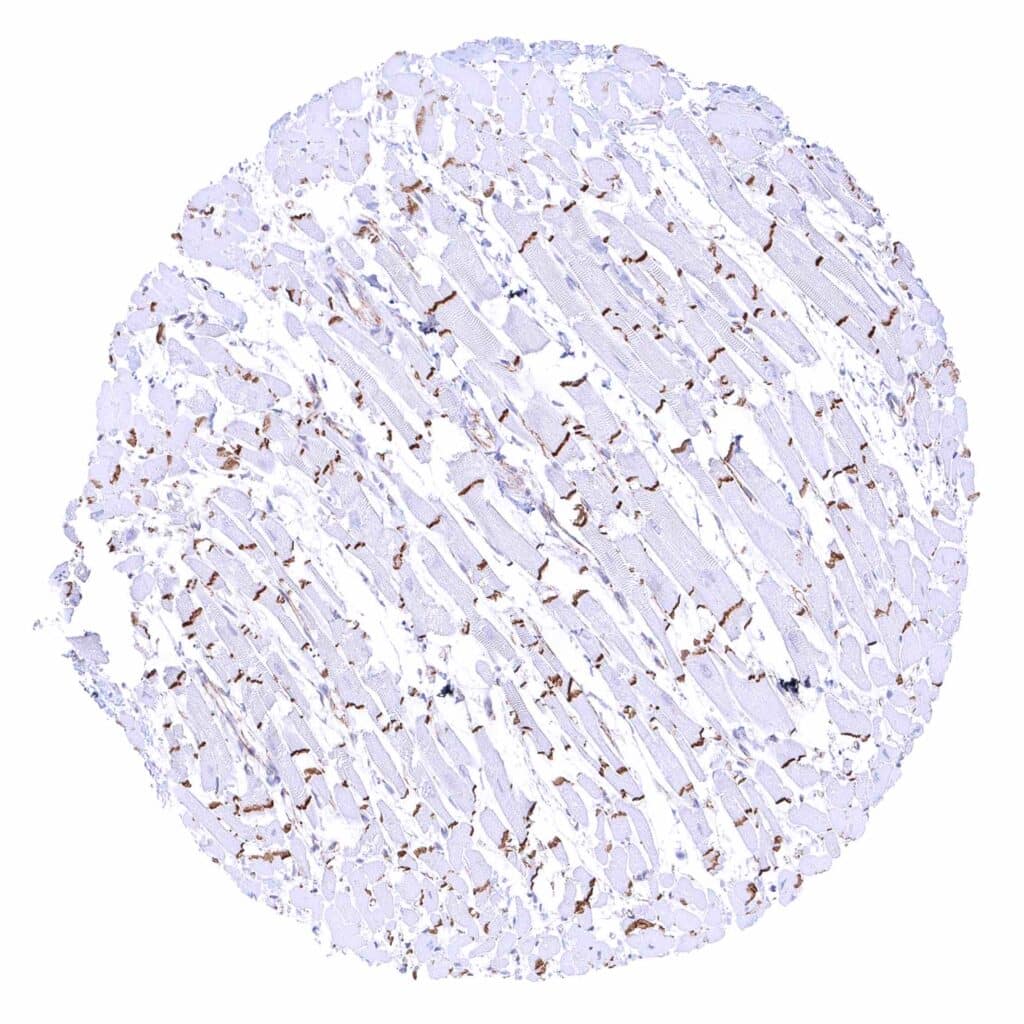
Heart muscle – Strong beta catenin staining of intercalated discs.
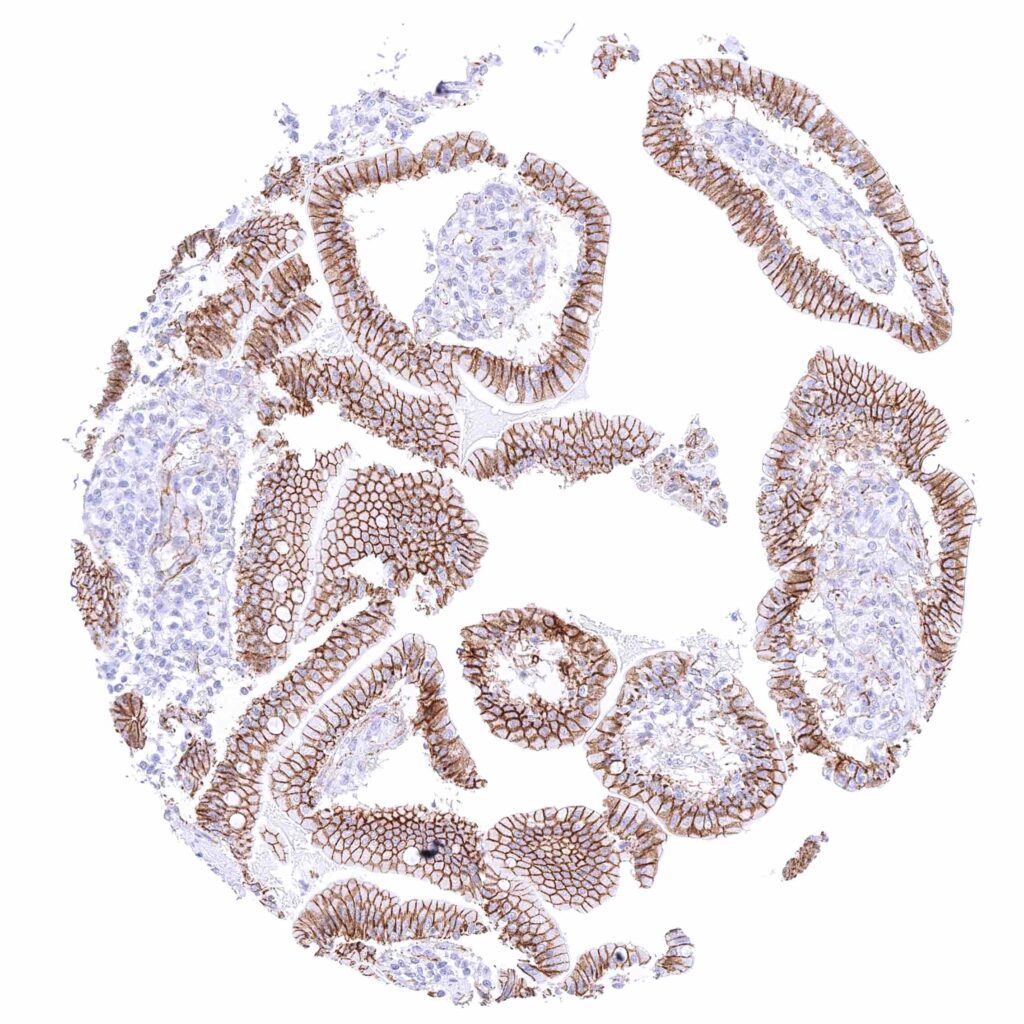
Ileum, mucosa – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of all epithelial cells. .jpeg
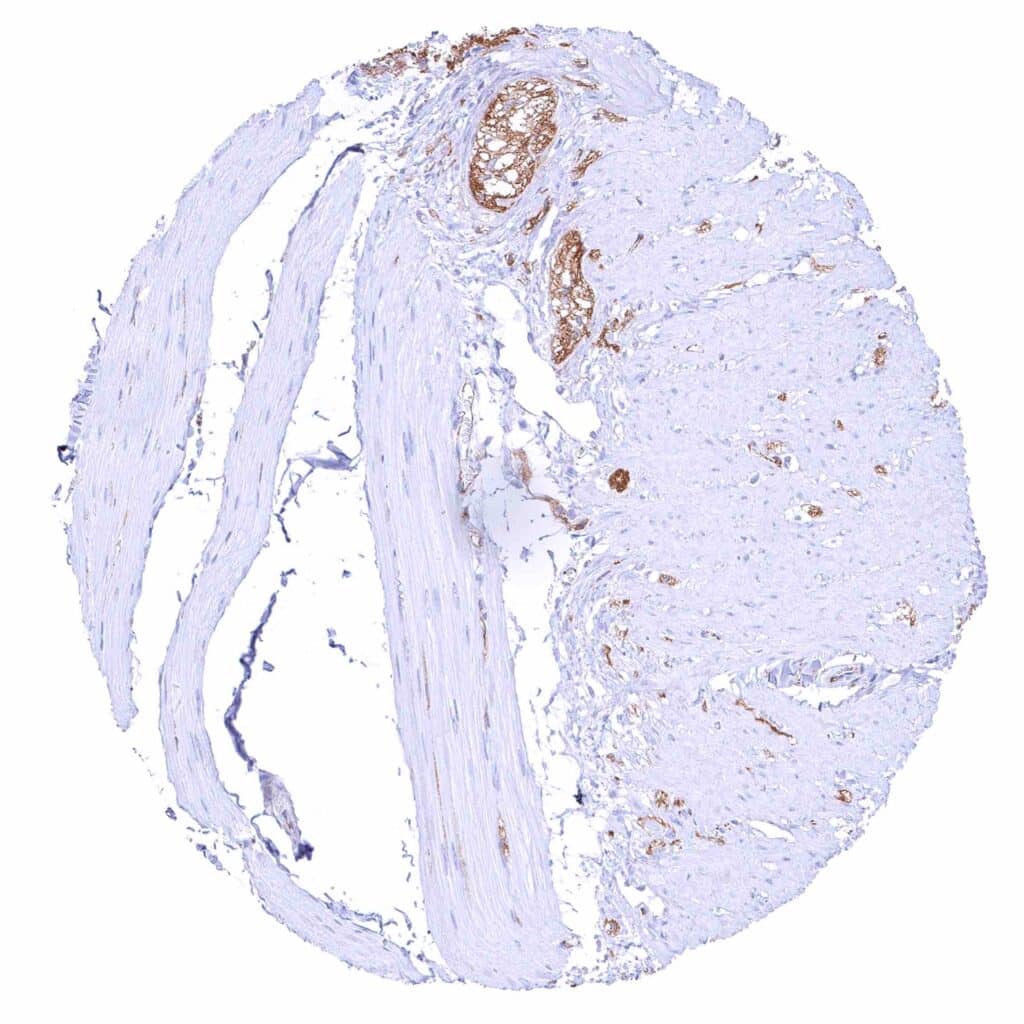
Ileum, muscularis – Strong beta catenin staining of nerves.
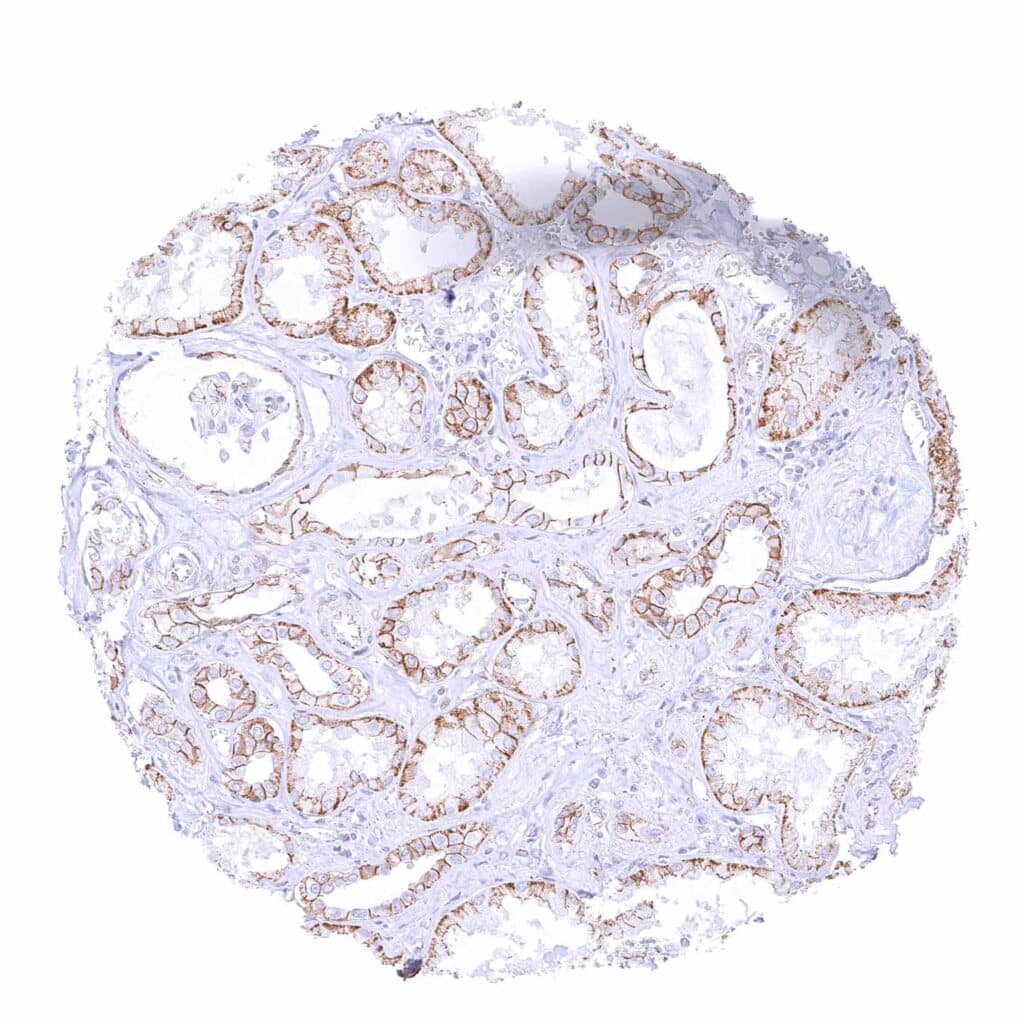
Kidney, cortex – Moderate to strong membranous beta catenin staining of tubular and collecting duct cells while staining is only weak at the capsule of Bowman. .jpeg
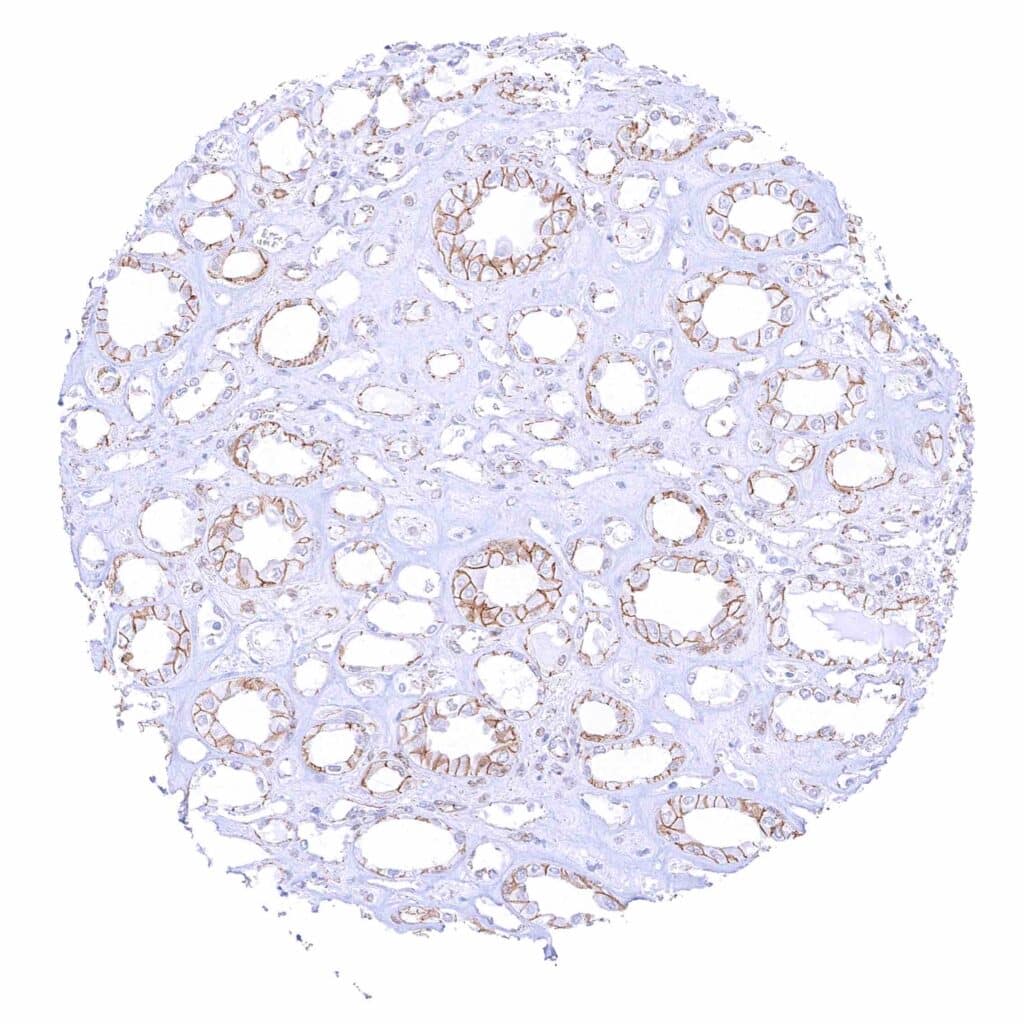
Kidney, medulla – Moderate to strong membranous beta catenin staining of collecting duct cells. .jpeg
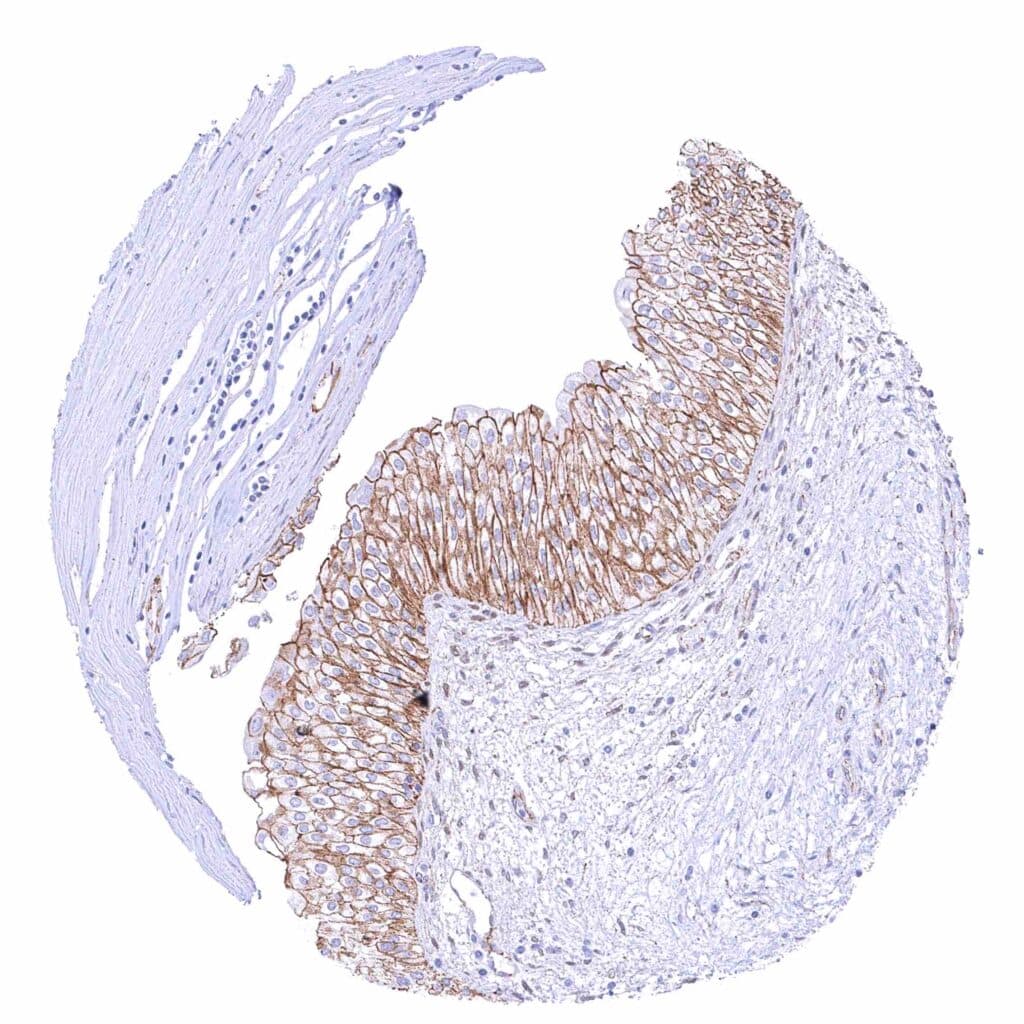
Kidney, pelvis, urothelium – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of urothelial cells .jpeg
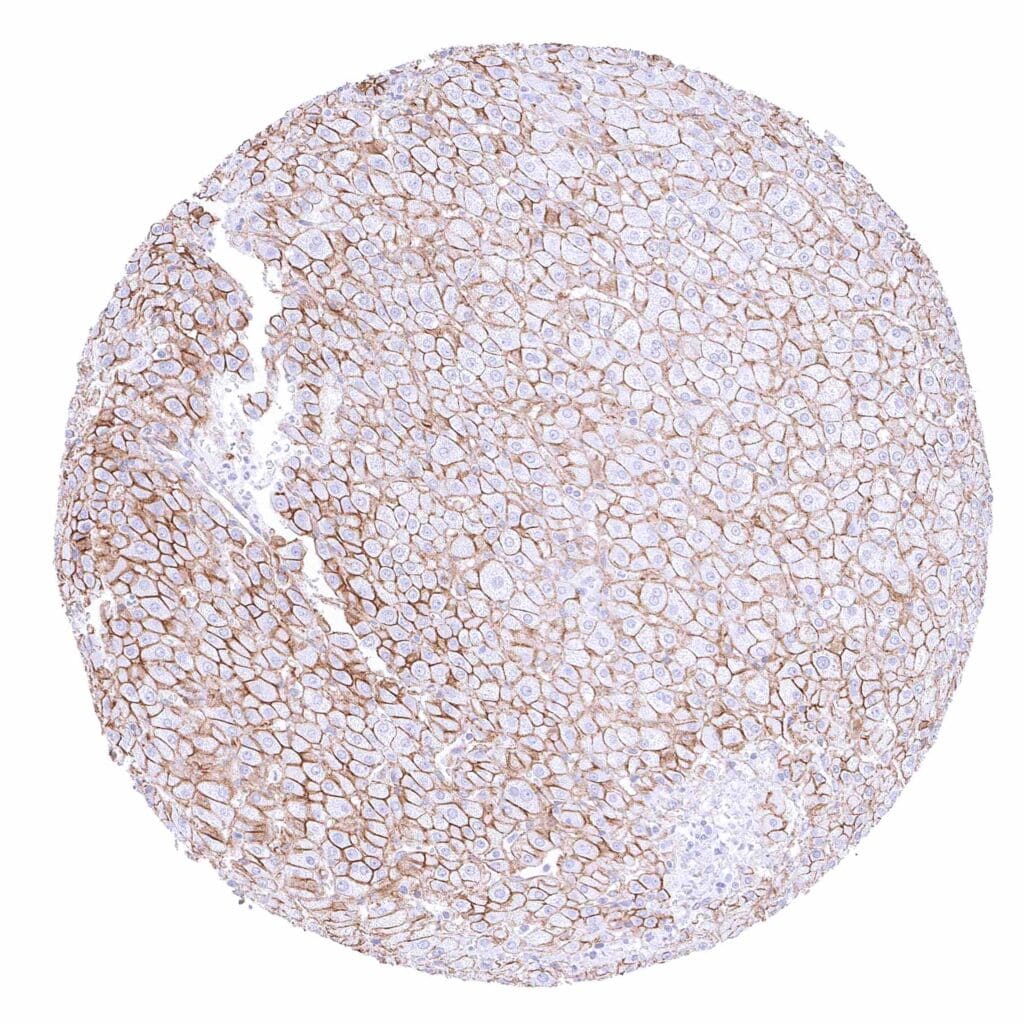
Liver – Moderate to strong membranous beta catenin staining of hepatocytes.
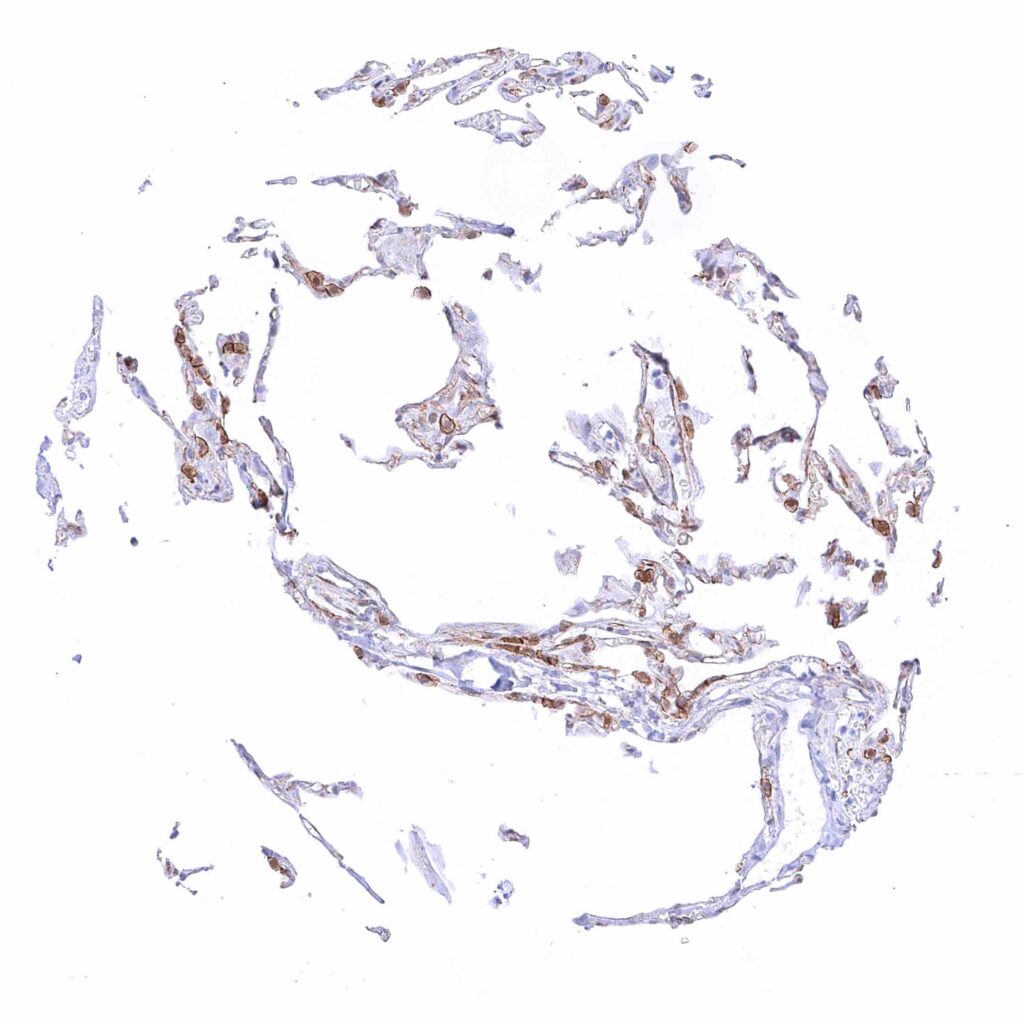
Lung – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of pneumocytes. .jpeg
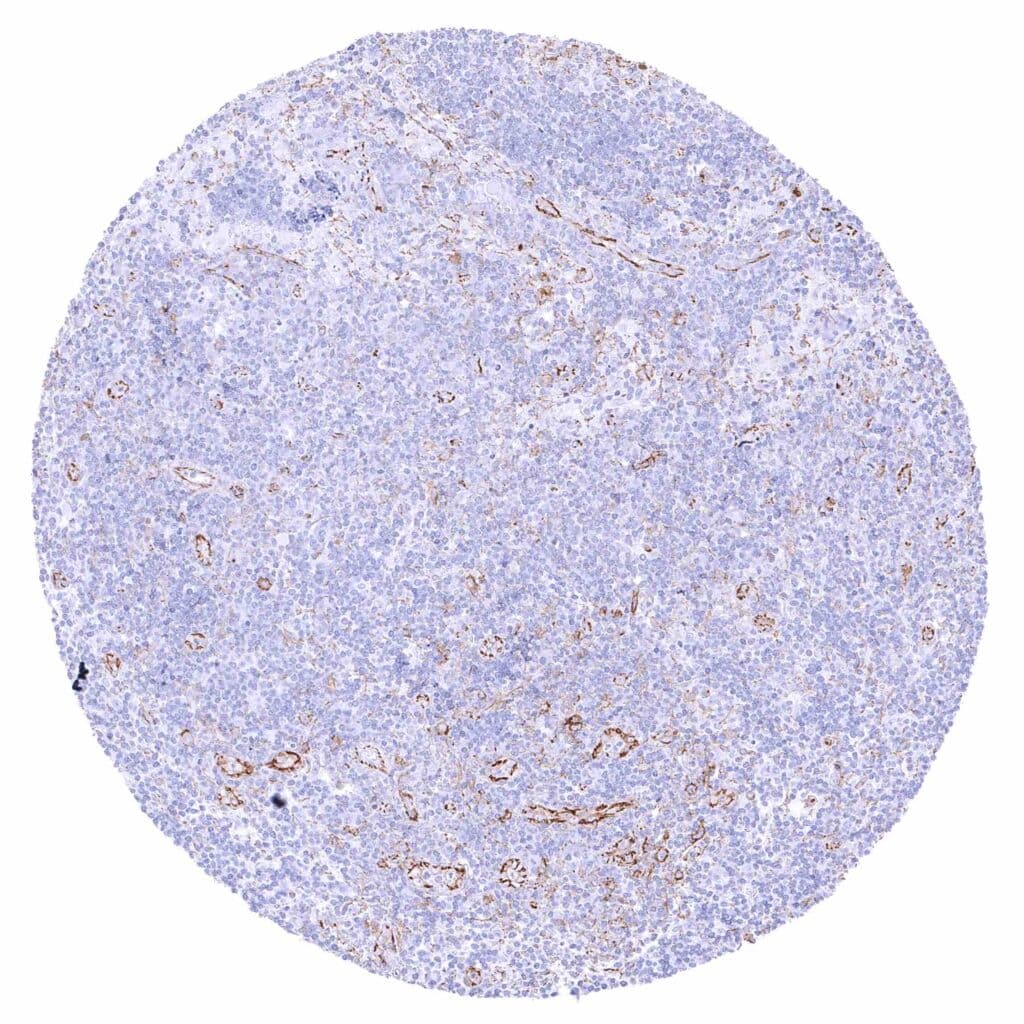
Lymph node – Weak to moderate membranous beta catenin staining of endothelial cells.
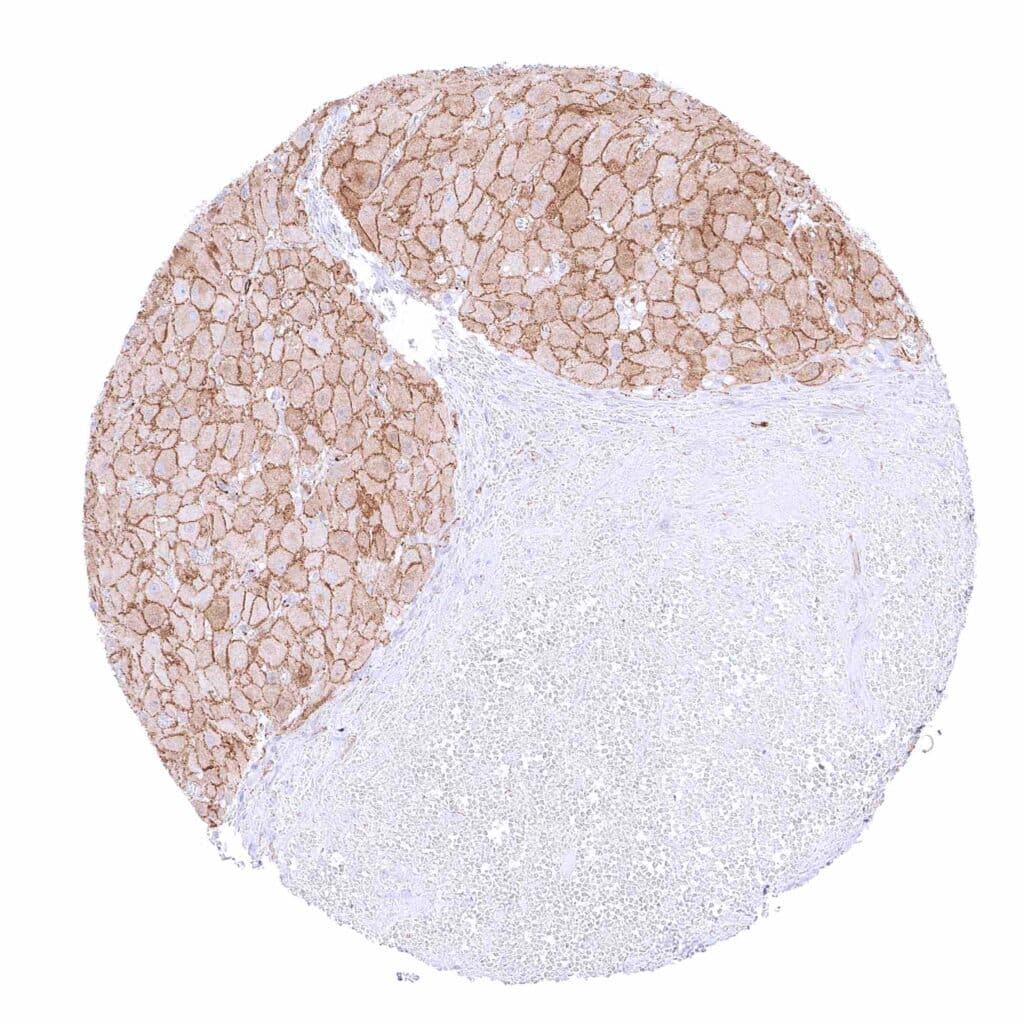
Ovary, corpus luteum – Moderate membranous beta catenin staining of corpus luteum cells. -
Ovary, stroma – Distinct membranous beta catenin staining of stroma cells.
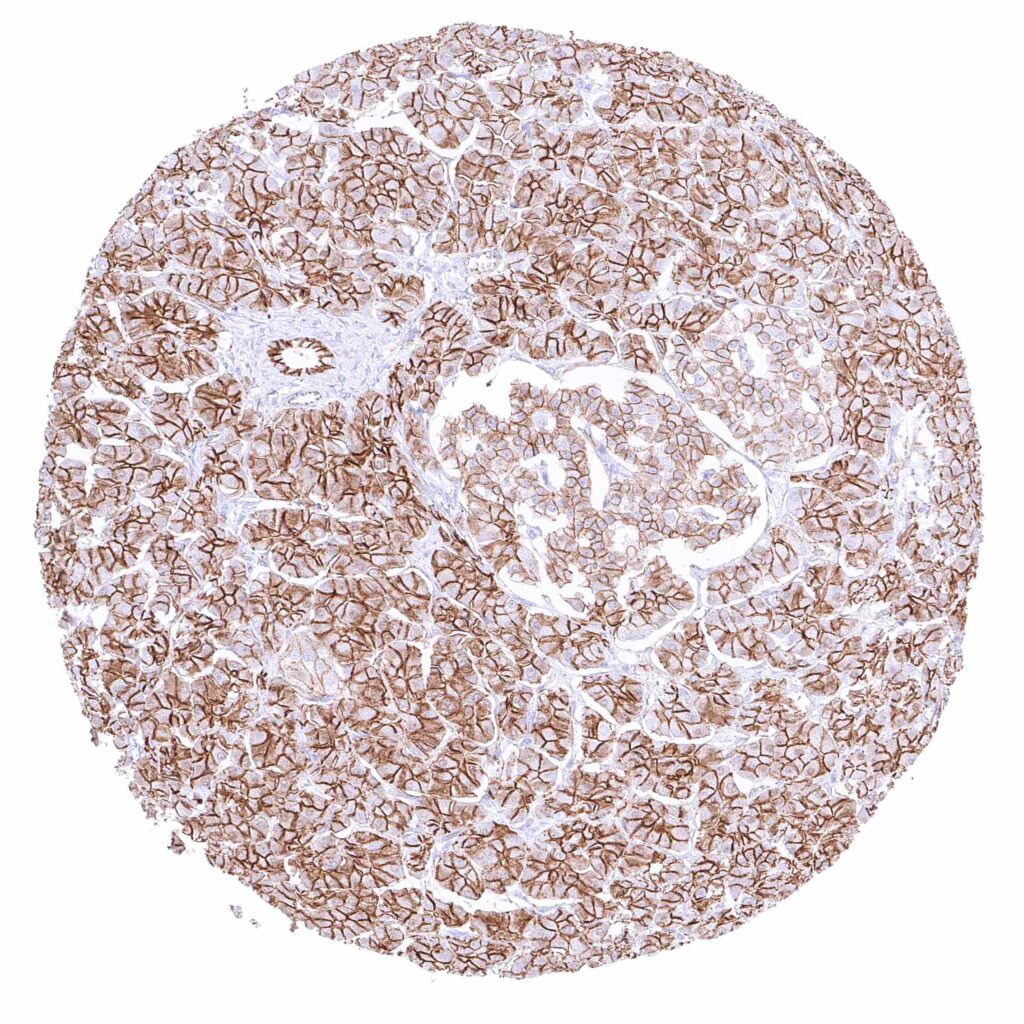
Pancreas – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of acinar and excretory duct cells while staining is less intense in islets.
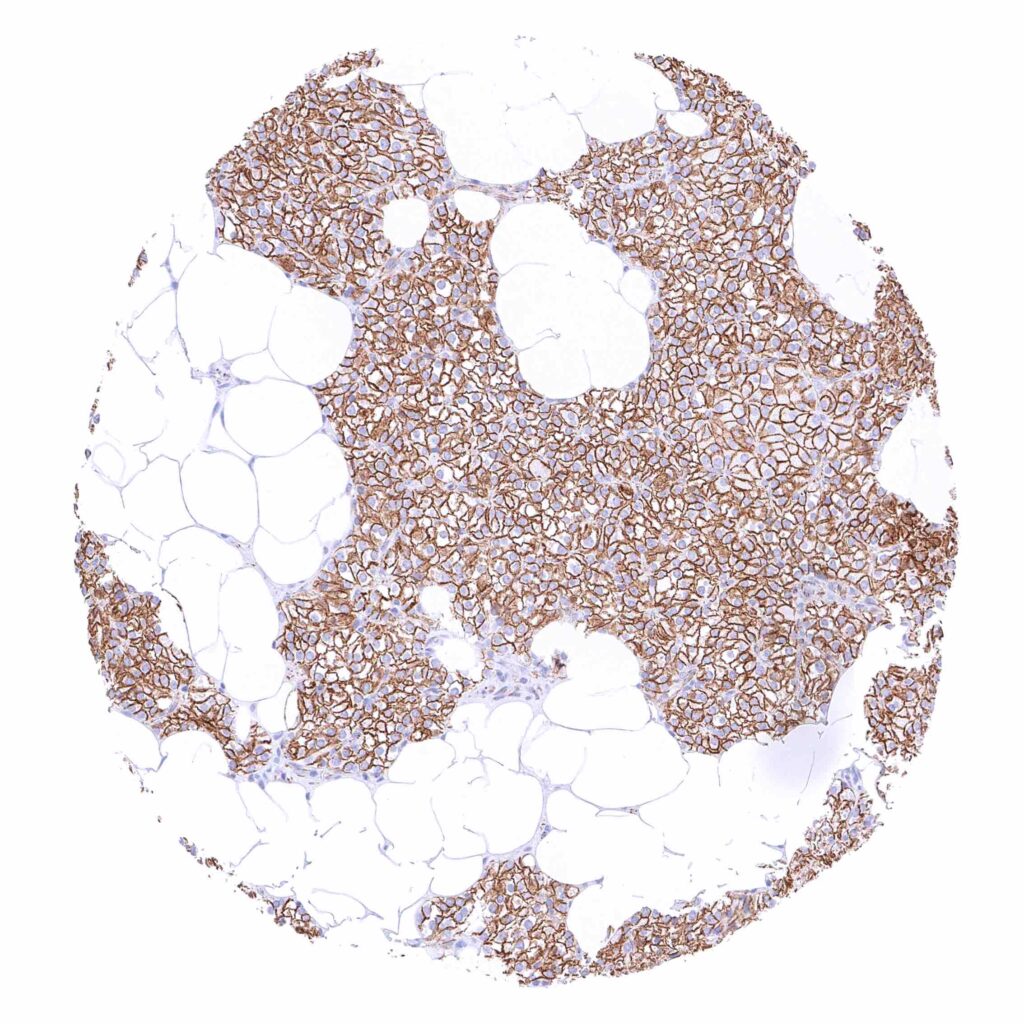
Parathyroid gland – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells.
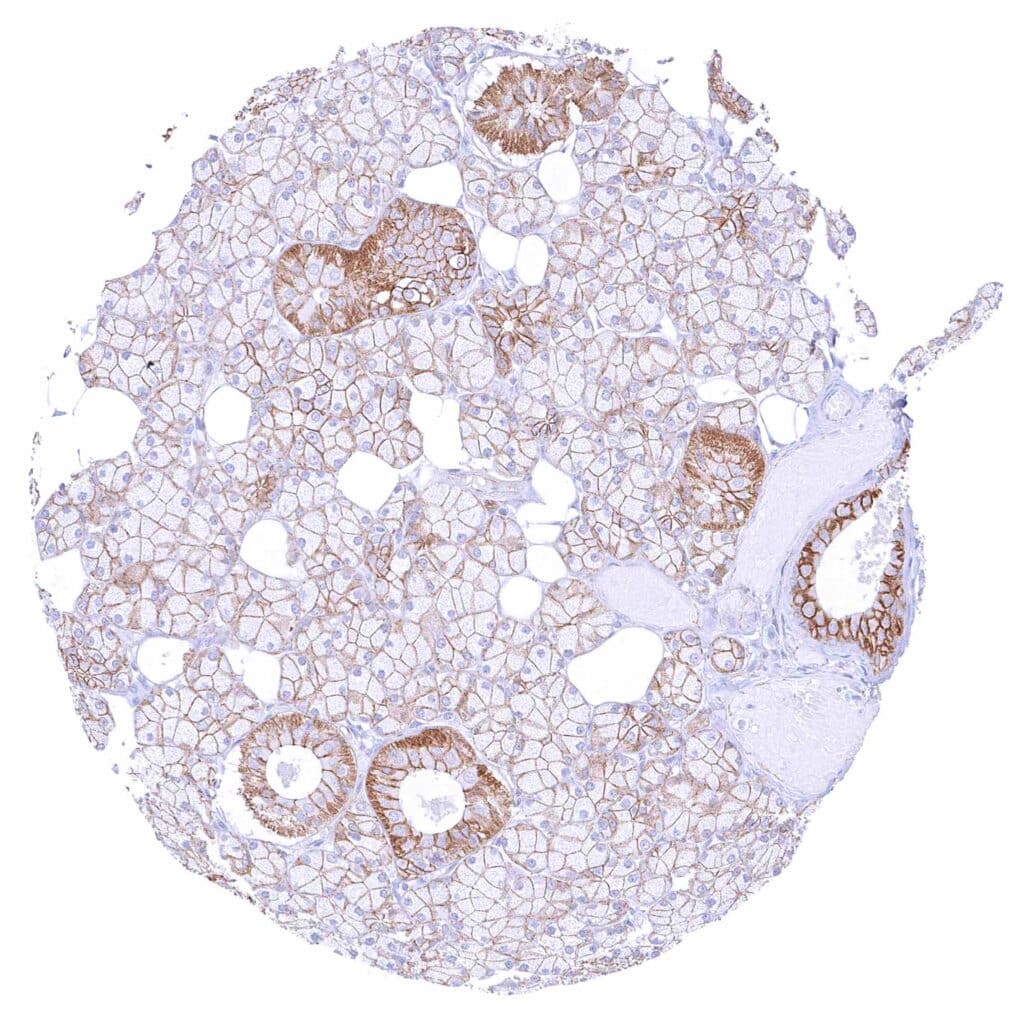
Parotid gland – Distinct membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells.
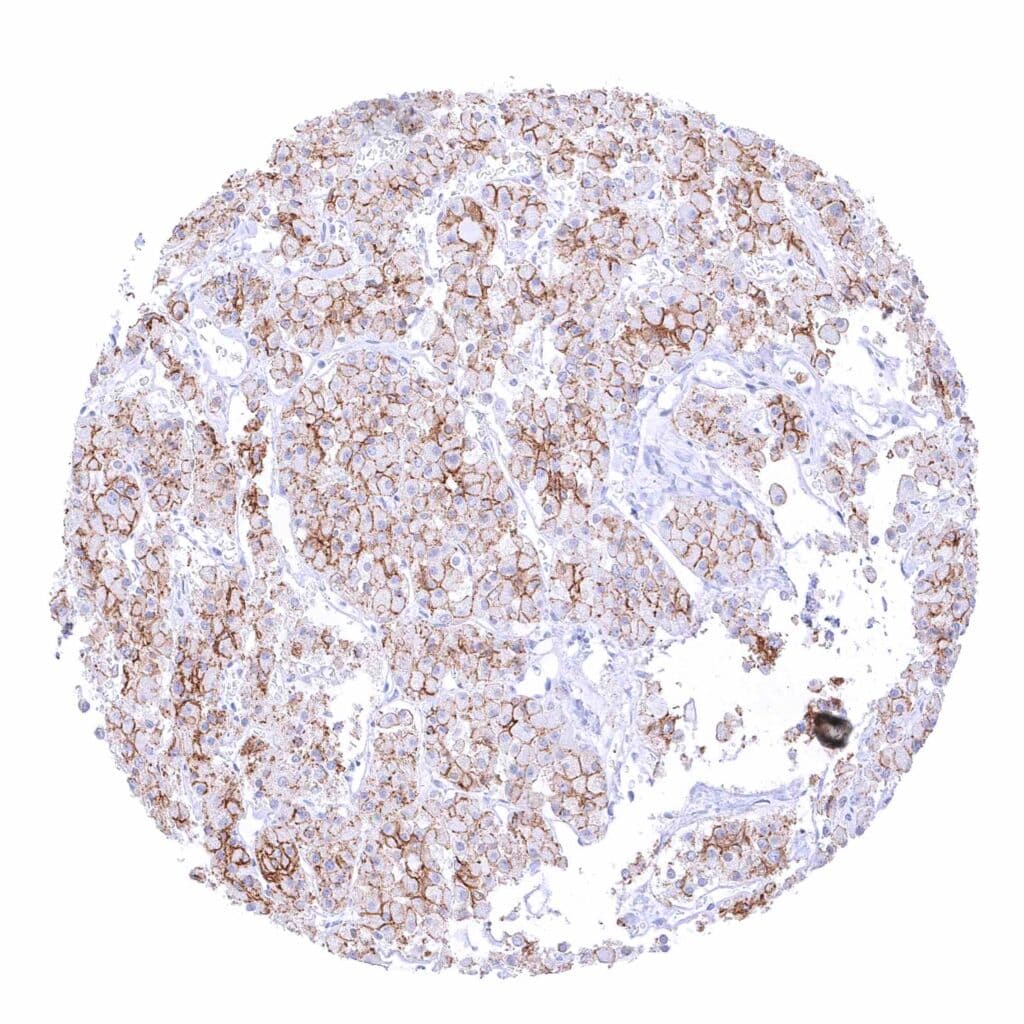
Pituitary gland, anterior lobe – Membranous beta catenin staining of variable intensity in most epithelial cells.
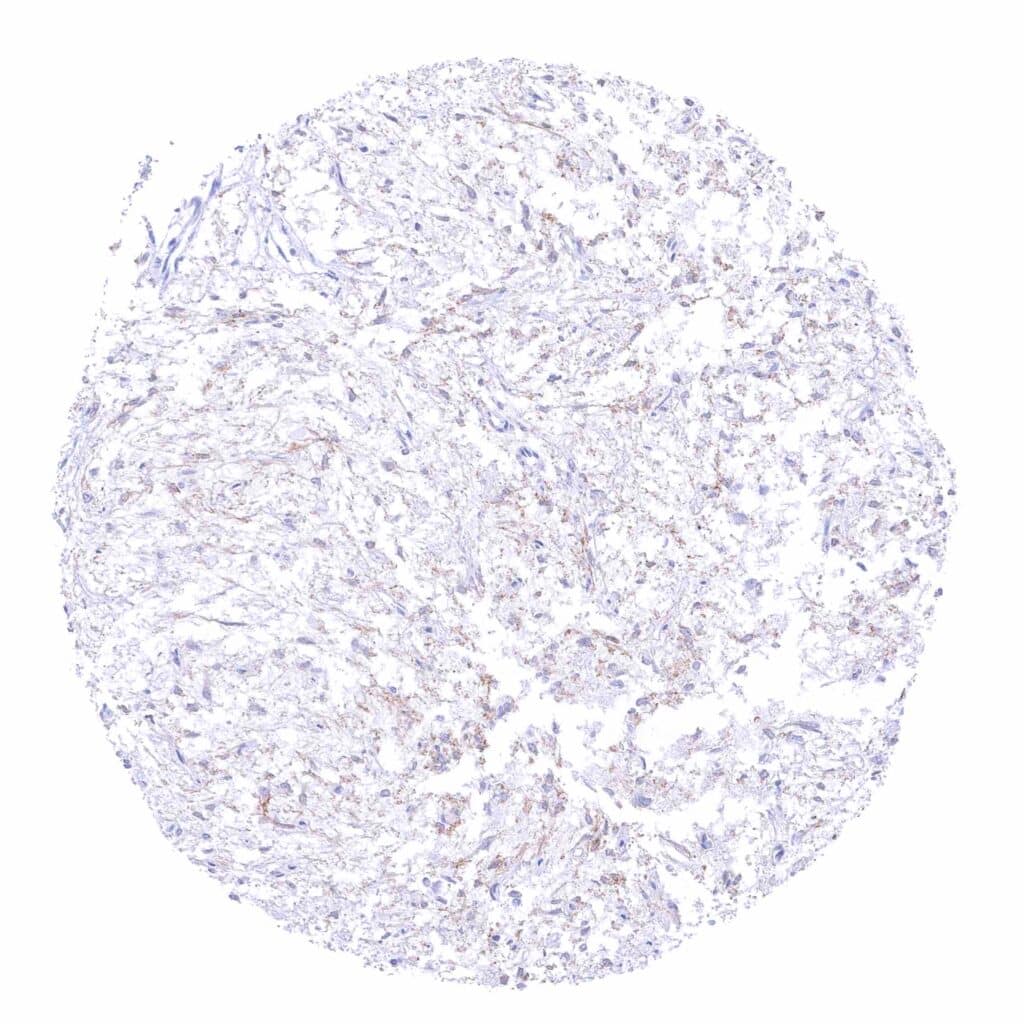
Pituitary gland, posterior lobe- infundibulum – Weak beta catenin positivity of fibers in the neurohypophysis.
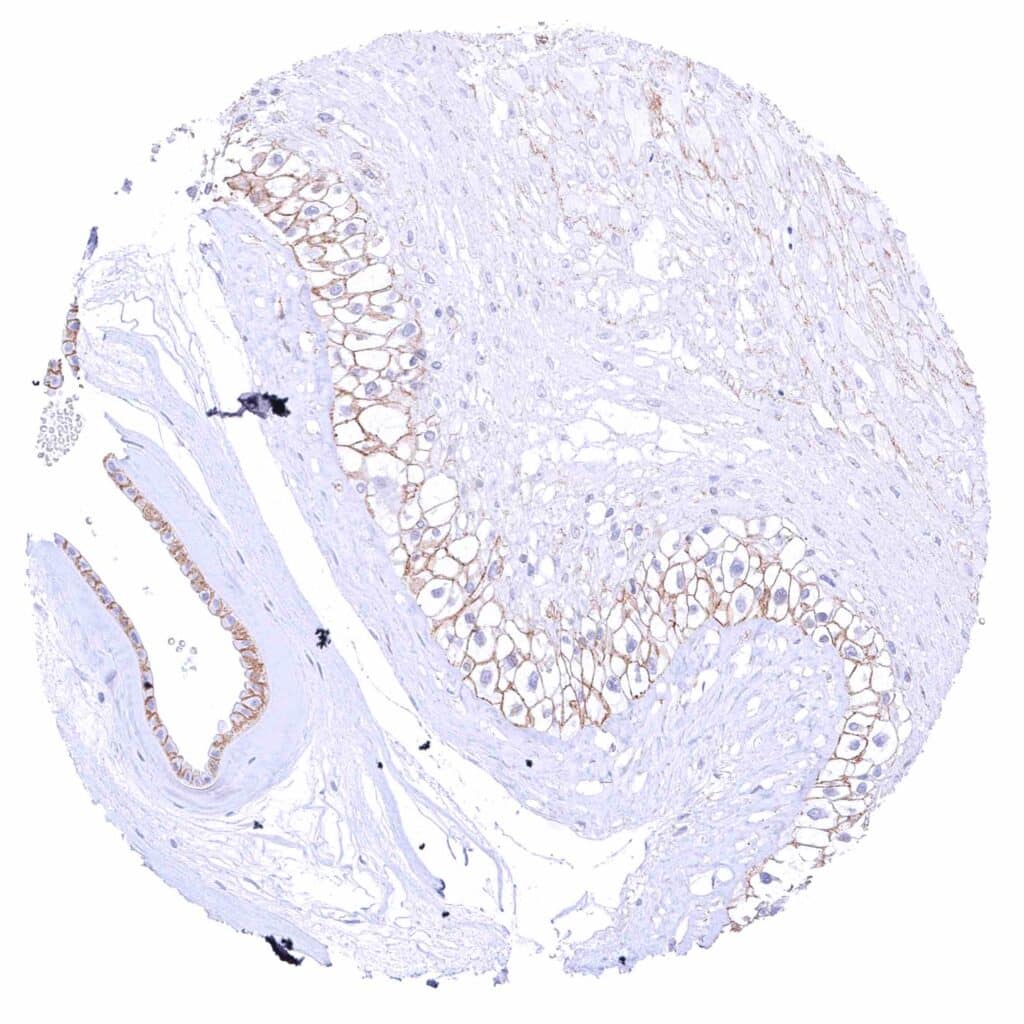
Placenta (amnion and chorion) – Moderate membranous beta catenin staining of amnion and chorion cells.
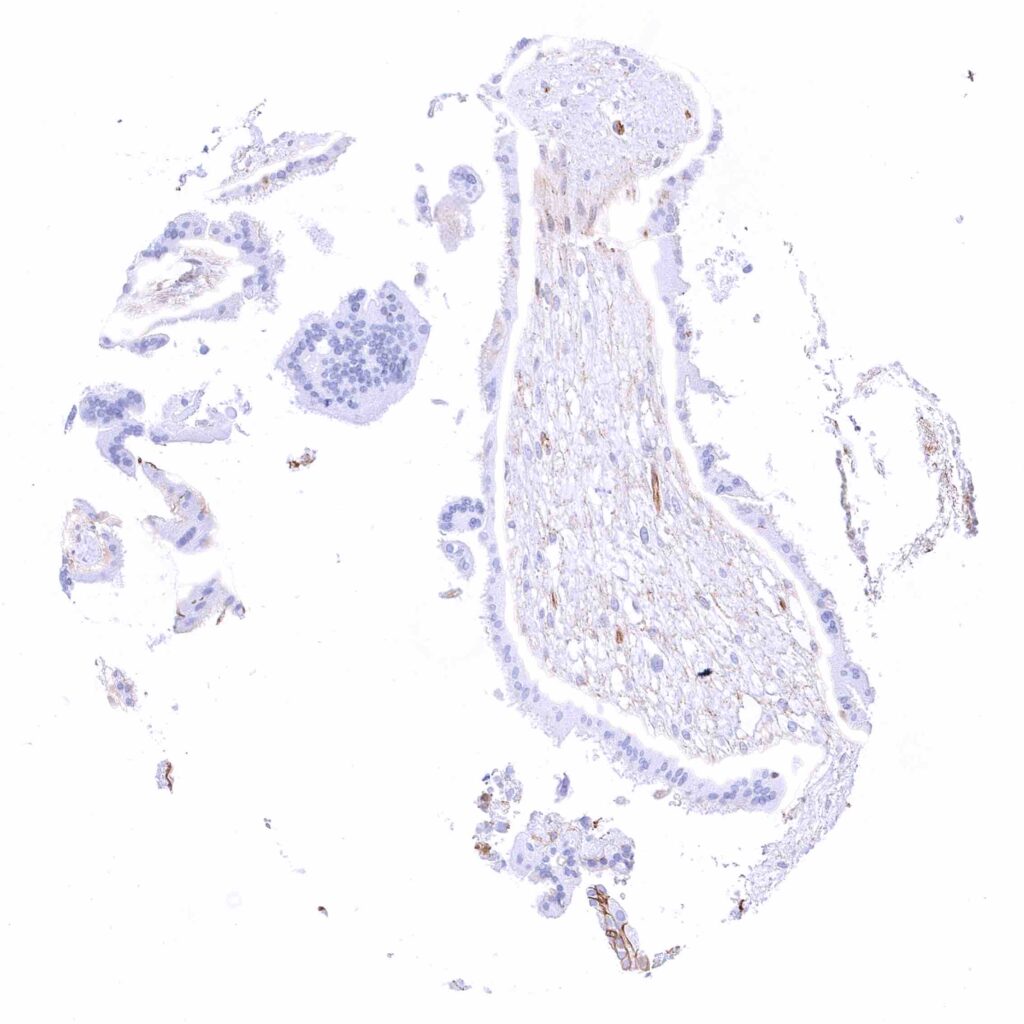
Placenta, early – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of cytotrophoblast cells, accompanied by a nuclear and cytoplasmic positivity in many cells. The syncytiotrophoblast is beta catenin negative.
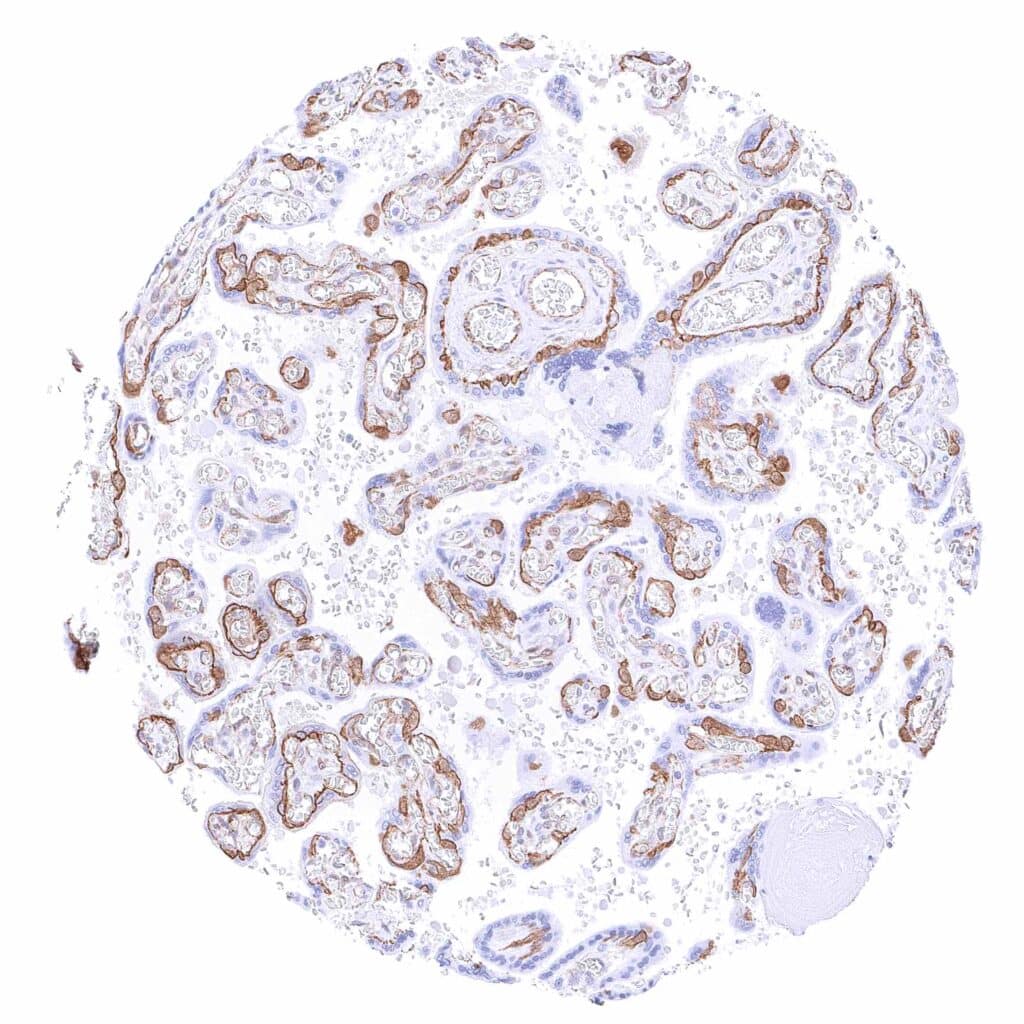
Placenta, mature – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of cytotrophoblast cells. In some of these cells, there is also a nuclear and cytoplasmic positivity. The syncytiotrophoblast is beta catenin negative.
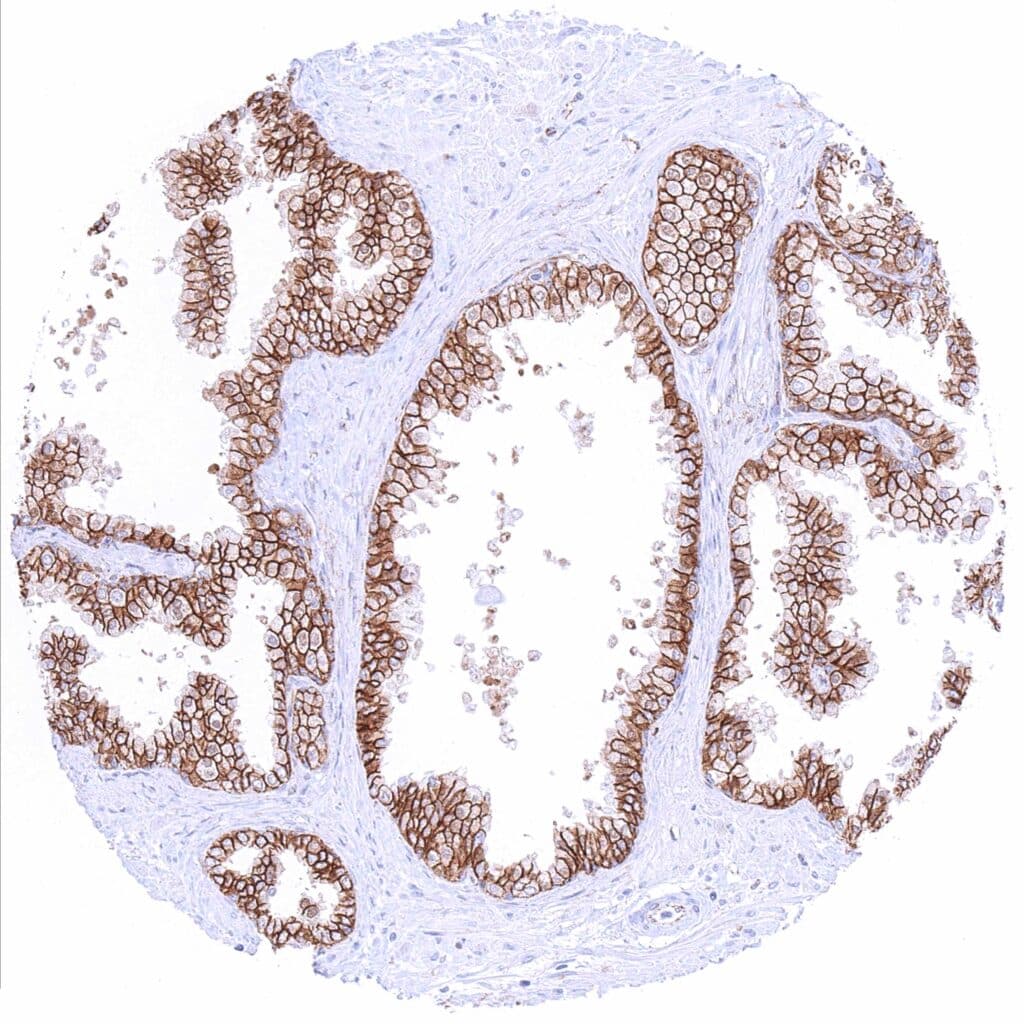
Prostate – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells
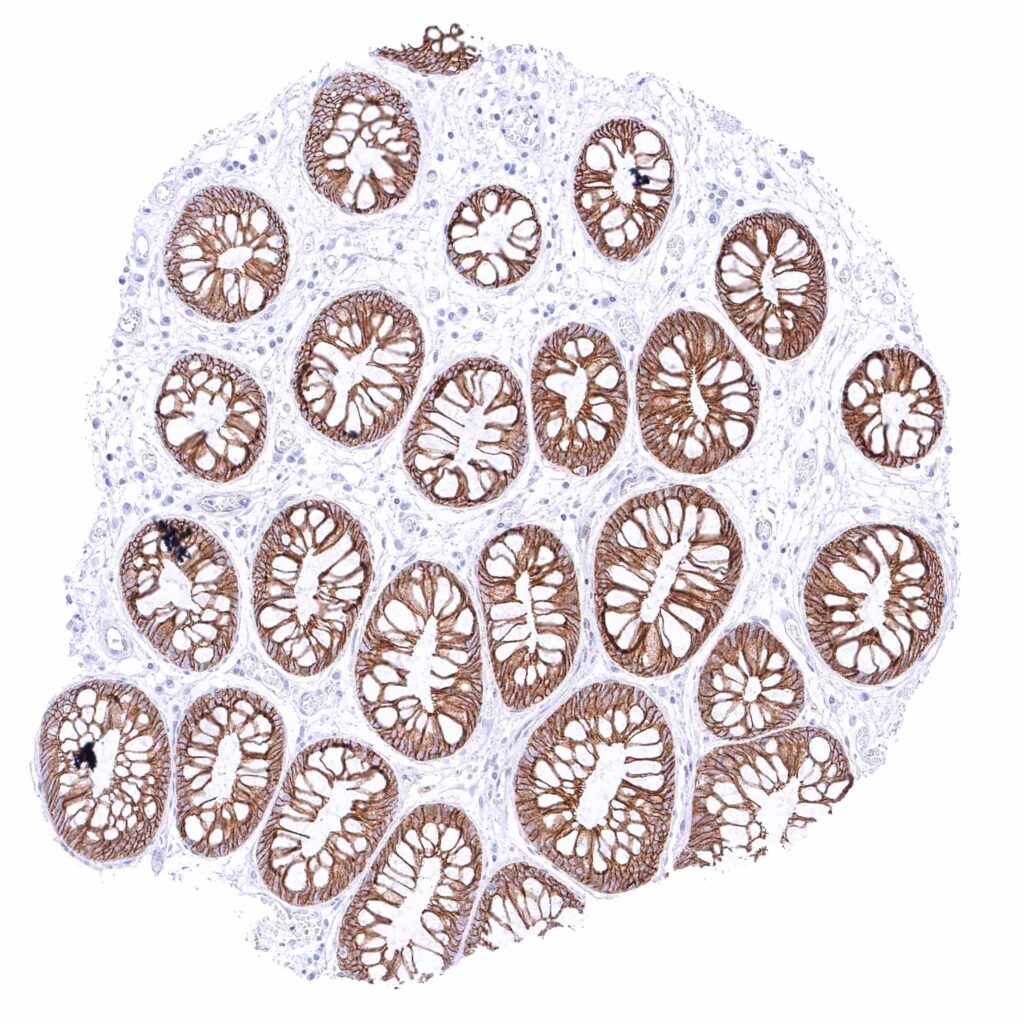
Rectum, mucosa – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of all epithelial cells.
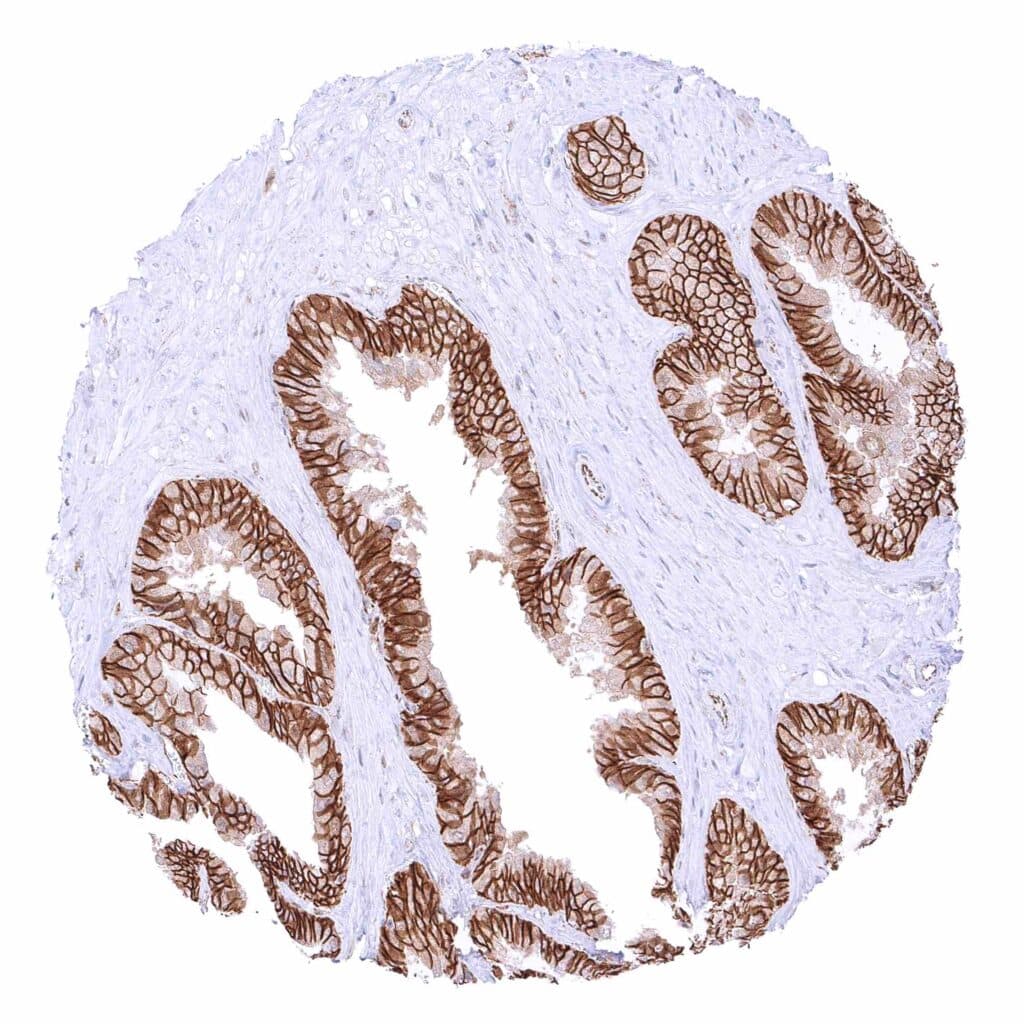
Seminal vesicle – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells.
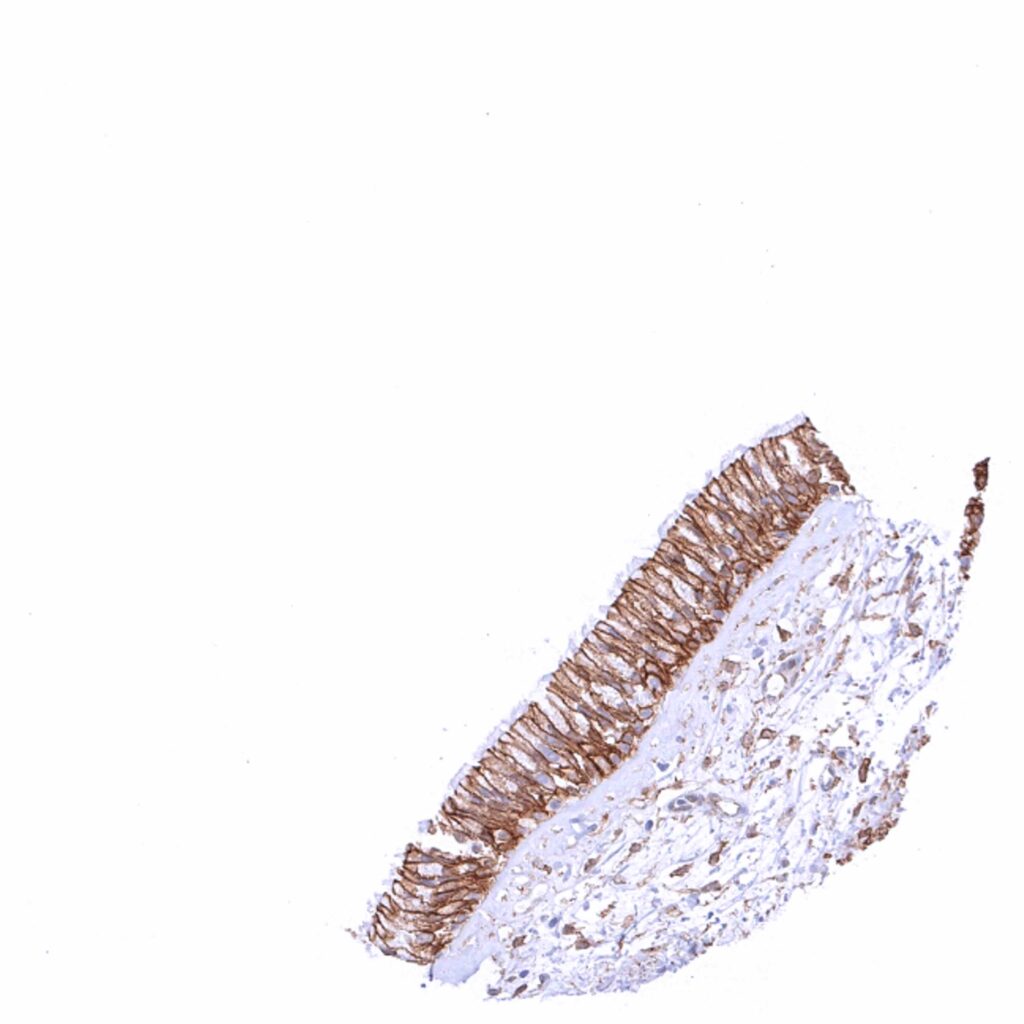

Sinus paranasales – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of respiratory epithelial cells. Ciliae are beta catenin negative
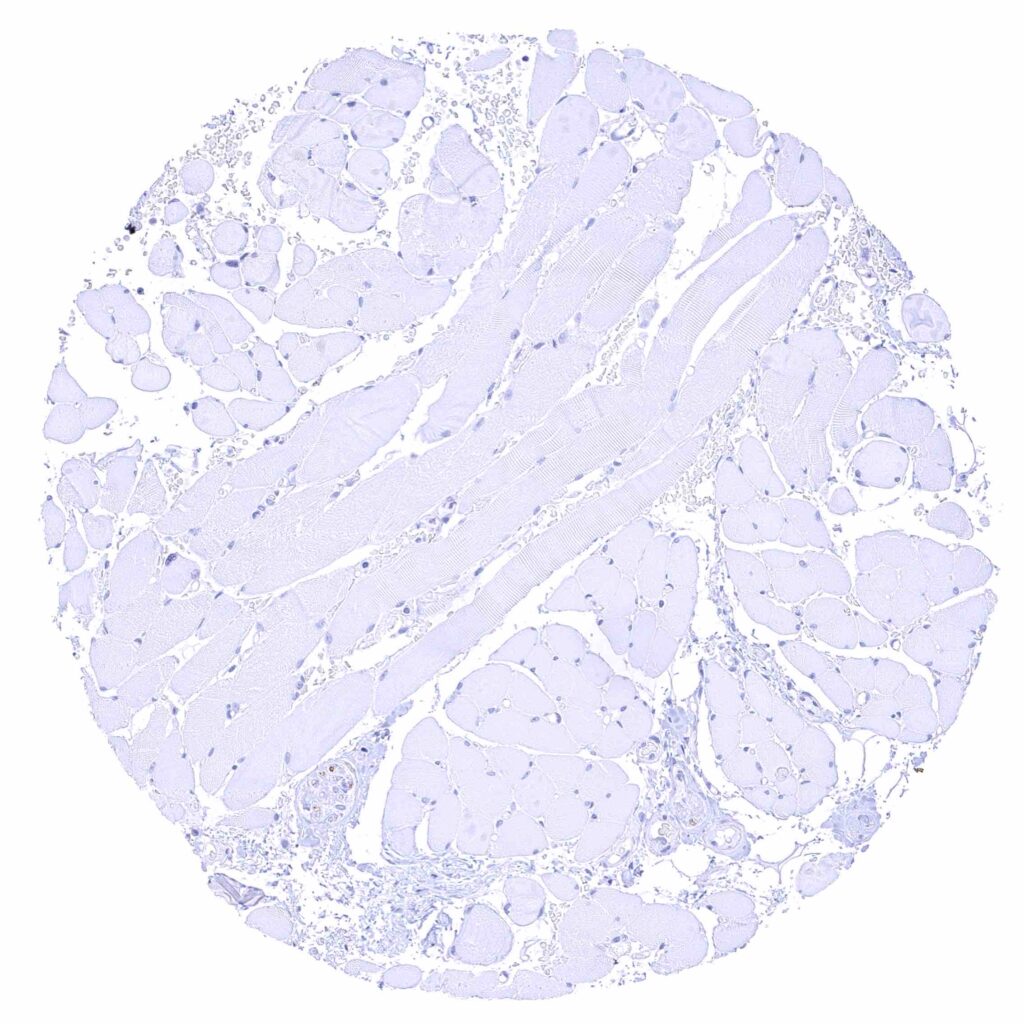
Skeletal muscle
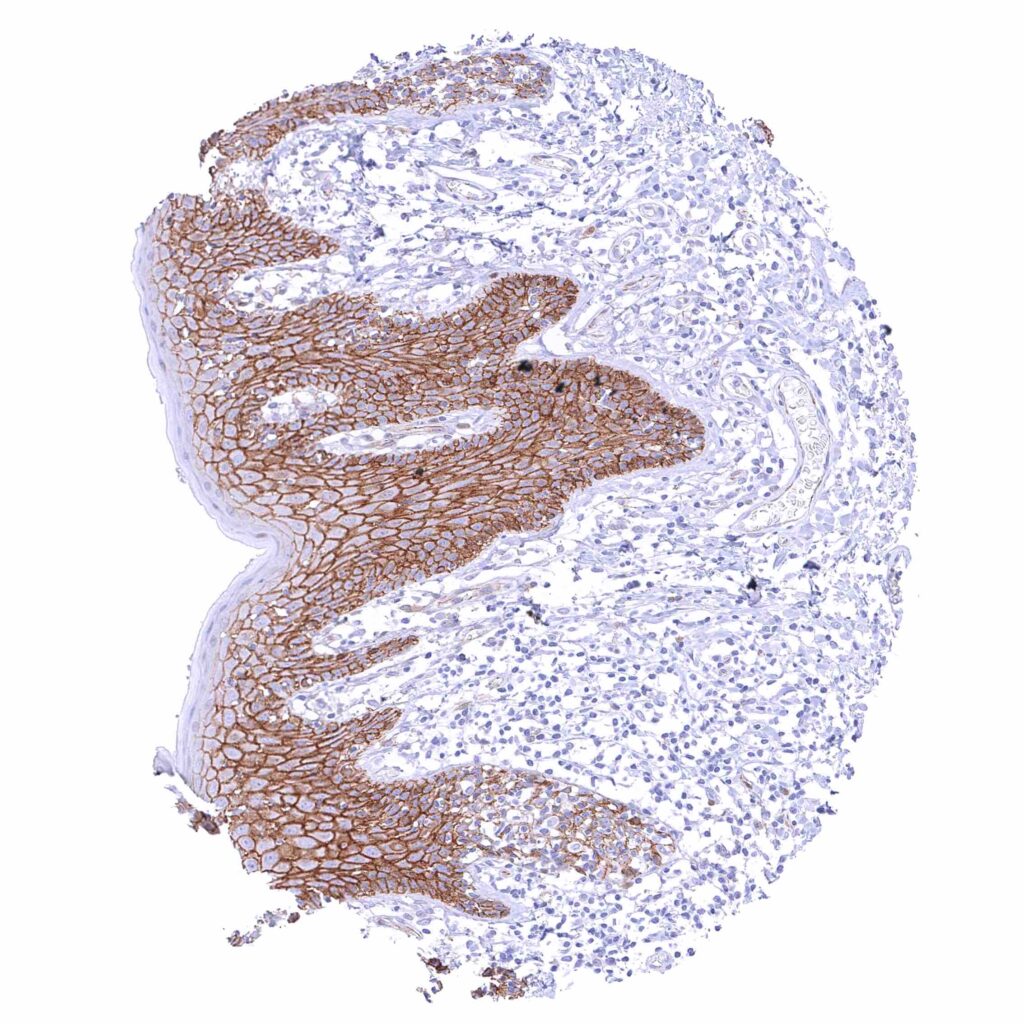
Skin – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of squamous epithelial cells. The staining intensity is lowest in the most superficial cell layers.
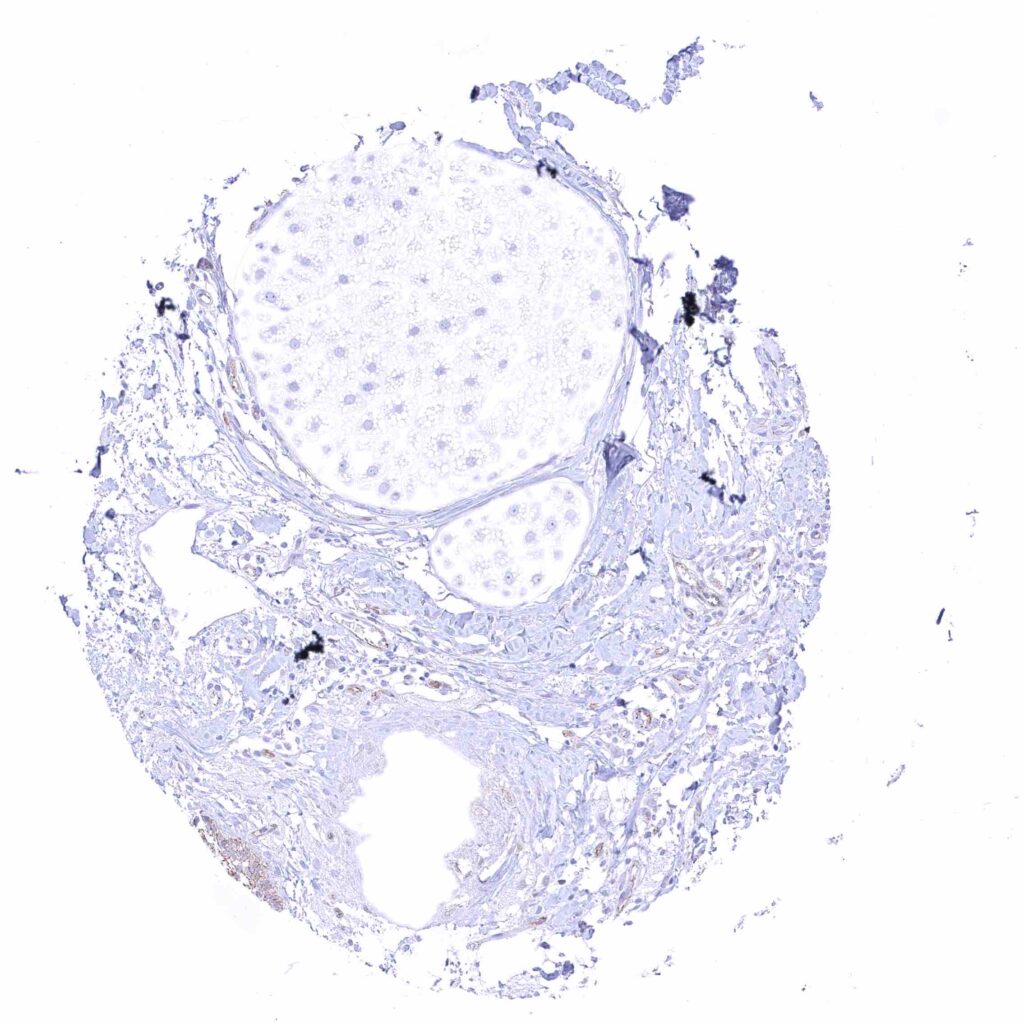
Skin, hairfollicel and sebaceous glands
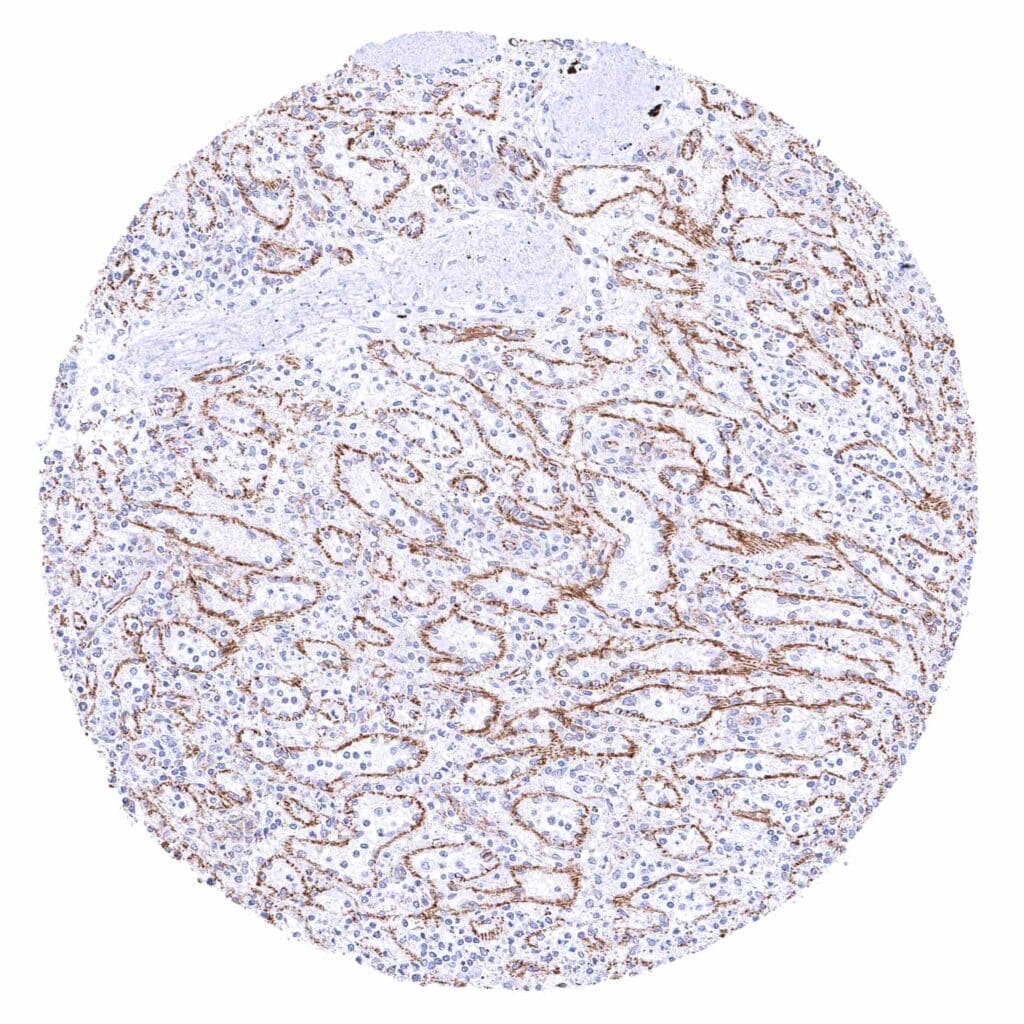
Spleen – Weak to moderate membranous beta catenin staining of endothelial cells of sinusoids.
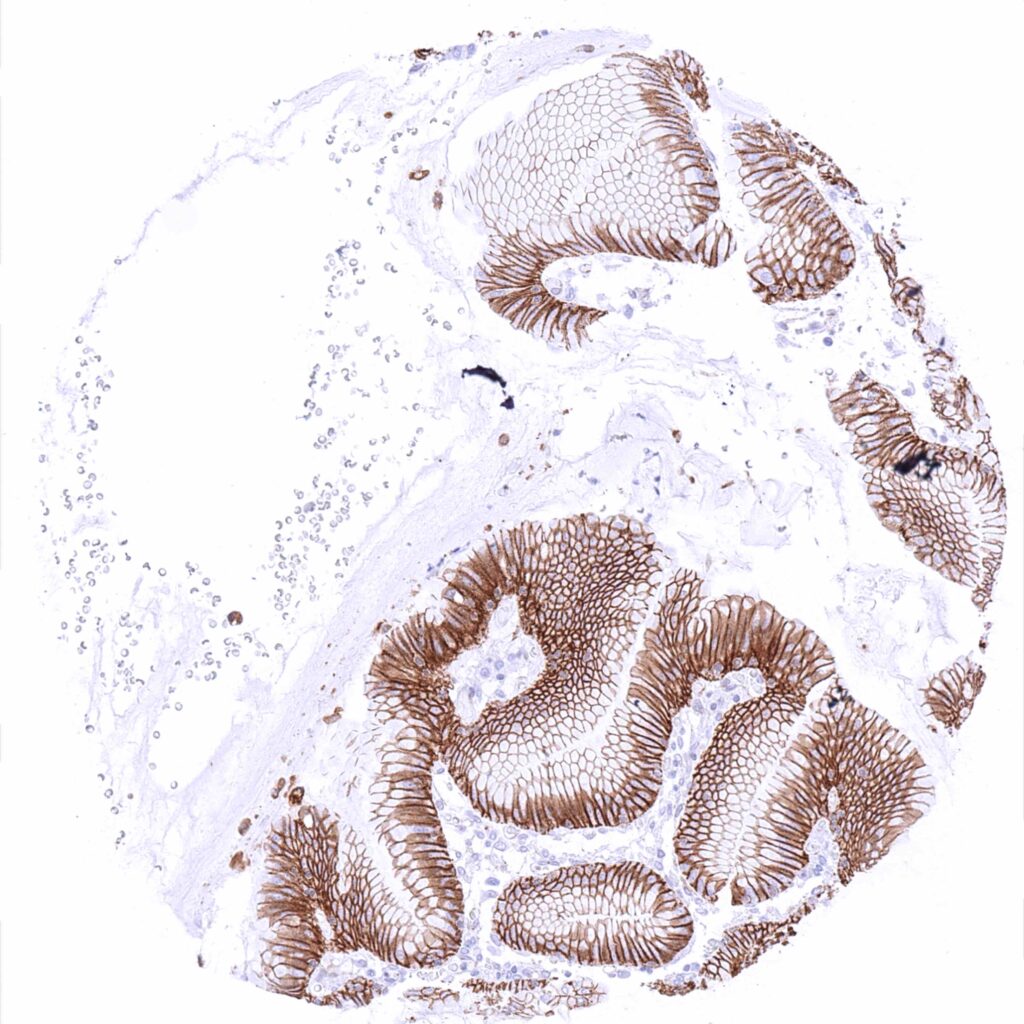
Stomach, antrum – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of surface epithelial cells
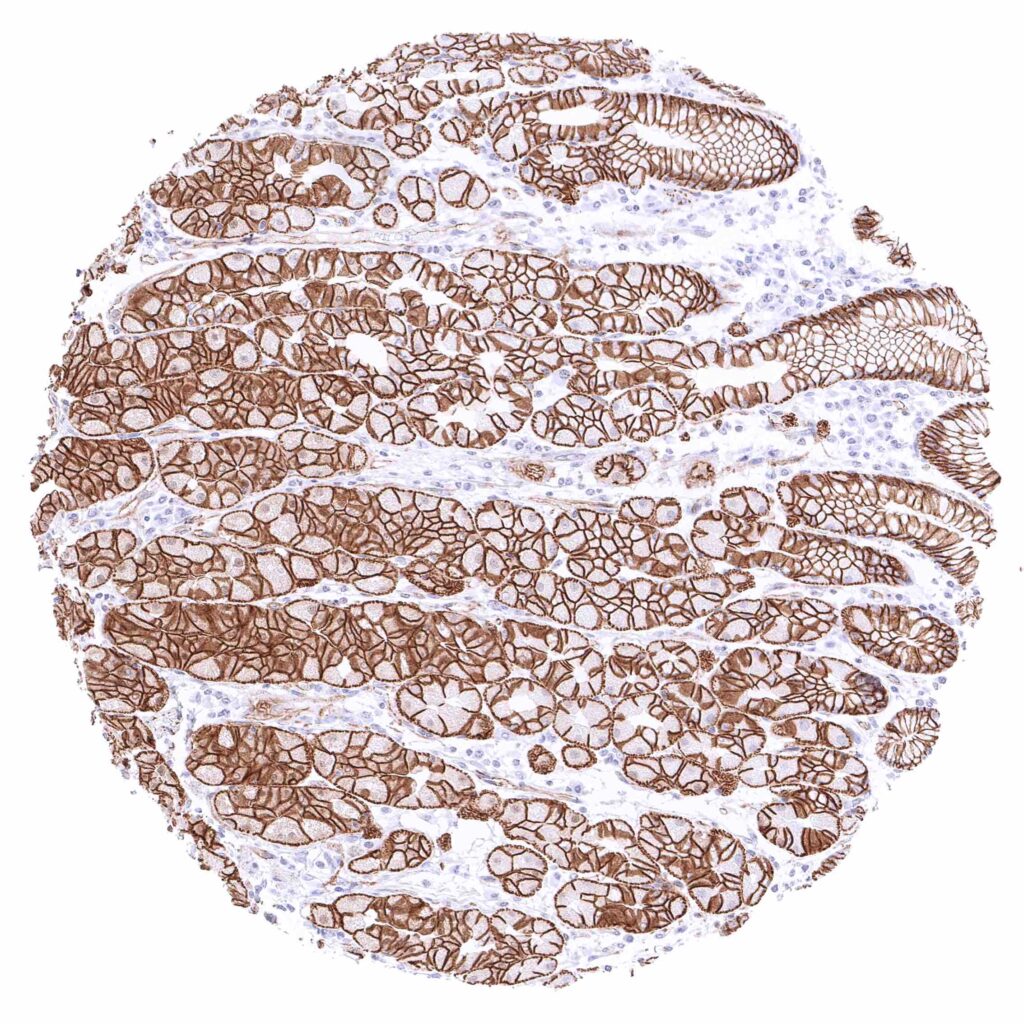
Stomach, corpus – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of all gastric epithelial cells.
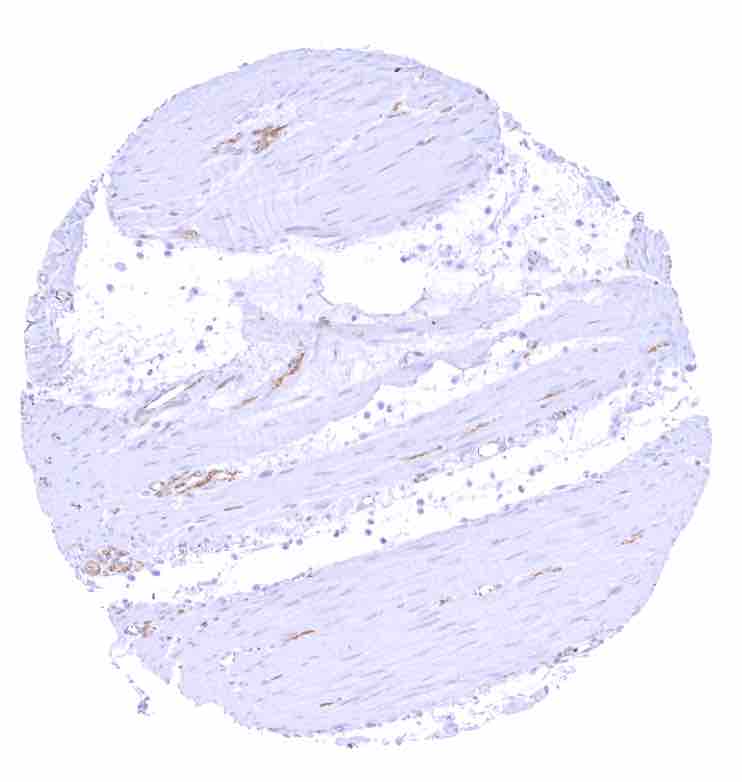
Stomach, muscular wall – Strong beta catenin staining of nerves.
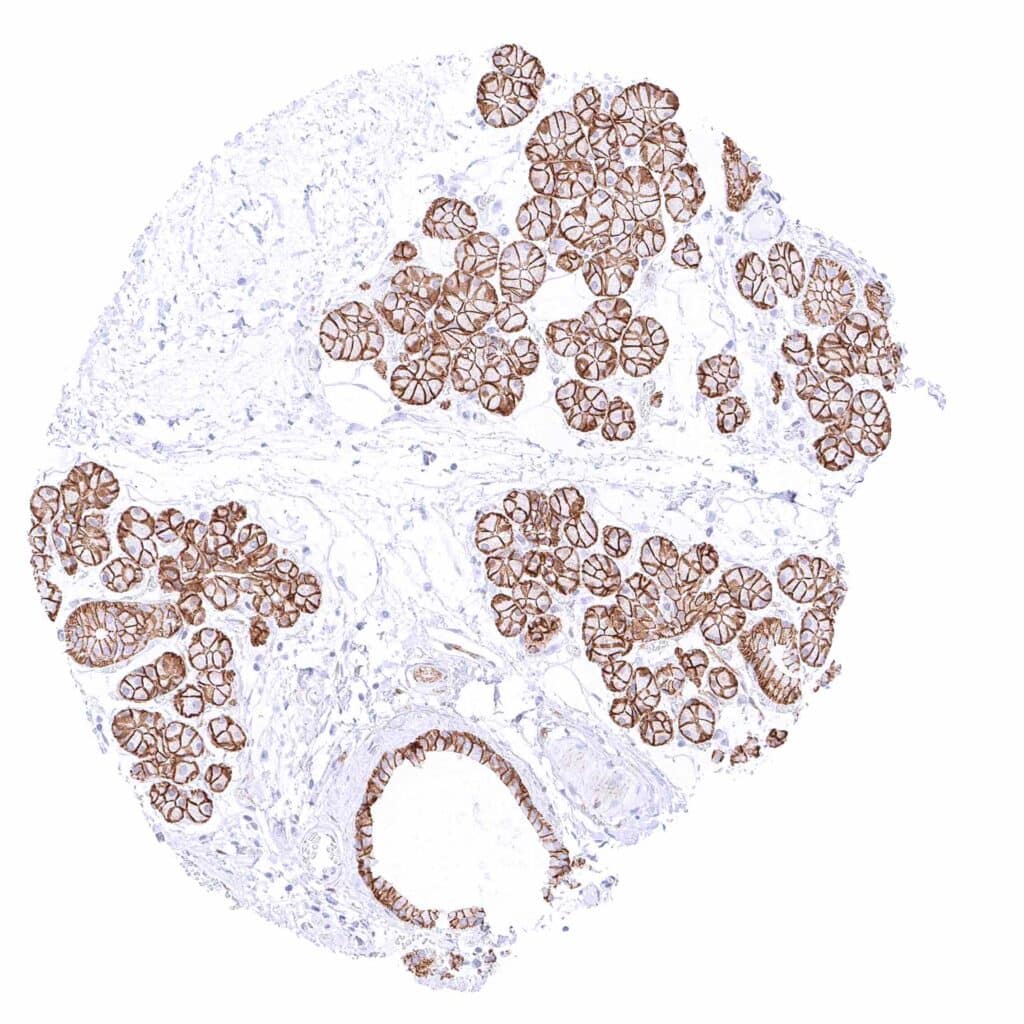
Submandibular gland – Distinct membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells.
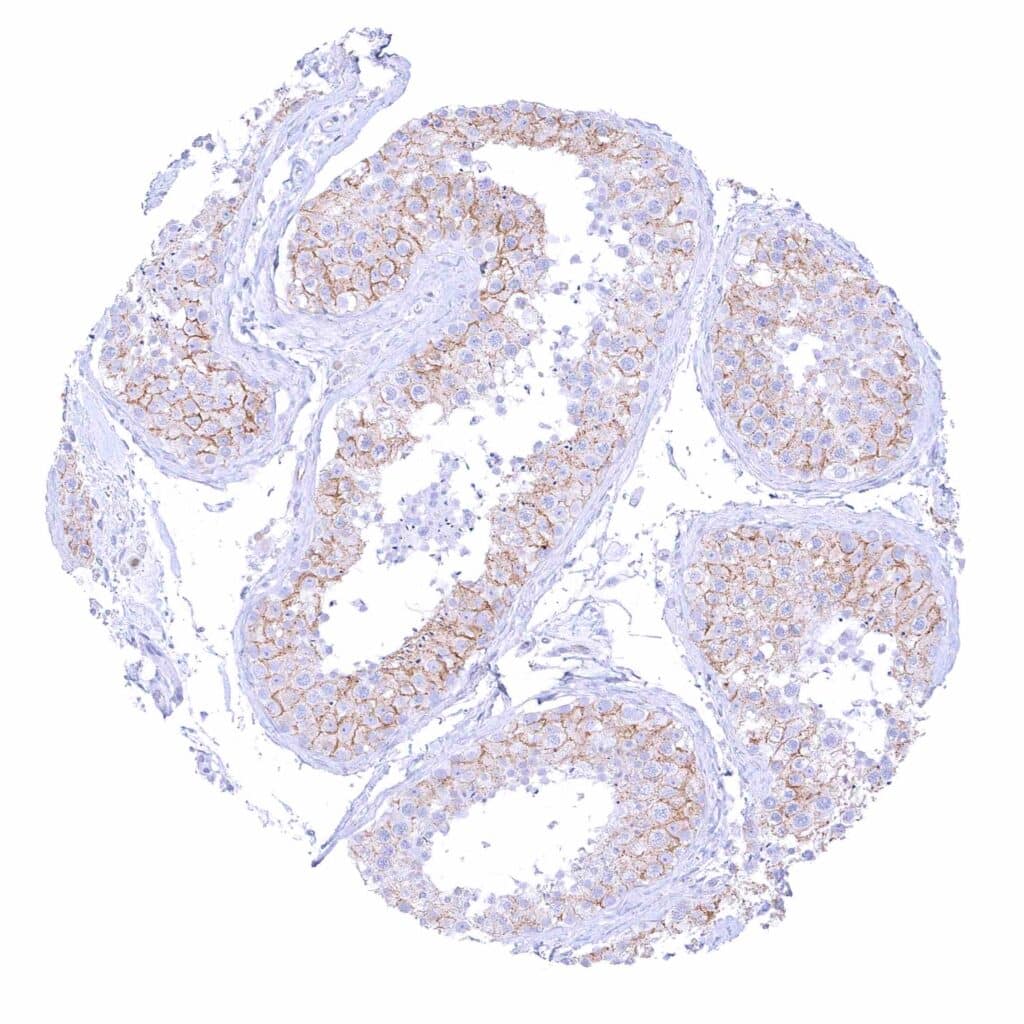
Testis – Moderate to strong membranous beta catenin staining of Sertoli cells while germ cells are largely negative.
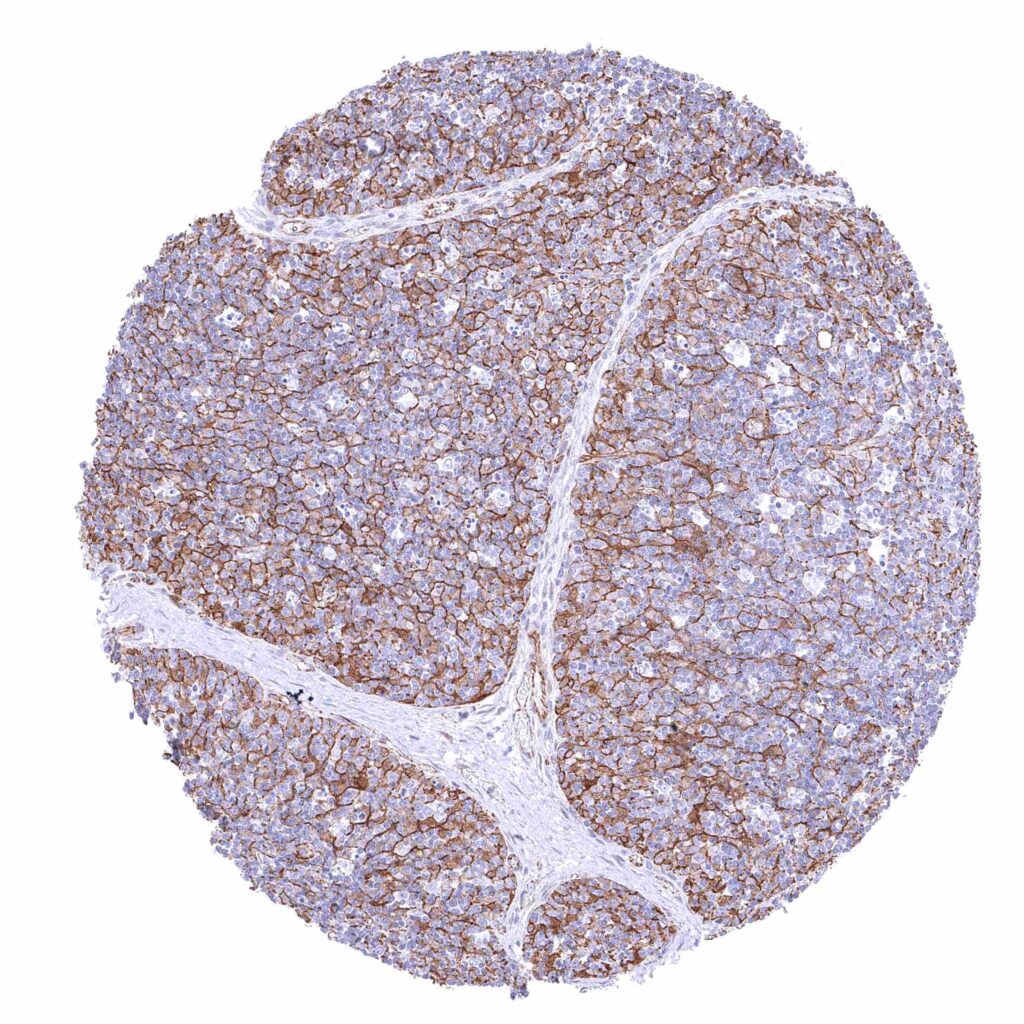
Thymus – Distinct membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial and endothelial cells
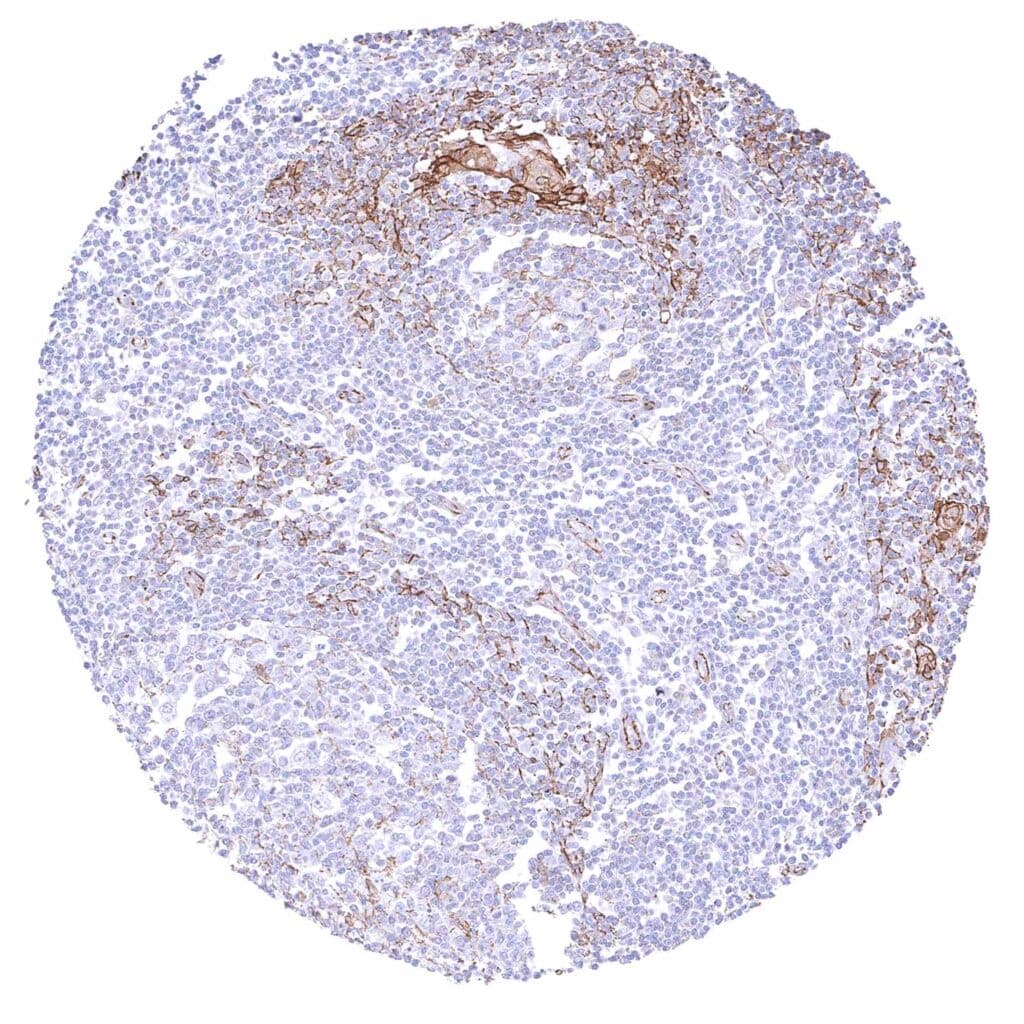
Thymus – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells including corpuscles of Hassall’s. Weak to moderate positivity of endothelial cells.
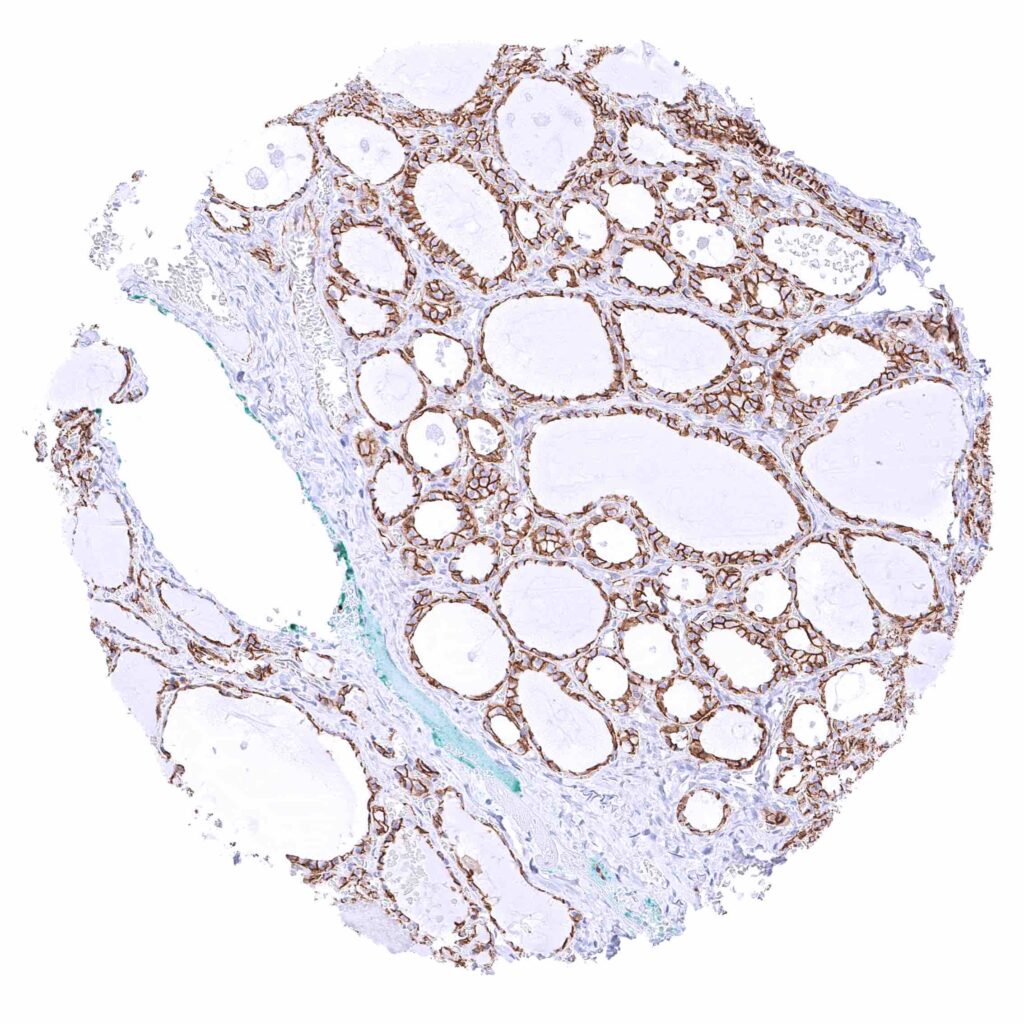
Thyroid gland – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells.
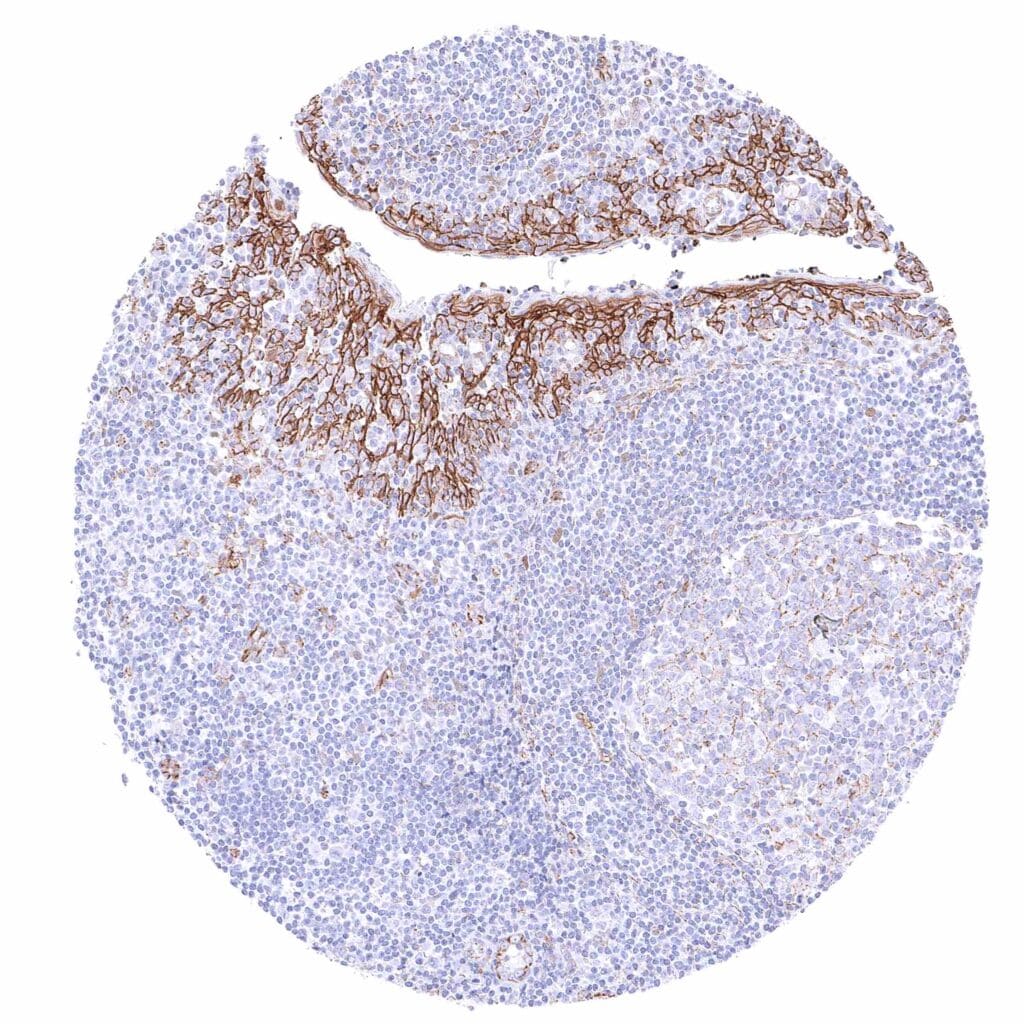
Tonsil – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of squamous epithelial cells. Weak to moderate positivity of endothelial cells.
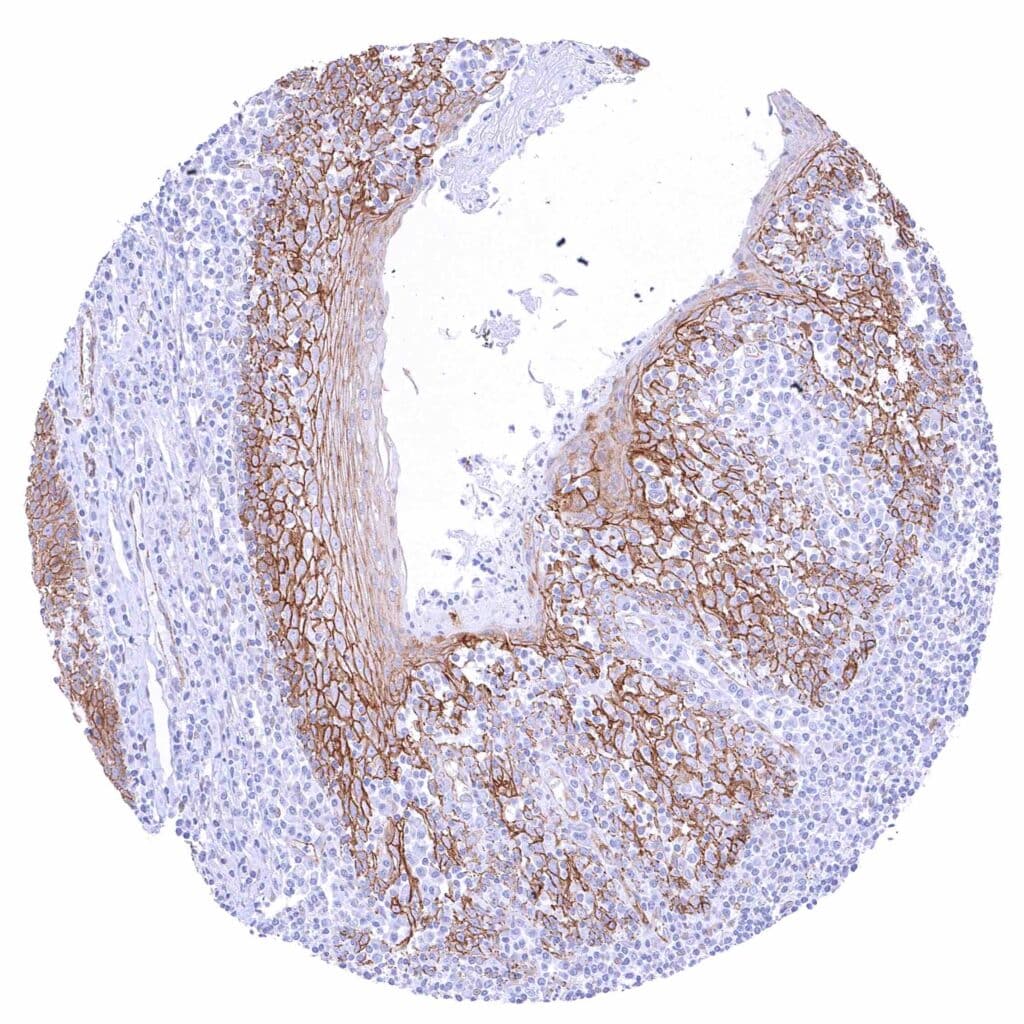
Tonsil, surface epithelium – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of squamous epithelial cells with decreasing staining intensity from the basal towards the superficial cell layers.
Urinary bladder, muscular wall
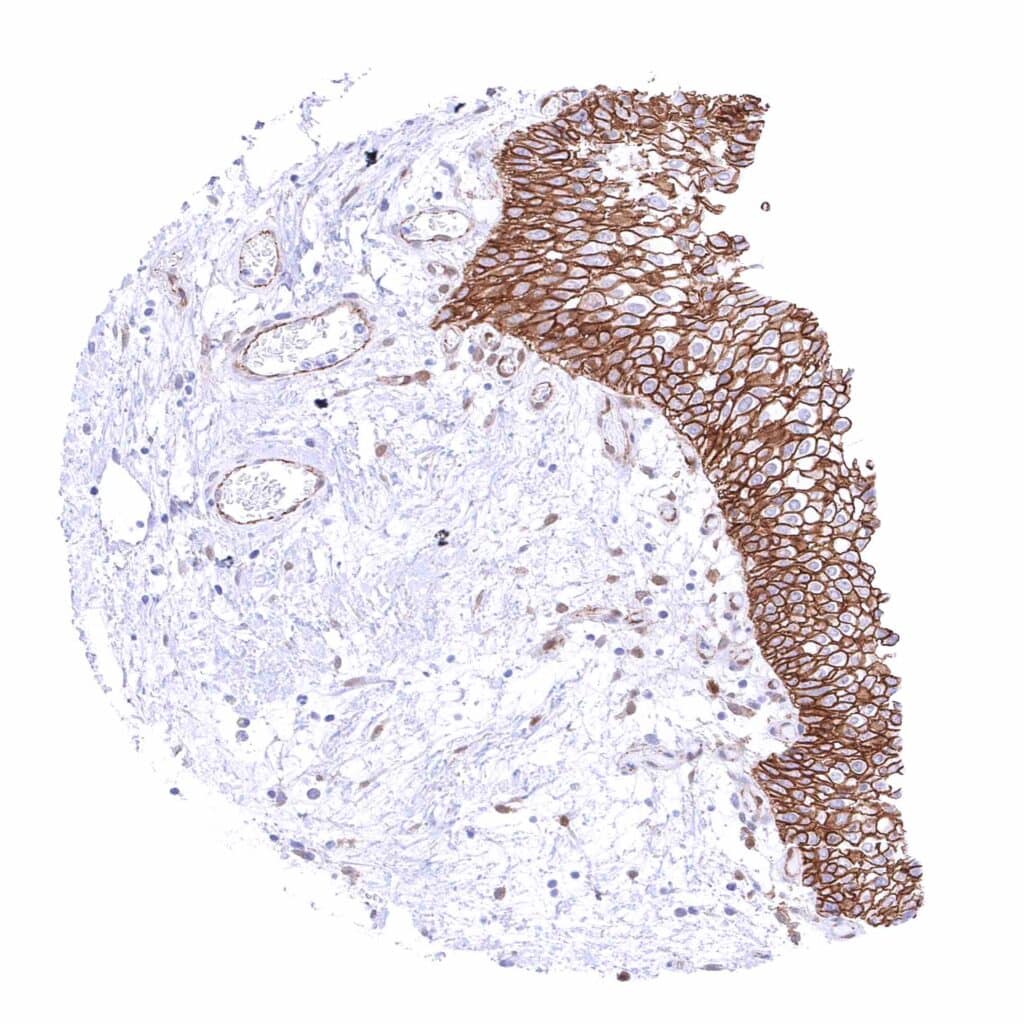
Urinary bladder, urothelium – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of urothelial cells.
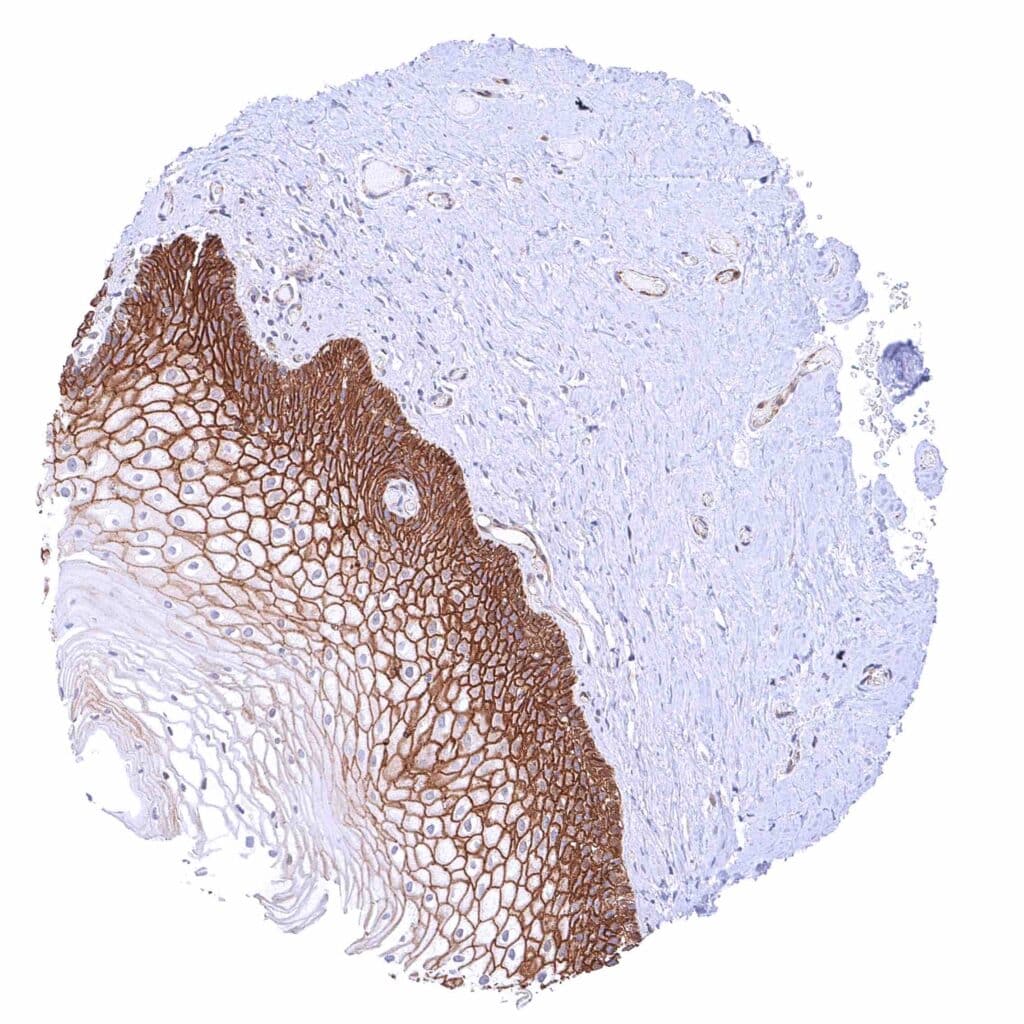
Uterus, ectocervix – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of squamous epithelial cells with decreasing staining intensity from the basal towards the superficial cell layers. Top cell layers are beta catenin negative
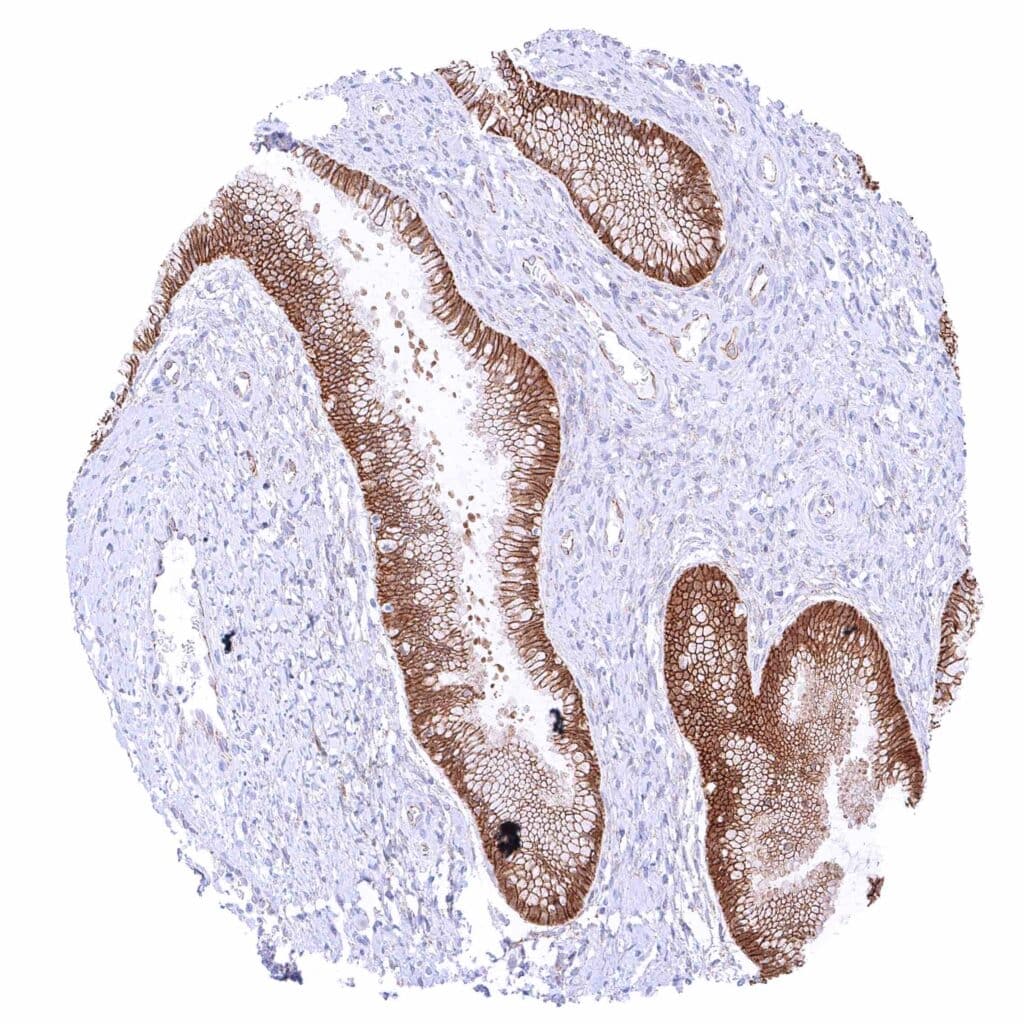
Uterus, endocervix – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells.
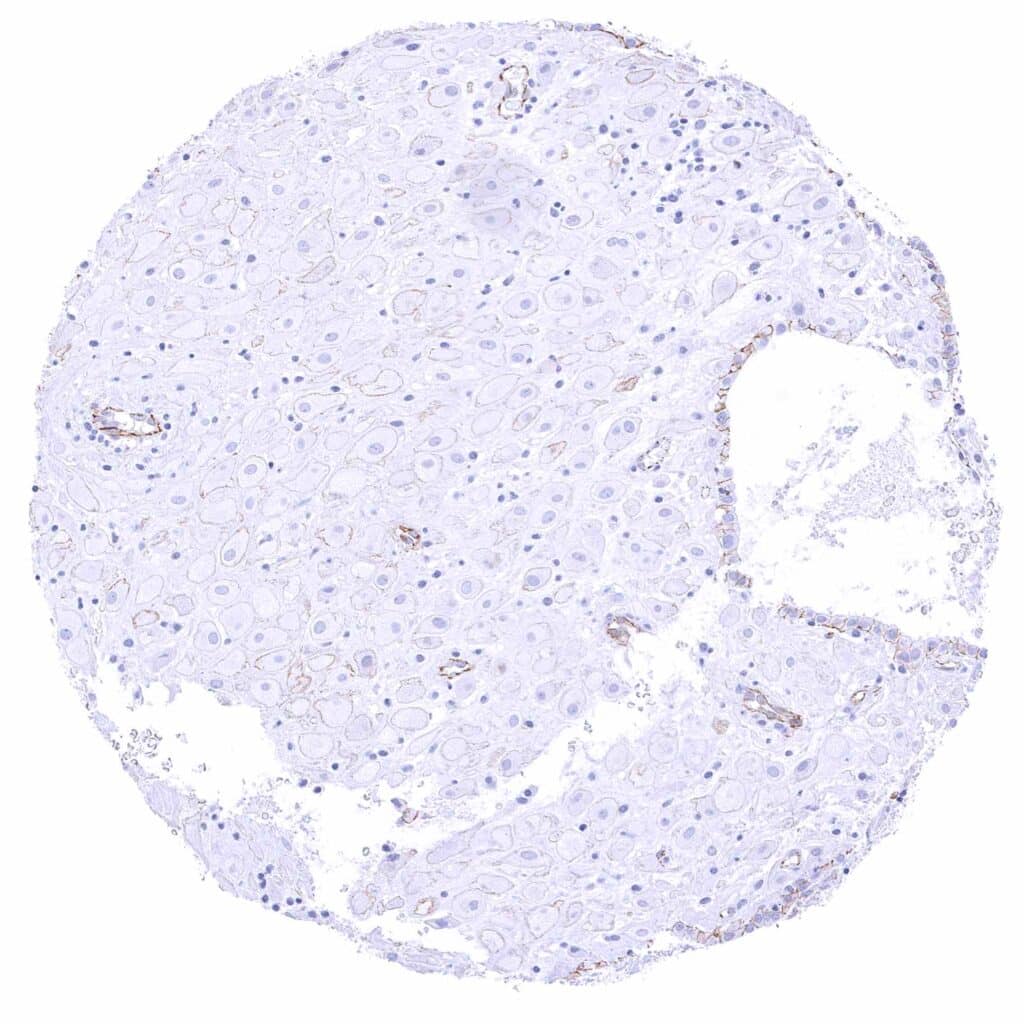
Uterus, endometrium (pregnancy) – Weak to moderate membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells and decidua cells. .jpeg
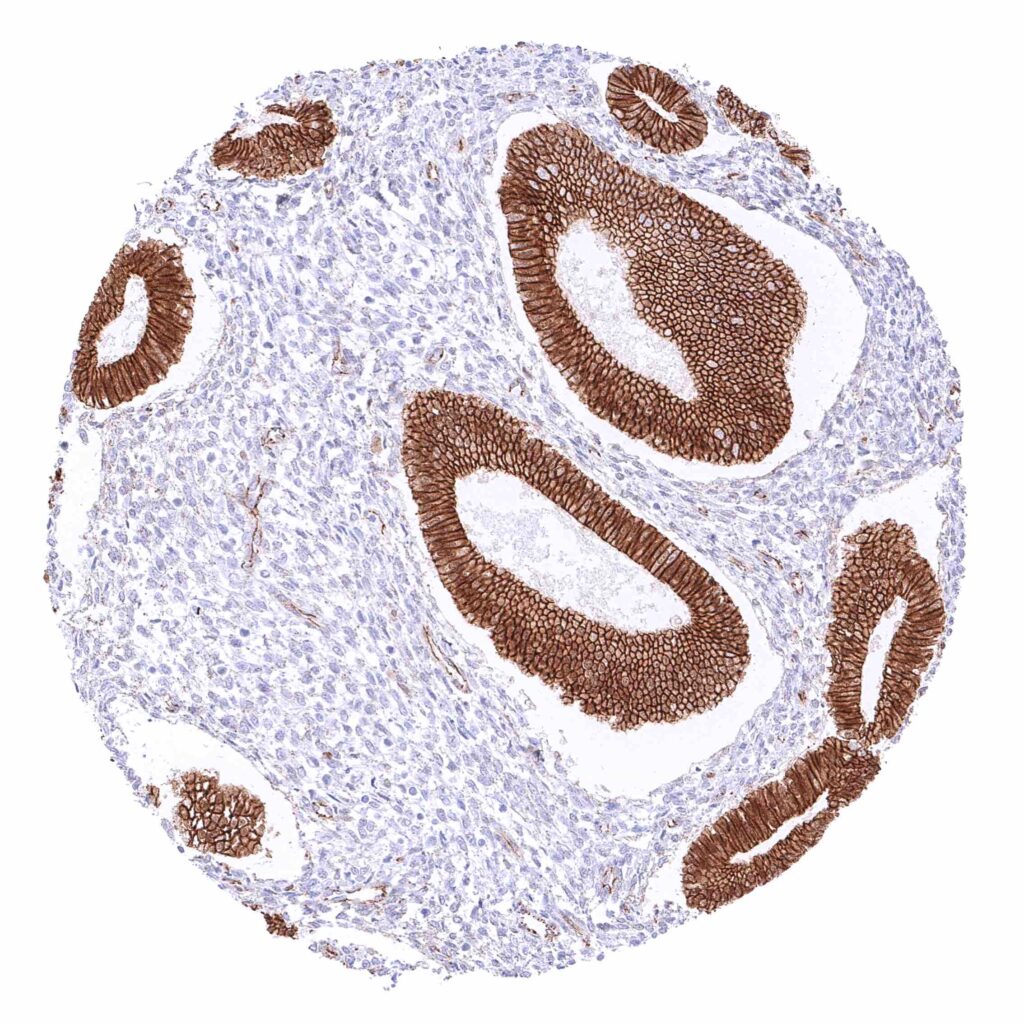
Uterus, endometrium (proliferation) – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells.
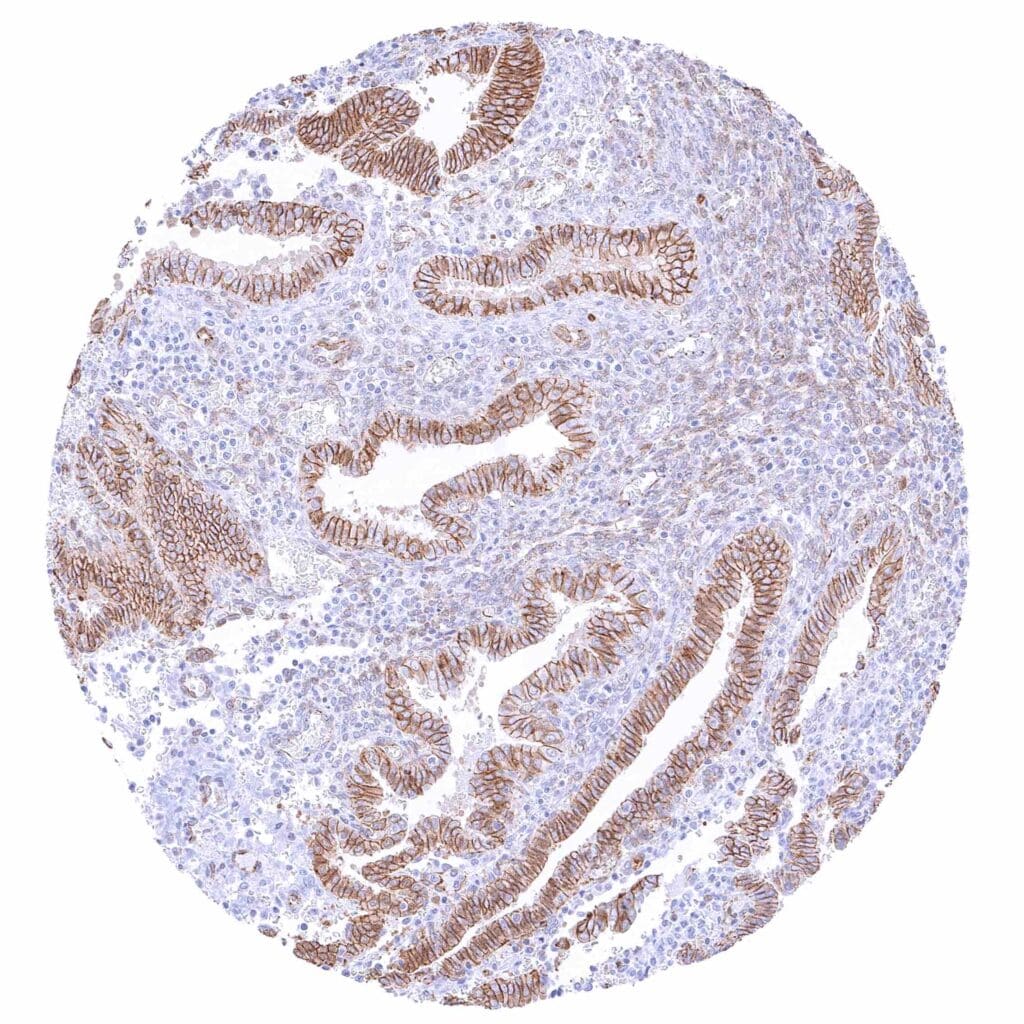
Uterus, endometrium (secretion) – Strong membranous beta catenin staining of epithelial cells.
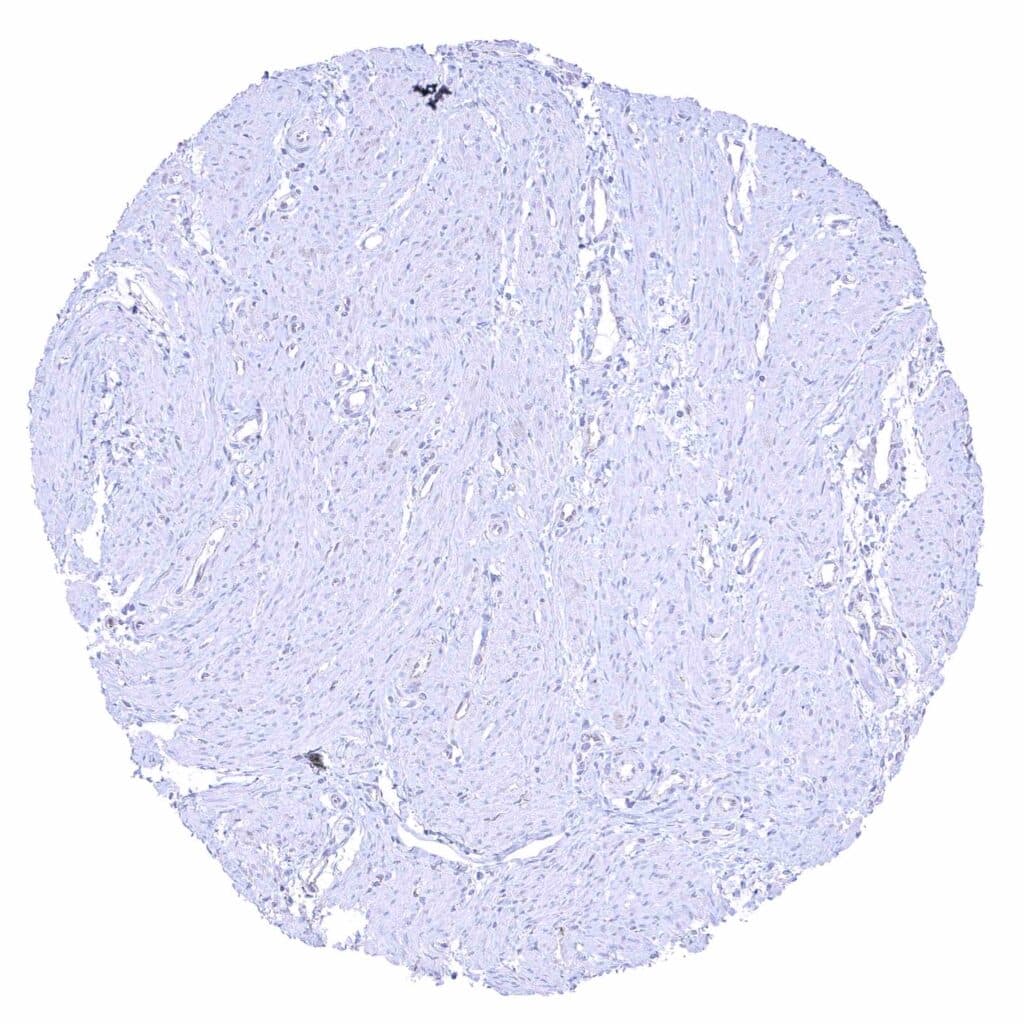
Uterus, myometrium
