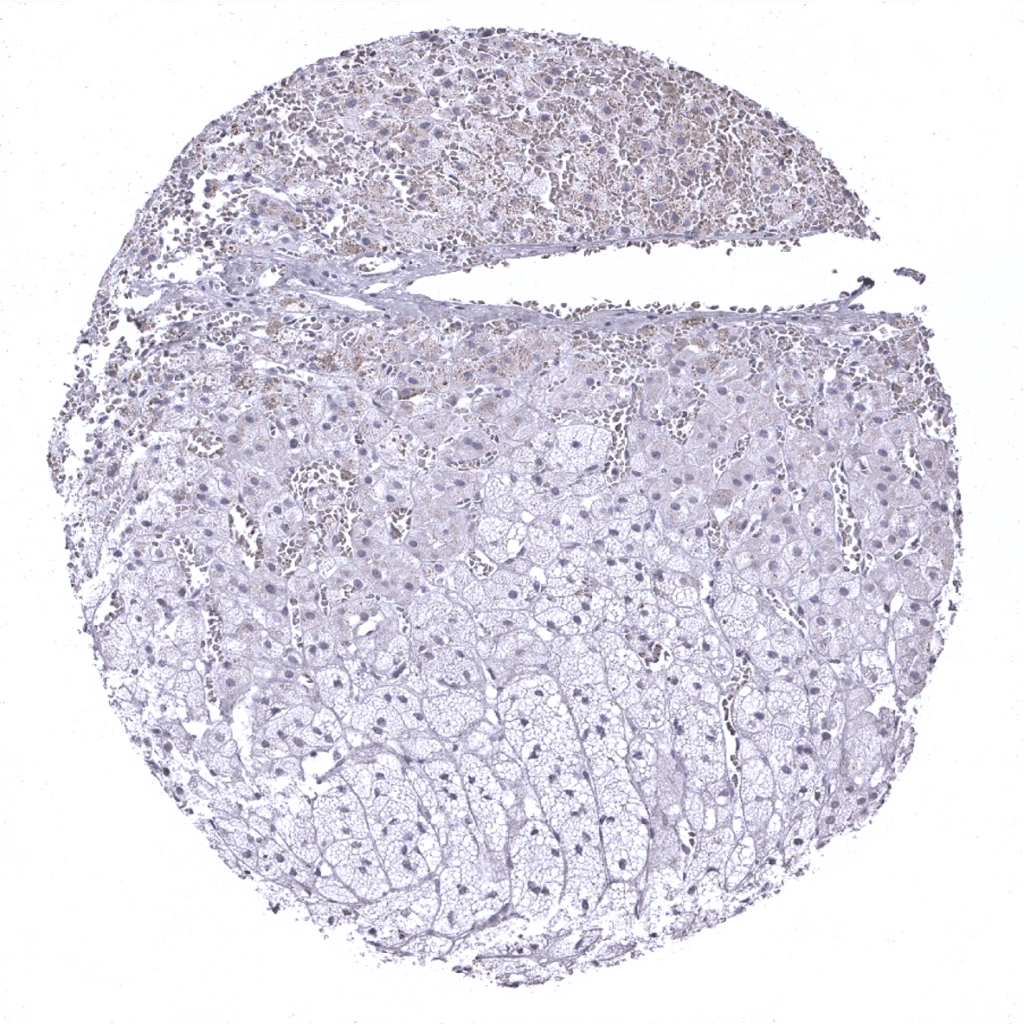
Adrenal gland
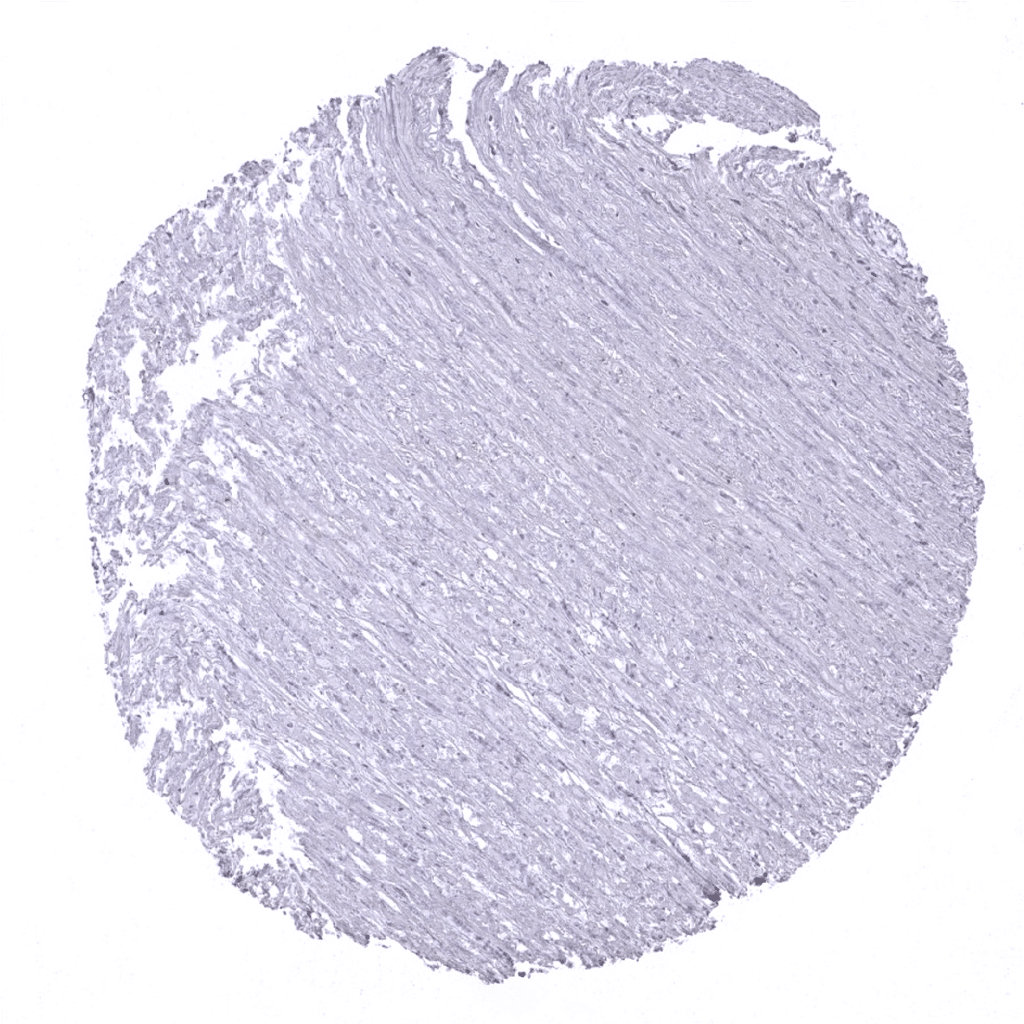
Aorta, media
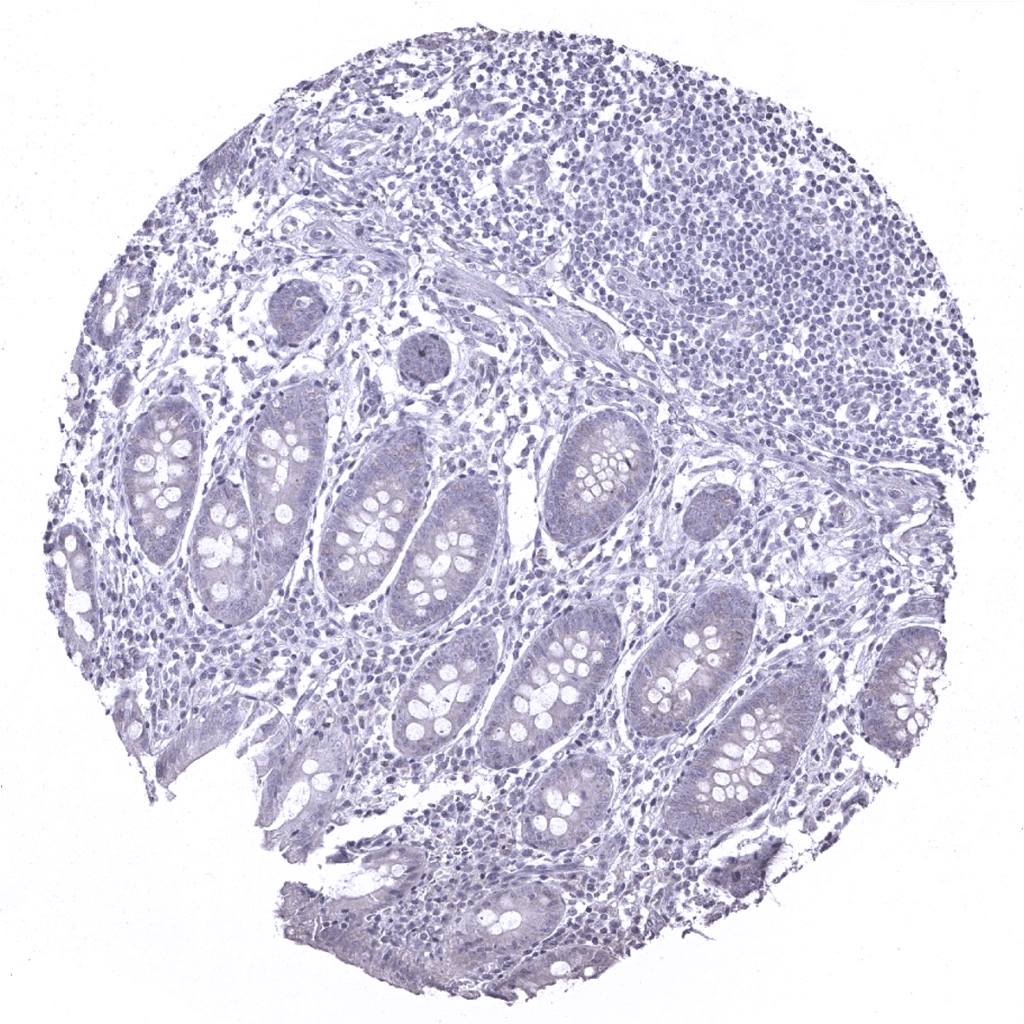
Appendix, mucosa
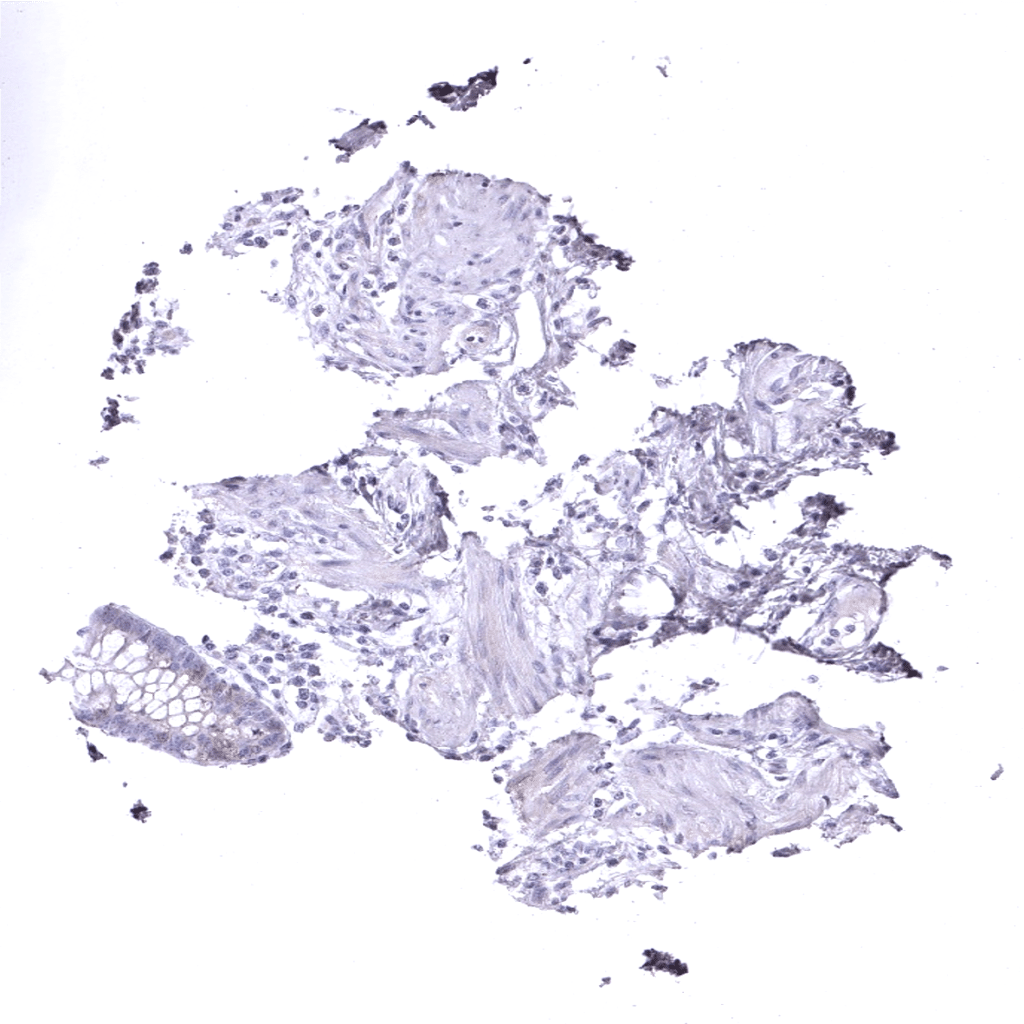
Appendix, muscular wall
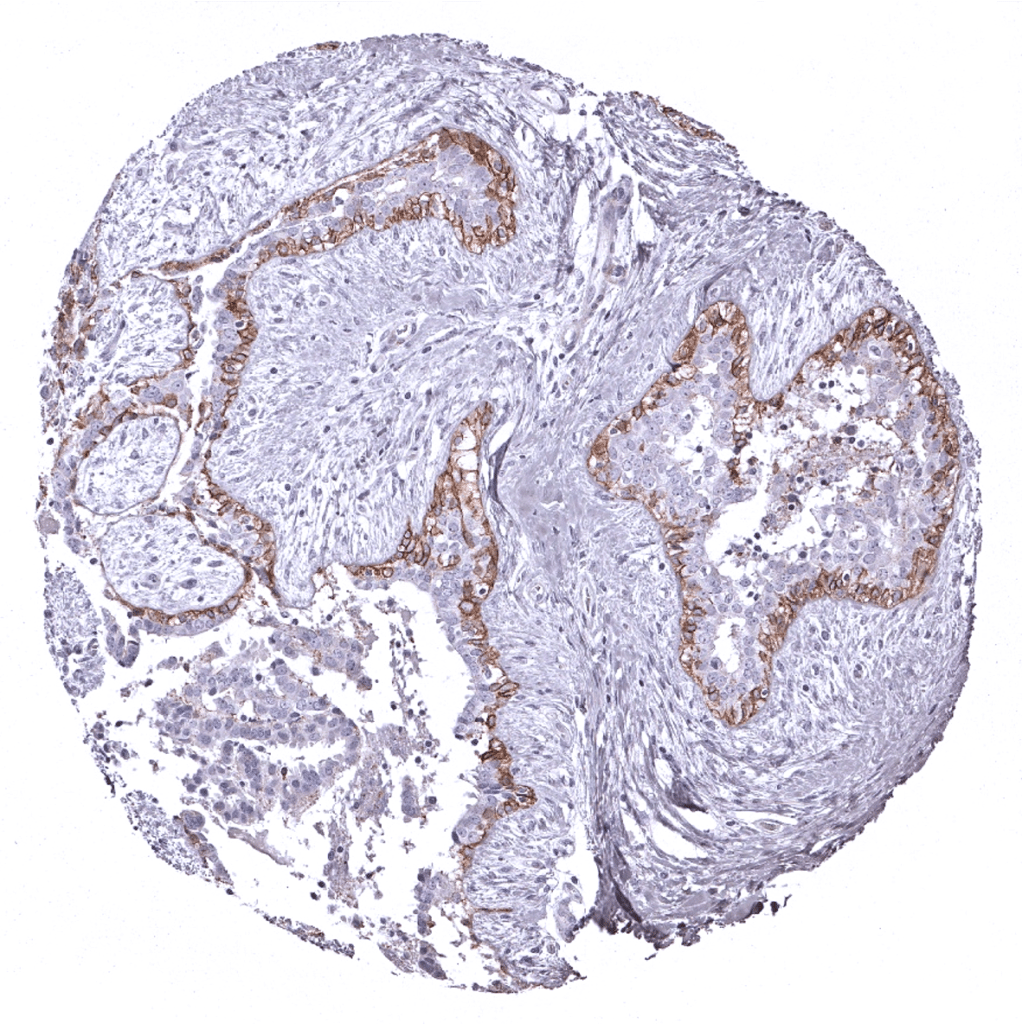
Breast: Prominent DOG-1 staining of myoepithelial cells.
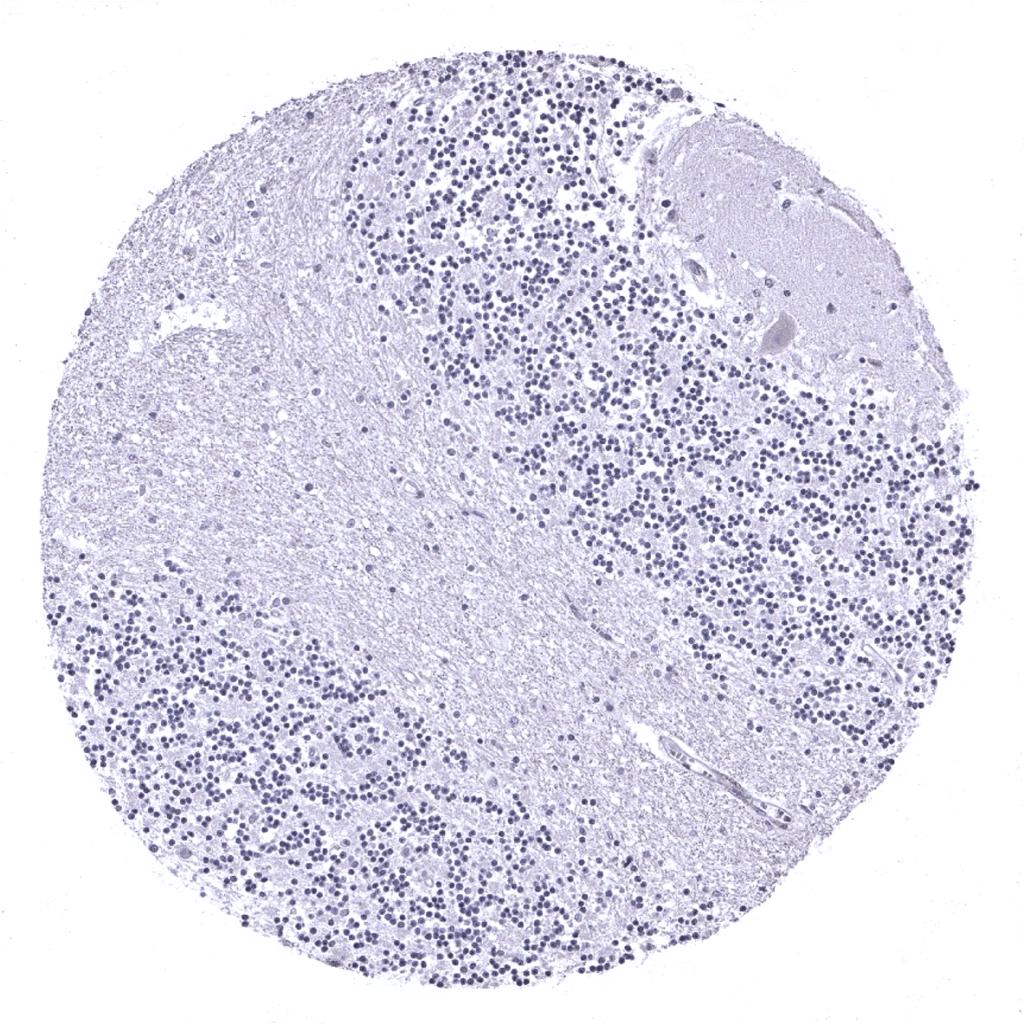
Cerebellum (molecular layer, Purkinje cell layer, granule cell layer, white matter)
Cerebellum (white matter)
Cerebrum, grey matter
Cerebrum, white matter
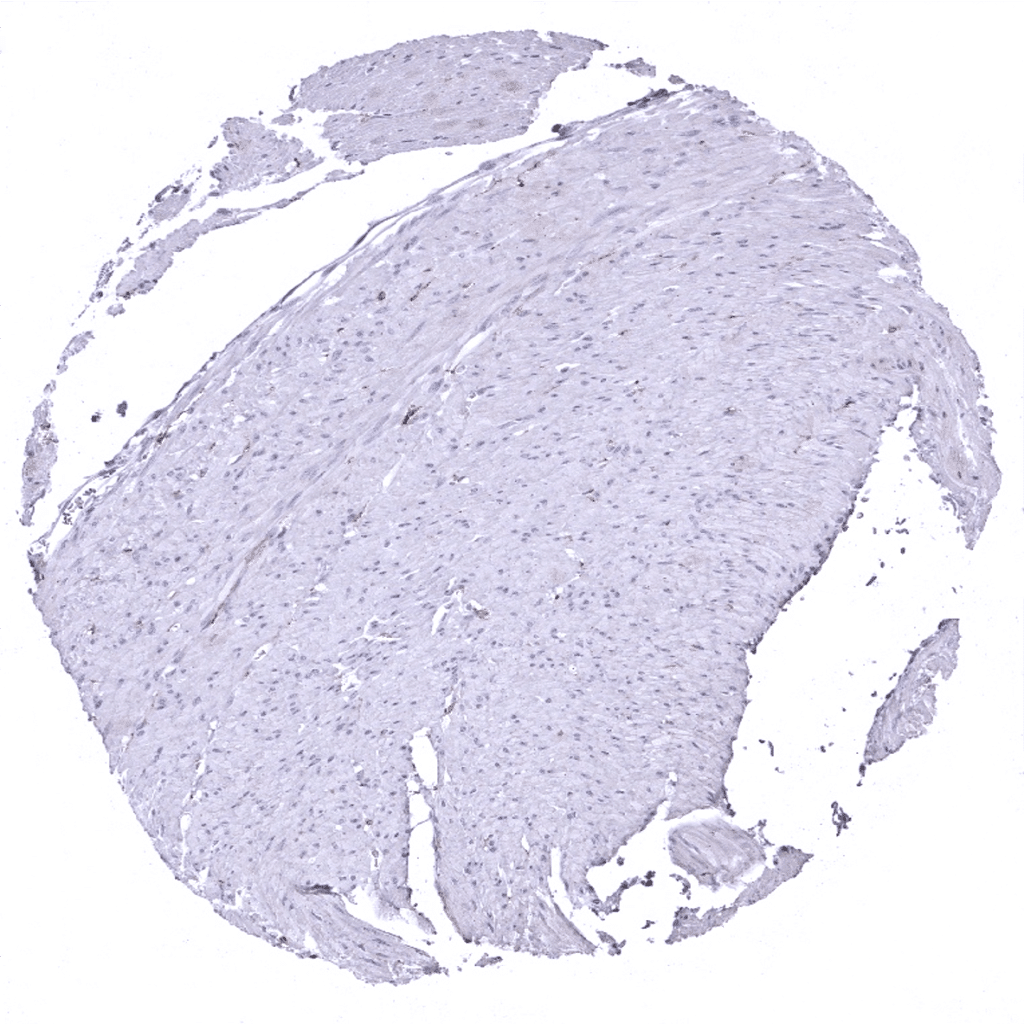
Colon descendens, muscular wall: Few interstitial cells of Cajal show a DOG-1 staining.
Duodenum, Brunner gland
Duodenum, mucosa
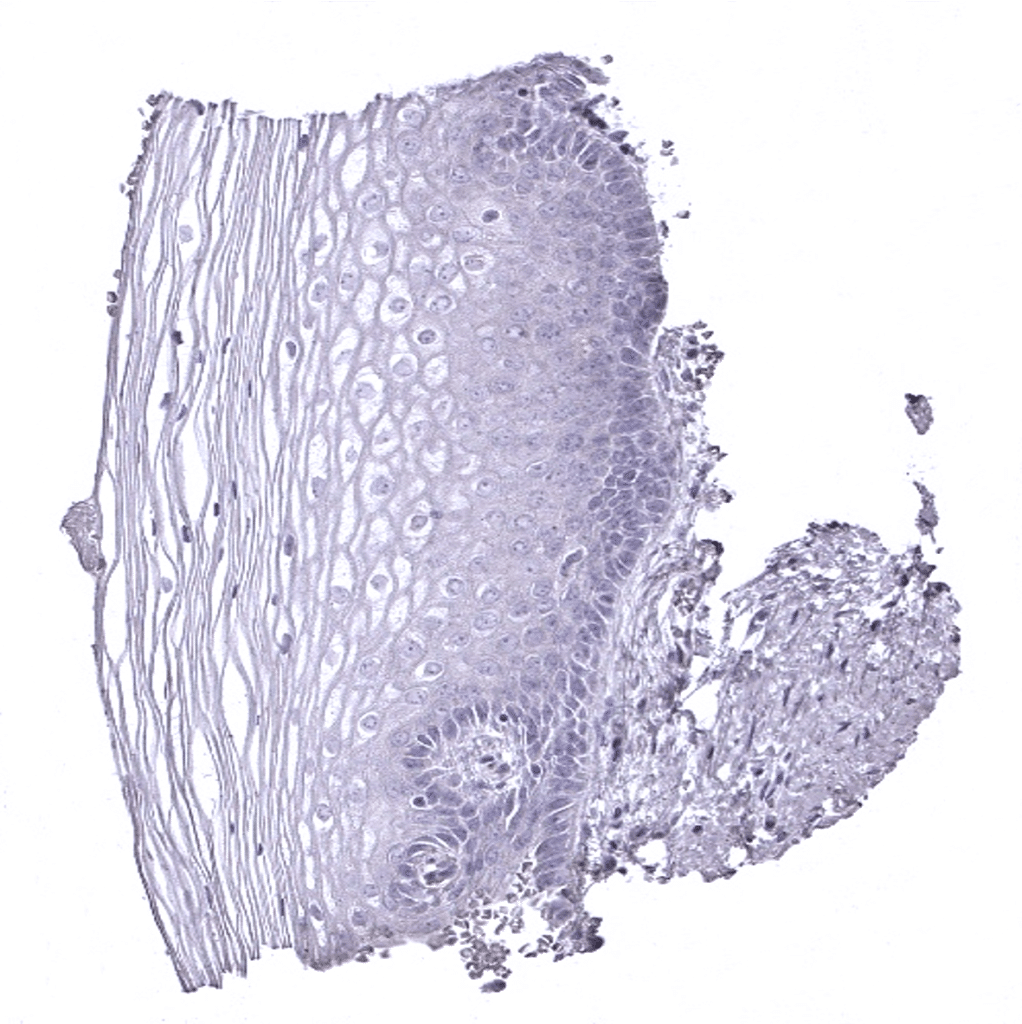
Ectocervix
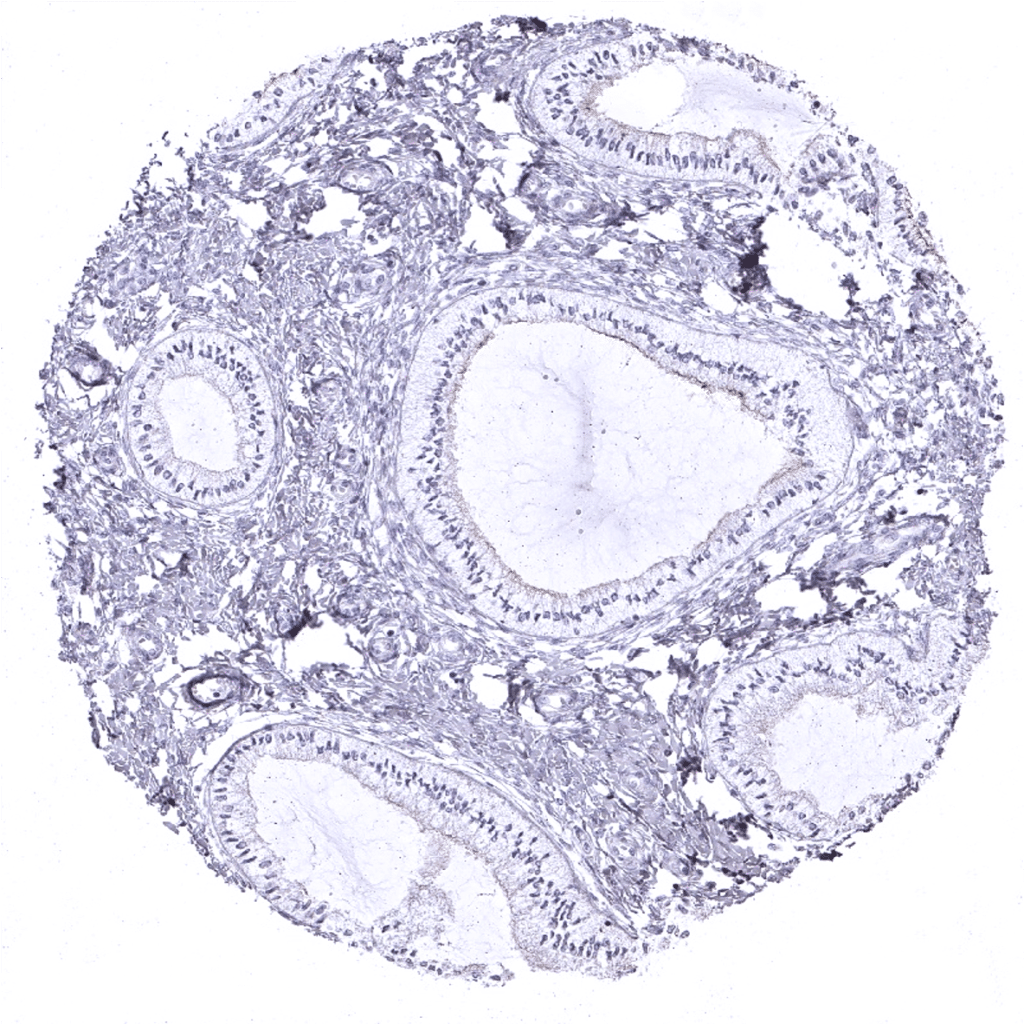
Endocervix
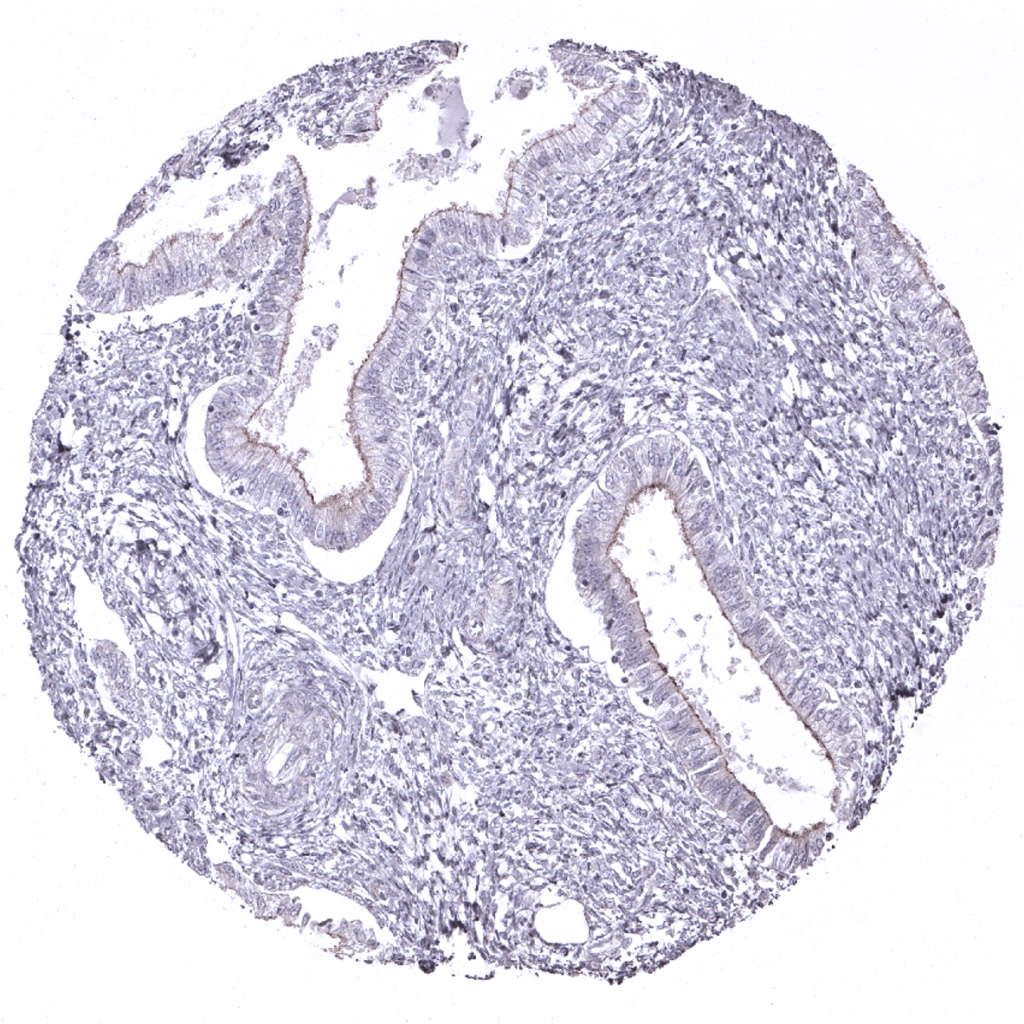
Endometrium, proliferation
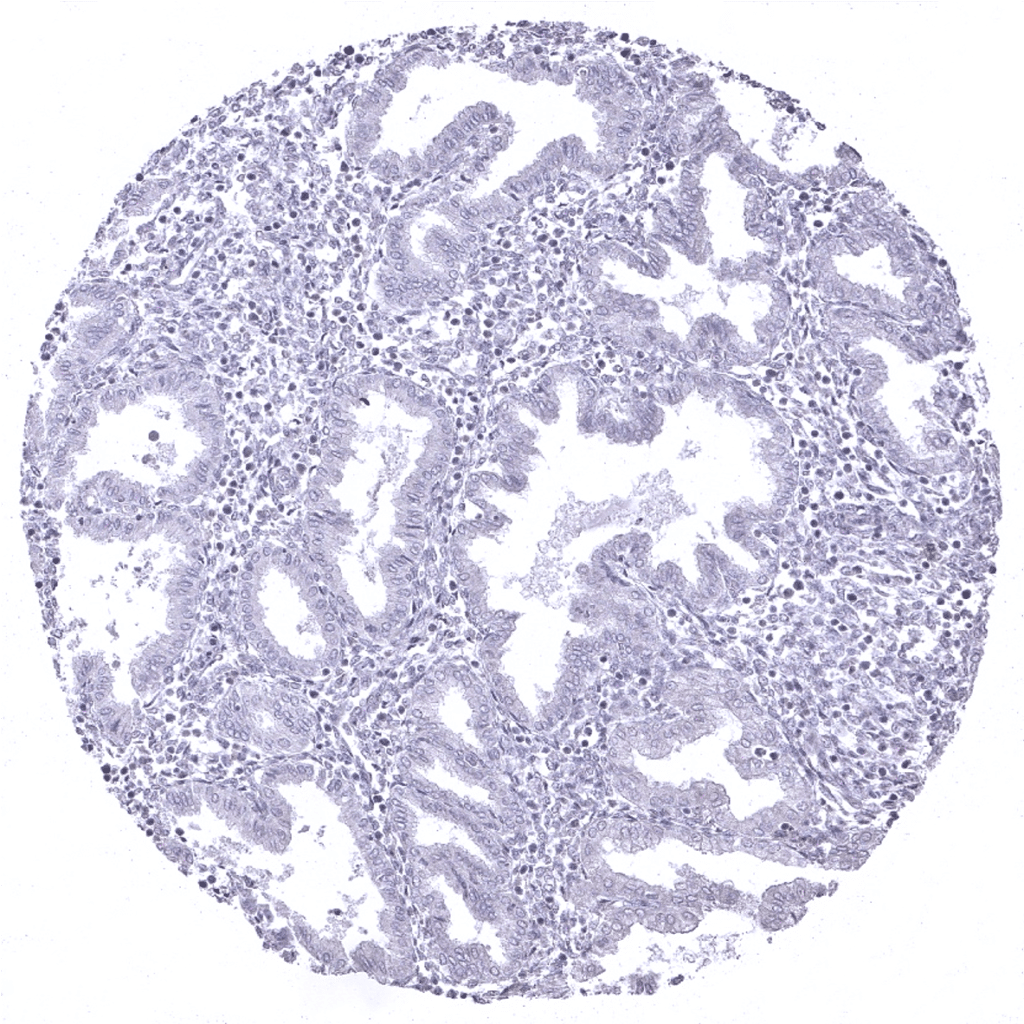
Endometrium, secretion
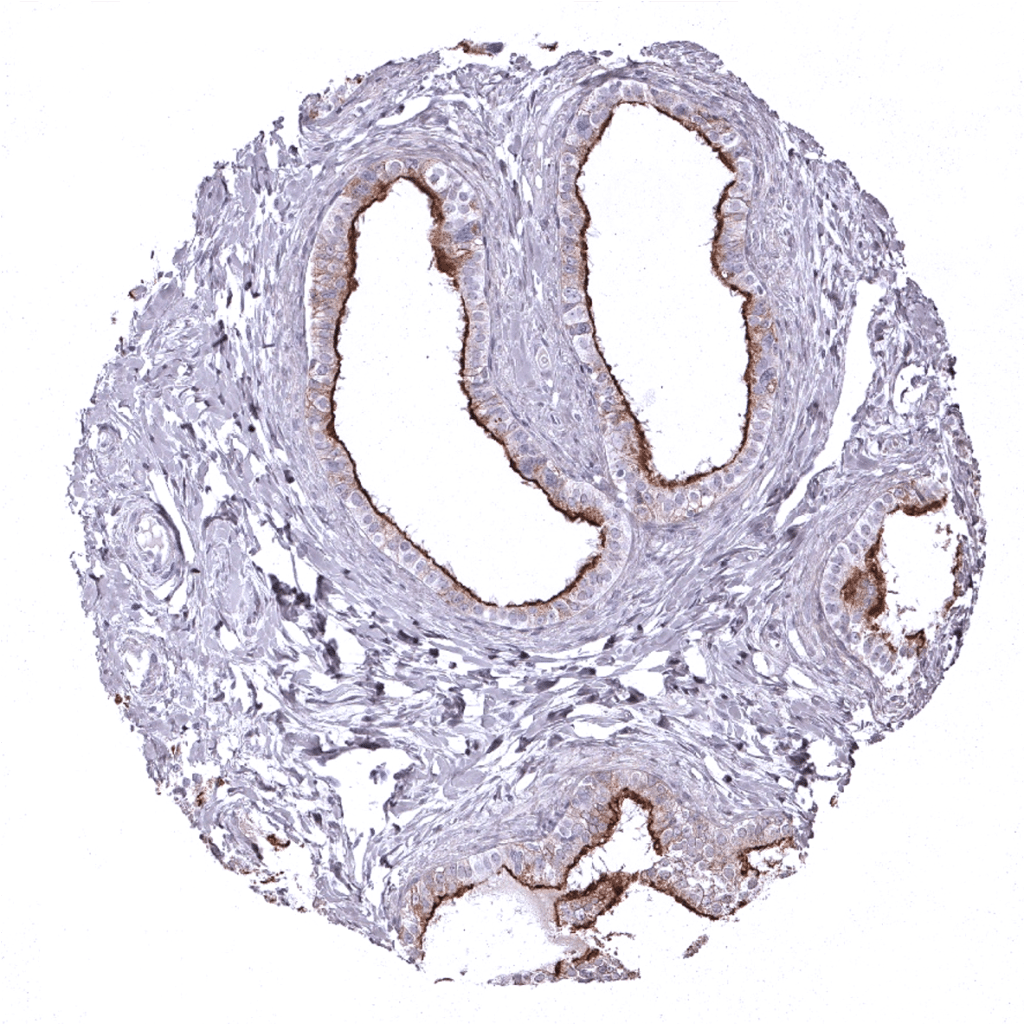
Epididymis: Strong DOG1 staining of the apical membrane of epithelial cells in the cauda epididymis.
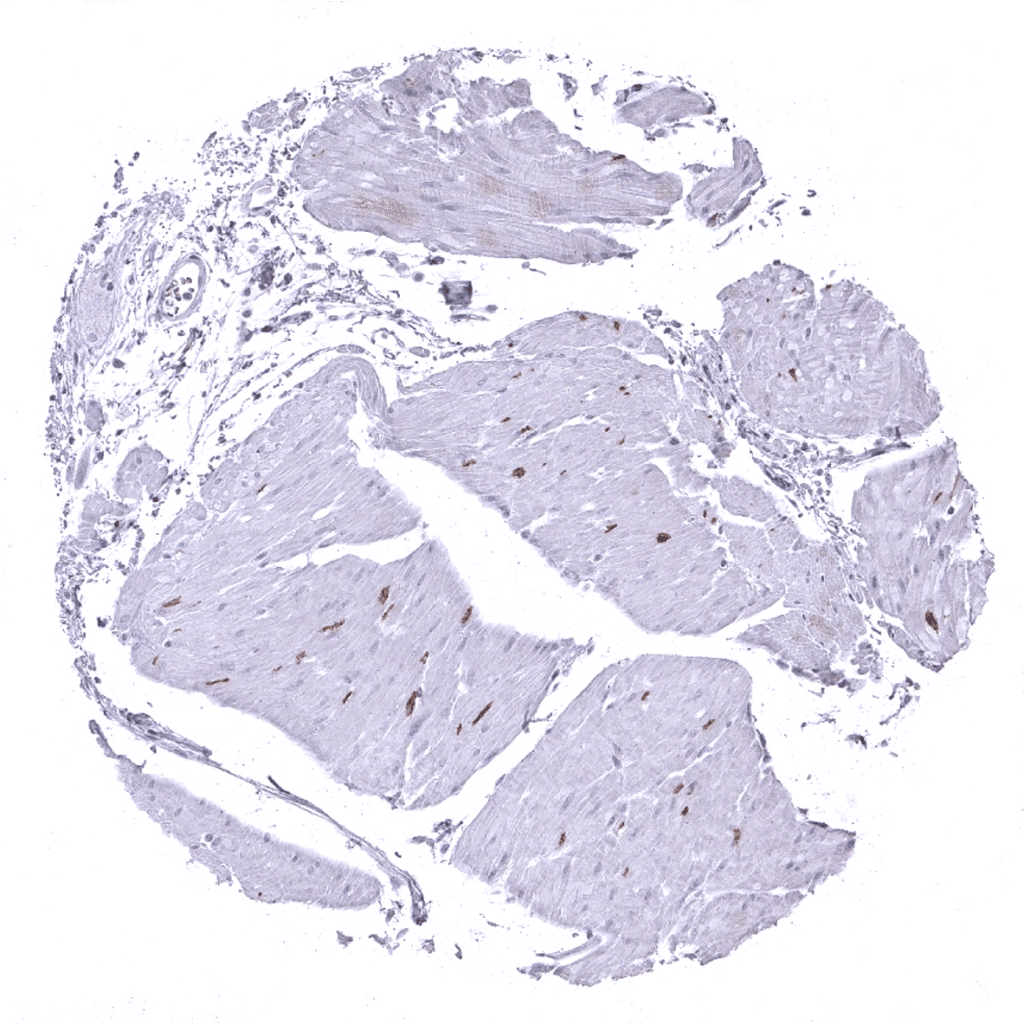
Esophagus, muscular wall: DOG1 immunostaining of interstitial cells of Cajal.
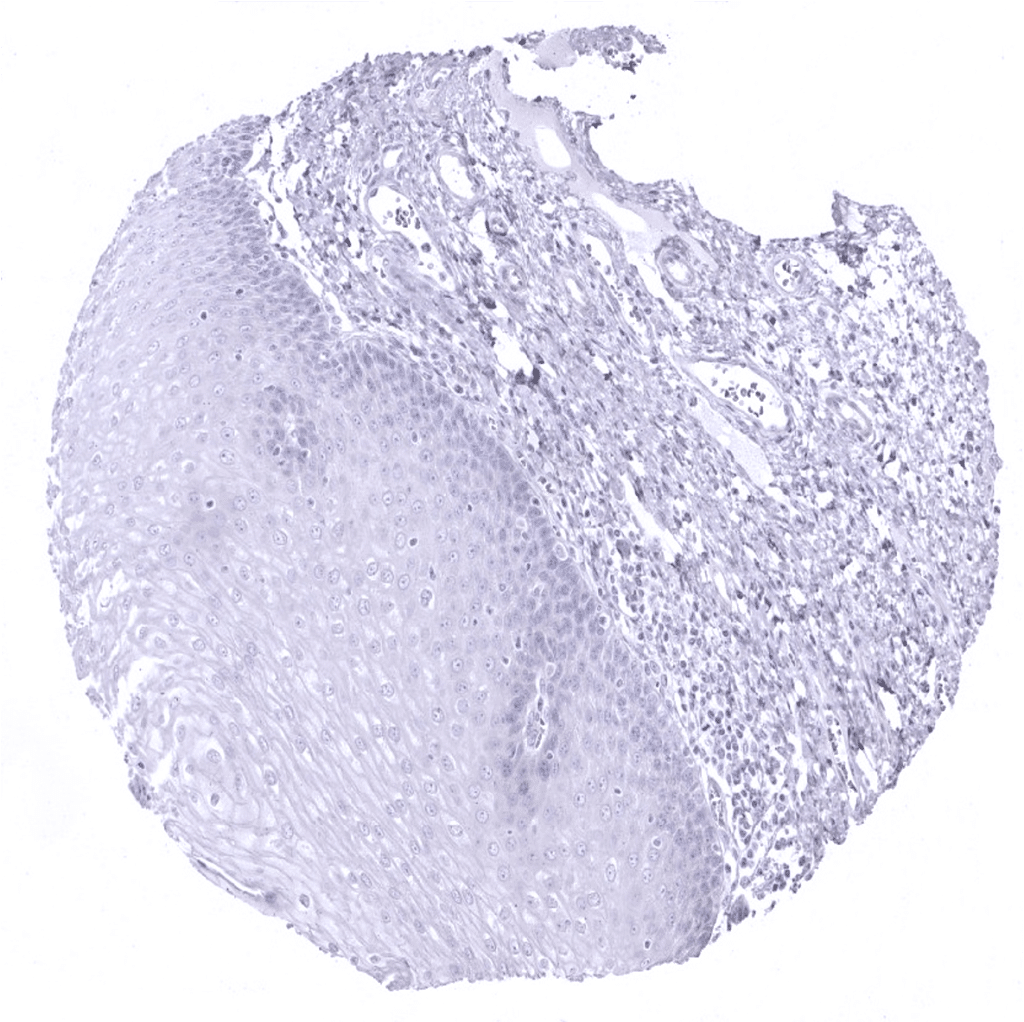
Esophagus, squamous epithelium
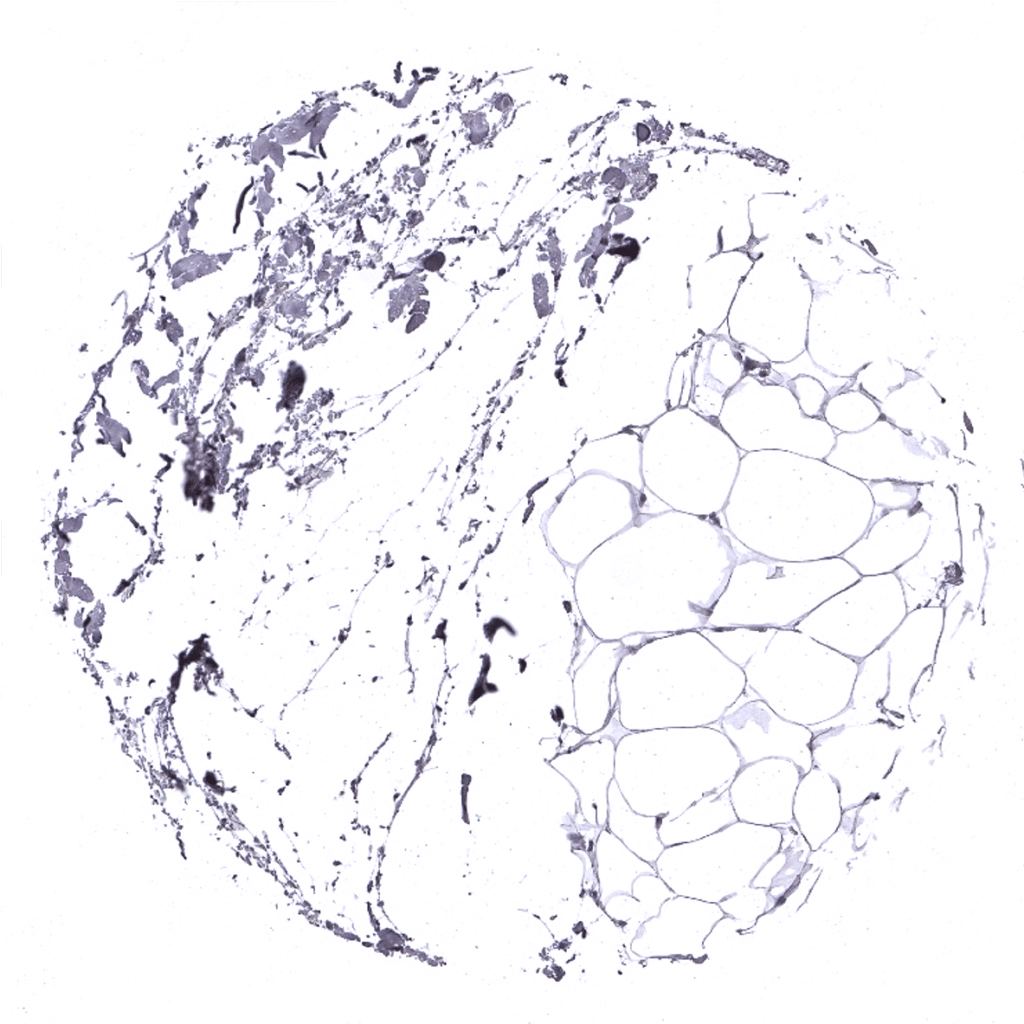
Fat
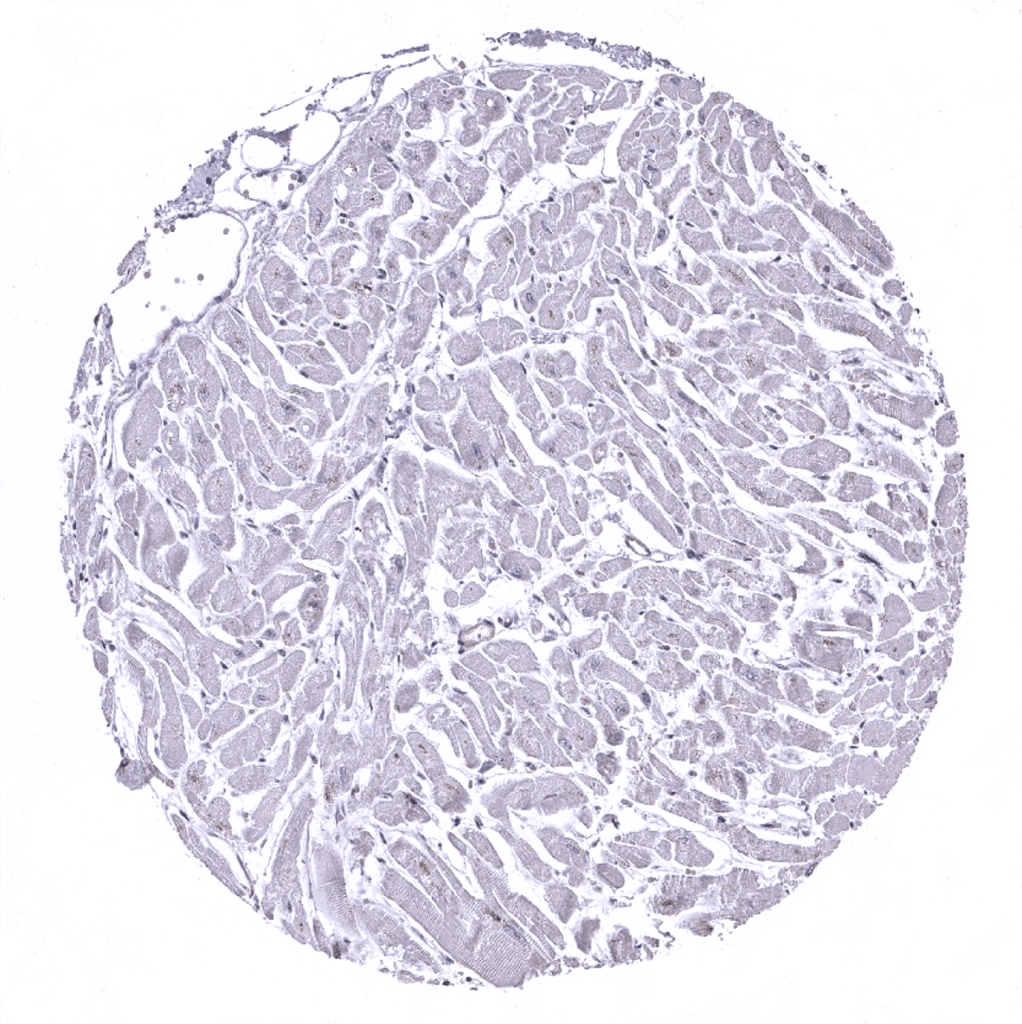
Heart
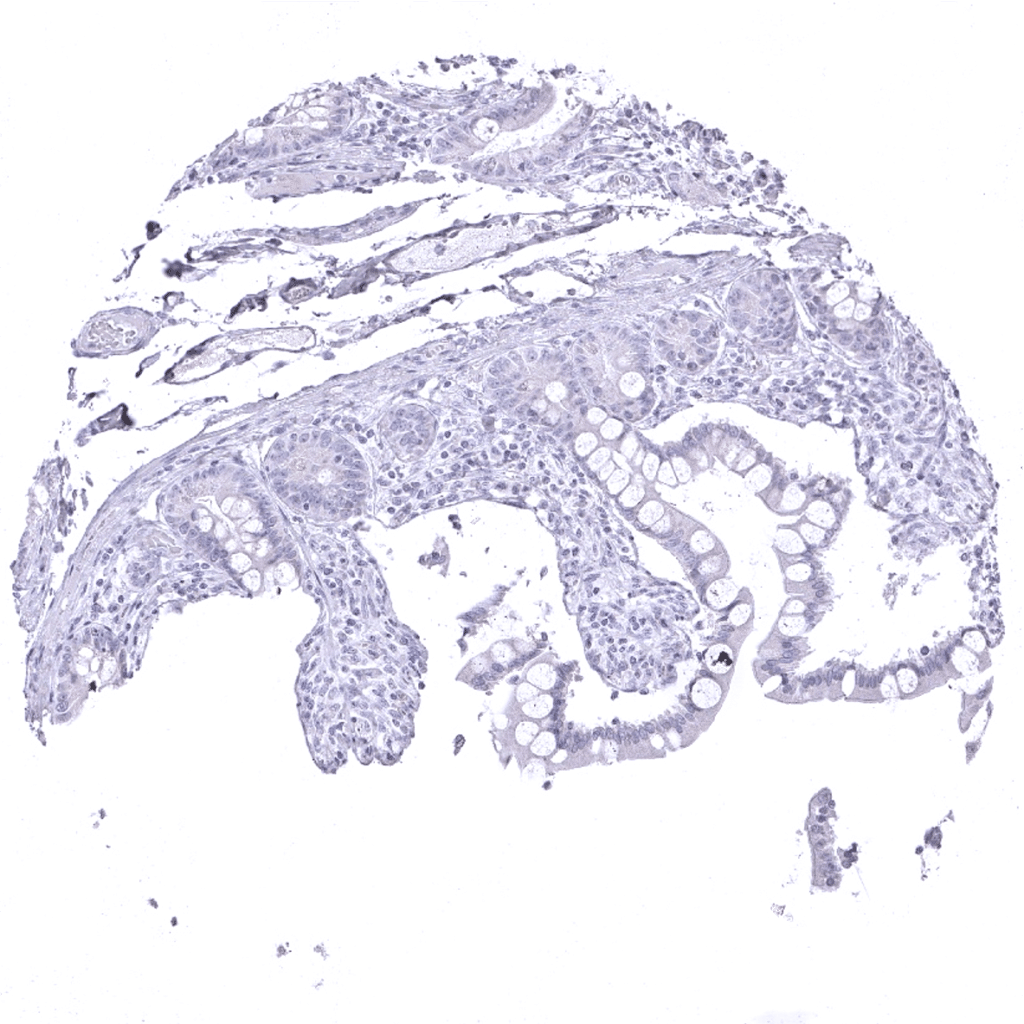
Ileum, mucosa
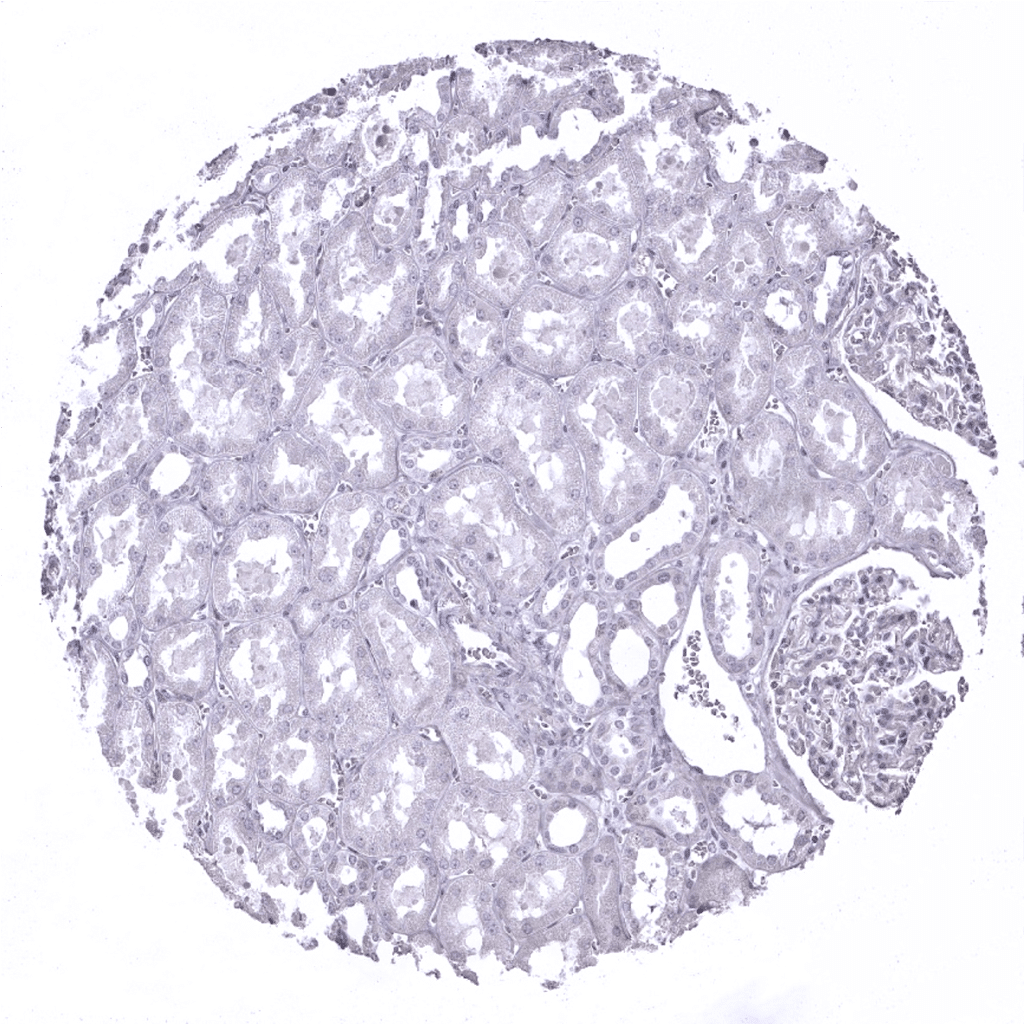
Kidney, cortex: DOG1 immunostaining is absent in the kidney.
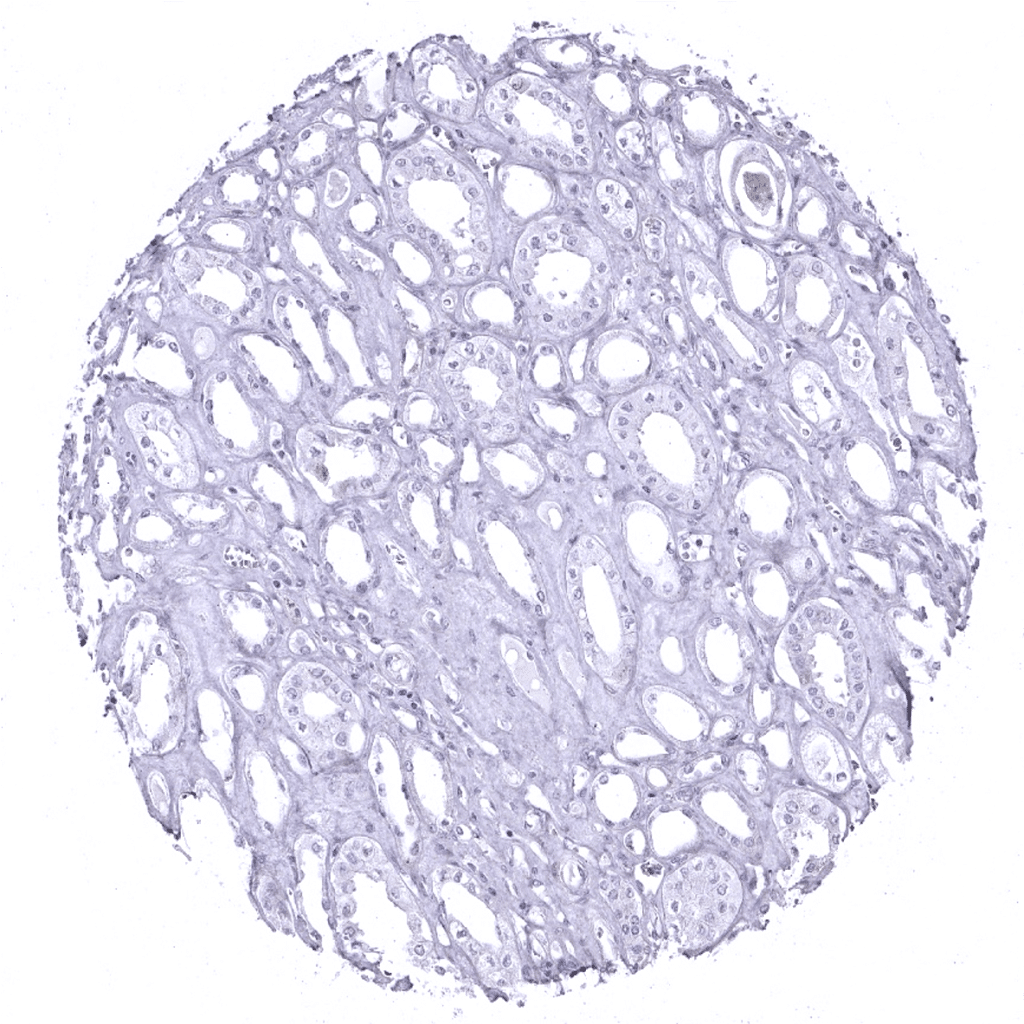
Kidney, medulla
Liver
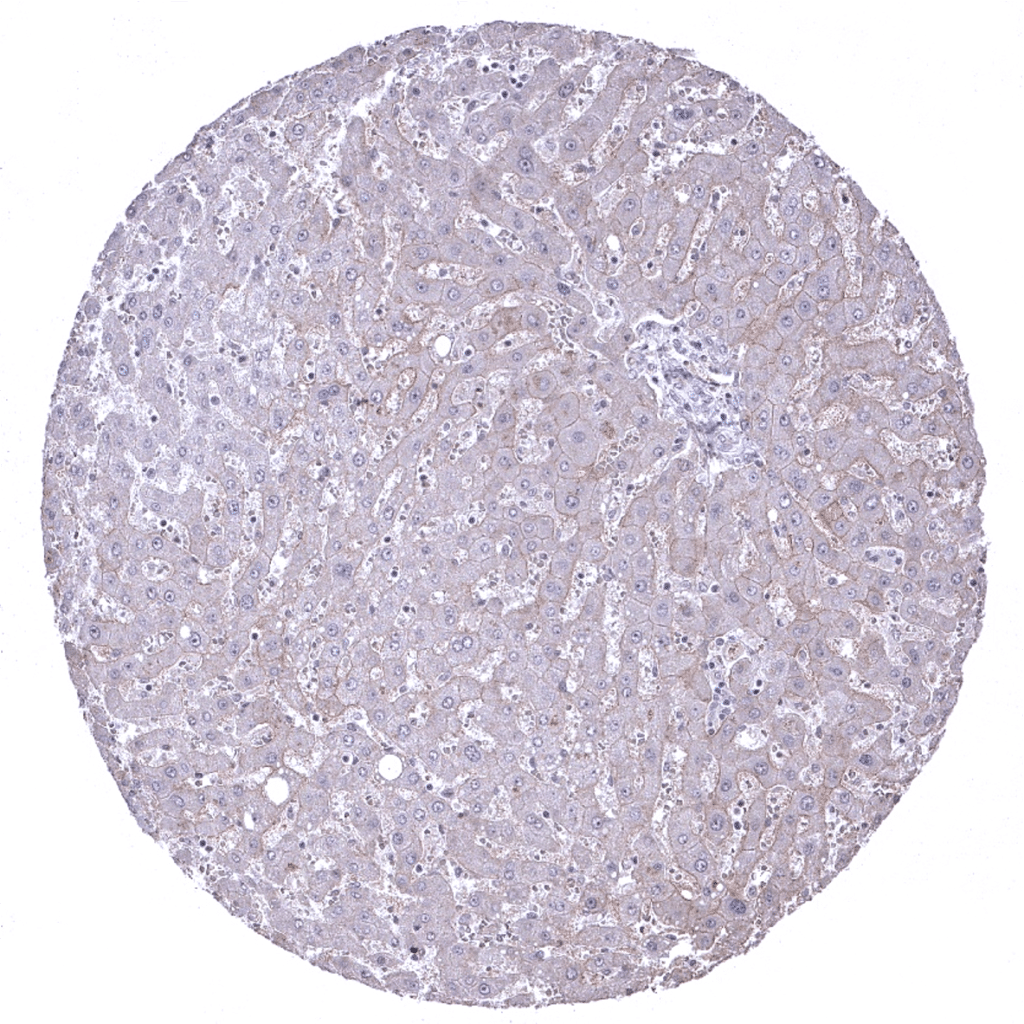
Liver: A weak to moderate membranous DOG1 staining should be seen in hepatocytes.
Lung
Lymph node
Ovary, stroma
Pancreas
Parathyroid
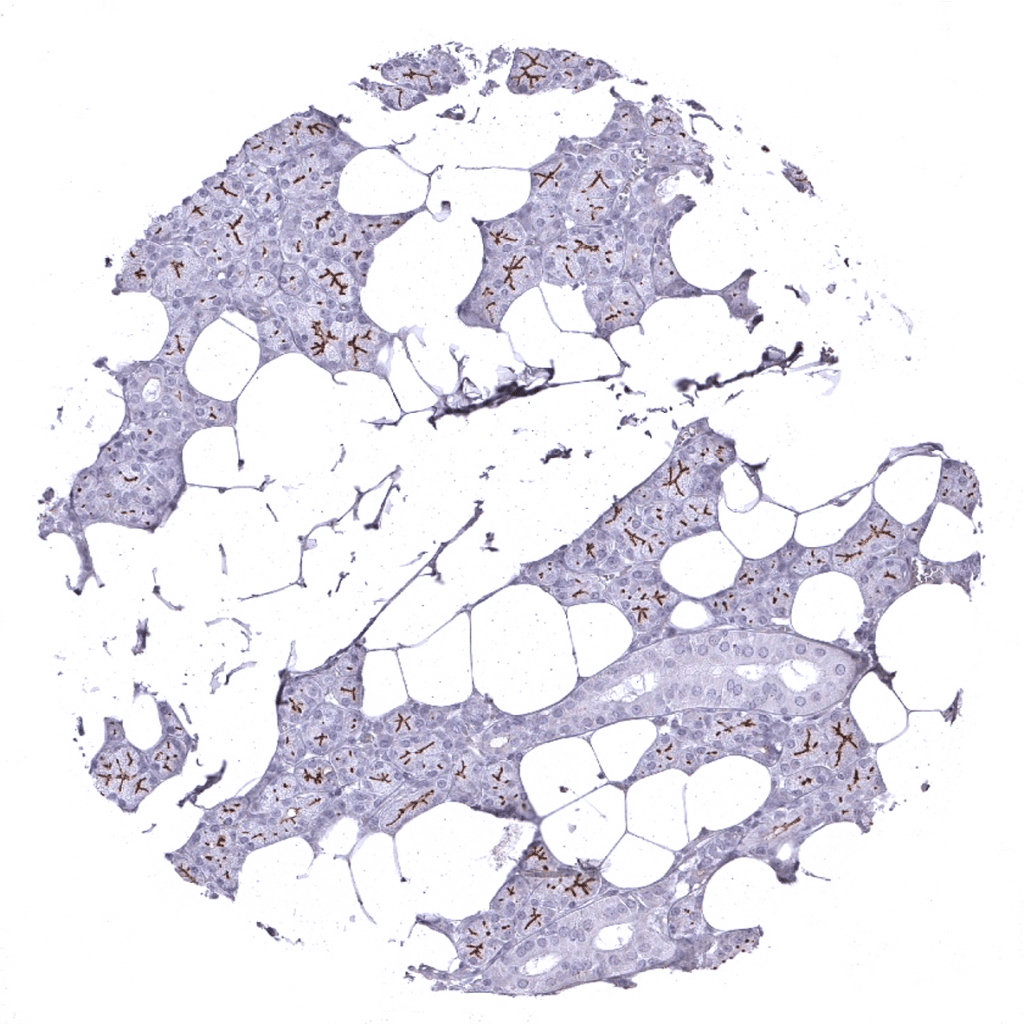
Parotid gland: Strong DOG1 staining of the apical membranes of secreting cells.
Pituitary gland, anterior lobe
Pituitary gland, posterior lobe
Pregnant uterus (decidua)
Placenta, early
Placenta, early
Placenta, mature
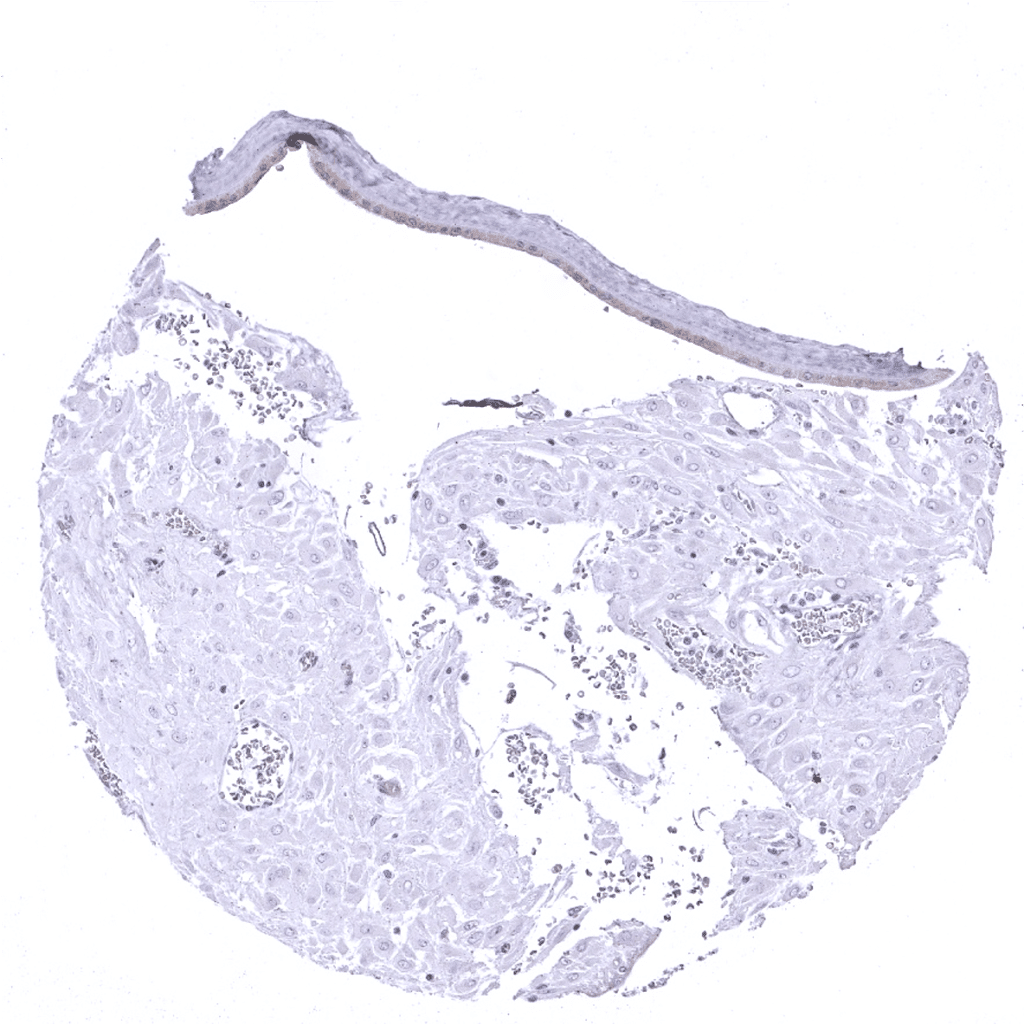
Placenta (amnion and chorion): Weak DOG1 staining of amnion cells.
Prostate
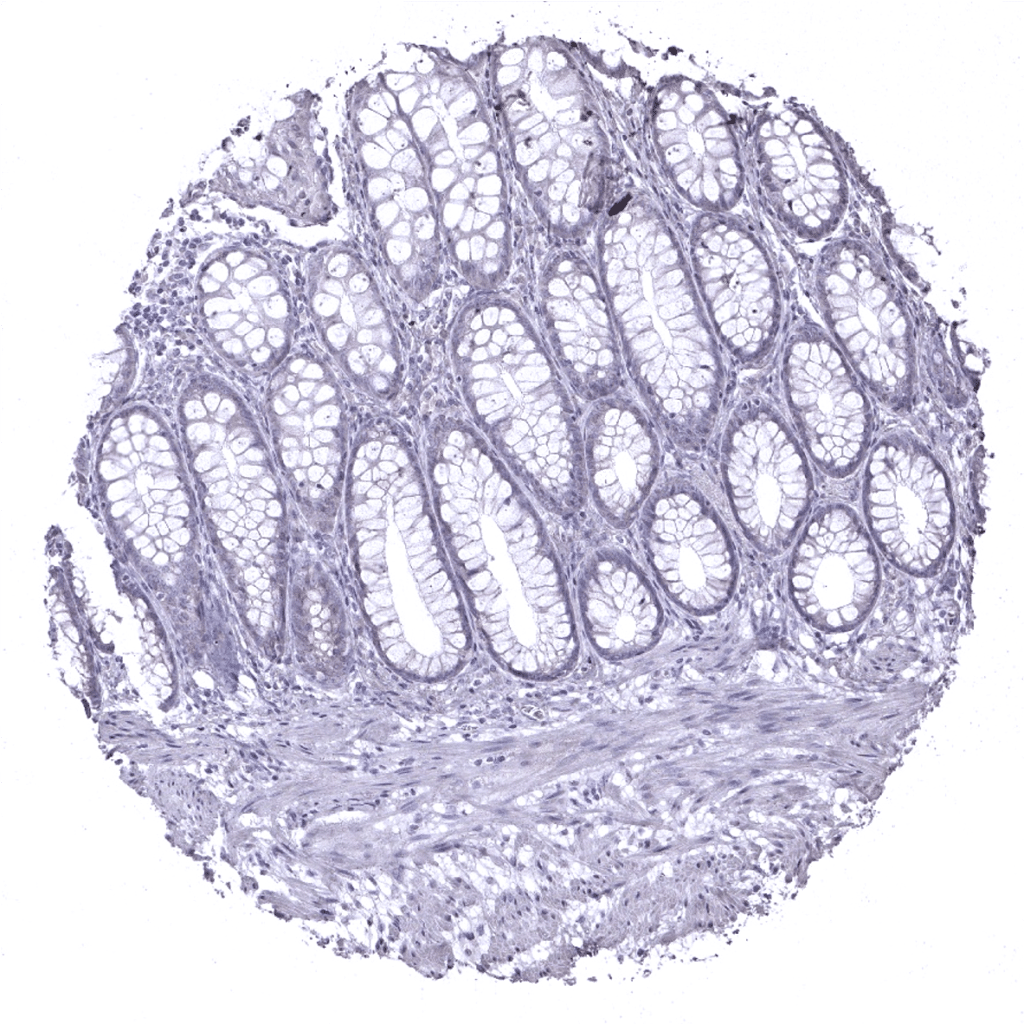
Rectum, mucosa
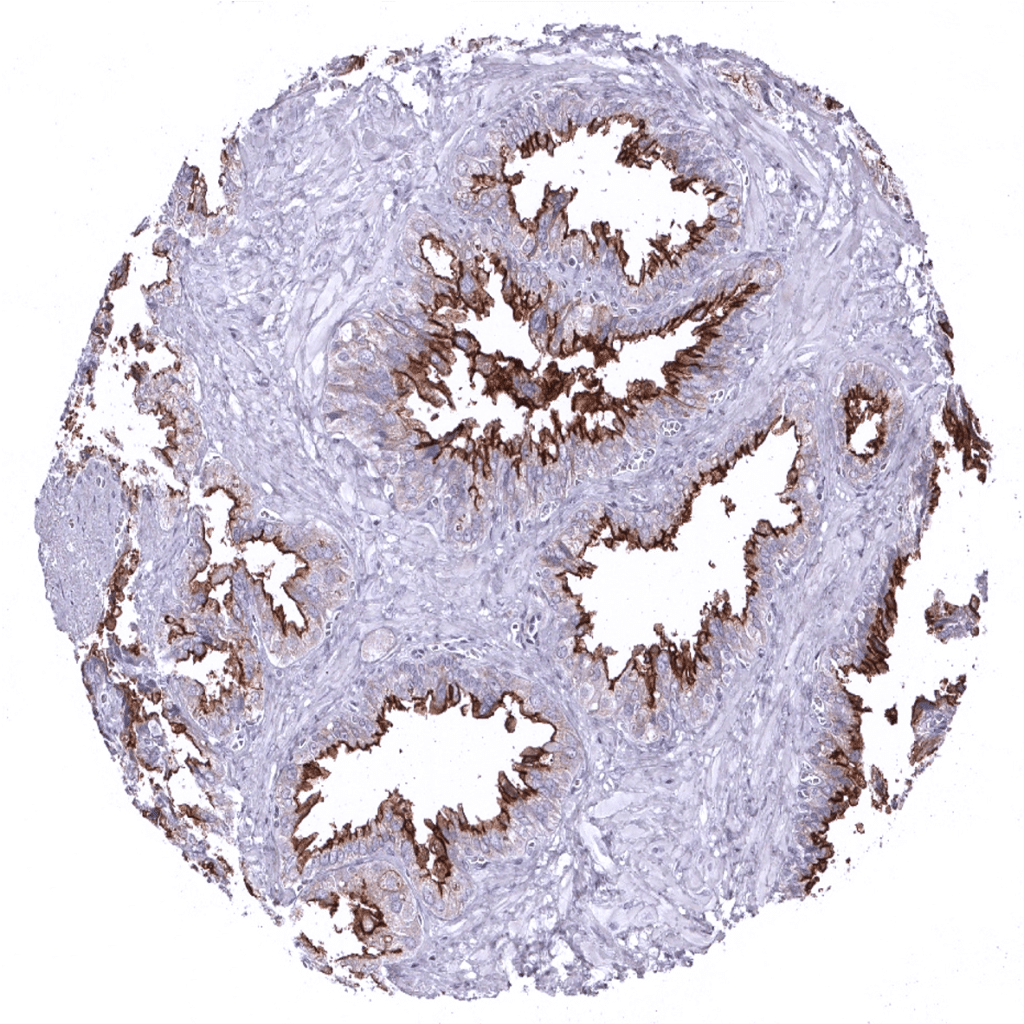
Seminal vesicle: Strong DOG1 staining of apical membranes of glandular cells.

Skin
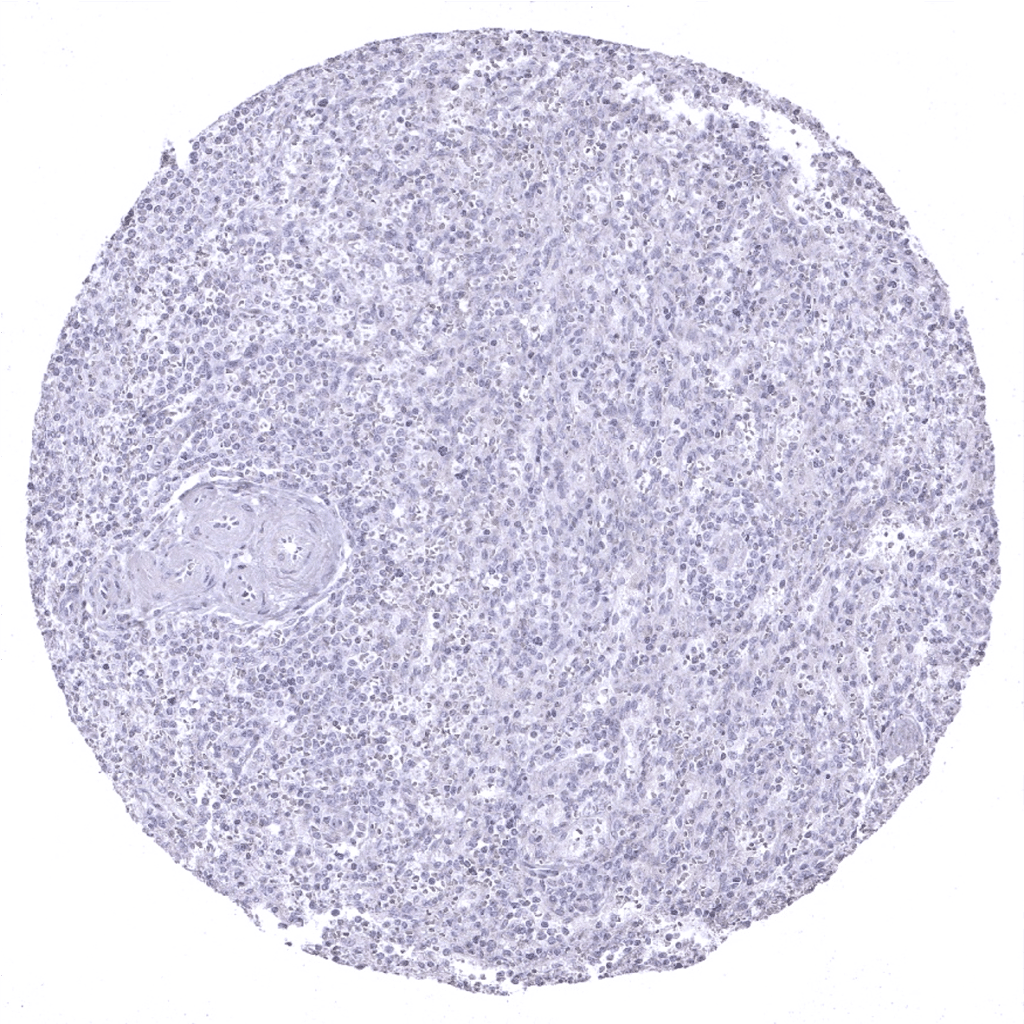
Spleen
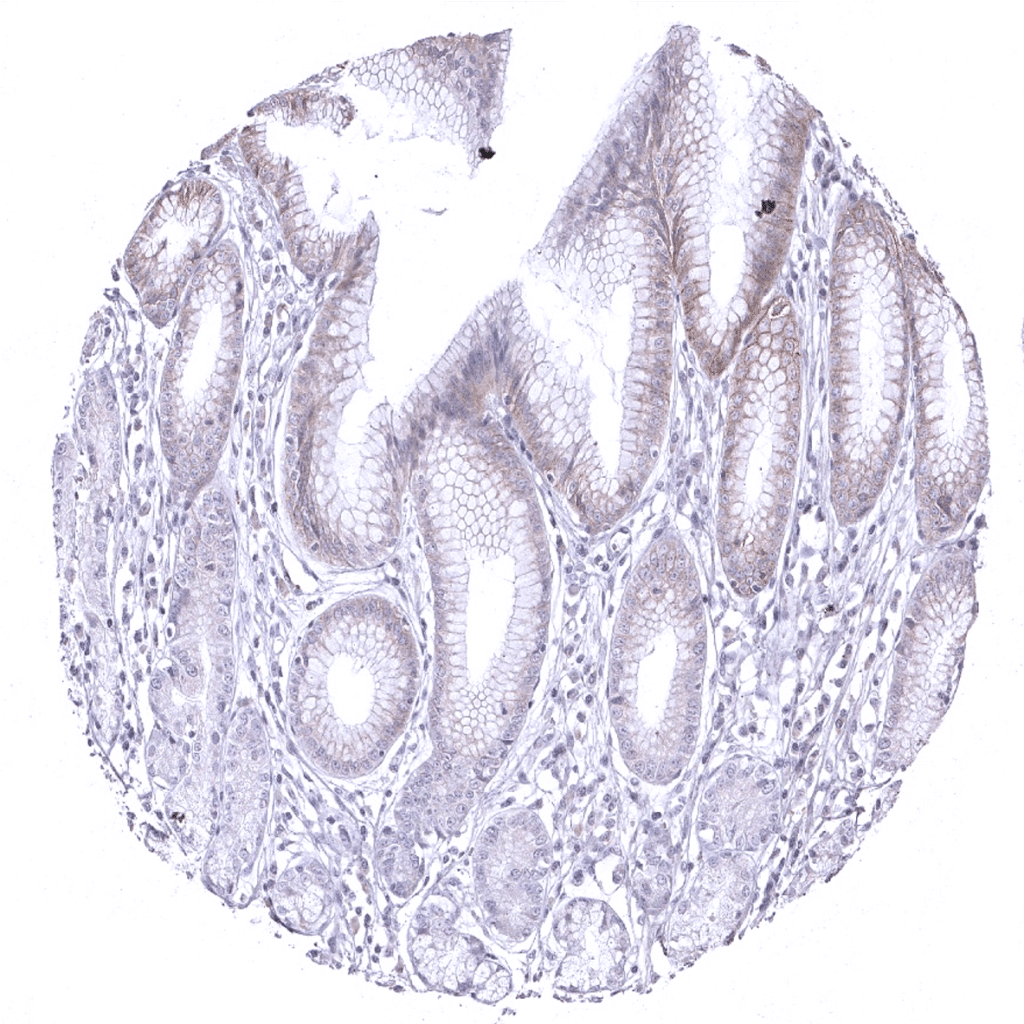
Stomach, antrum: Weak DOG1 staining of epithelial cells, mainly in the isthmus/neck region but also of the surface cell layer.
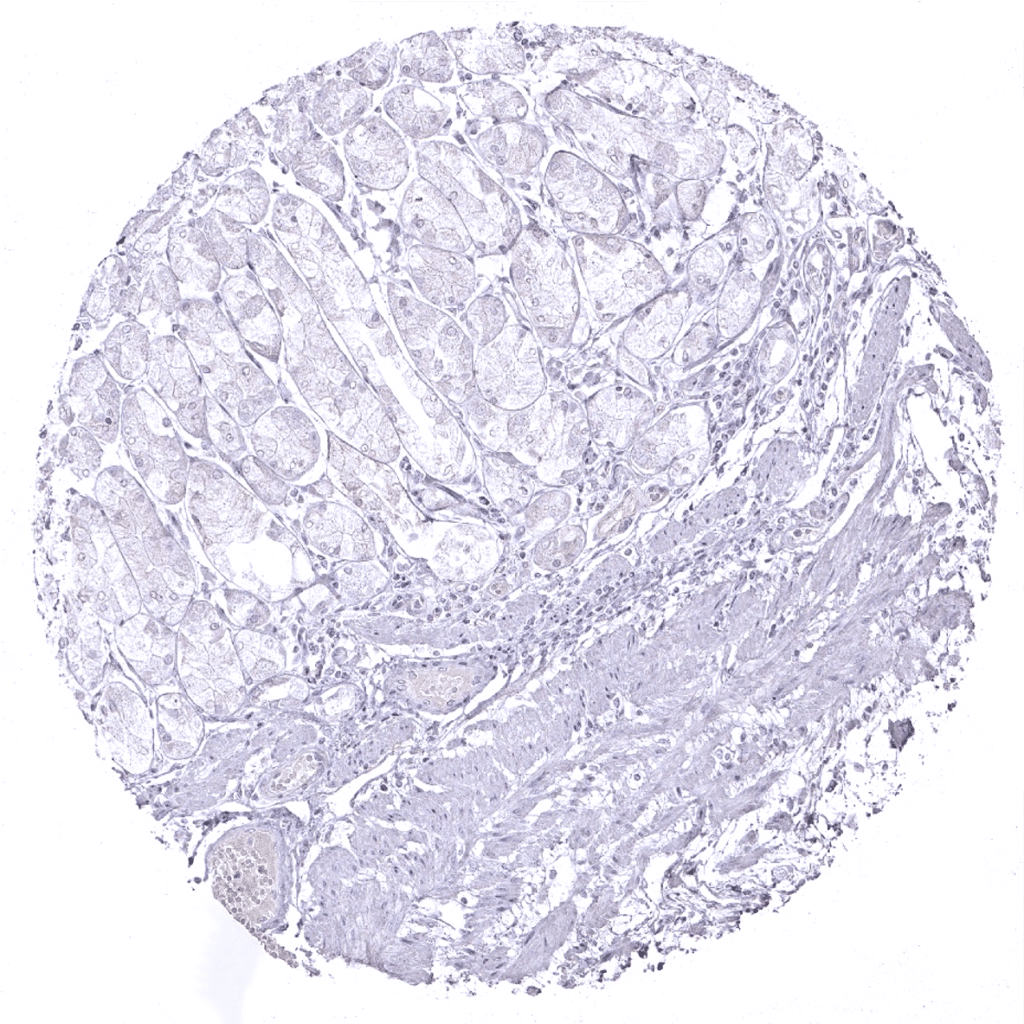
Stomach, corpus
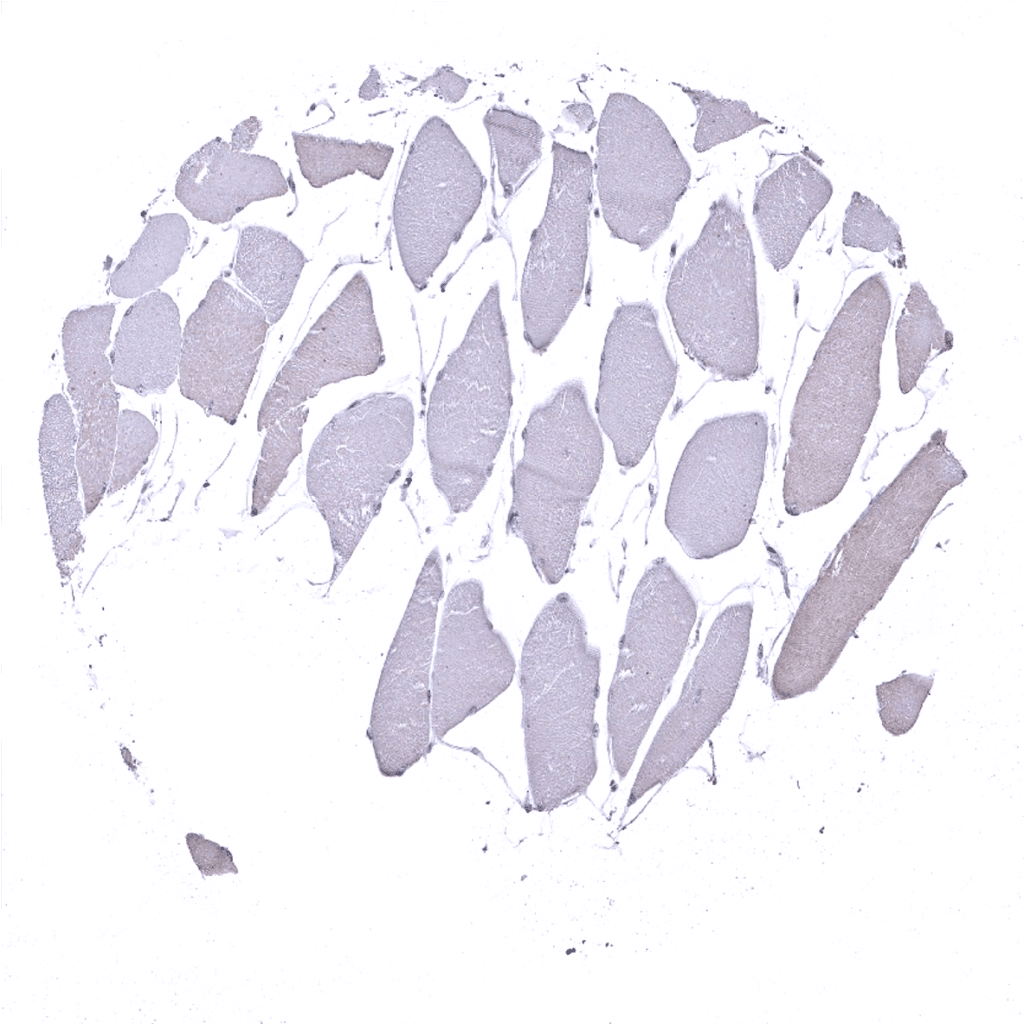
Striated muscle
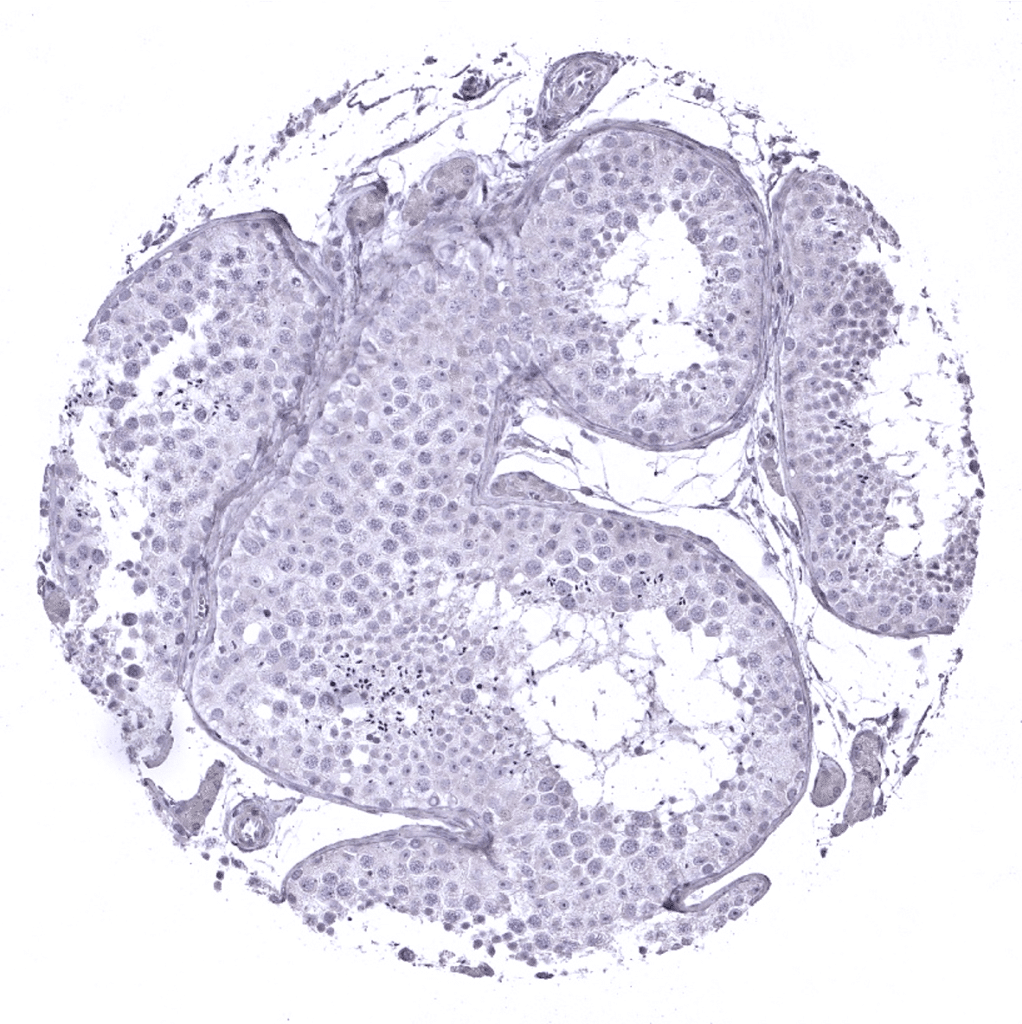
Testis
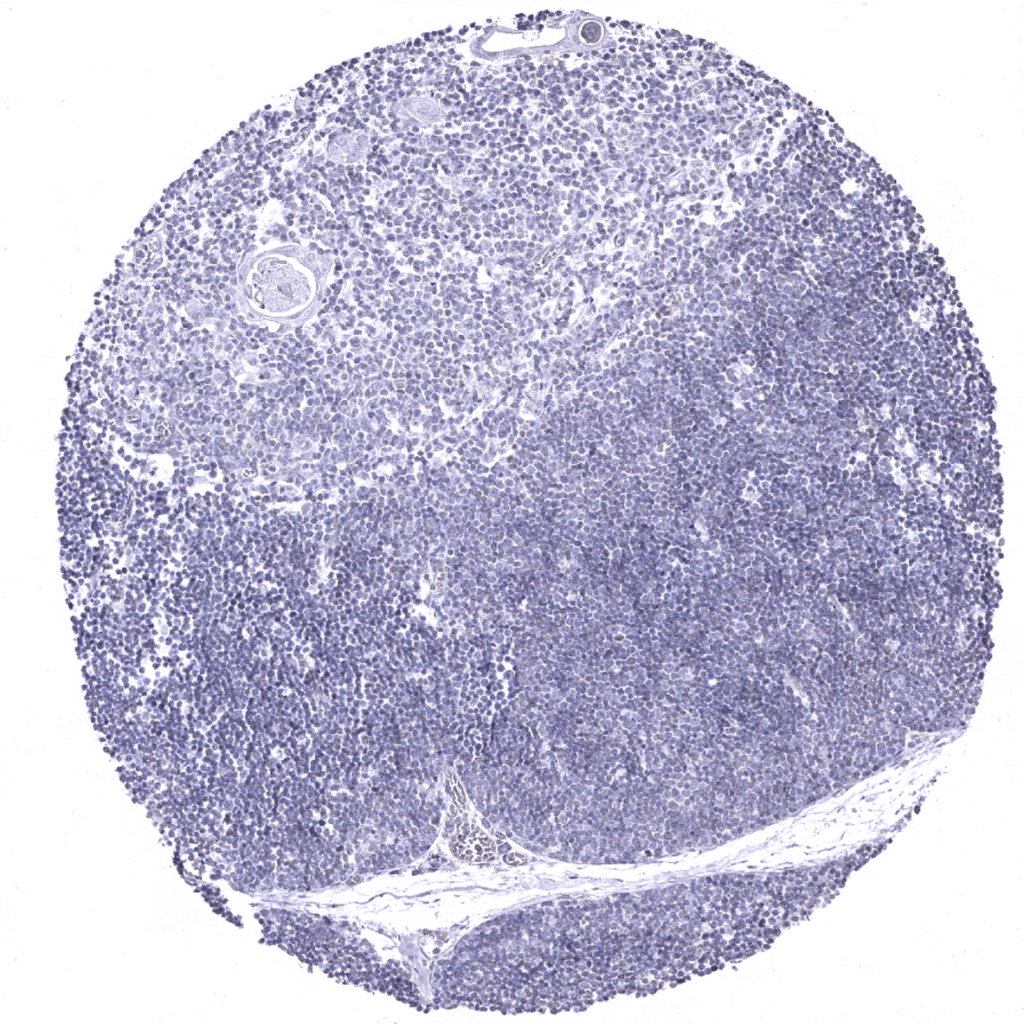
Thymus
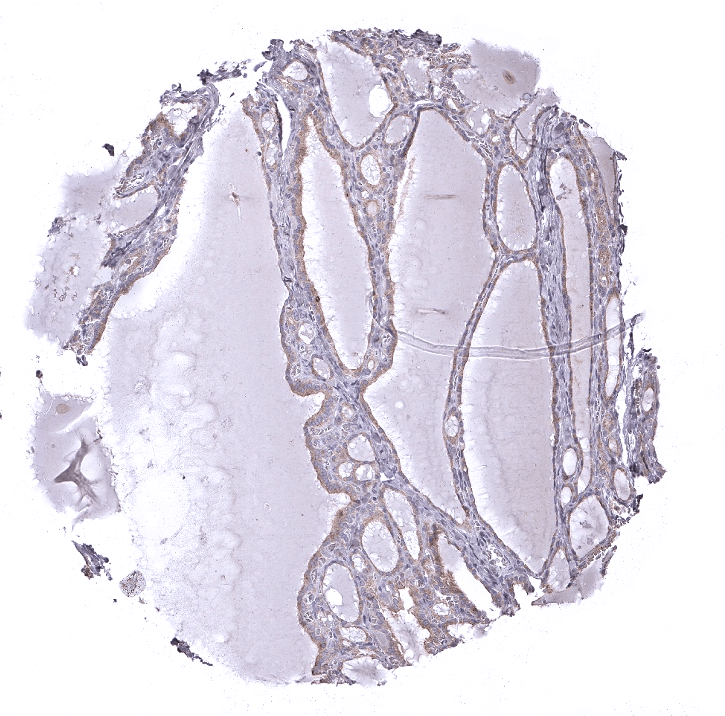
Thyroid gland
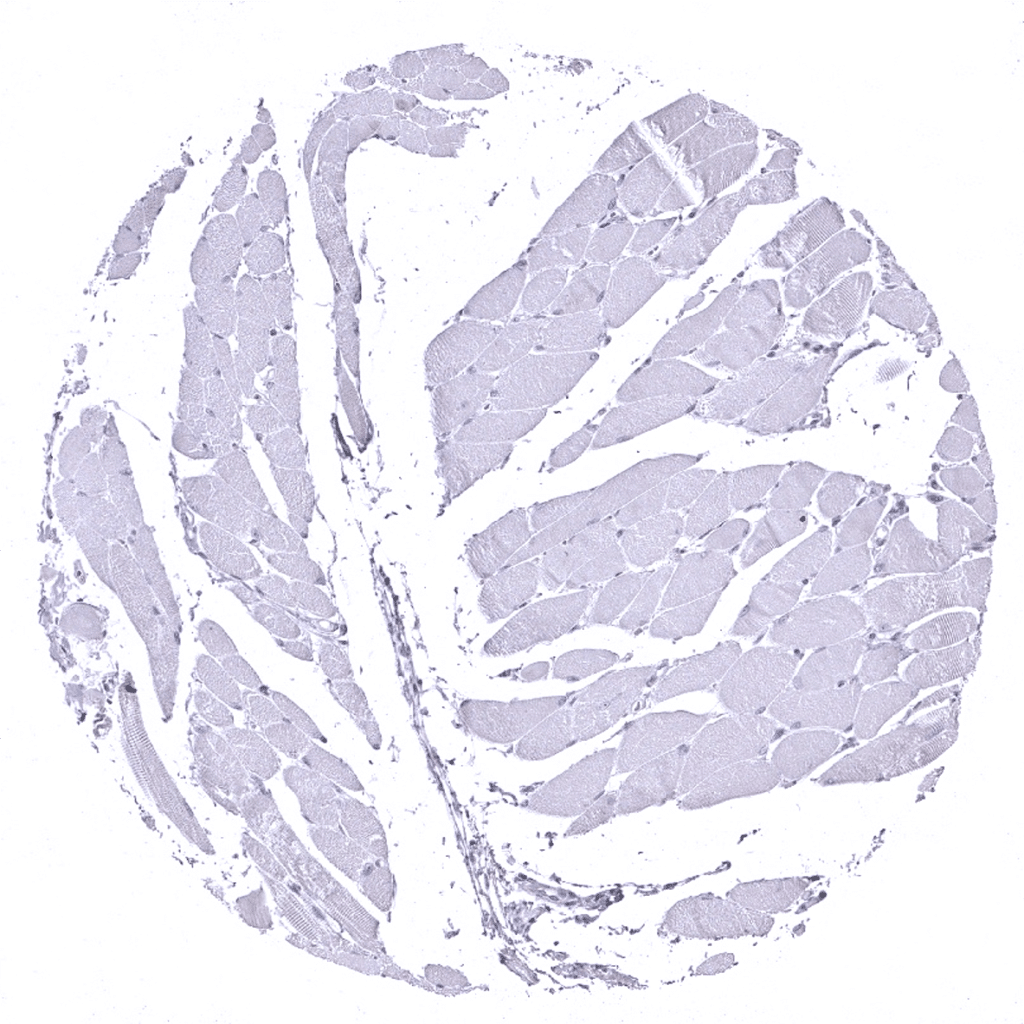
Tongue, muscle
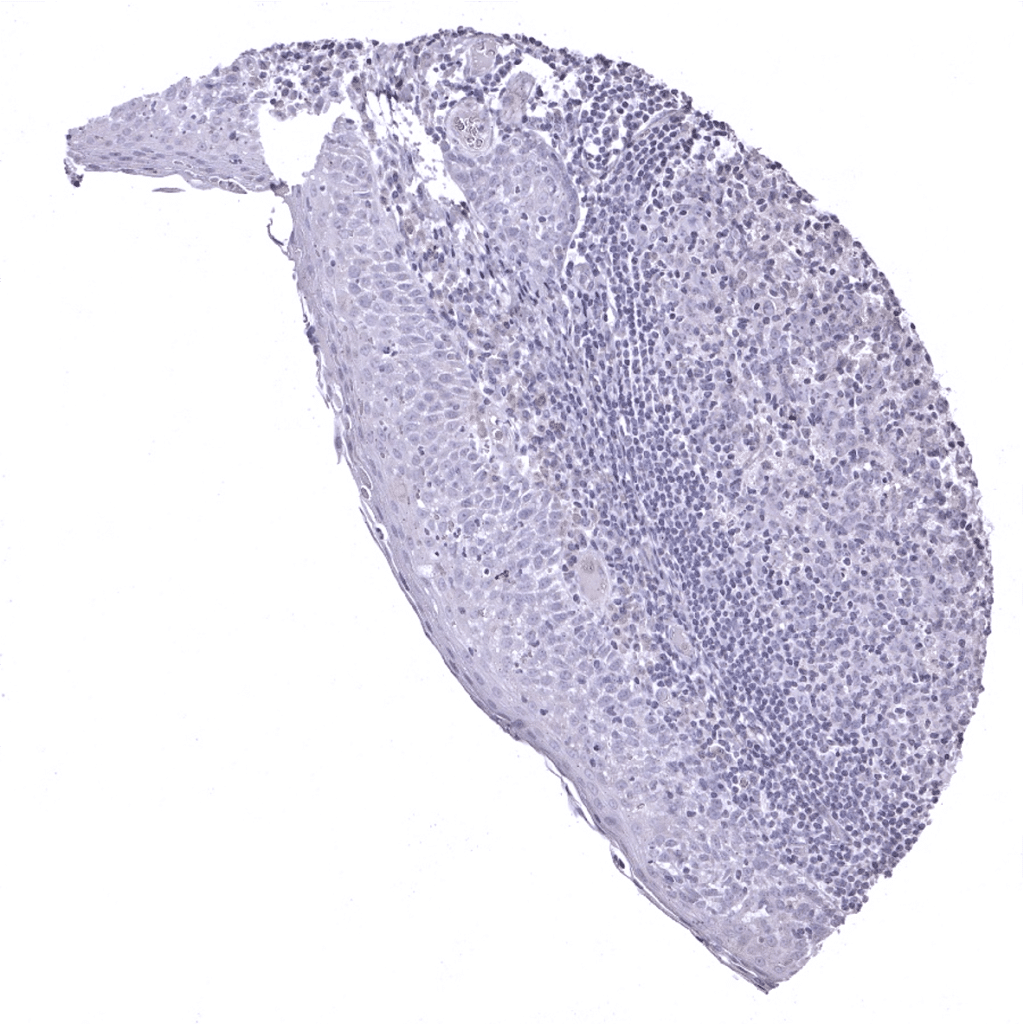
Tonsil, surface epithelium
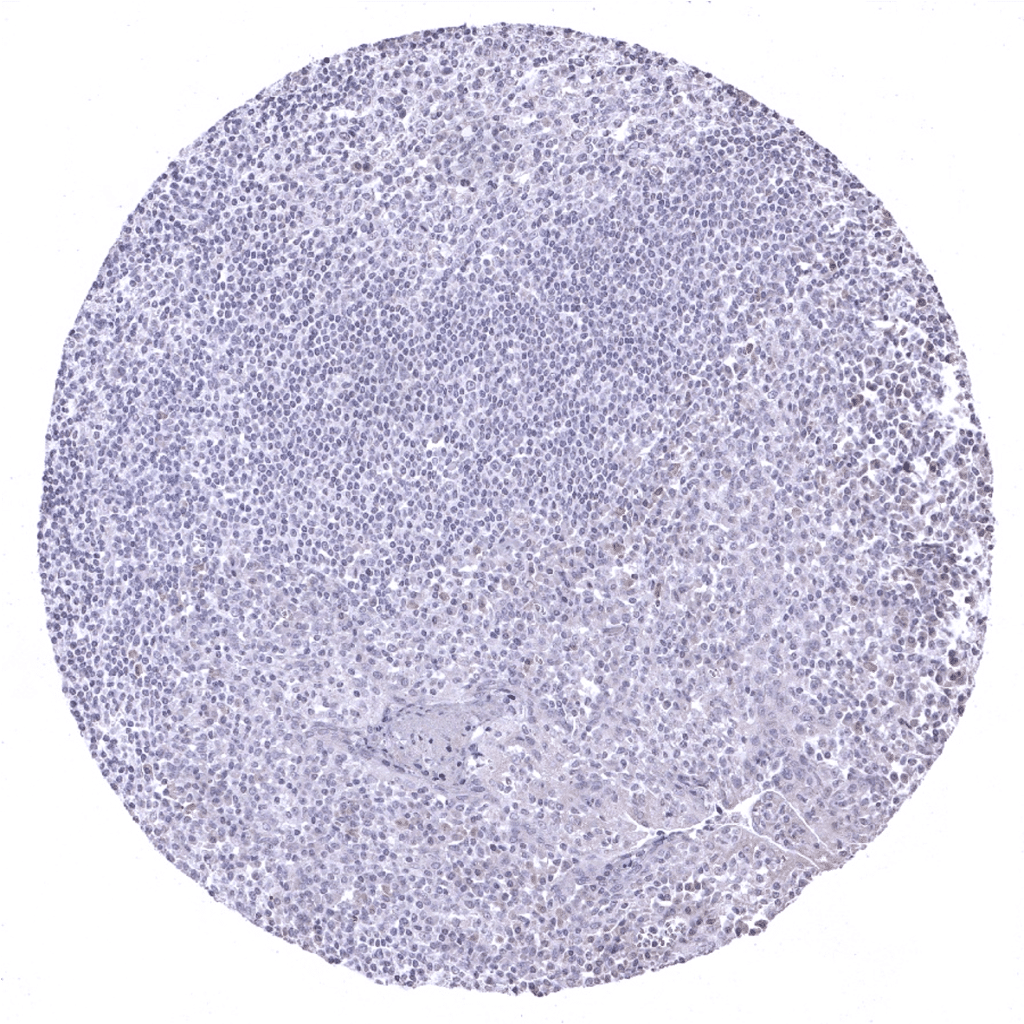
Tonsil
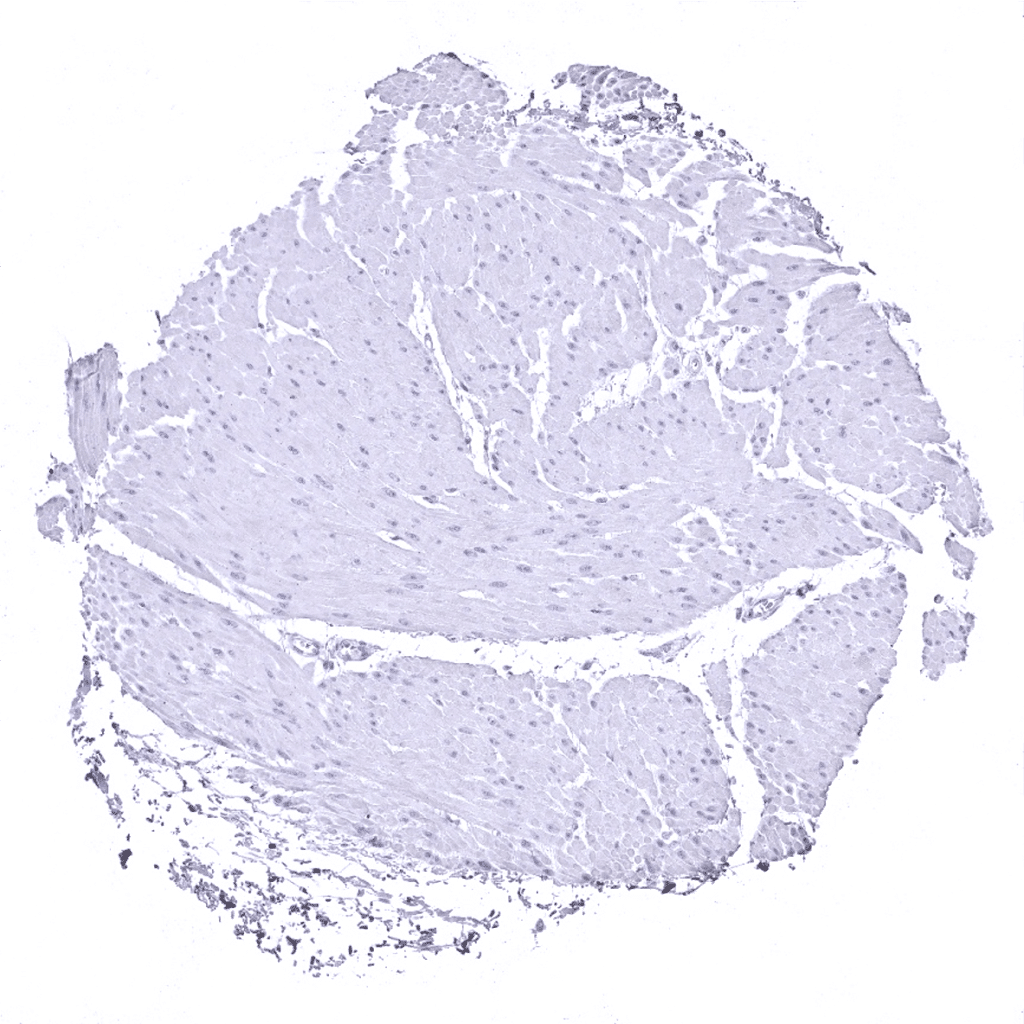
Urinary bladder, muscular wall
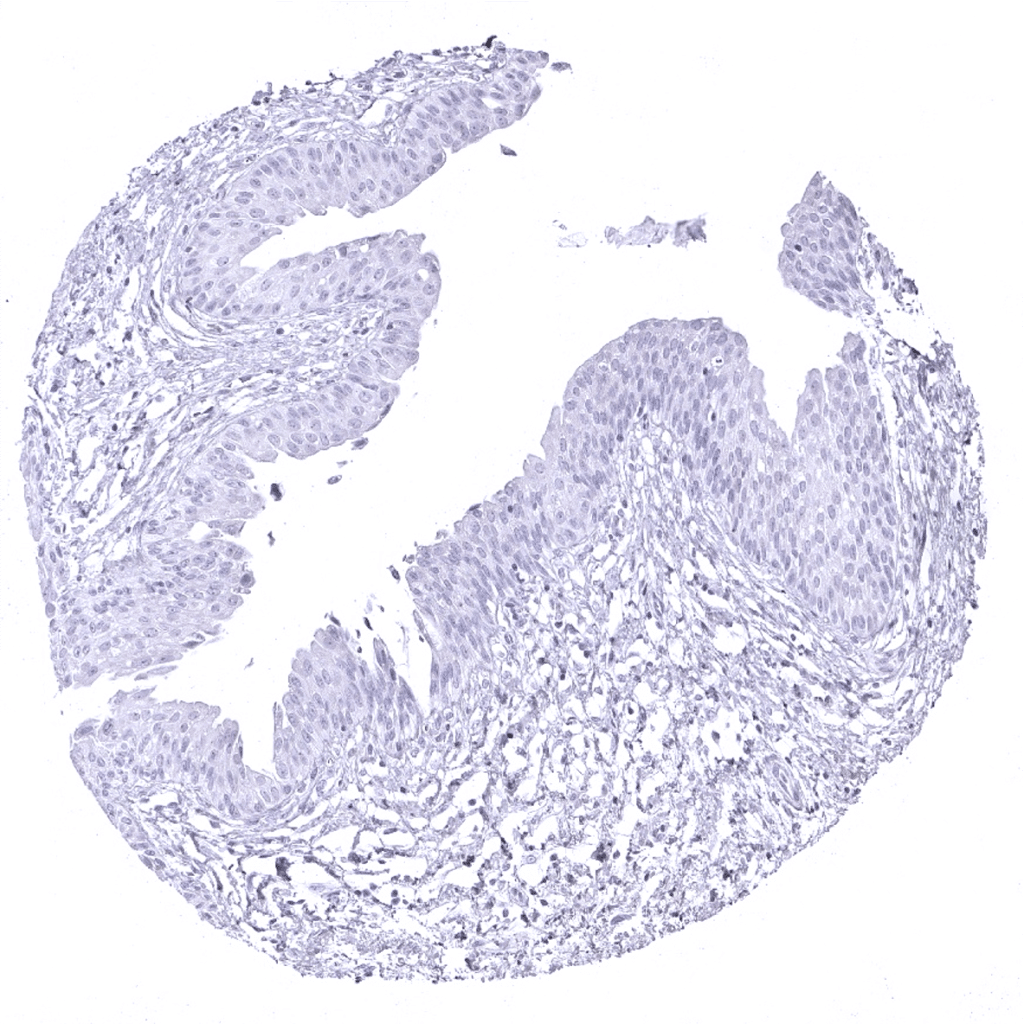
Urinary bladder, urothelium

Uterus, myometrium
