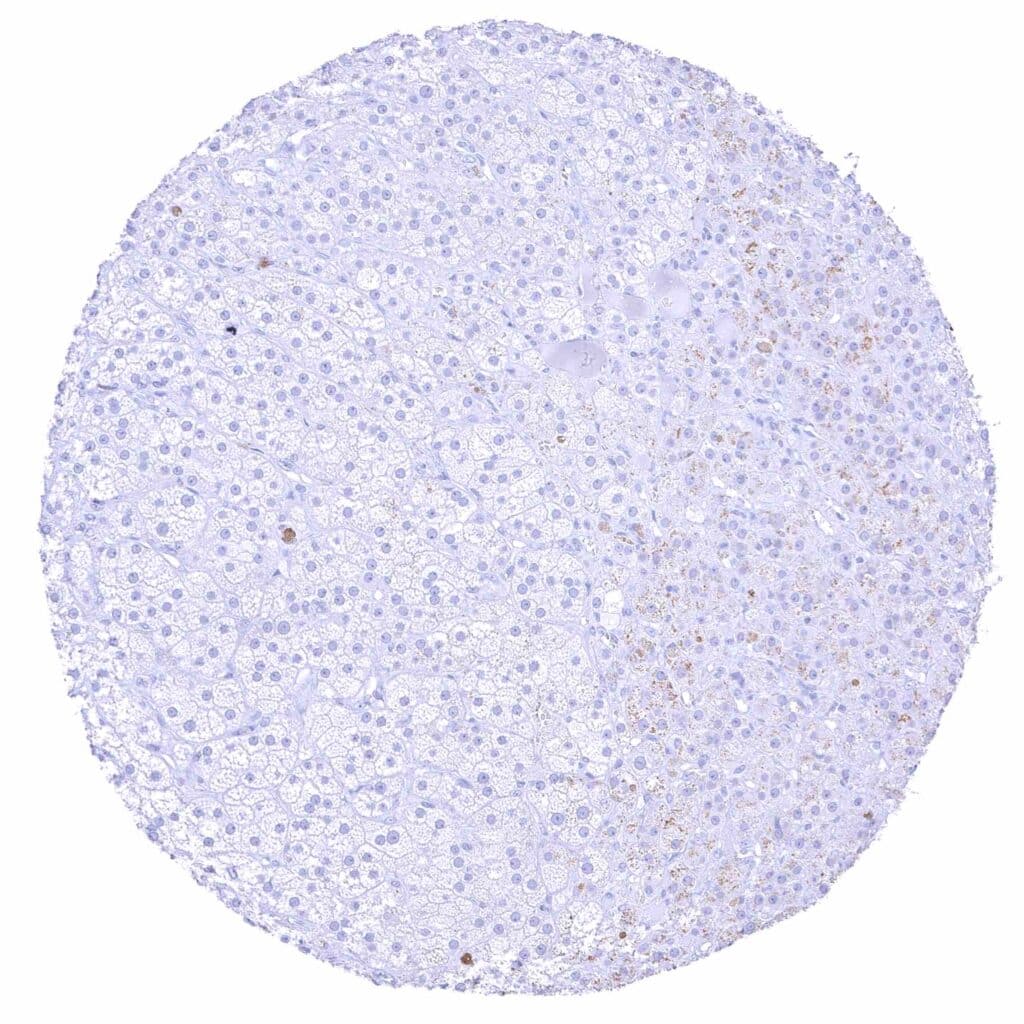
Adrenal gland

Aorta, endothelium
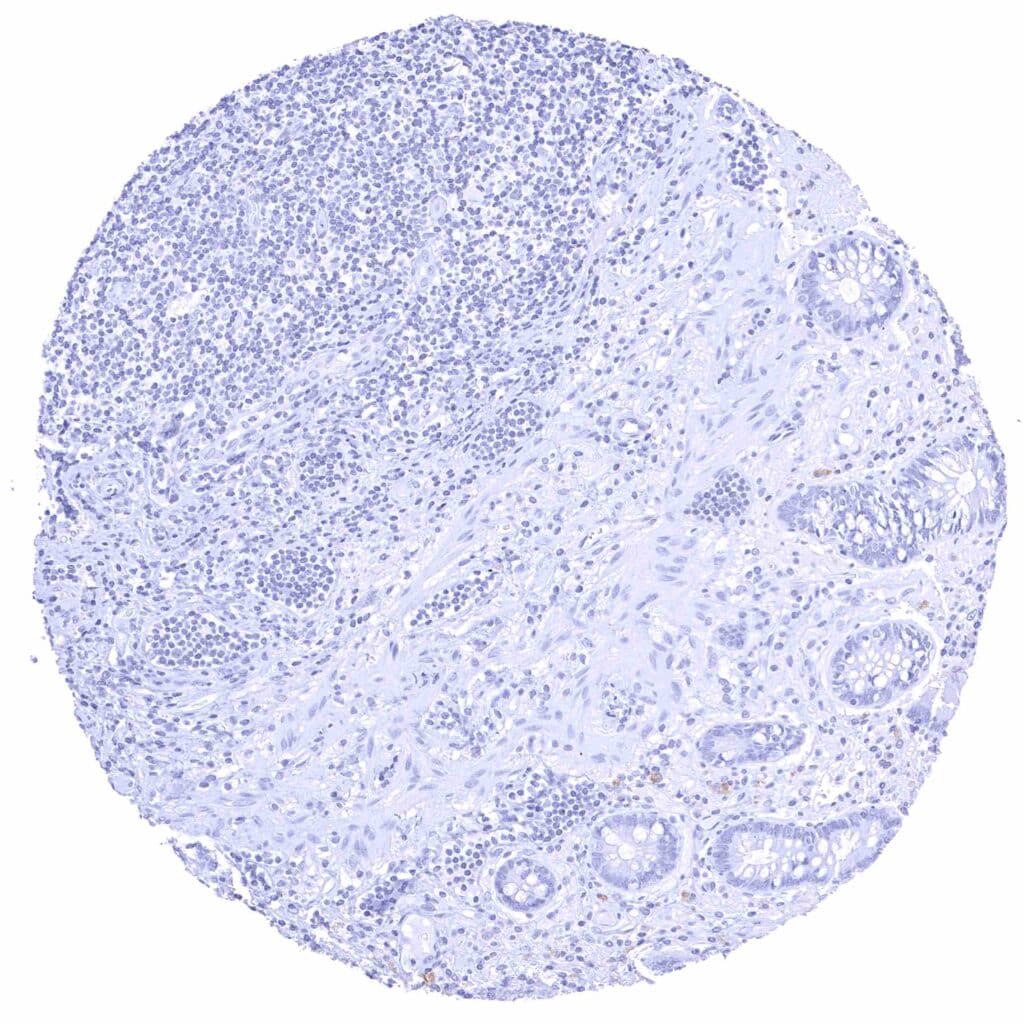
Appendix, mucosa.jpeg
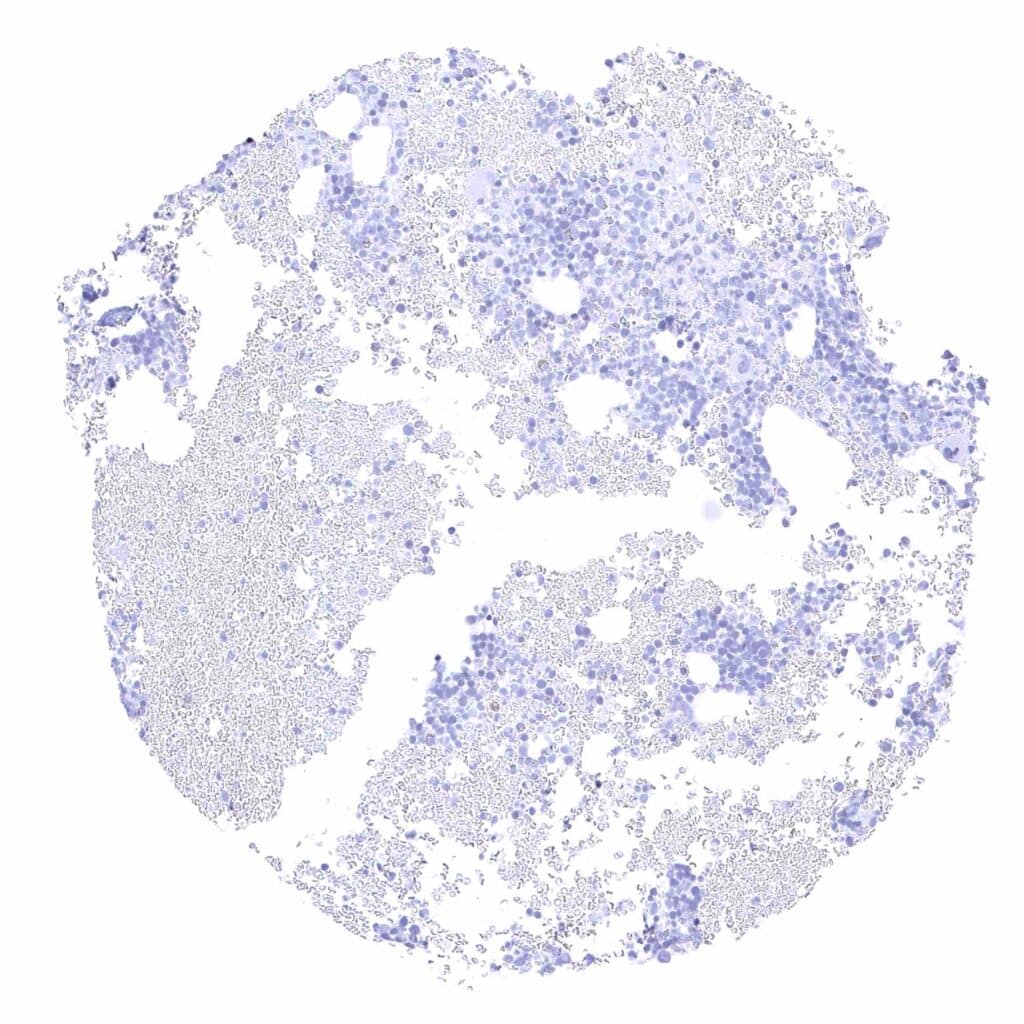
Bone marrow
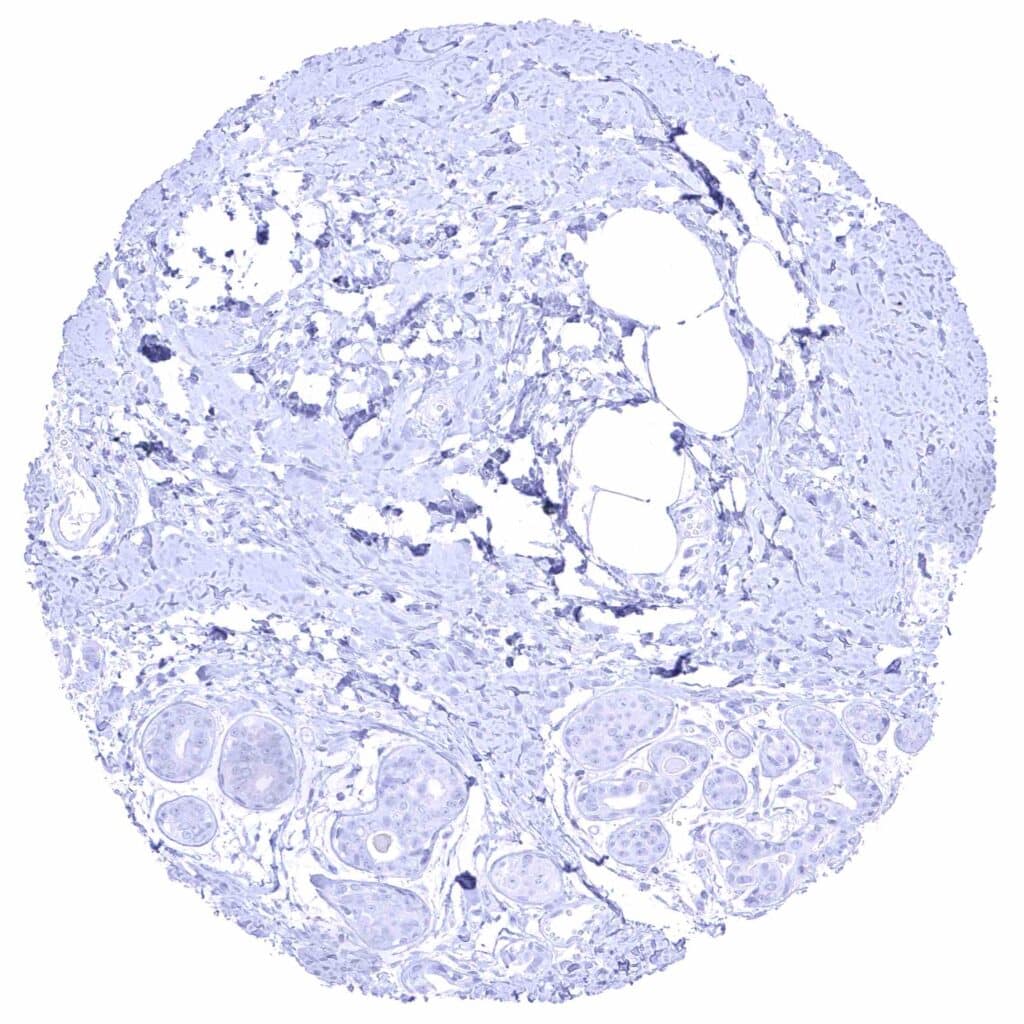
Breast
Bronchus, mucosa
Cerebellum (white matter)
Cerebellum, cortex (molecular layer, Purkinje cell layer, granule cell layer) .jpeg
Cerebrum, grey matter
Cerebrum, white matter.jpeg
Colon descendens, mucosa
Duodenum, Brunner gland
Duodenum, mucosa
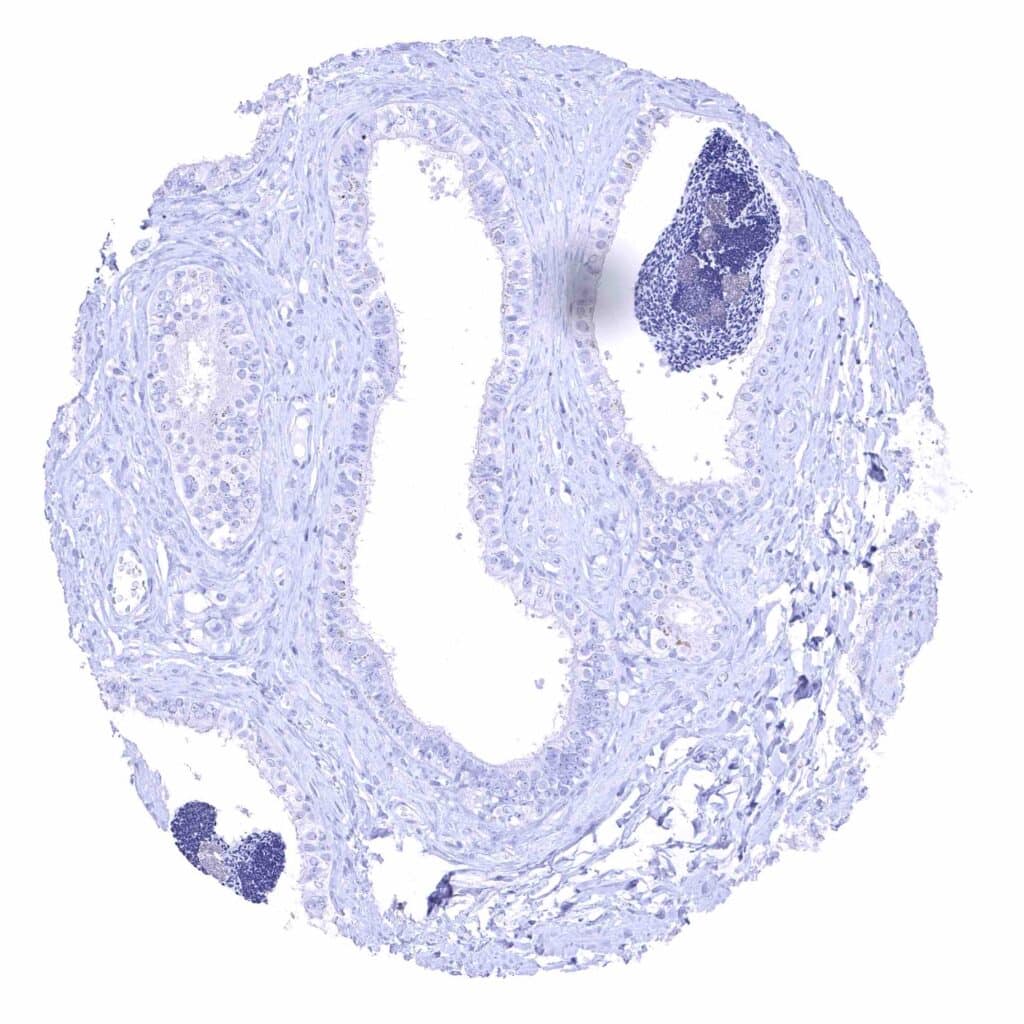
Epididymis (Cauda)
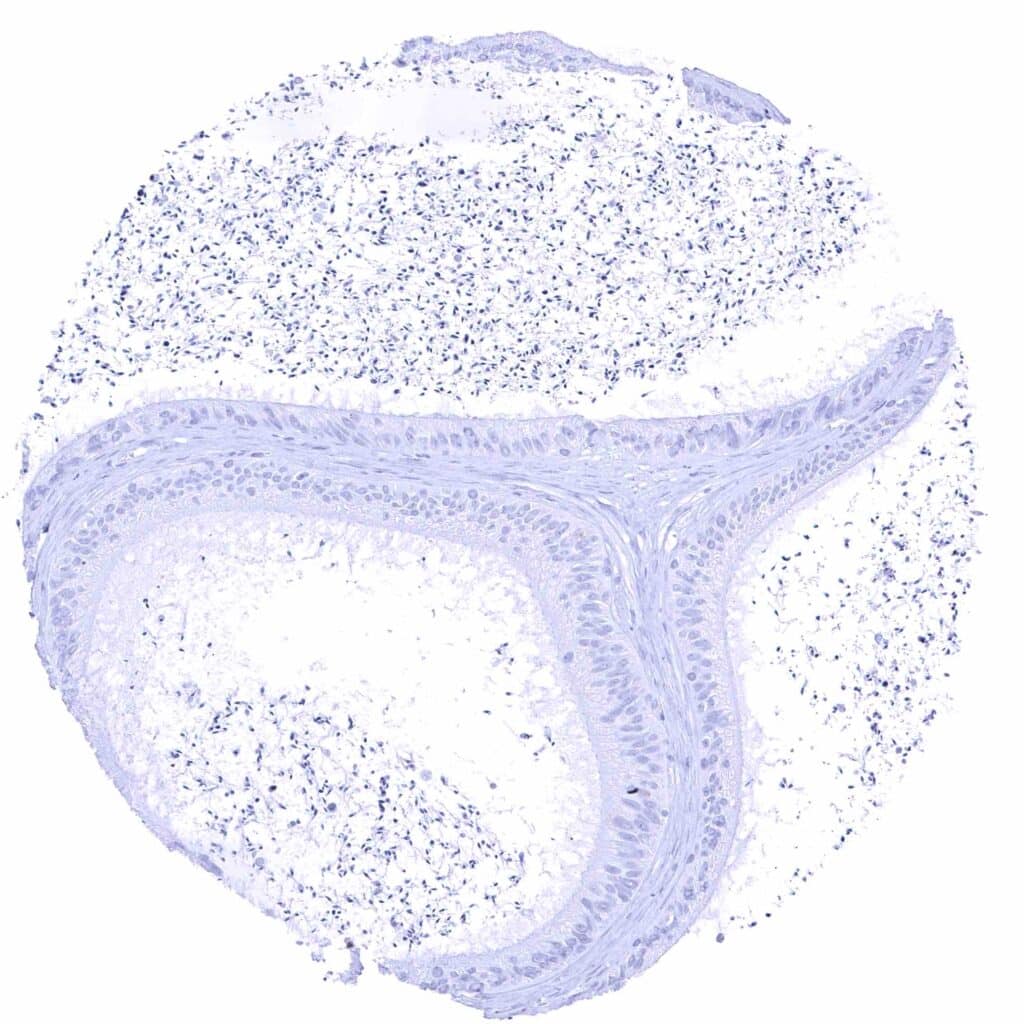
Epididymis (Corpus)
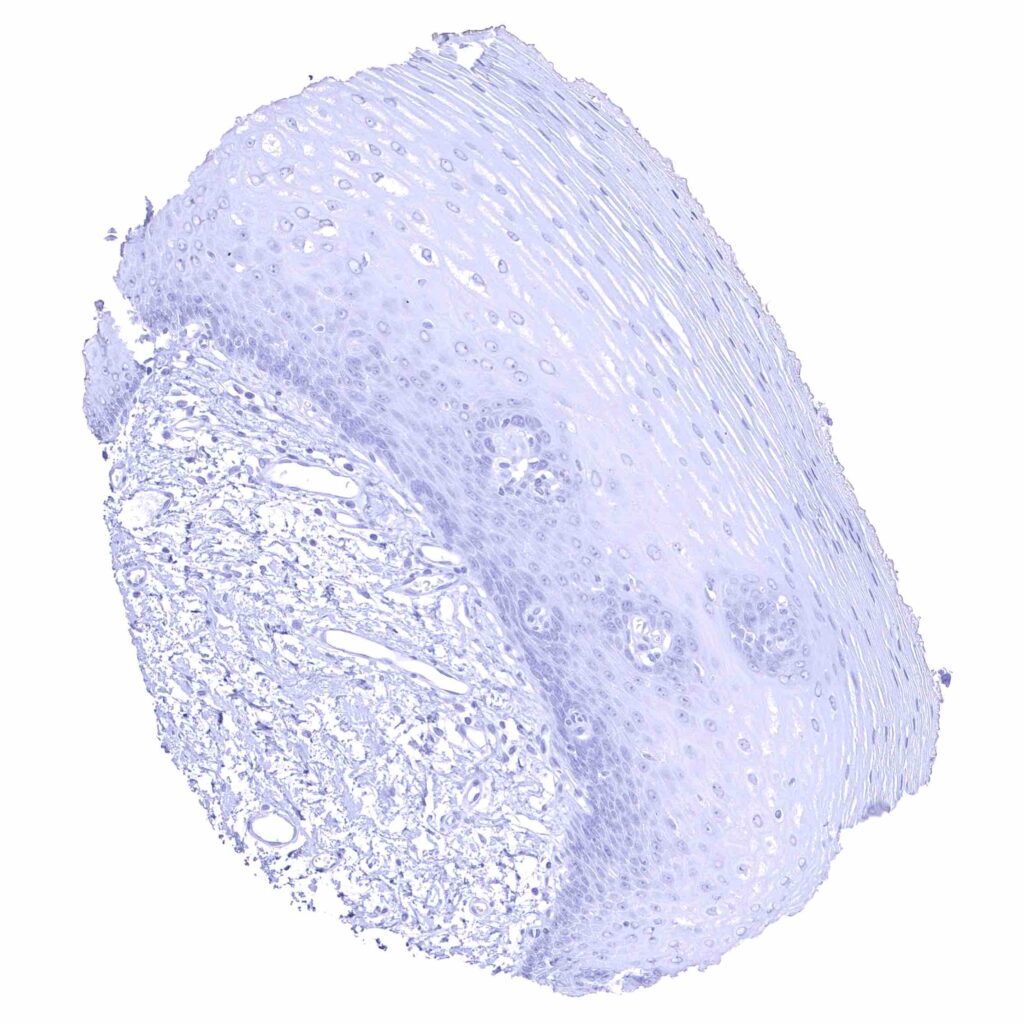
Esophagus, squamous epithelium
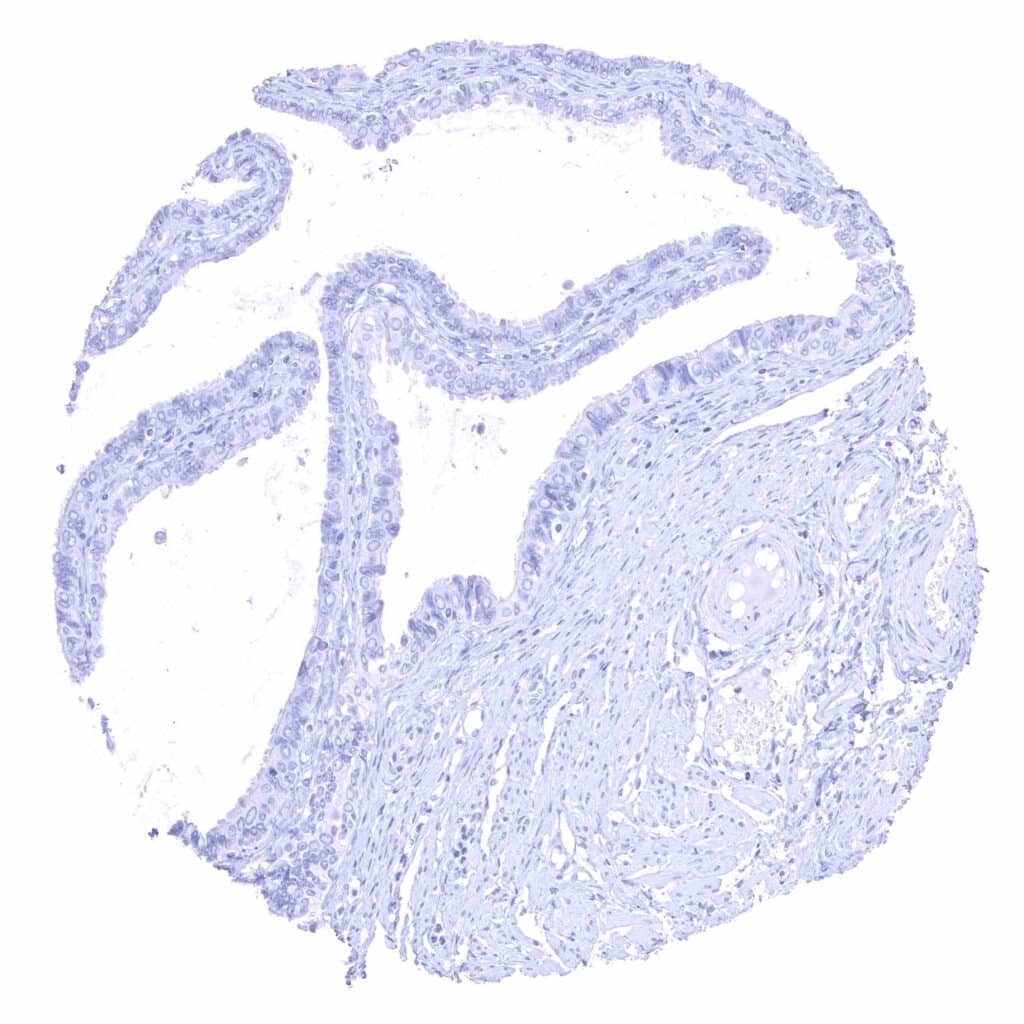
Fallopian tube, mucosa
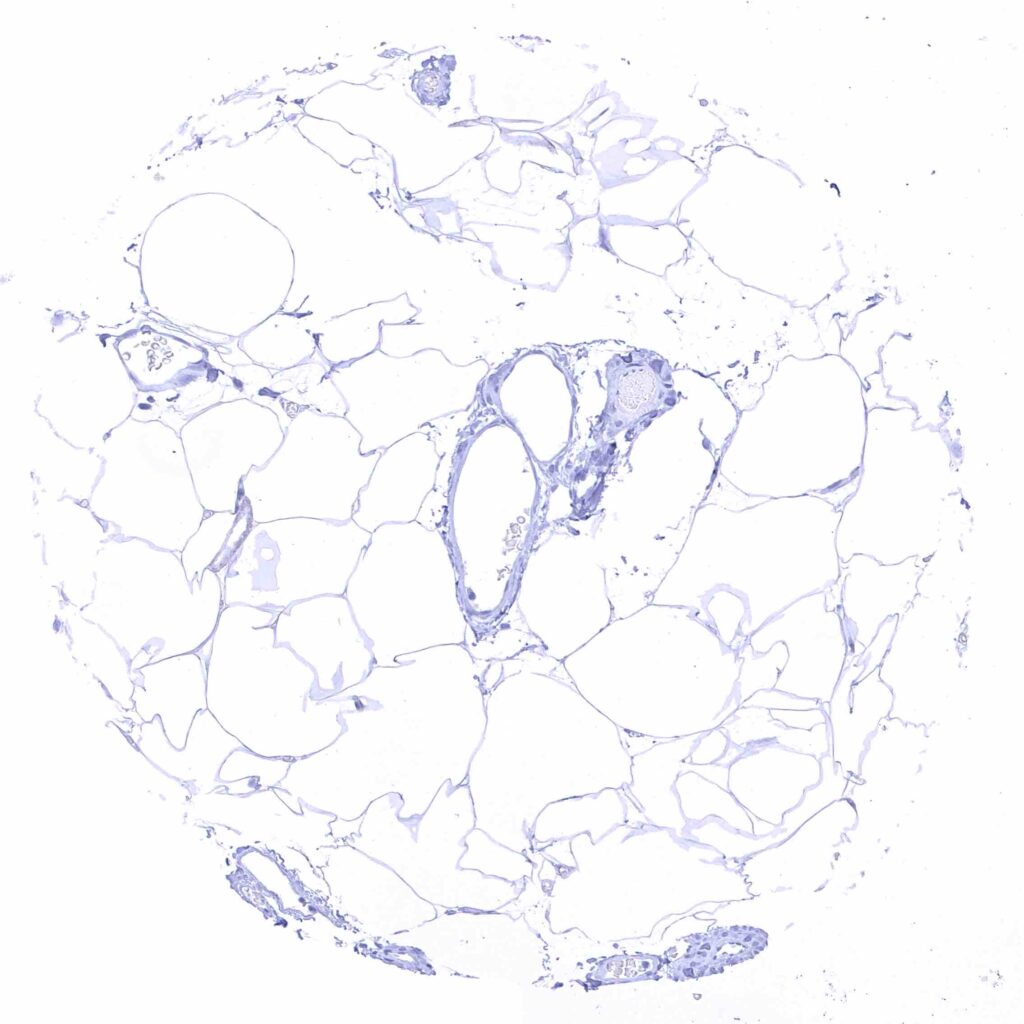
Fat
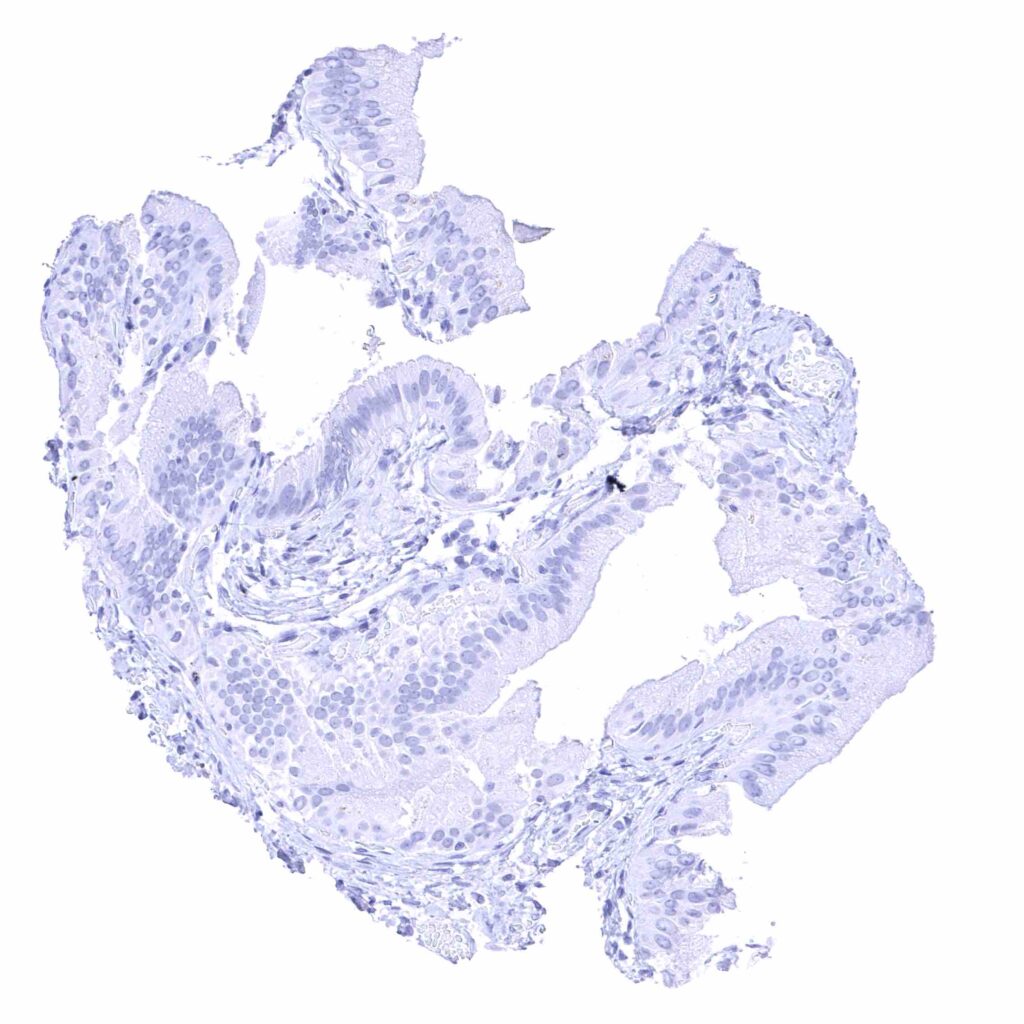
Gallbladder, epithelium
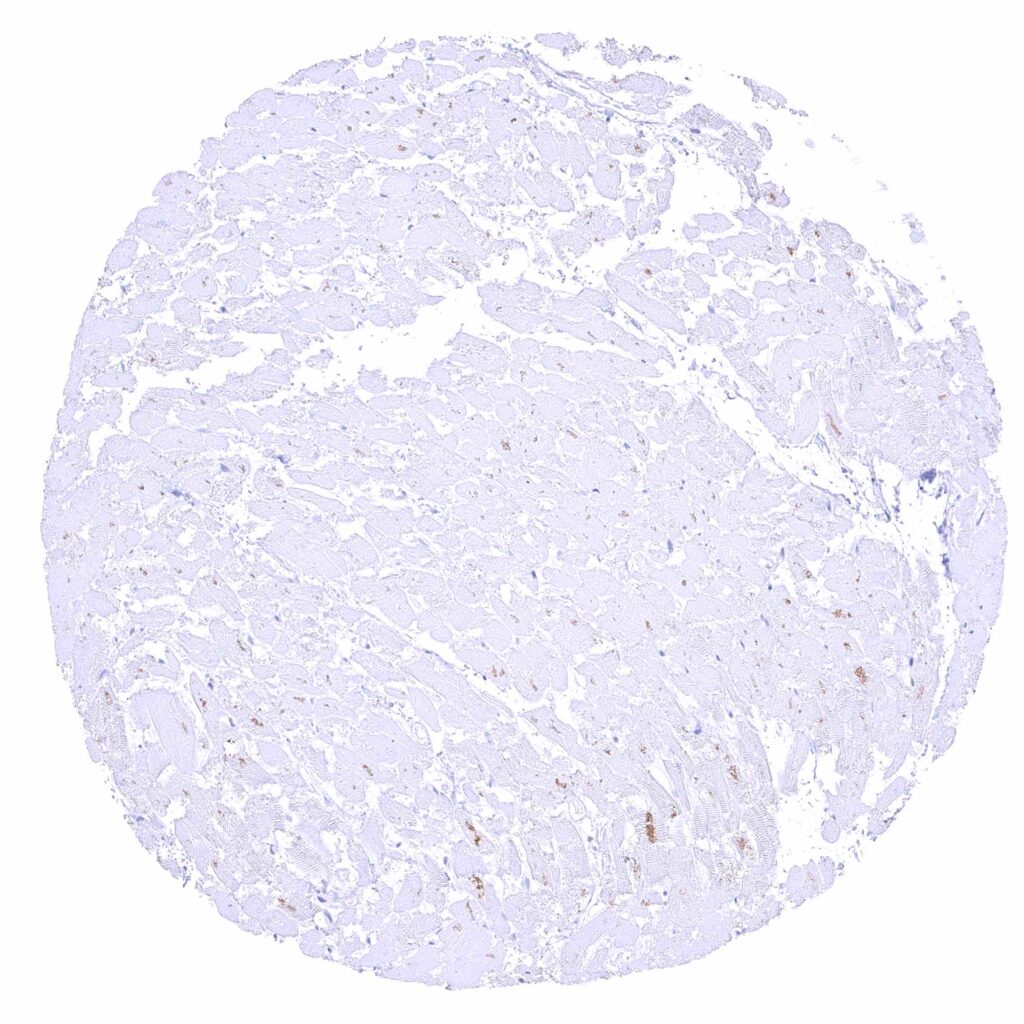
Heart muscle
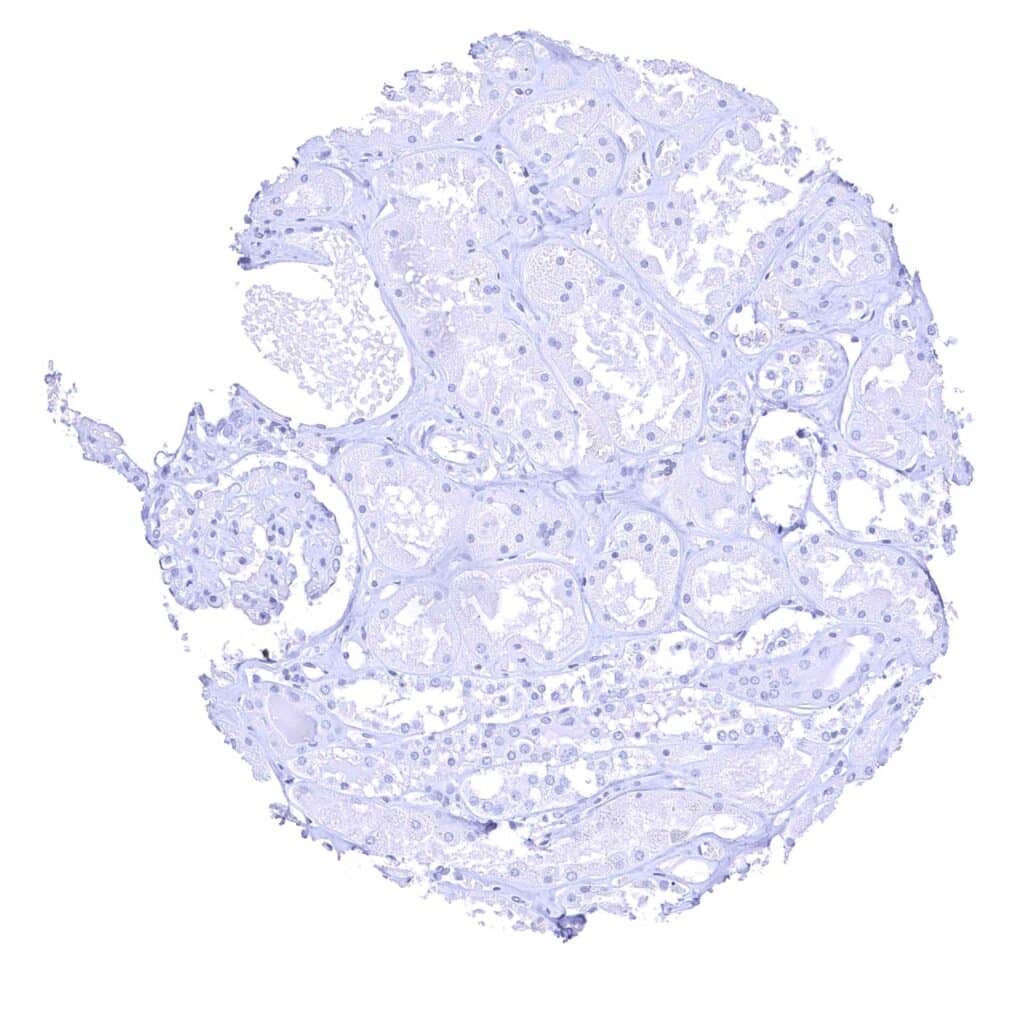
Kidney, cortex
Kidney, medulla
Liver

Lung
Lymph node
Ovary, corpus luteum
Ovary, stroma
Pancreas
Pancreas
Parathyroid gland
Parotid gland
Pituitary gland, anterior lobe
Pituitary gland, posterior lobe
Placenta (amnion and chorion)
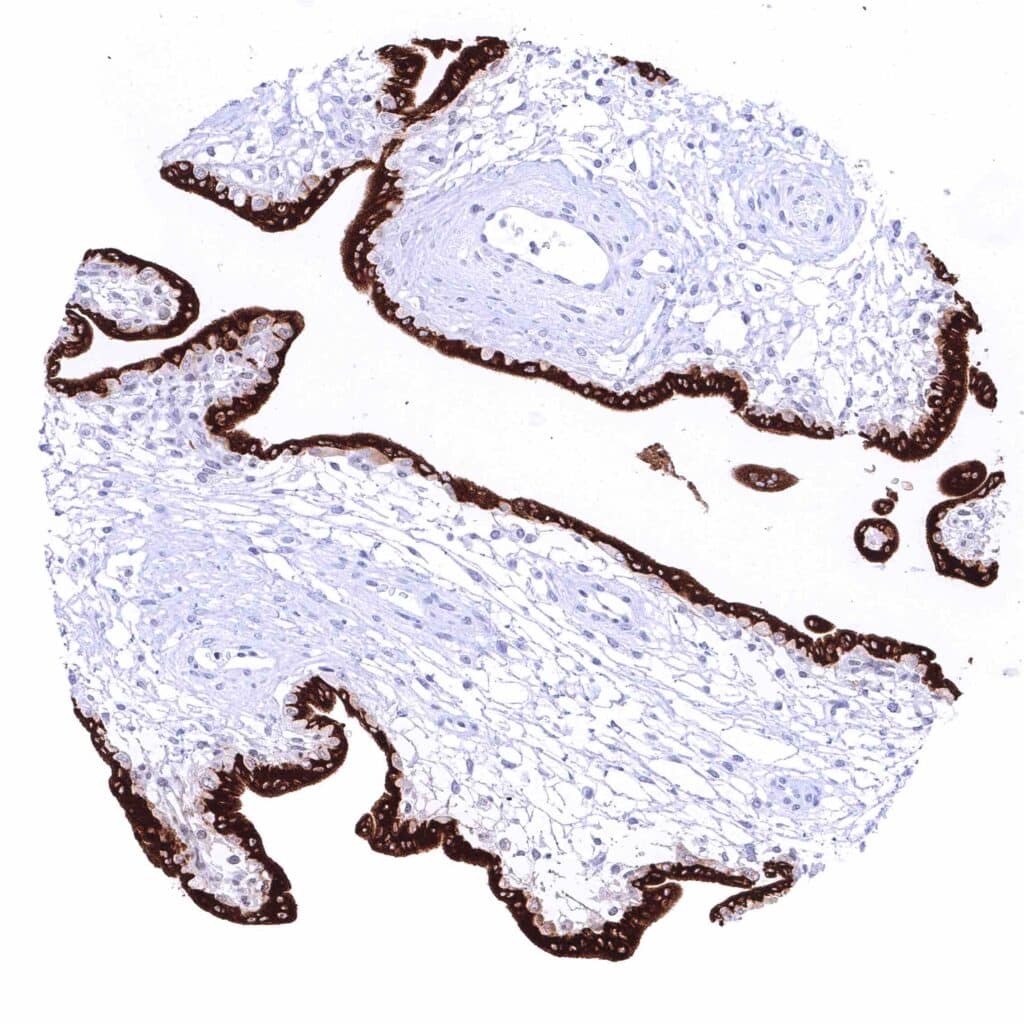
Placenta (first Trimenon) – Intense cytoplasmic KISS1 staining of the syncytiotrophoblast while cytotrophoblast and other cells remain KISS1 negative.
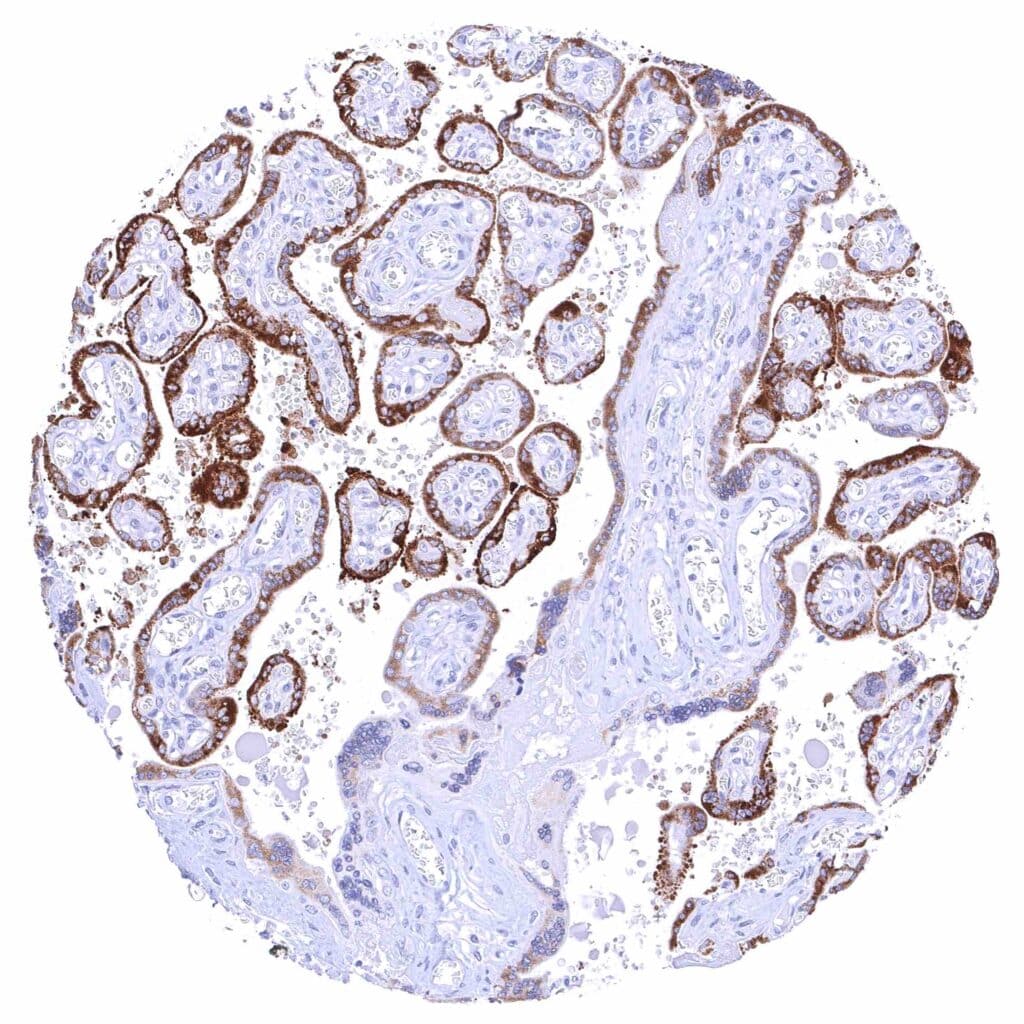
Placenta, mature – Strong cytoplasmic KISS1 staining of most cells of the syncytiotrophoblast.
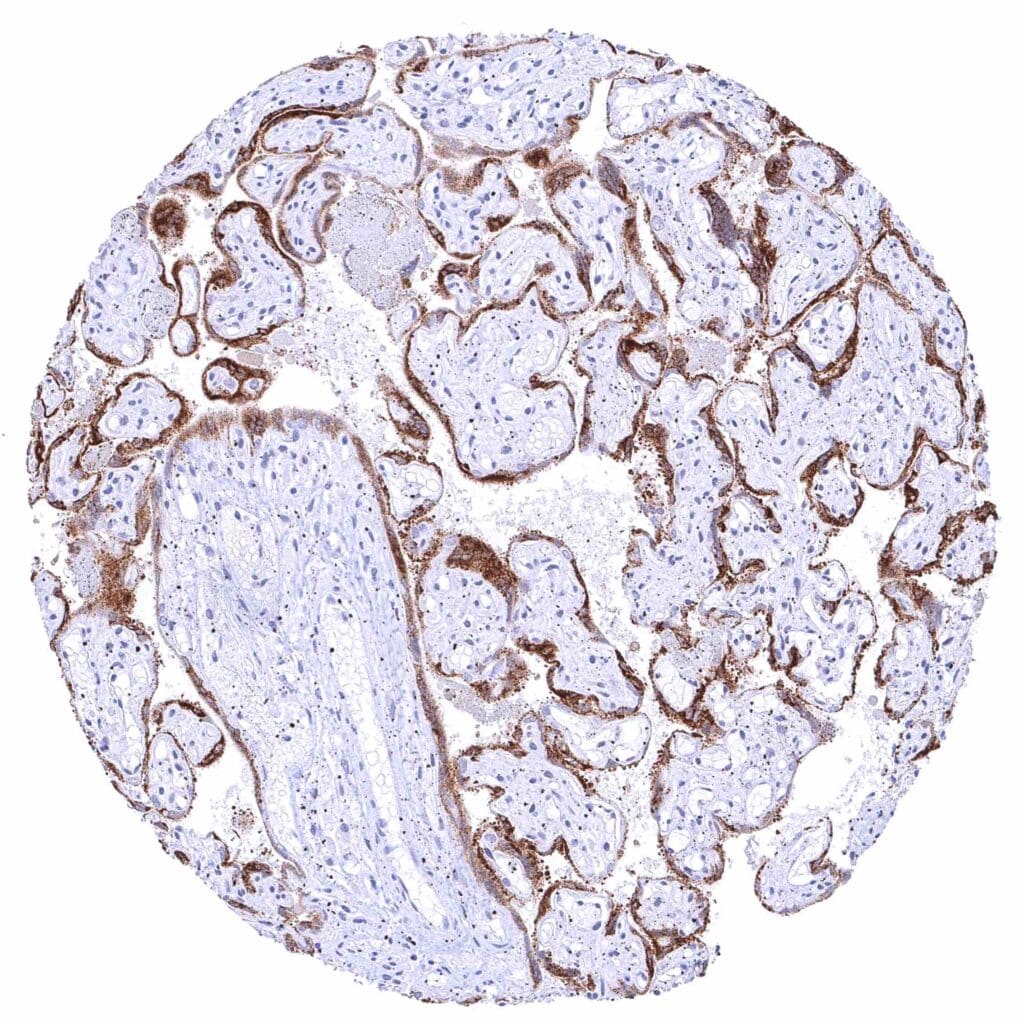
Placenta, mature – Strong cytoplasmic KISS1 staining of the majority of the syncytiotrophoblast cells.
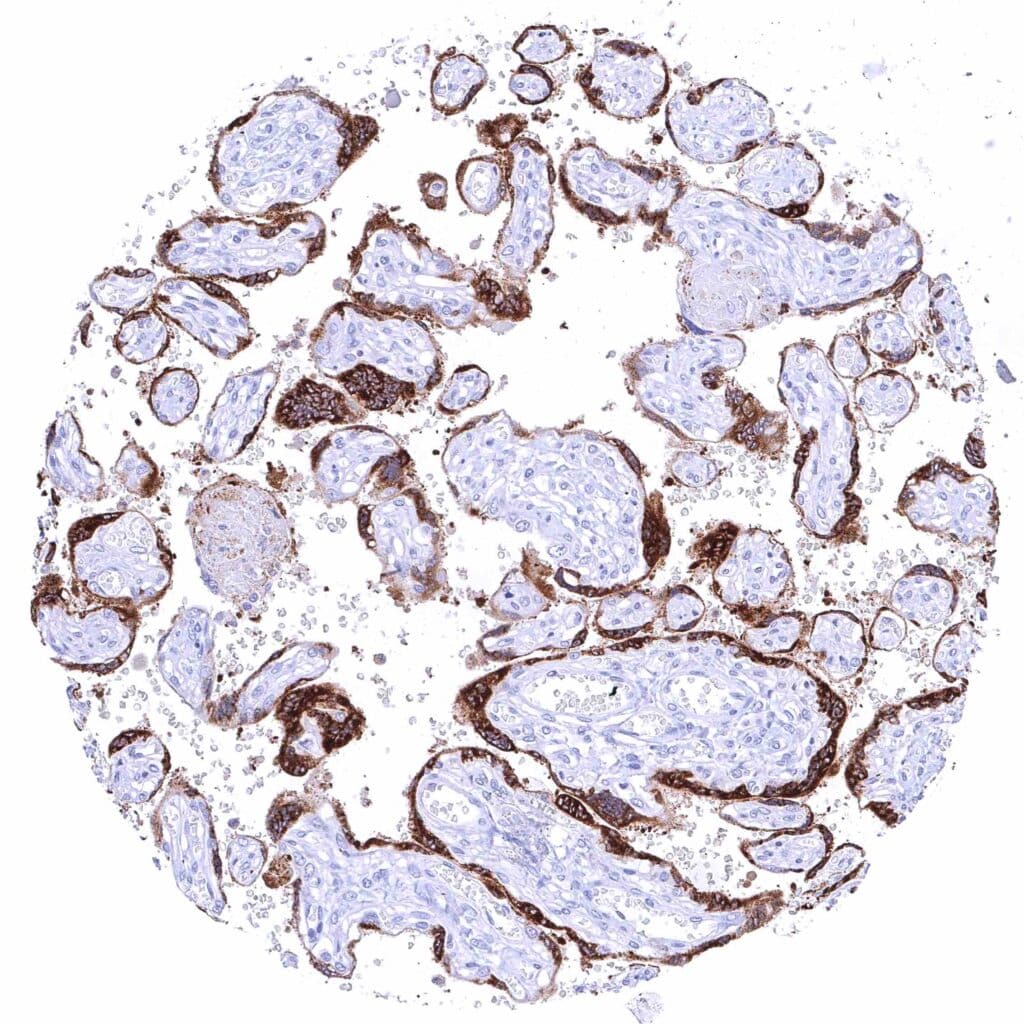
Placenta, mature – Strong cytoplasmic KISS1 staining of the syncytiotrophoblast.
Prostate
Rectum, mucosa
Seminal vesicle
Skeletal muscle
Skin, sebaceous gland
Skin
Spleen
Stomach, antrum
Stomach, corpus
Stomach, muscular wall
Submandibular gland
Testis
Thymus
Thyroid gland
Tonsil, surface epithelium
Tonsil
Urinary bladder, muscular wall
Urinary bladder, urothelium
Uterus, endocervix
Uterus, endometrium (pregnancy)
Uterus, endometrium (proliferation).jpeg
Uterus, endometrium (secretion)
Uterus, myometrium
