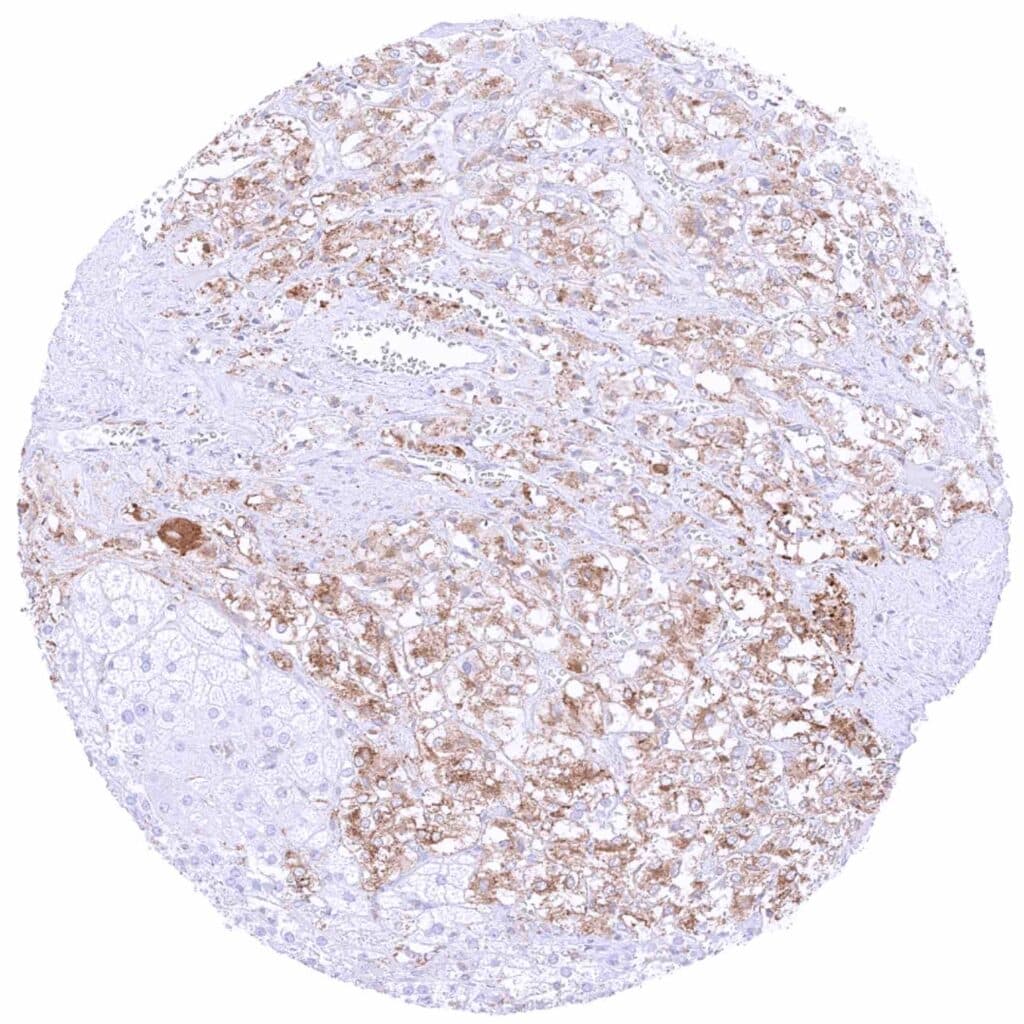
Adrenal gland – Moderate MX1 staining of medullary cells. Adrenocortical cells are MX1 negative
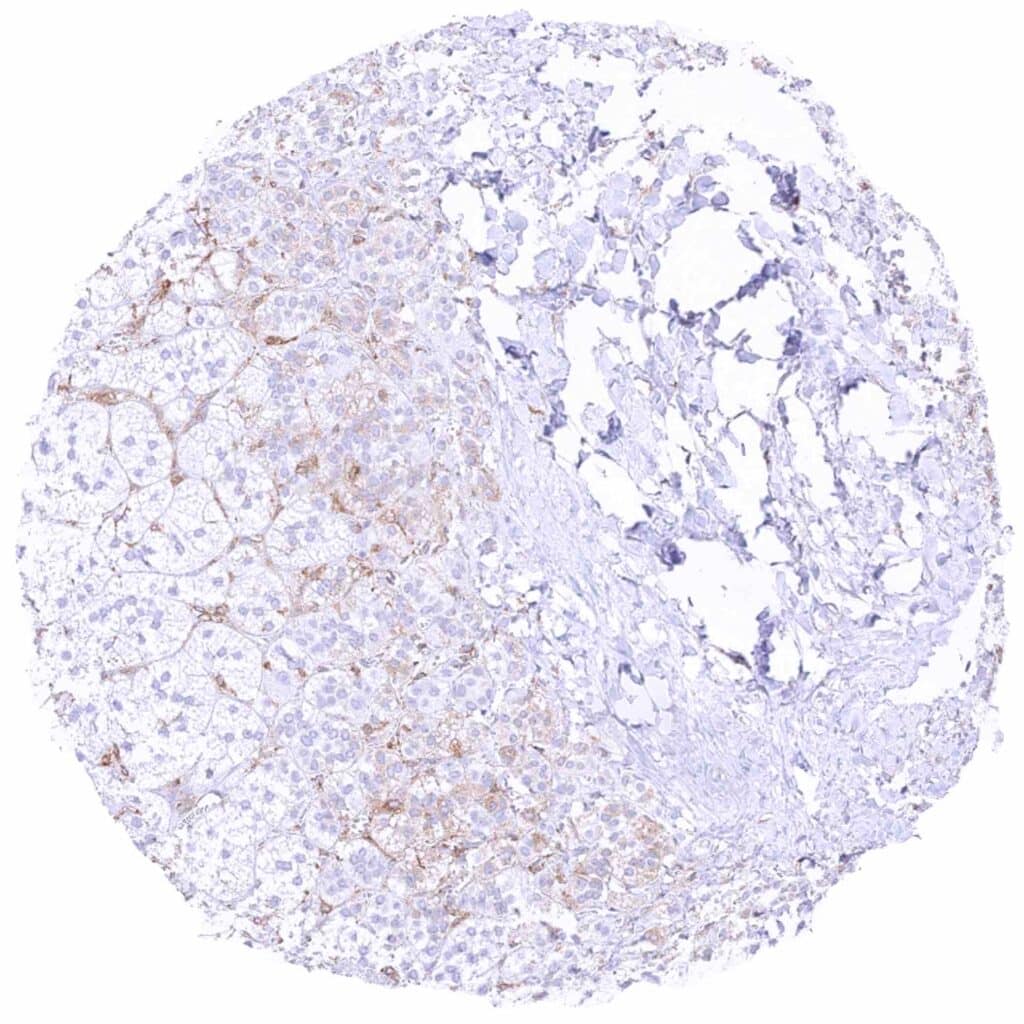
Adrenal gland – Very weak cytoplasmic MX1 staining of some adrenocortical cells. Moderate staining of endothelial cells
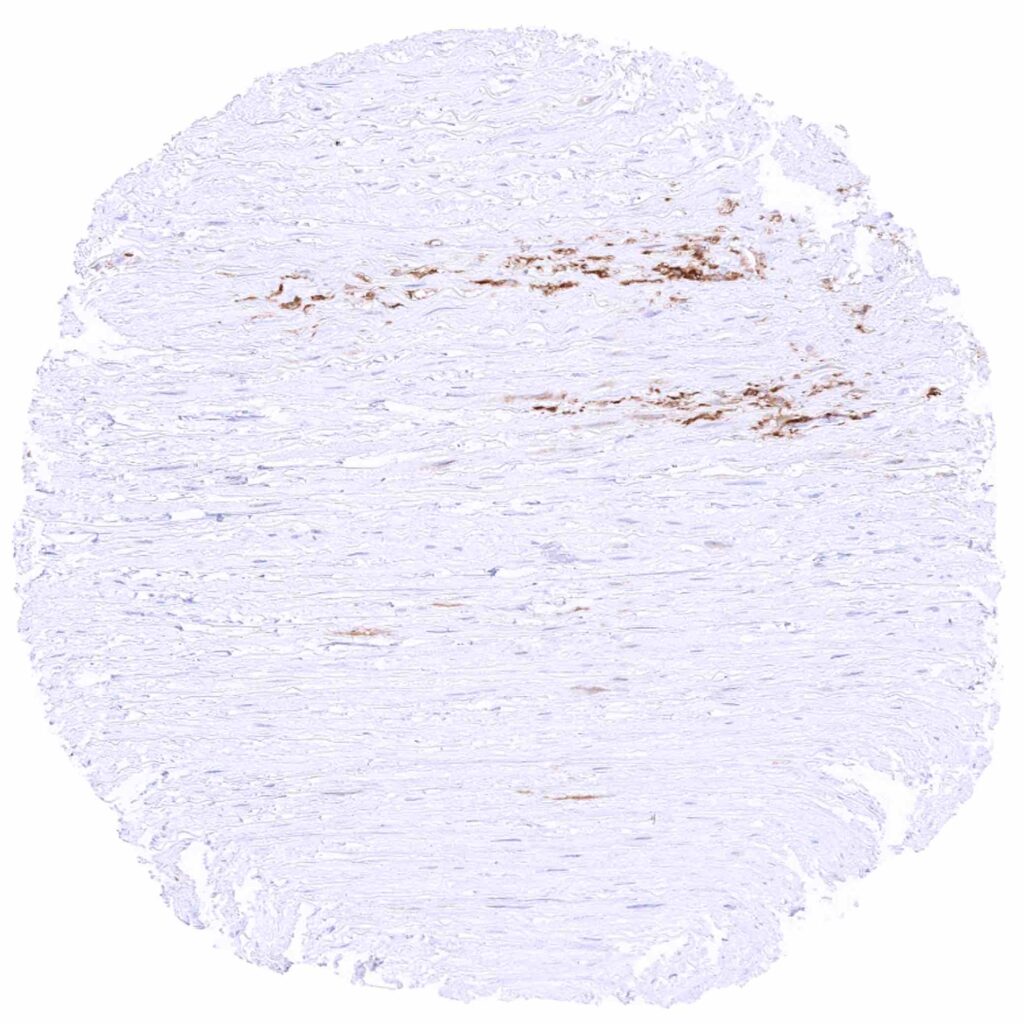
Aorta, media – MX1 positive material can be seen in this sample
Aorta, media
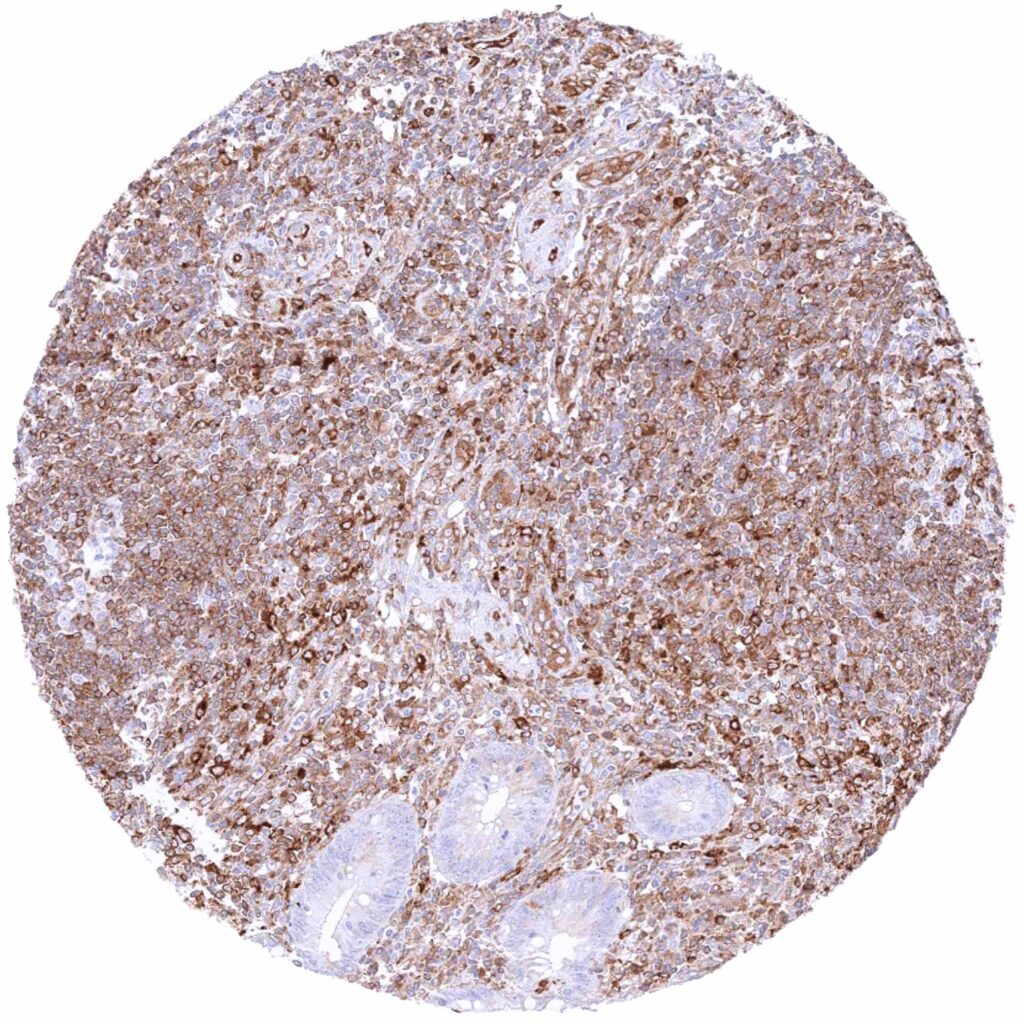
Appendix, mucosa – Abundant cytoplasmic MX1 staining of lymphocytic cells. Crypt epithelial cells are MX1 negative
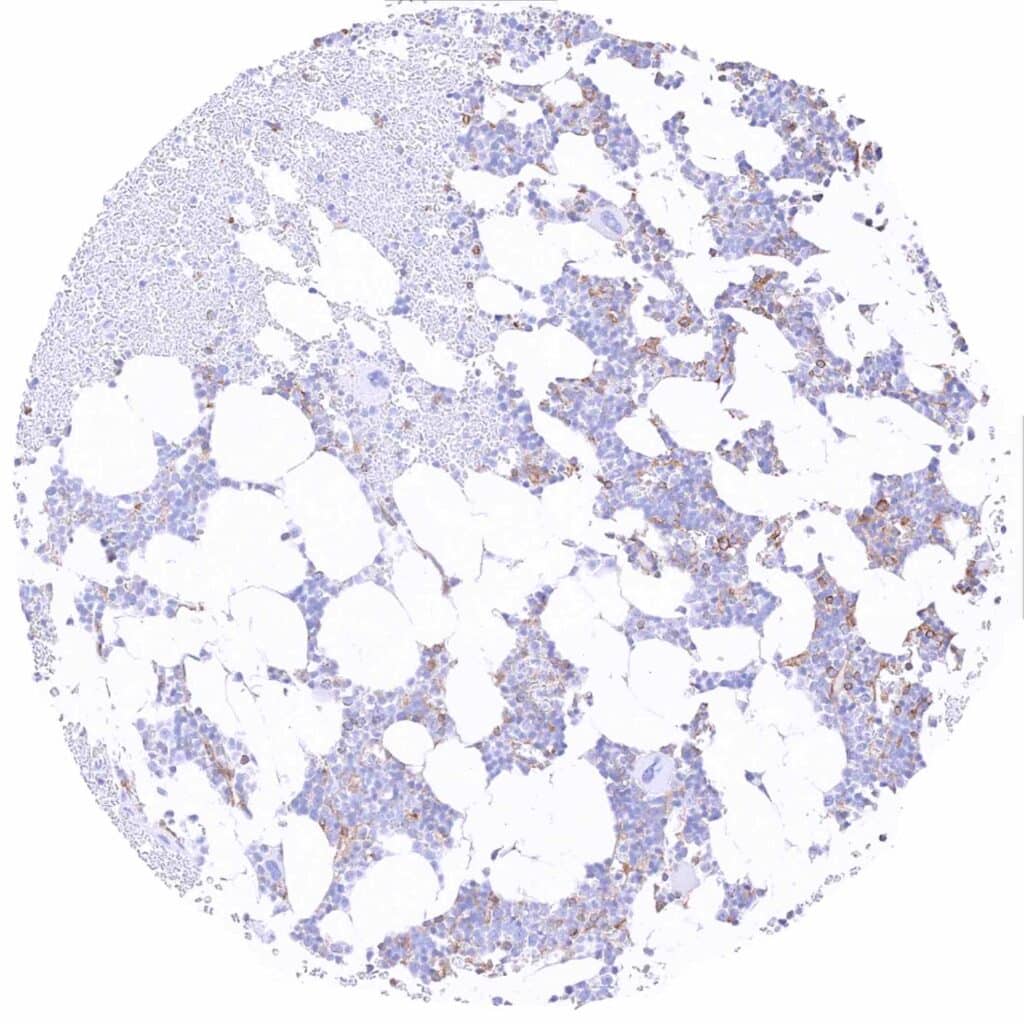
Bone marrow – Moderate MX1 staining of several hematopoetic cell types
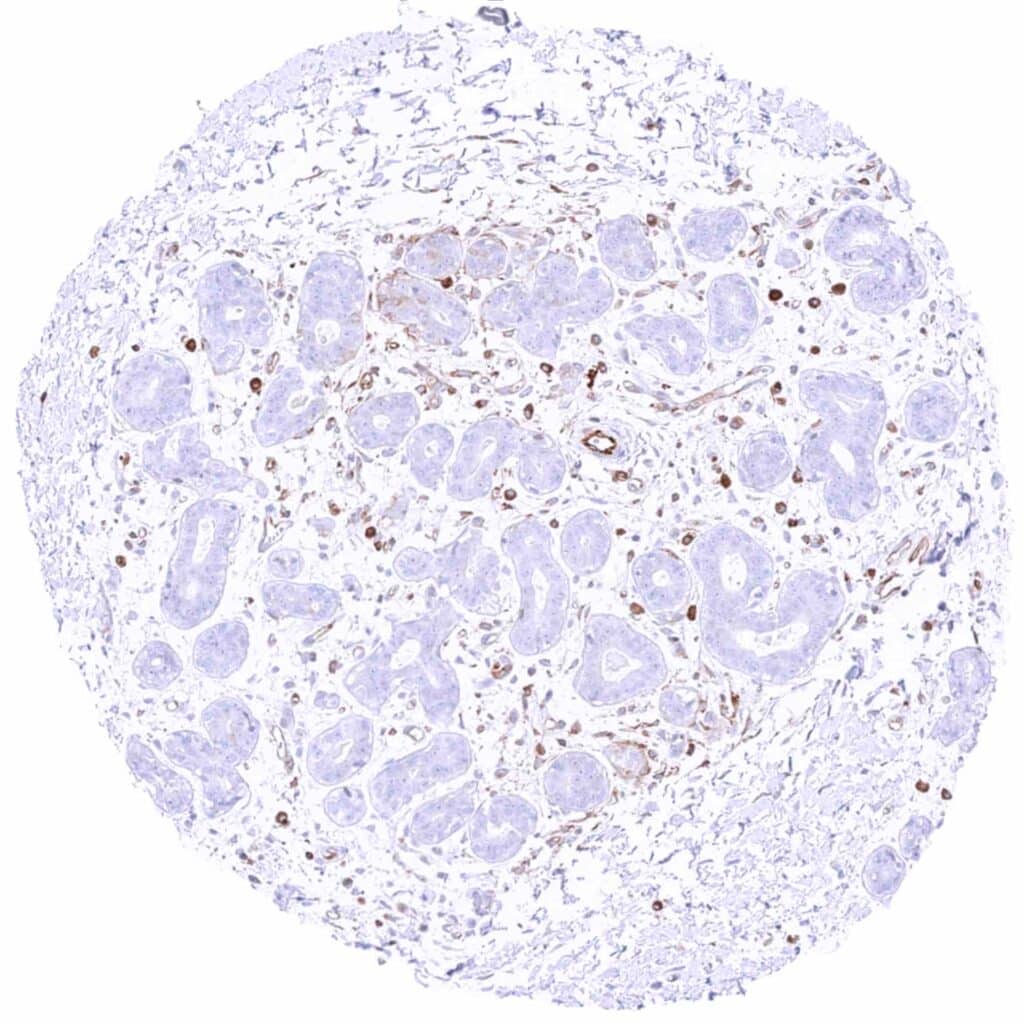
Breast – MX1 staining is limited to inflammatory and endothelial cells
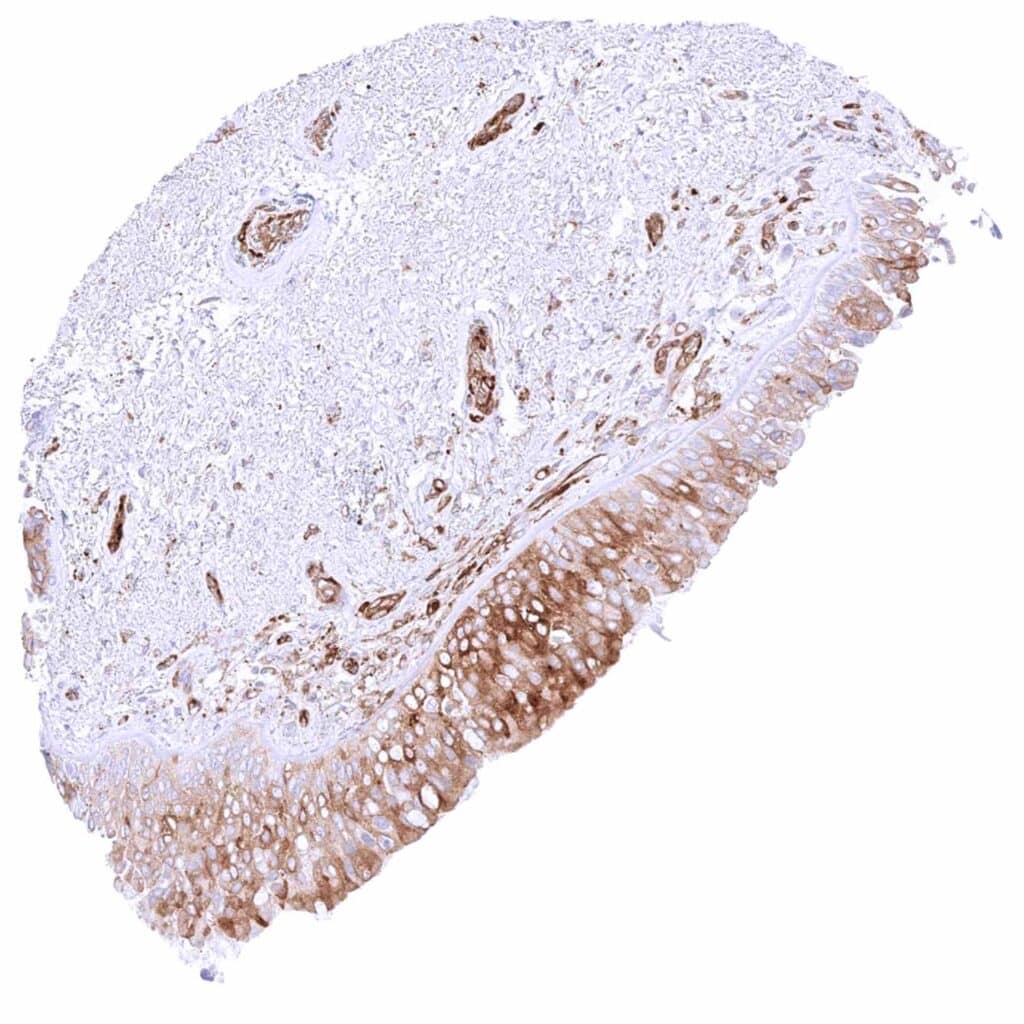
Bronchus, glands – Moderate to strong cytoplasmic MX1 staining in subsets of epithelial cells
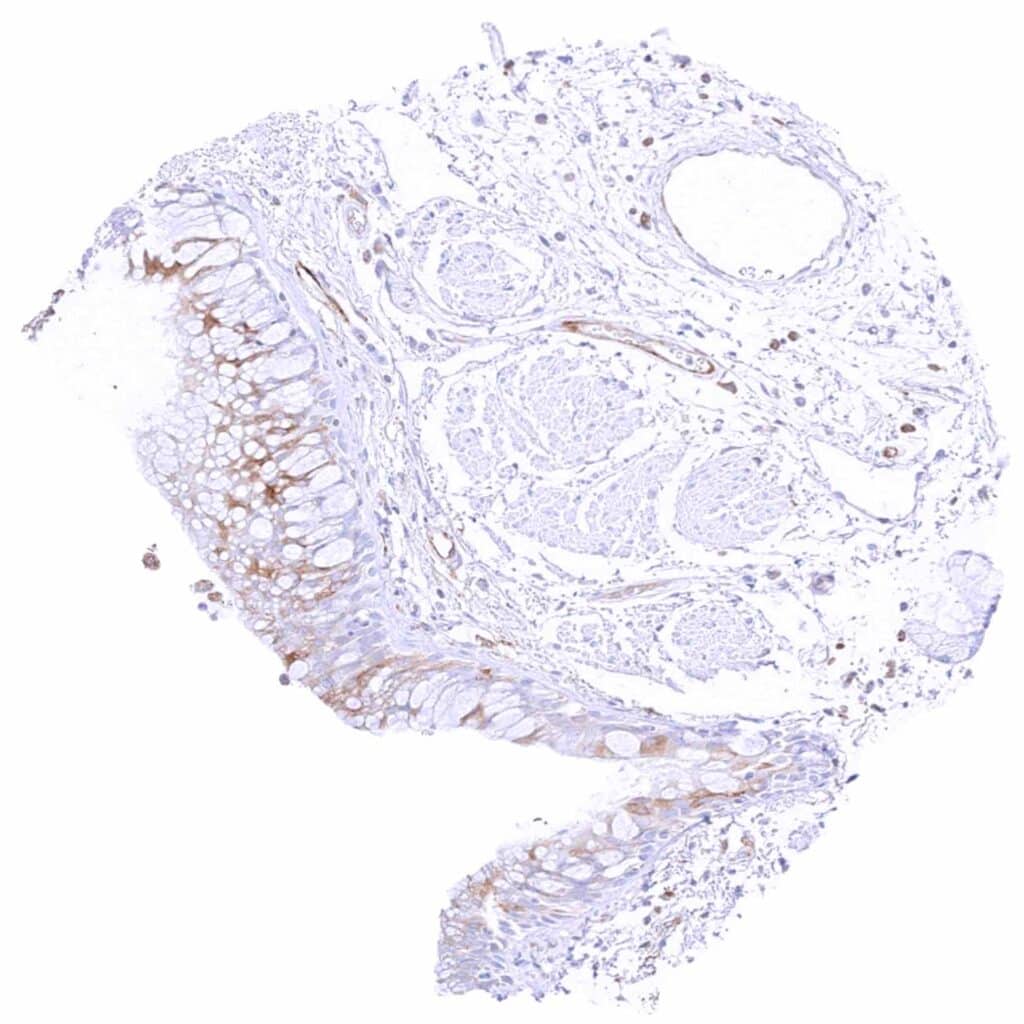
Bronchus, glands – Weak to moderate cytoplasmic MX1 staining in subsets of epithelial cells
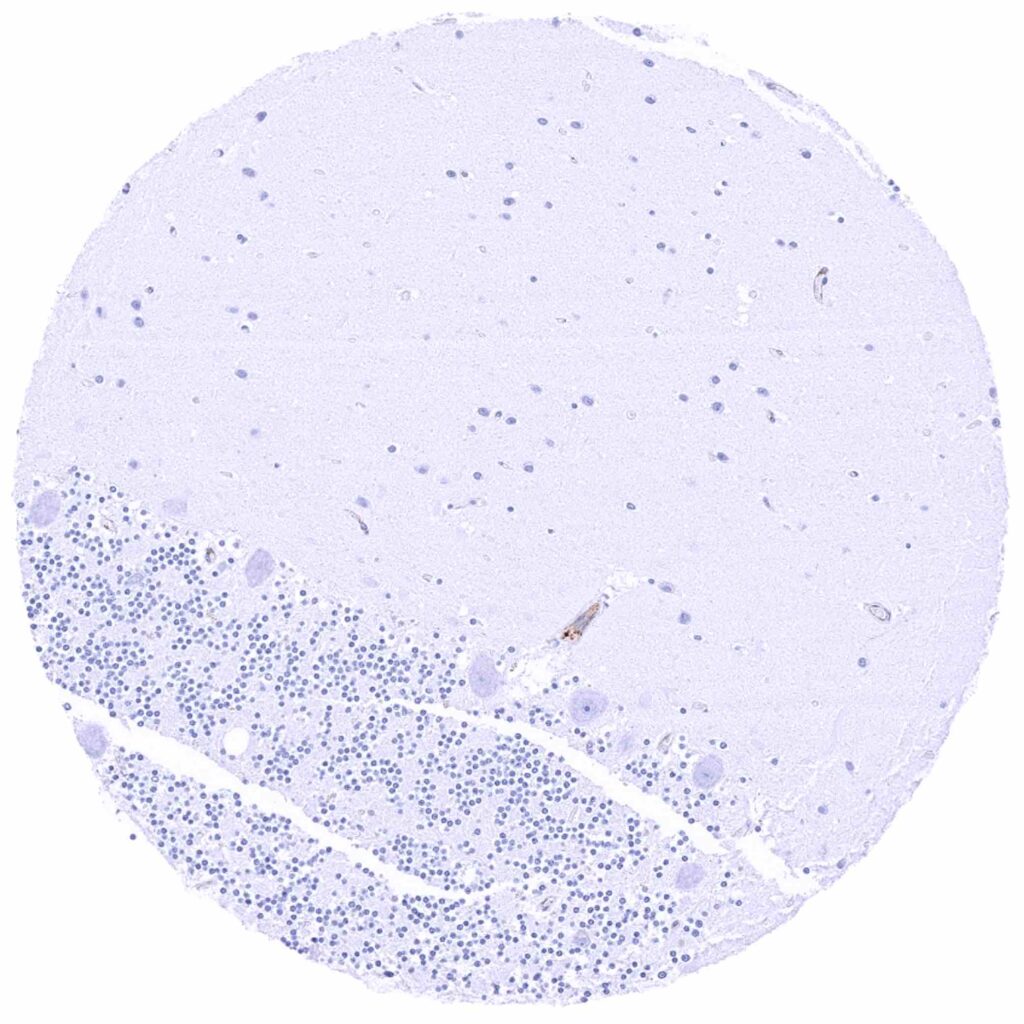
Cerebellum (molecular layer, purkinje cell layer, granule cell layer)
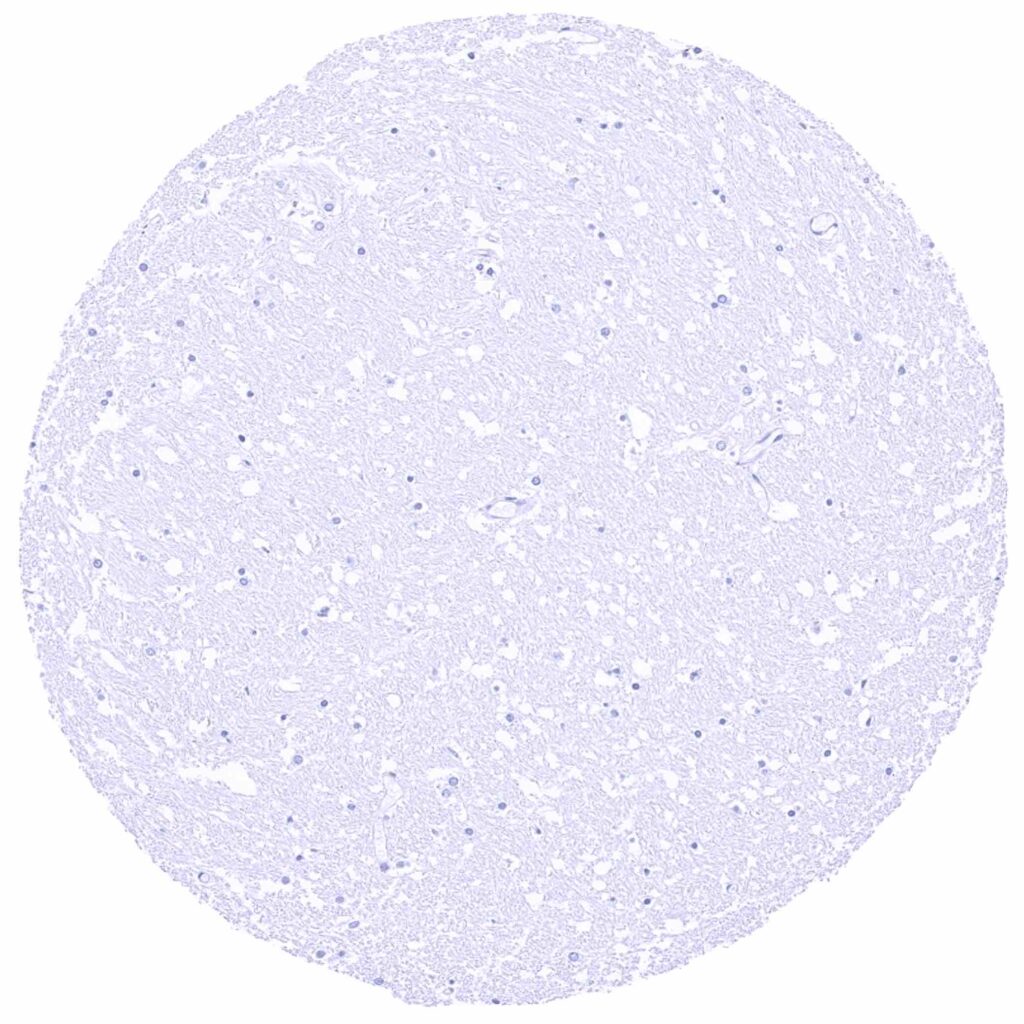
Cerebellum (white matter)
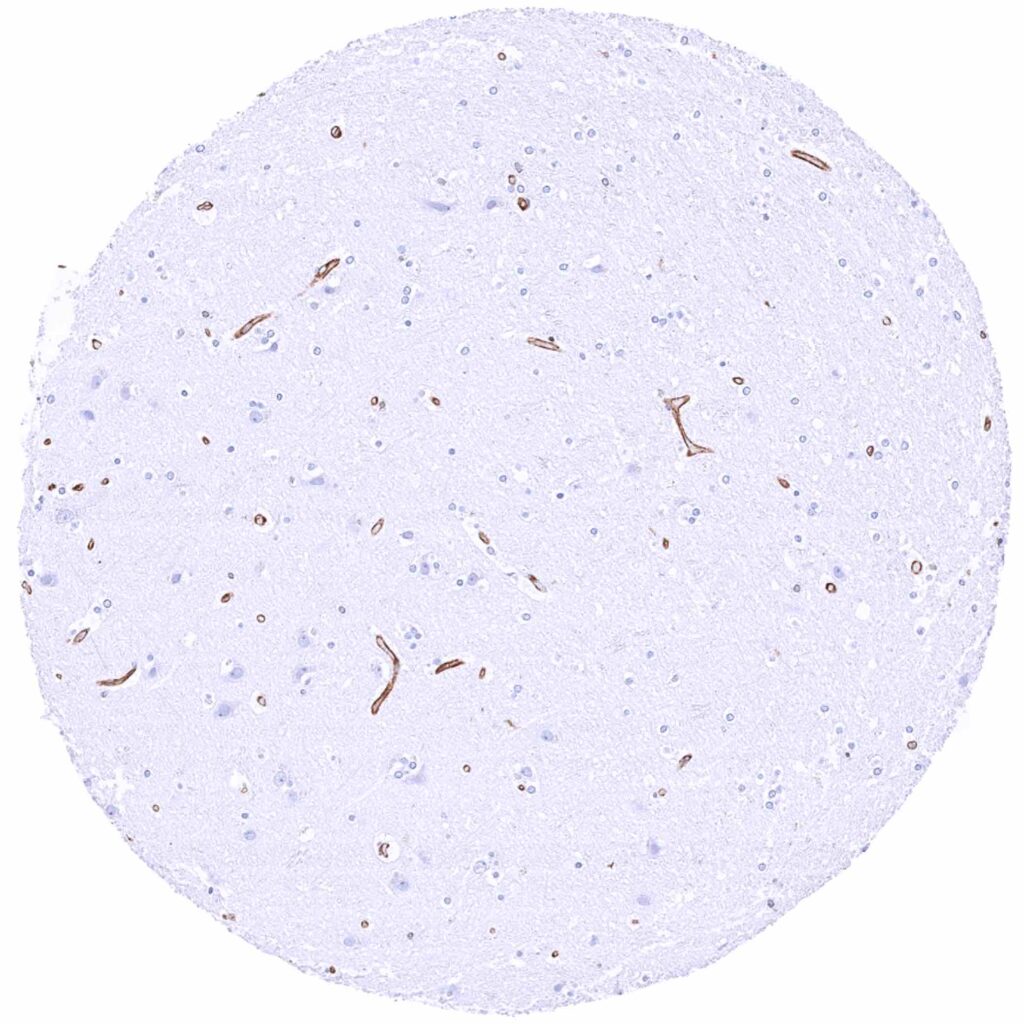
Cerebrum, grey matter
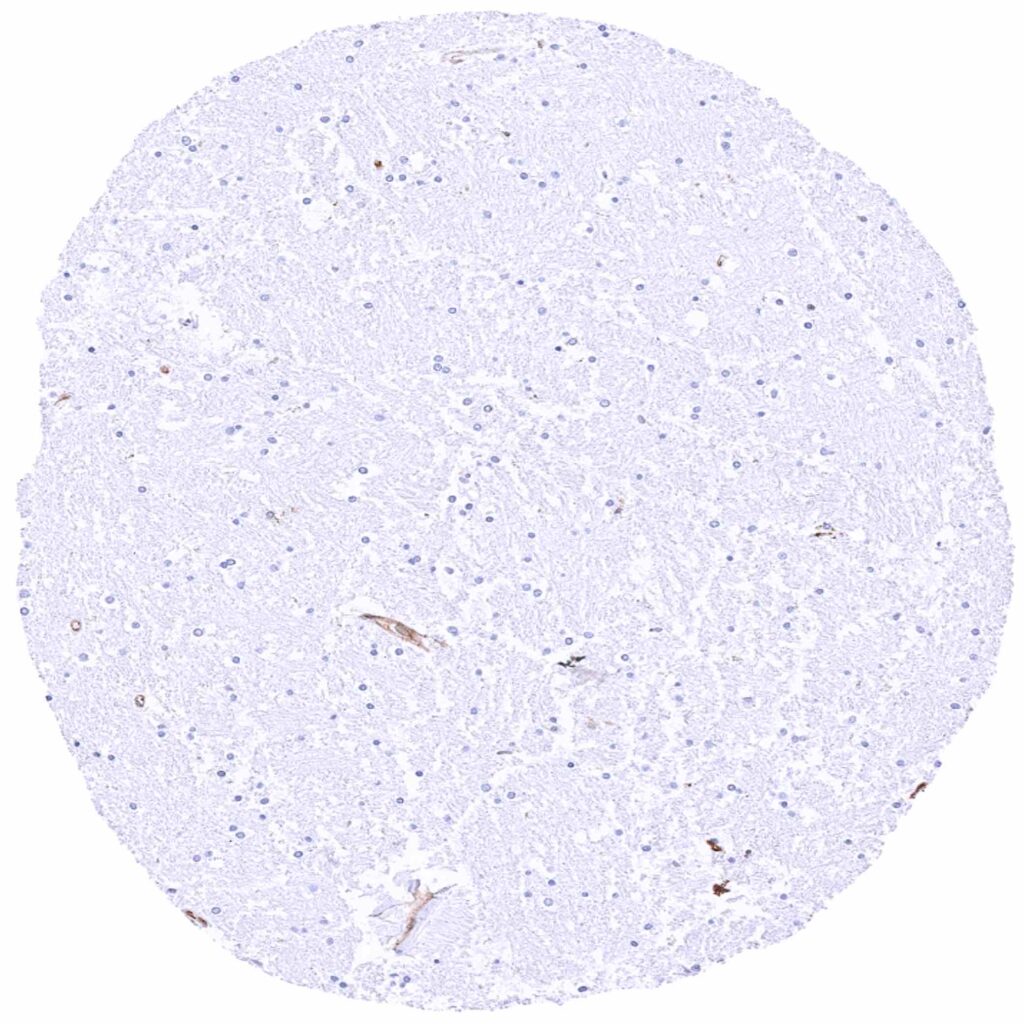
Cerebrum, white matter
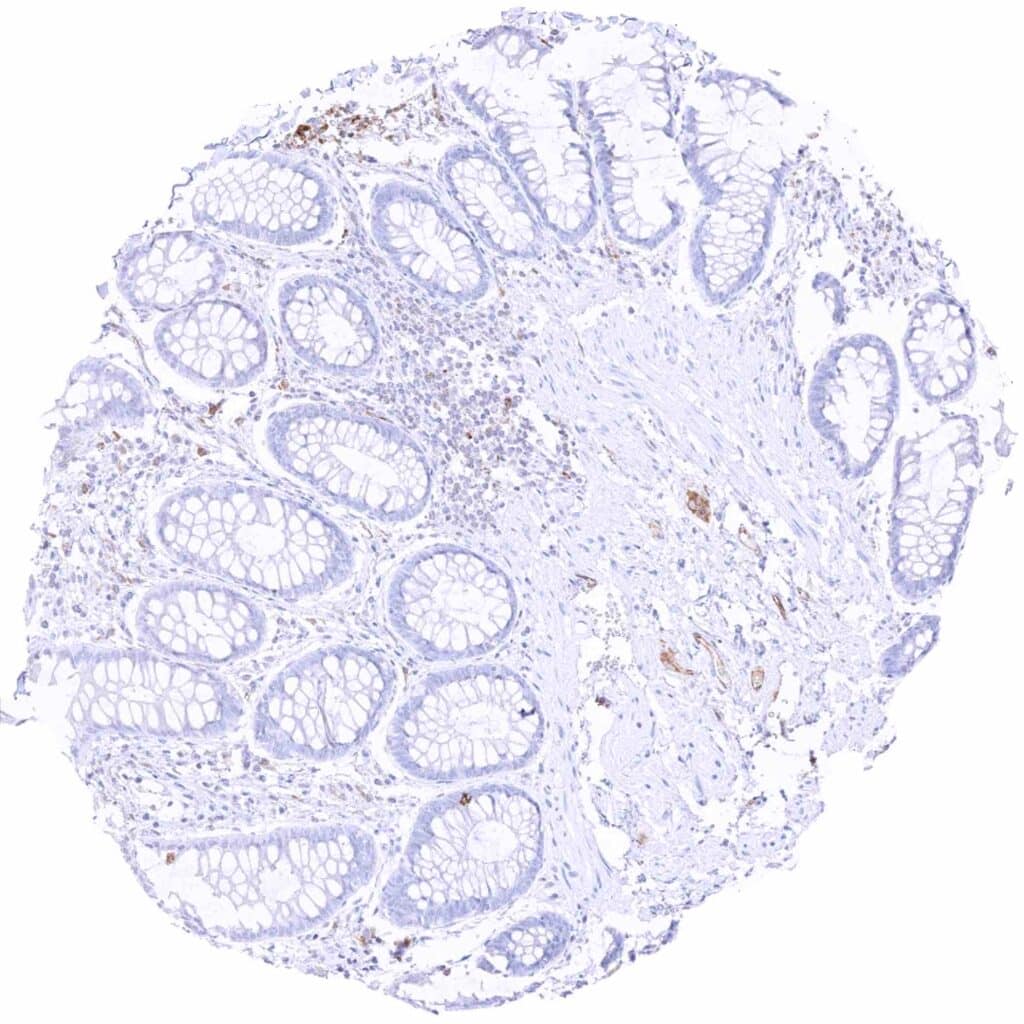
Colon descendens, mucosa – Crypt epithelial cells are largely MX1 negative
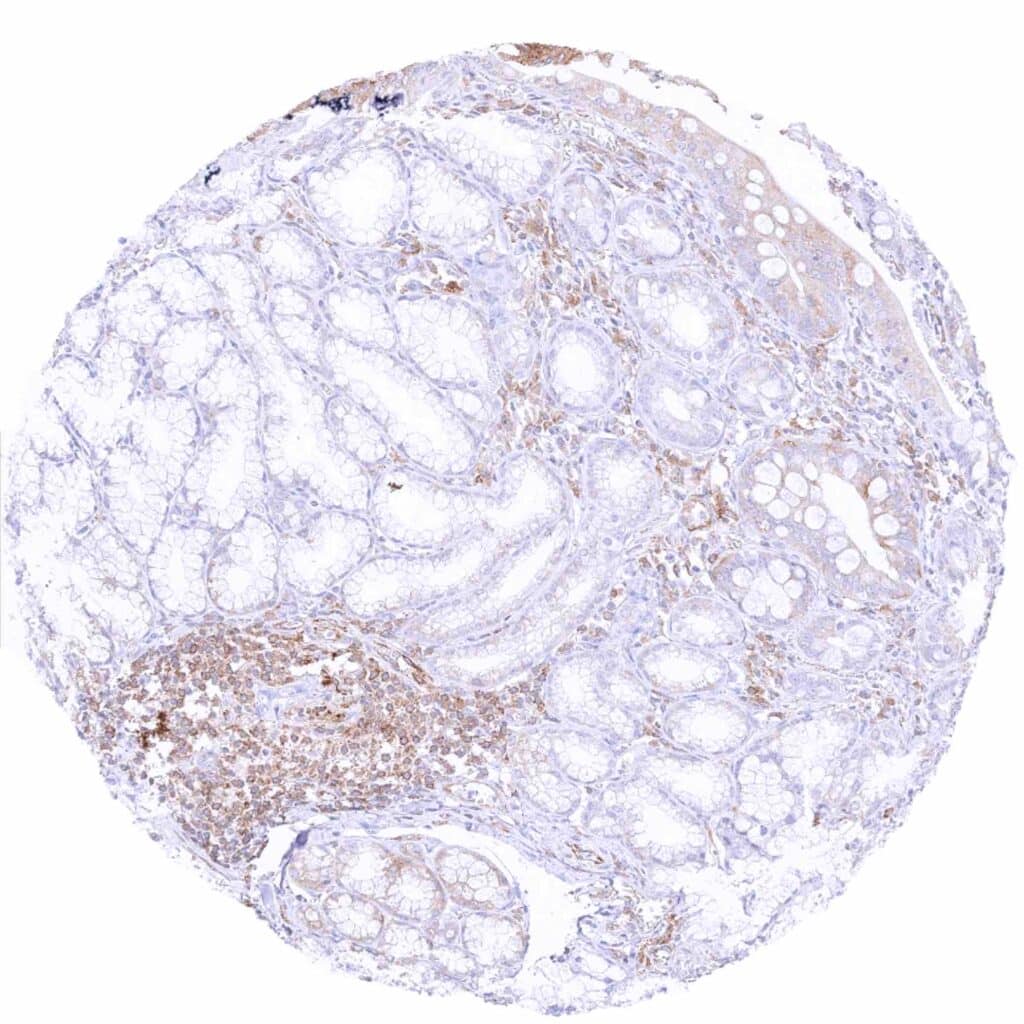
Duodenum, brunner gland – Brunner gland cells are MX1 negative
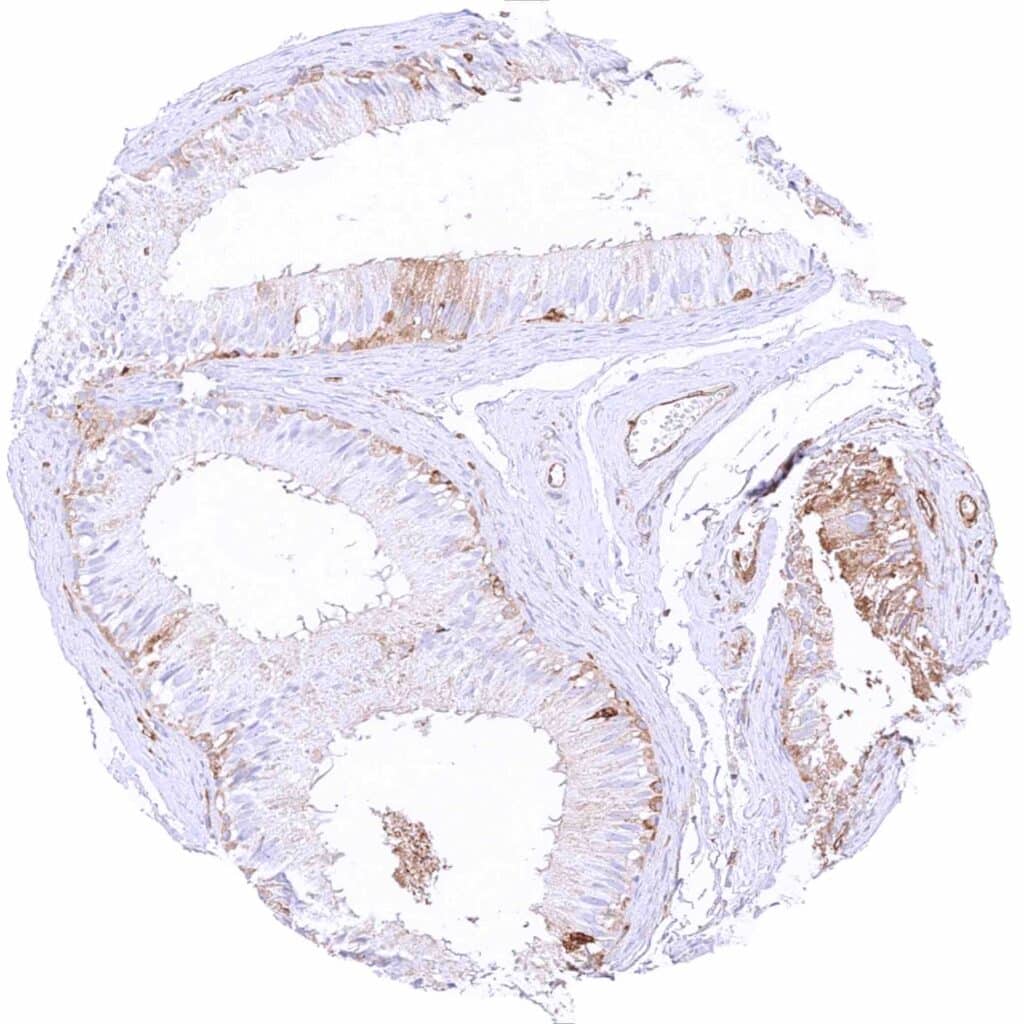
Epididymis – In the corpus, a cytoplasmic MX1 staining mainly occurs in basal cells and in subset of chief cells
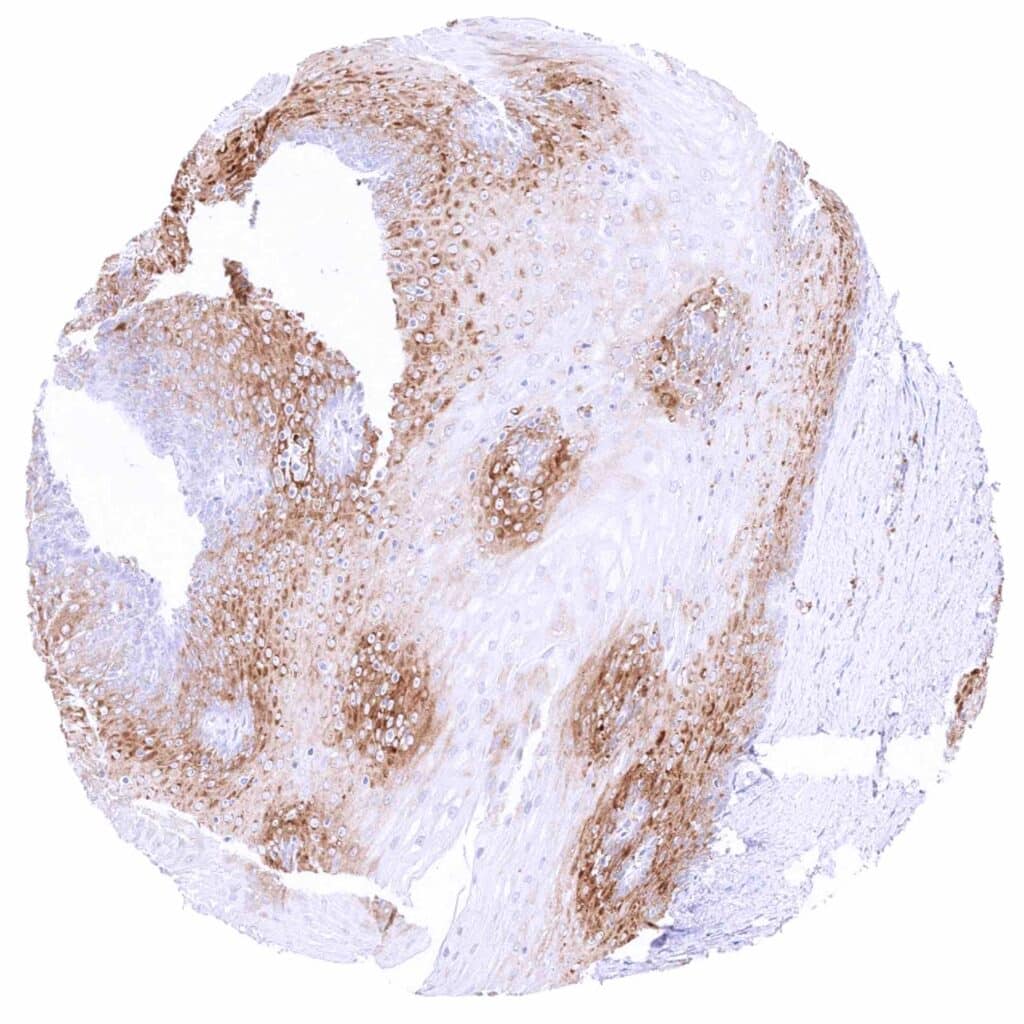
Esophagus, squamous epithelium – Moderate cytoplasmic MX1 staining of suprabasal cell layers
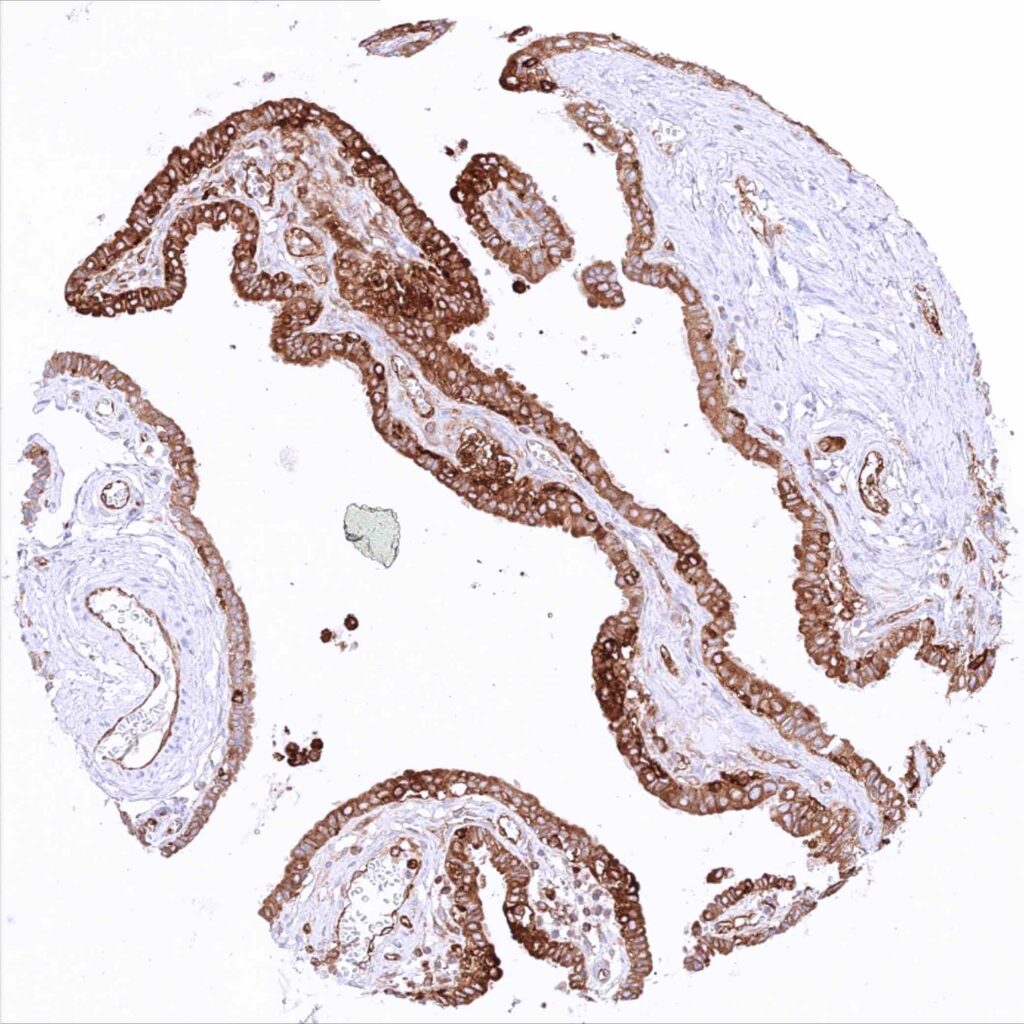
Fallopian tube, mucosa – Strong cytoplasmic MX1 staining of epithelial cells in this sample
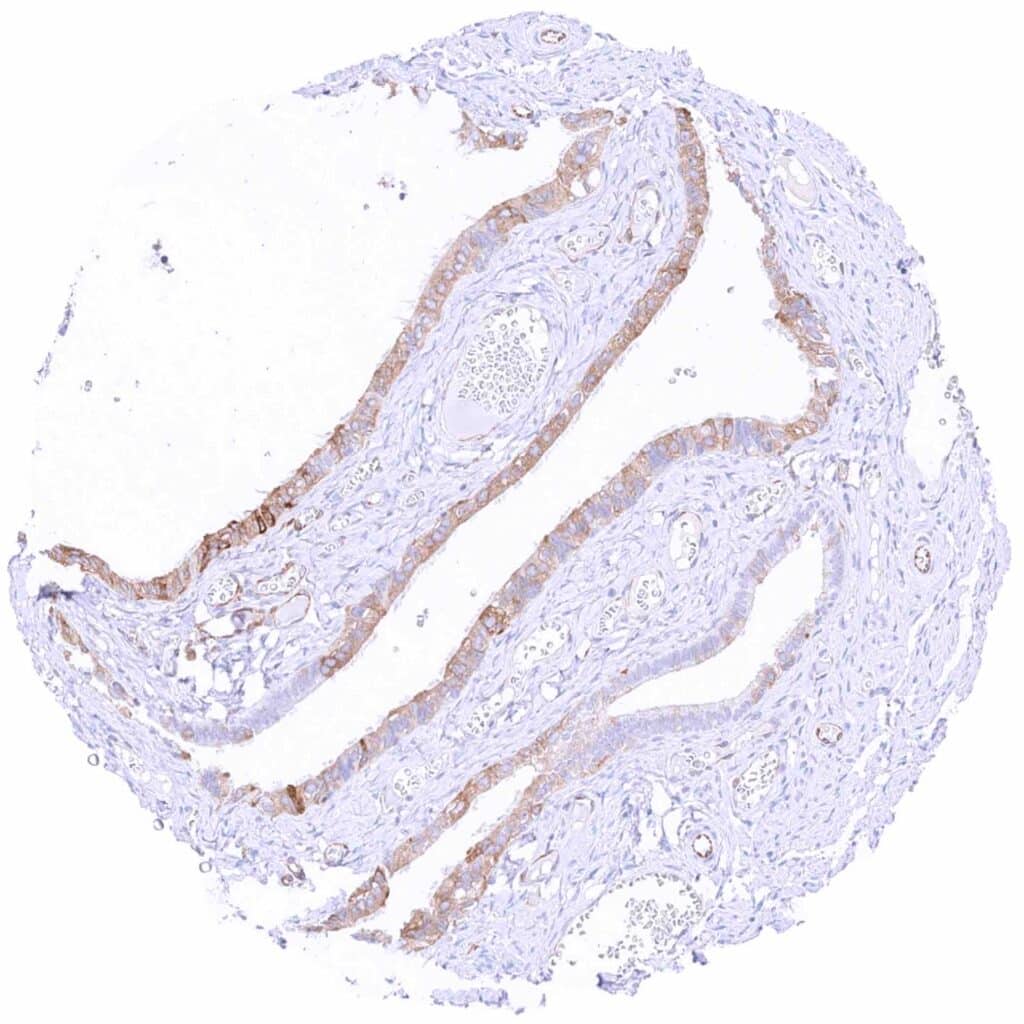
Fallopian tube, mucosa – Weak to moderate cytoplasmic MX1 staining of epithelial cells
Fat
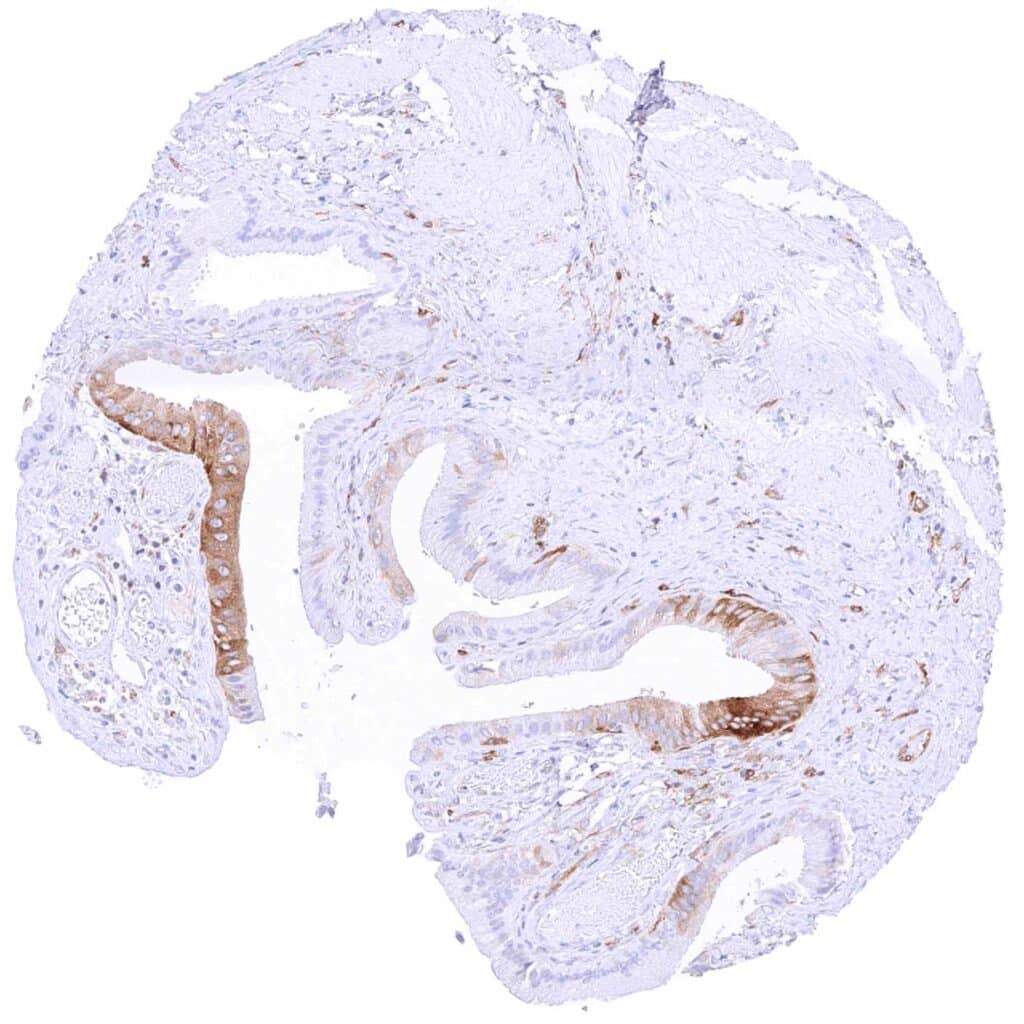
Gallbladder, epithelium – Strong focal MX1 staining of epithelial cells while other regions remain MX1 negative
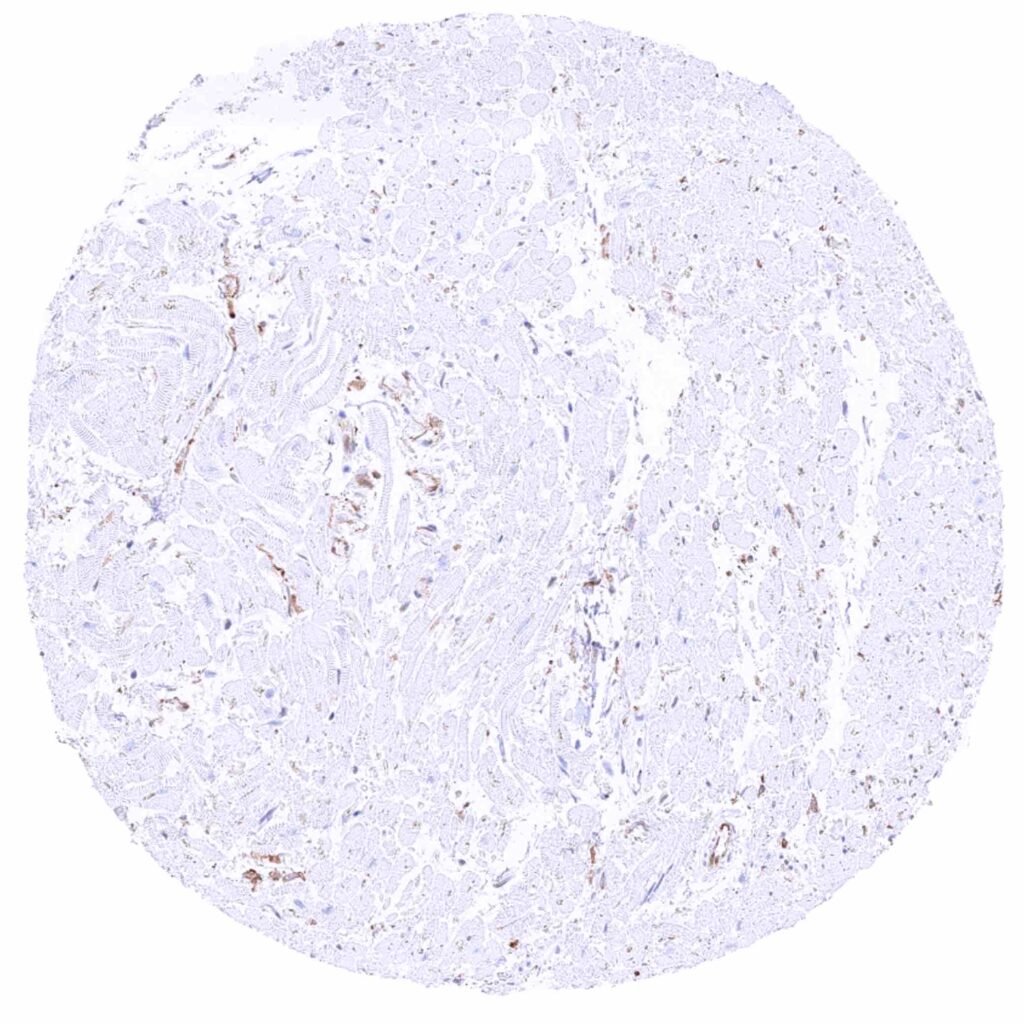
Heart muscle – MX1 staining prdominates in the endothelium of small vessels
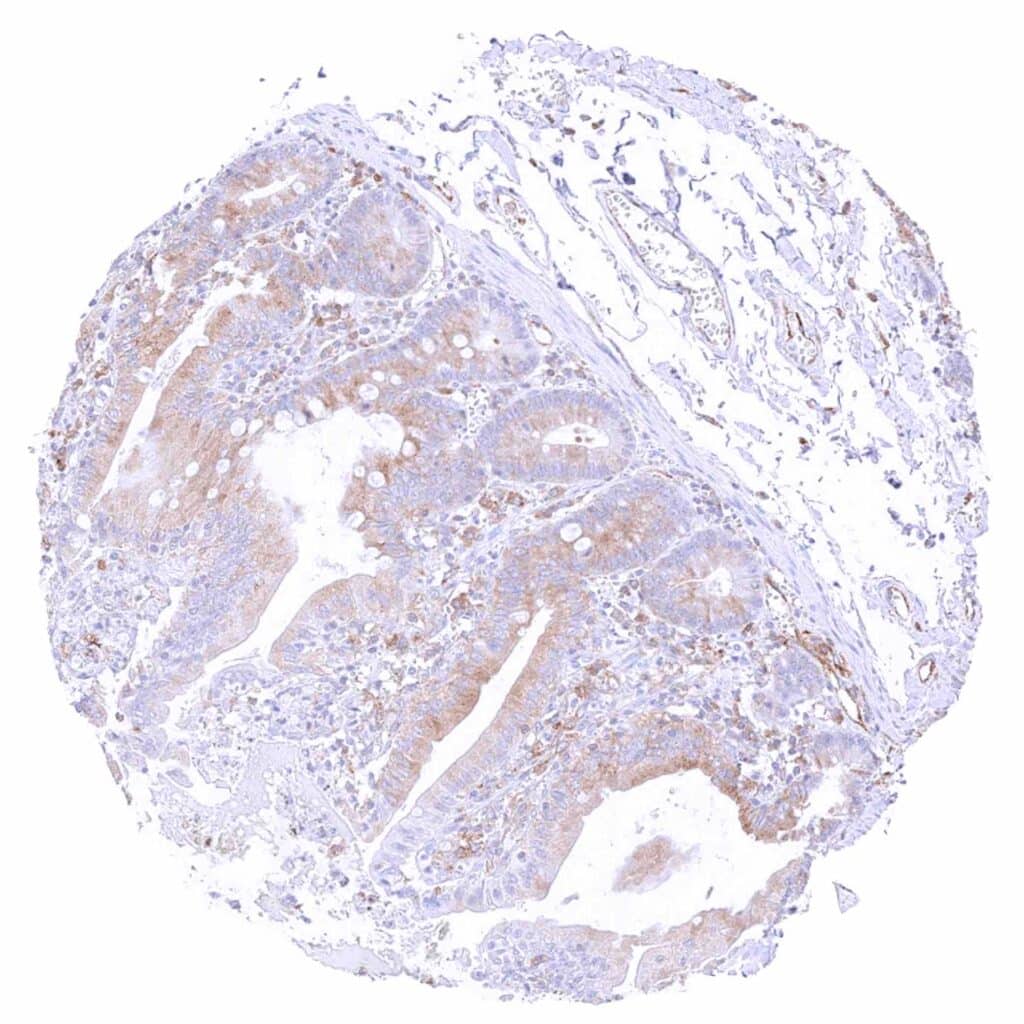
Ileum, mucosa – Weak to moderate cytoplasmic MX1 staining of epithelial cells
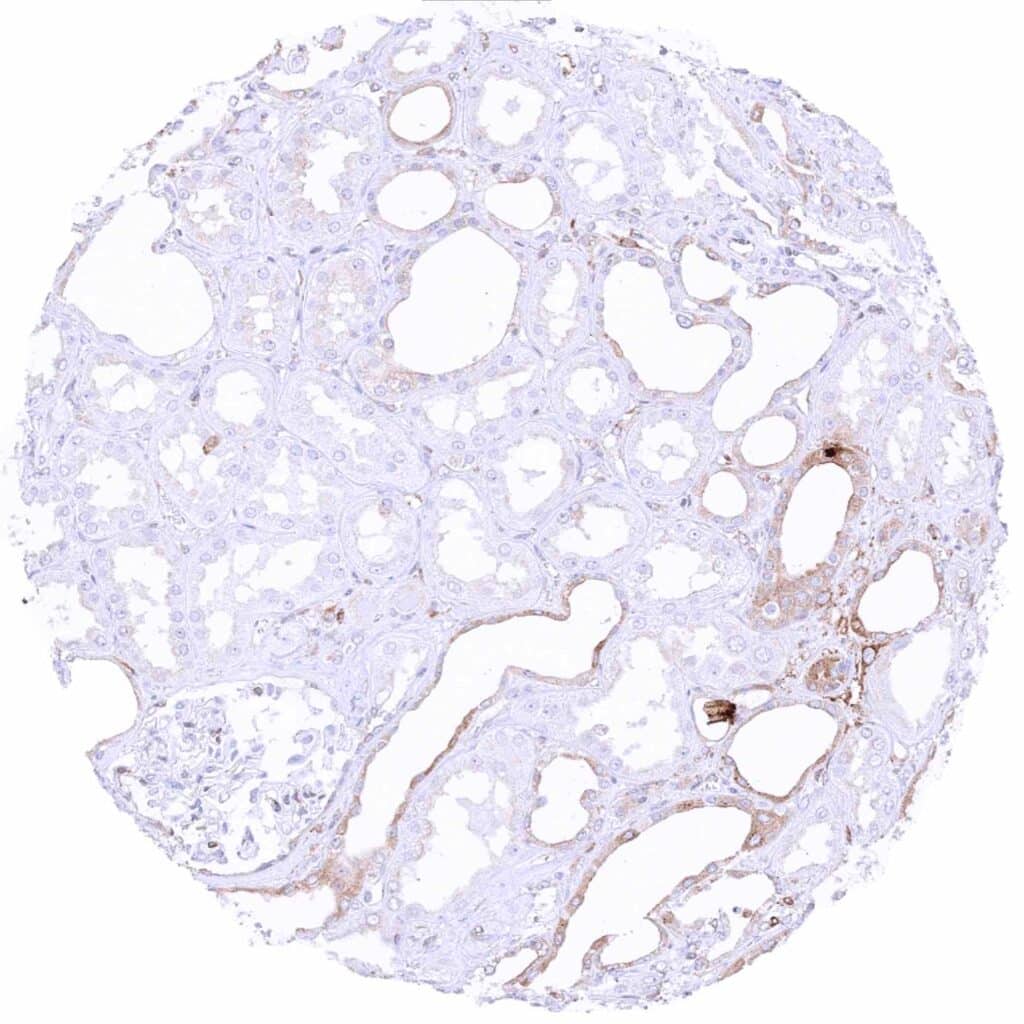
Kidney, cortex – Cytoplasmic MX1 staining mainly occurs in atrophic tubuli
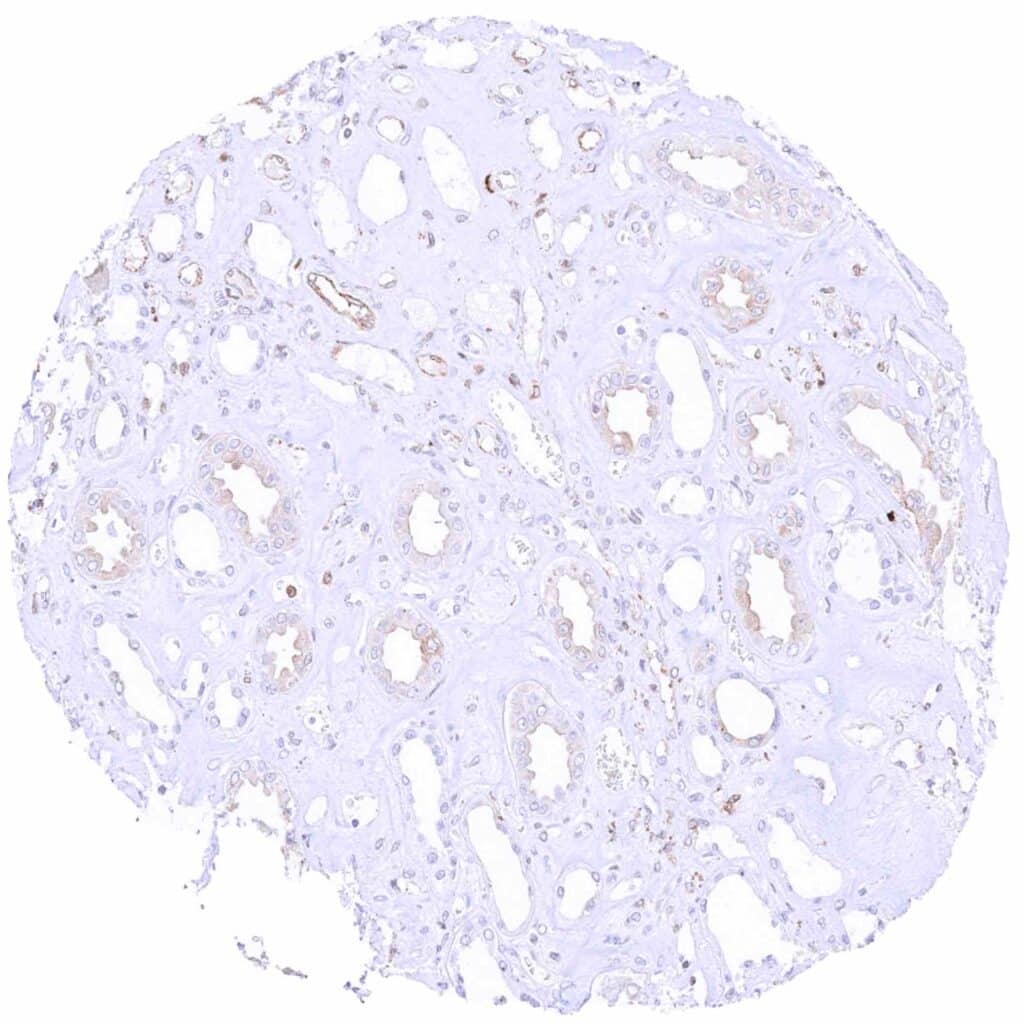
Kidney, medulla – Some cytoplasmic MX1 staining in most ceollecting ducts of this sample
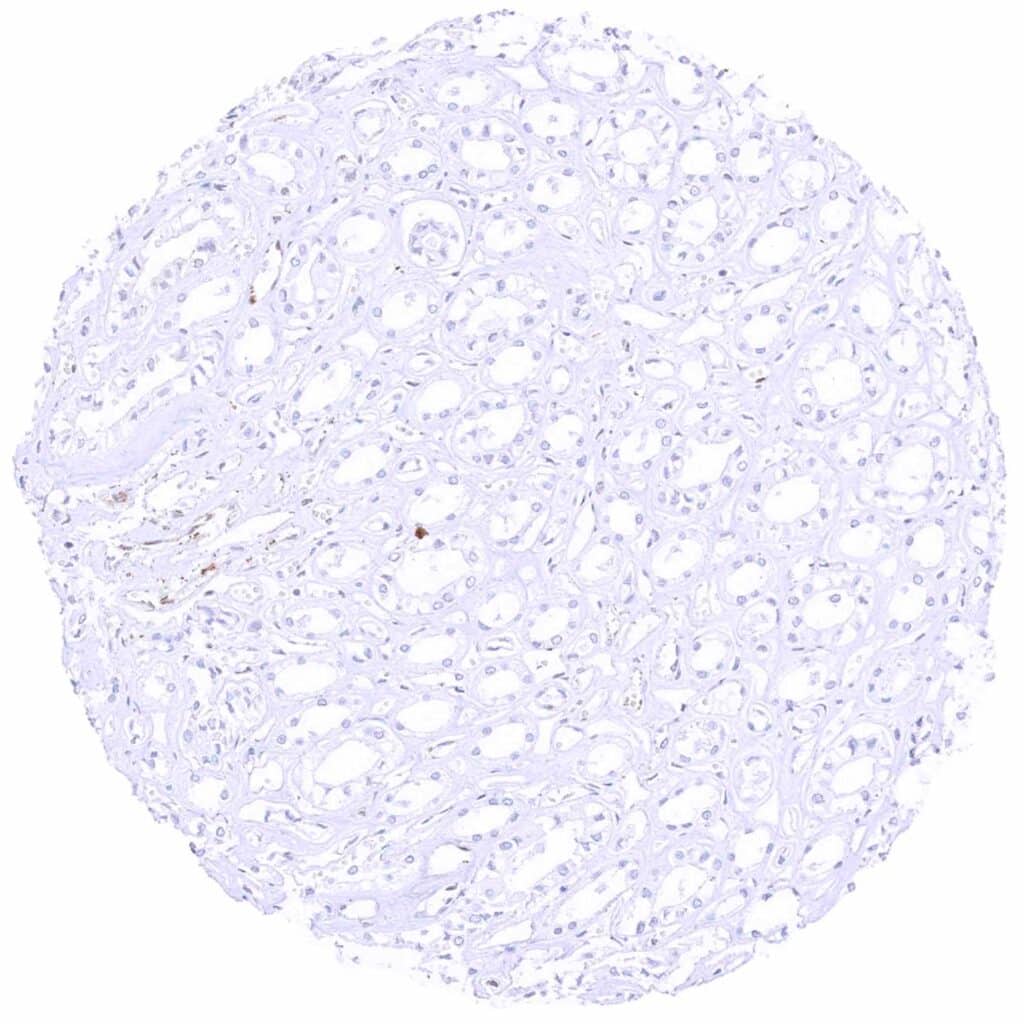
Kidney, medulla
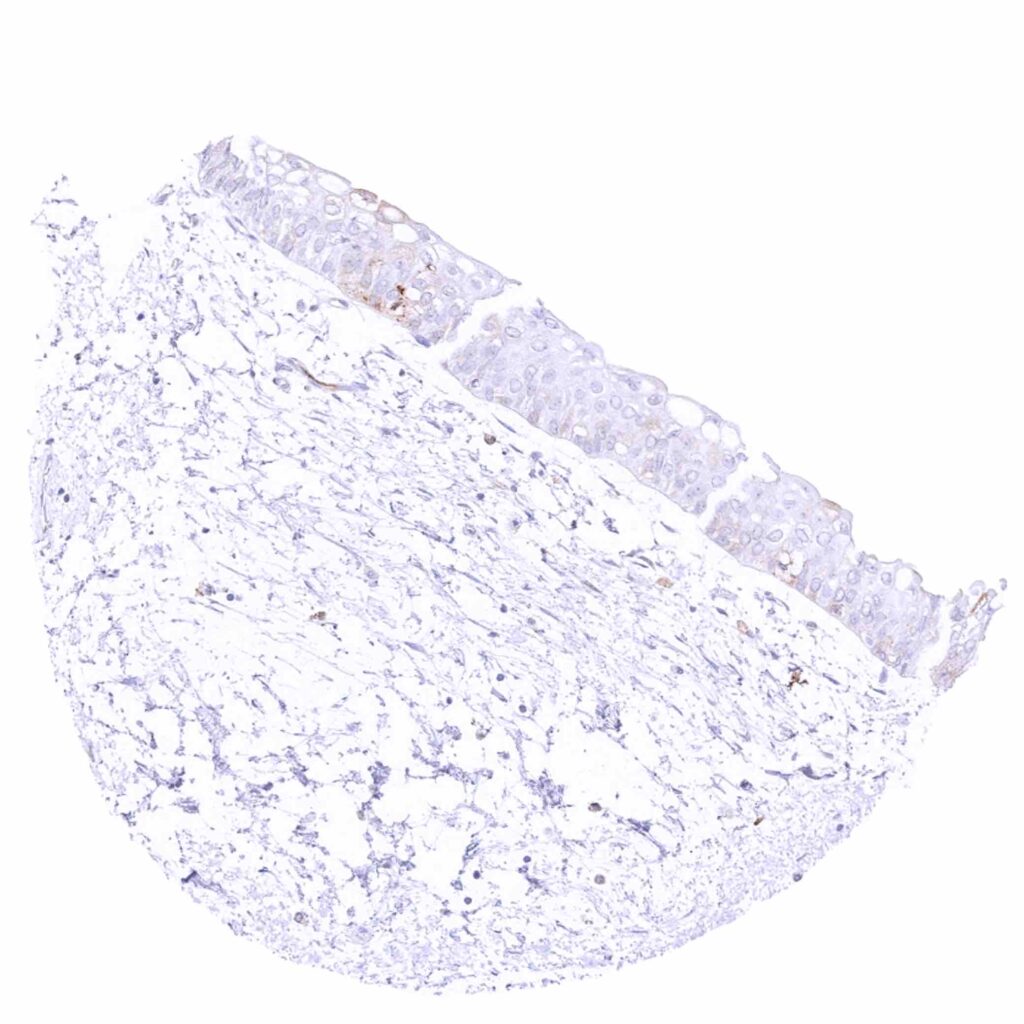
Kidney, pelvis, urothelium
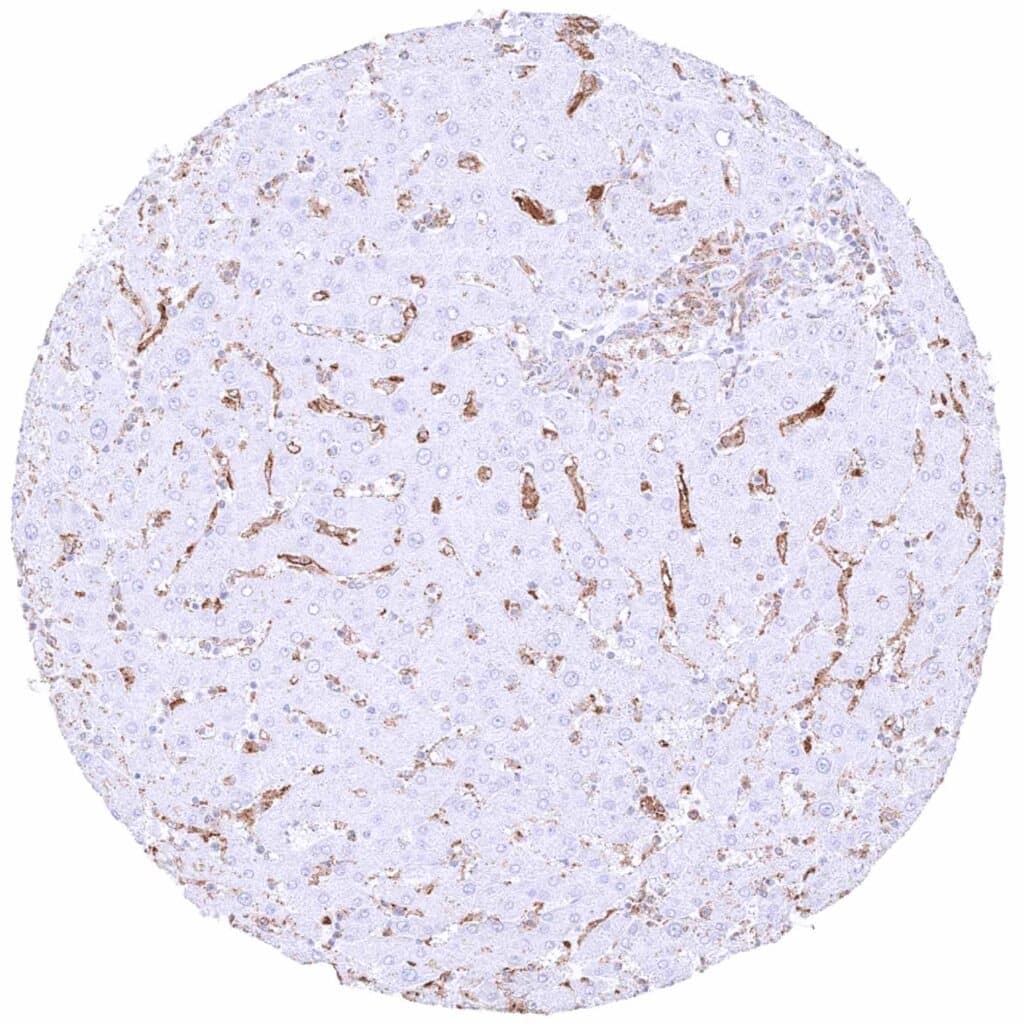
Liver – Strong MX1 staining of sinus cells while hepatocytes are MX1 negative
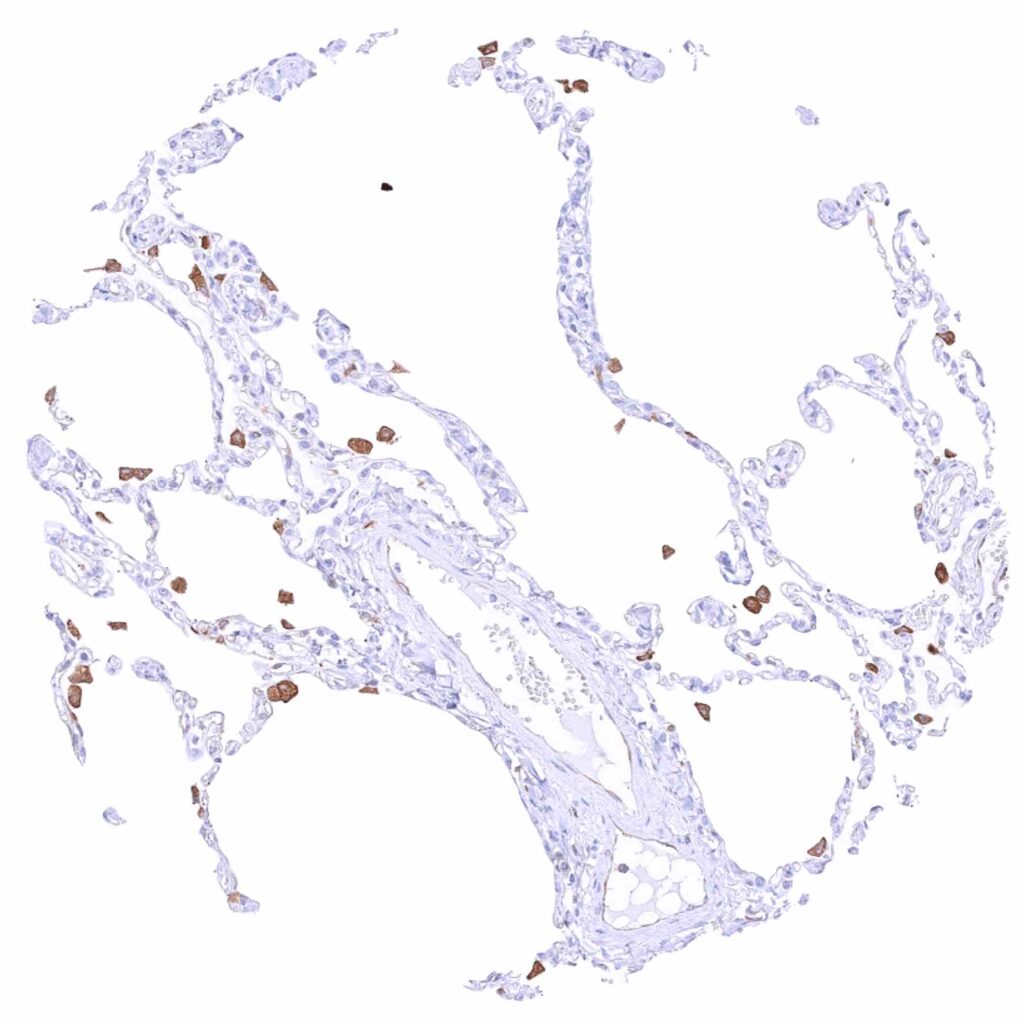
Lung – Moderate to strong cytoplasmic MX1 staining of macrophages
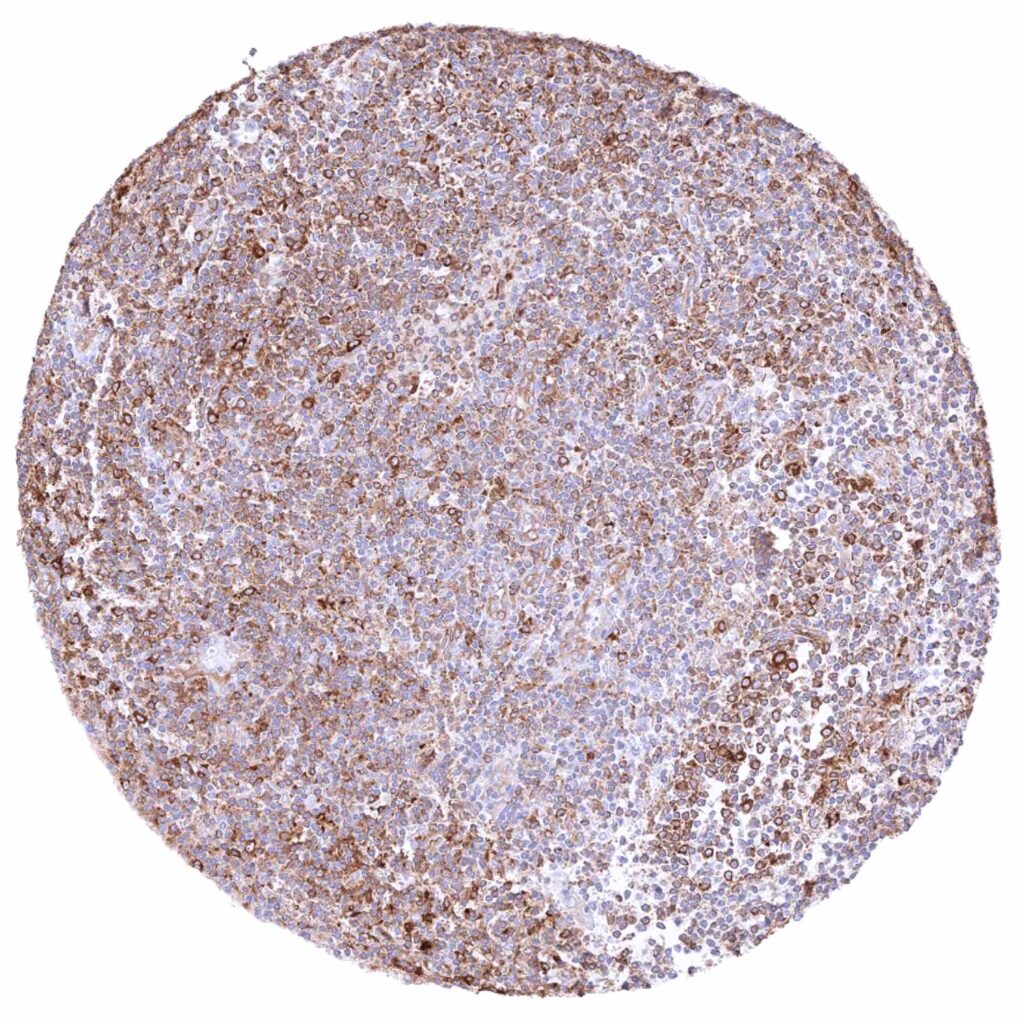
Lymph node – Cytoplasmic MX1 staining at variable intensity of a large fraction of cells
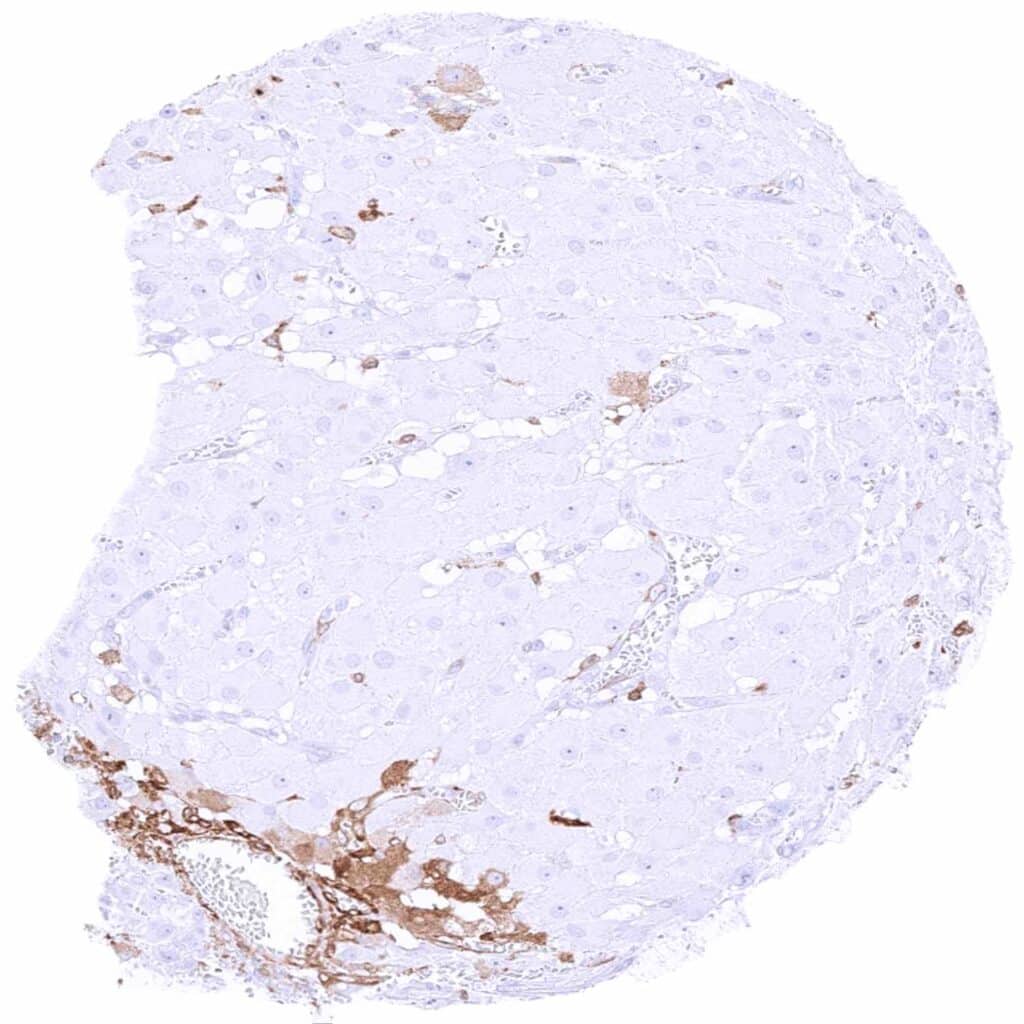
Ovary, corpus luteum – Most corpus luteum cells are MX1 negative
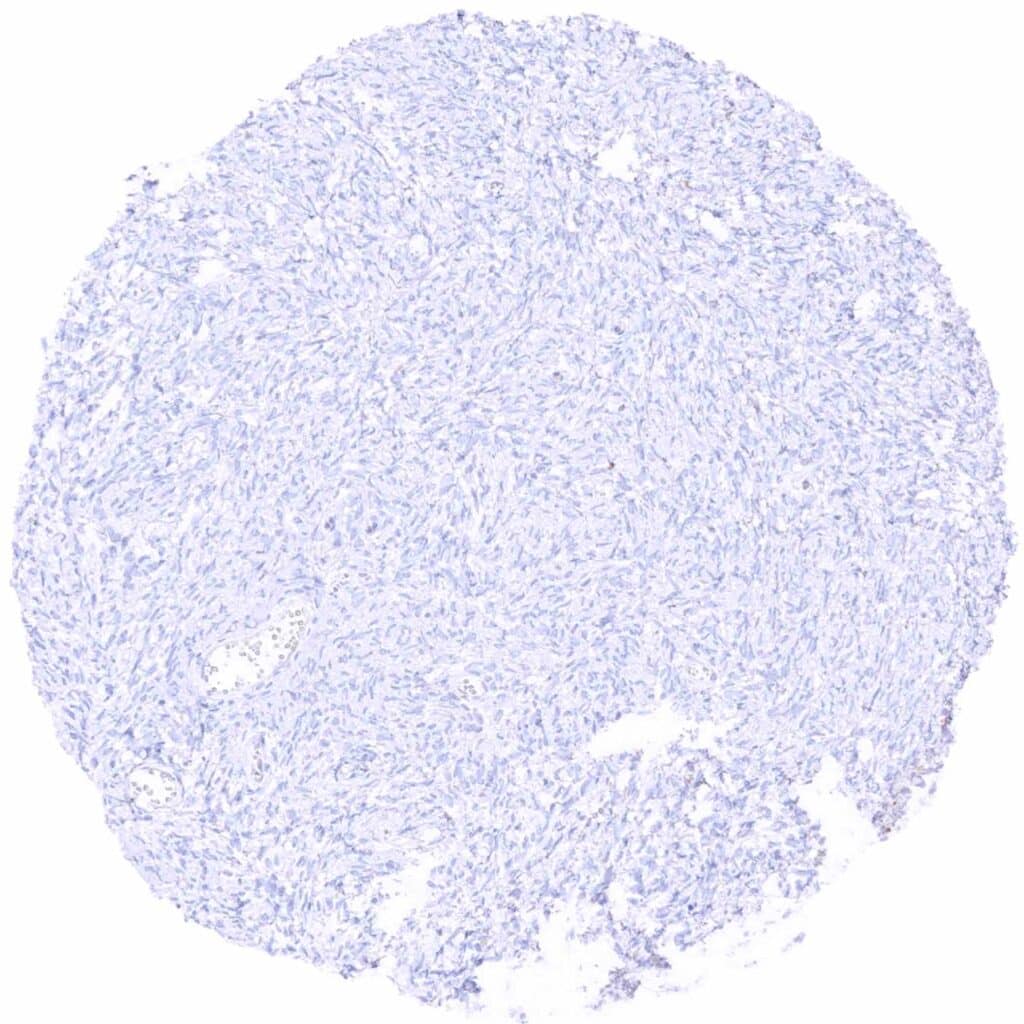
Ovary, stroma
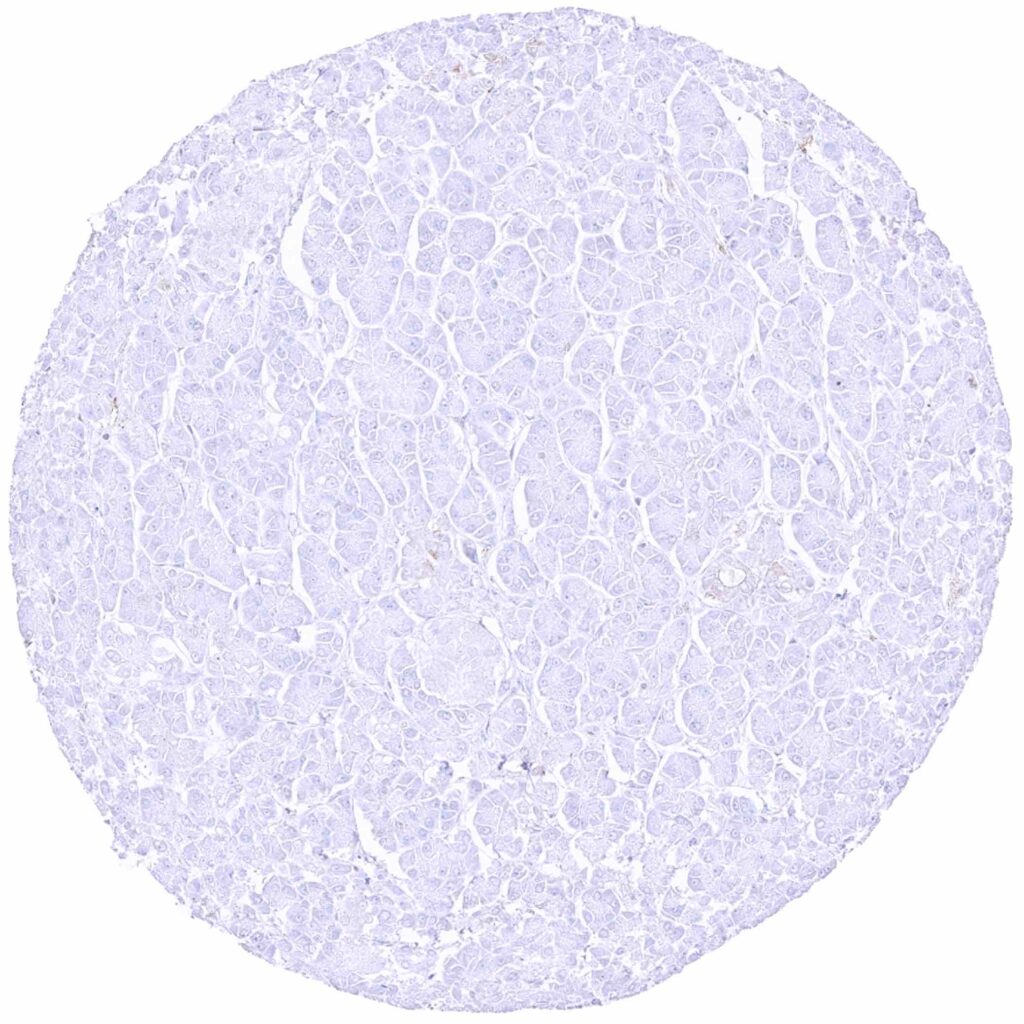
Pancreas – MX1 staining is completely absent in this sample
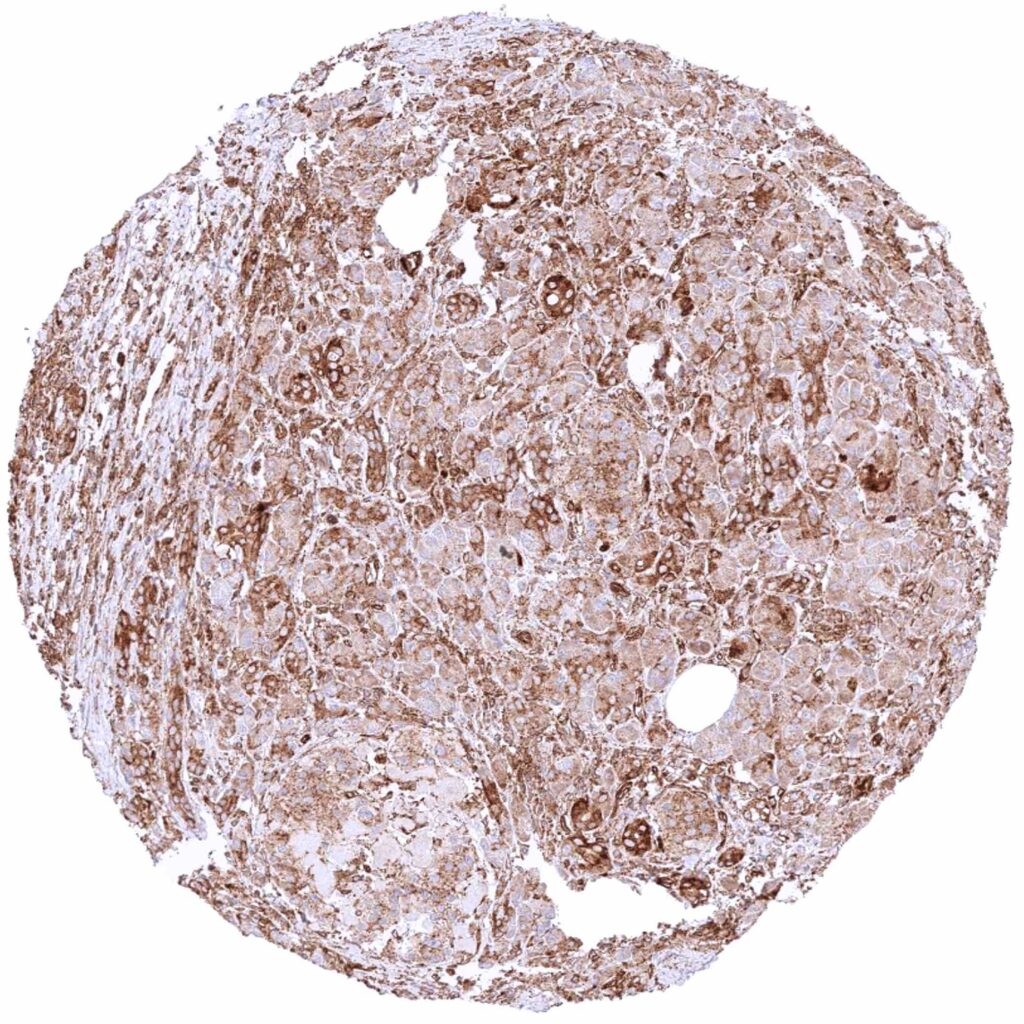
Pancreas – Strong cytoplasmic MX1 staining of all epithelial cell types in a sample with some inflammation and scar formation
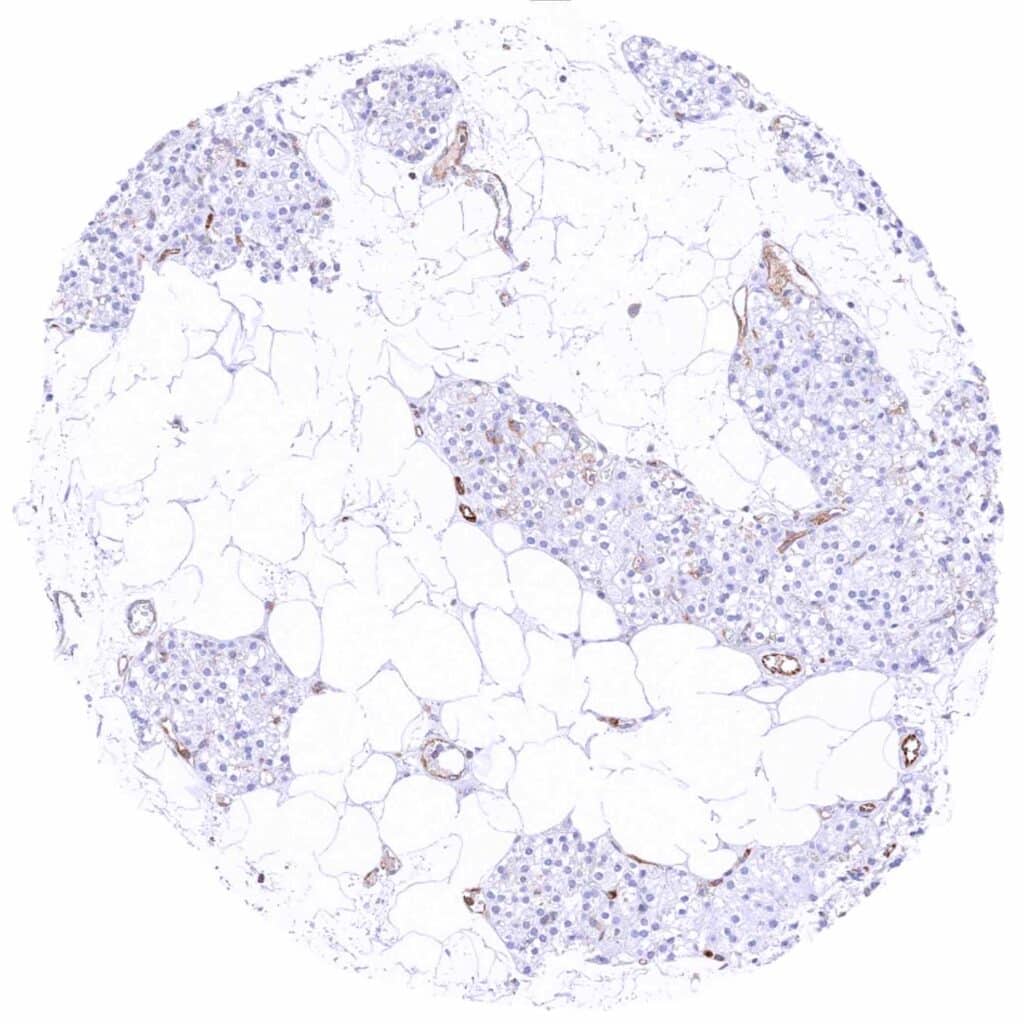
Parathyroid gland – MX1 staining is limited to endothelial cells
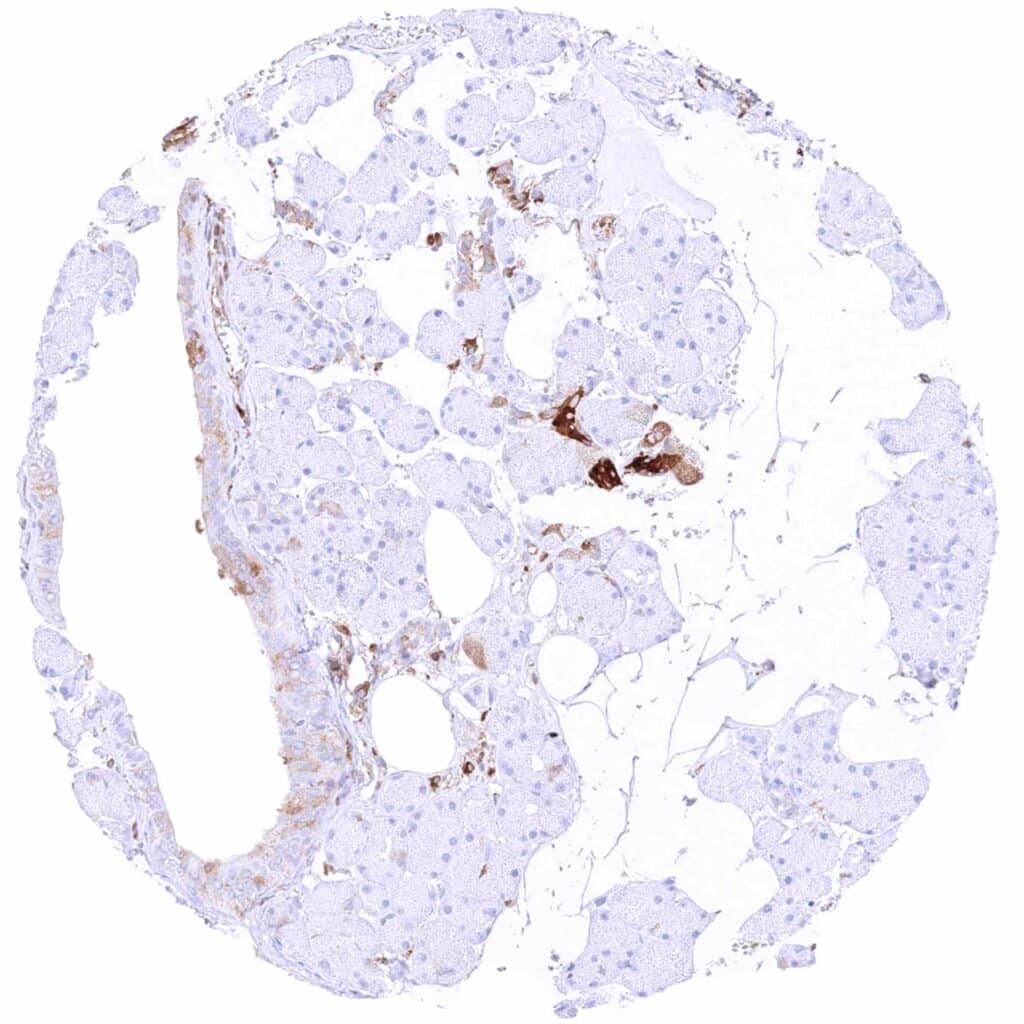
Parotid gland – Moderate to strong cytoplasmic MX1 staining can be seen in some epithelial cell groups
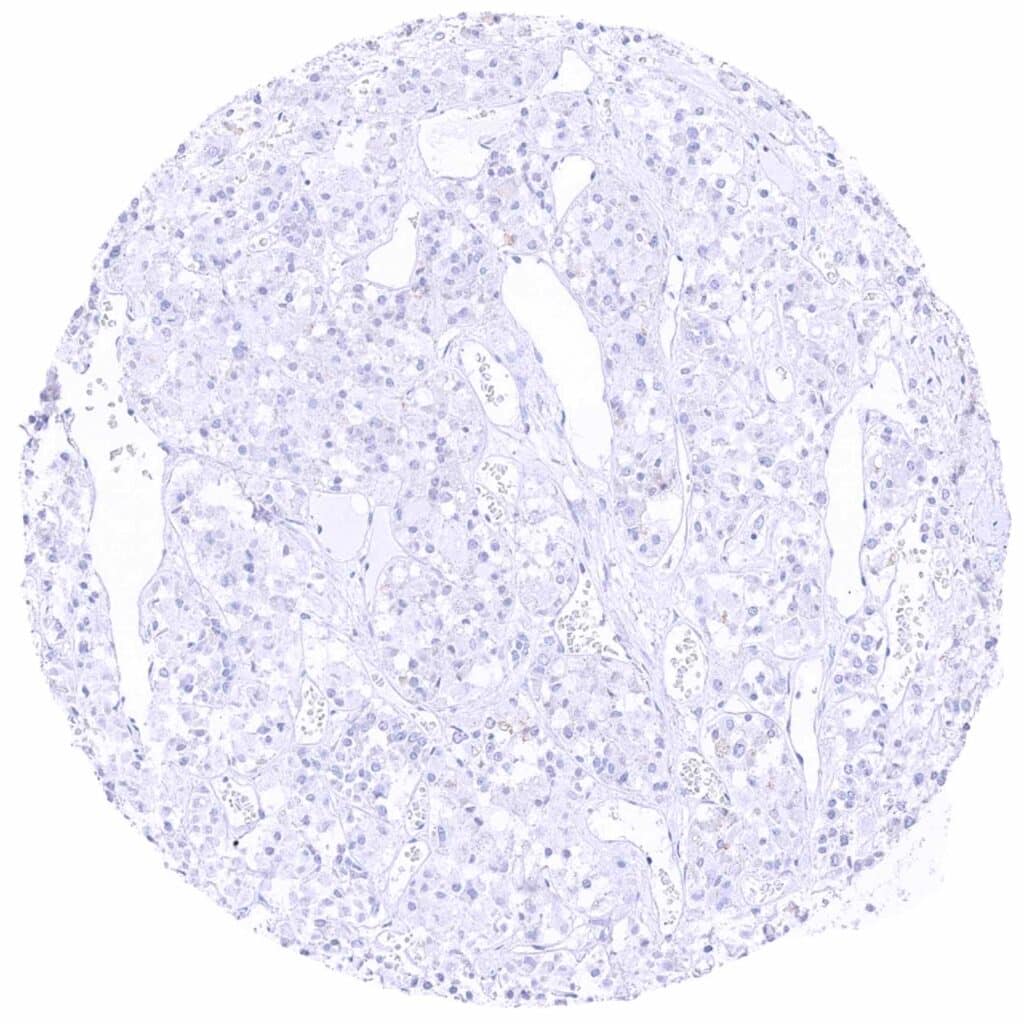
Pituitary gland, posterior lobe
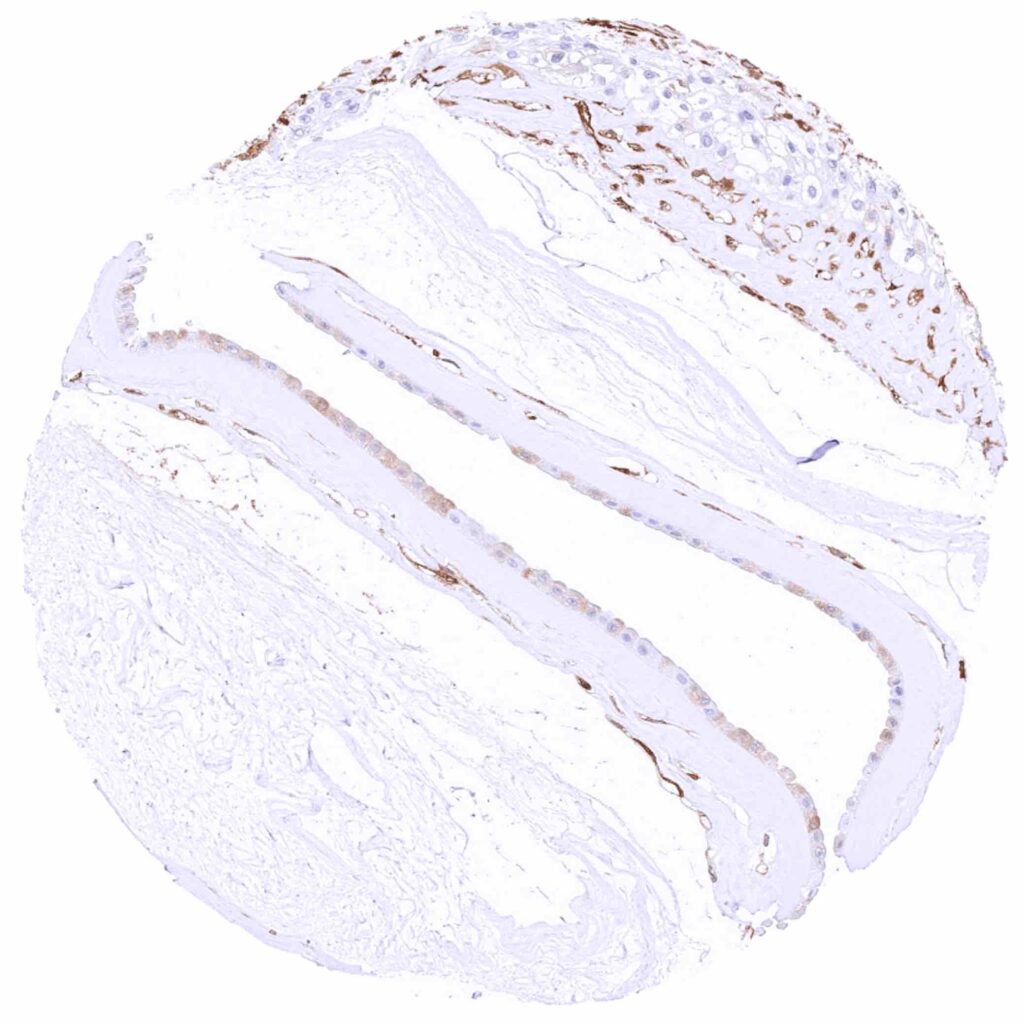
Placenta (amnion and chorion) – Weak cytoplasmic MX1 staining of some amnion cells while chorion cells are negative. Strong staining of small vessels
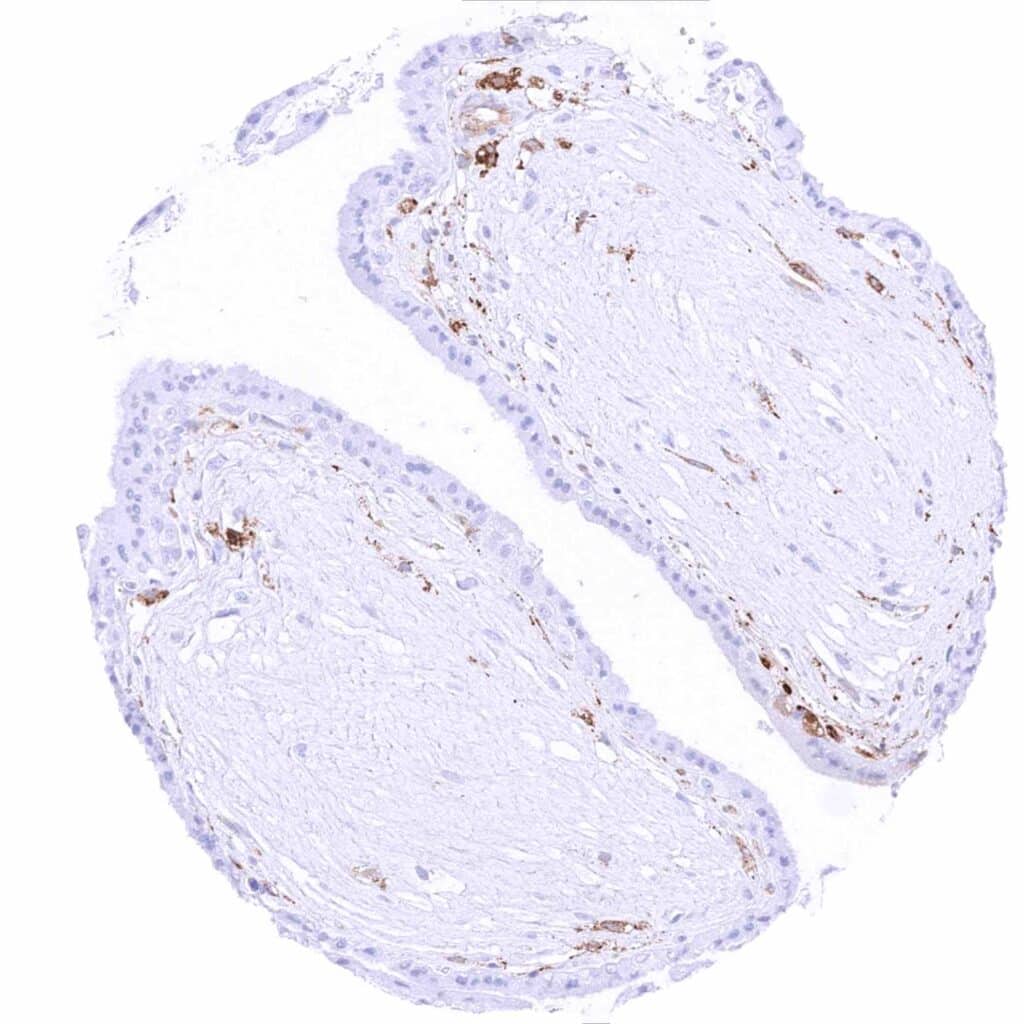
Placenta, early – Trophoblast cells are MX1 negative. Strong staining is only seen in endothelial cells
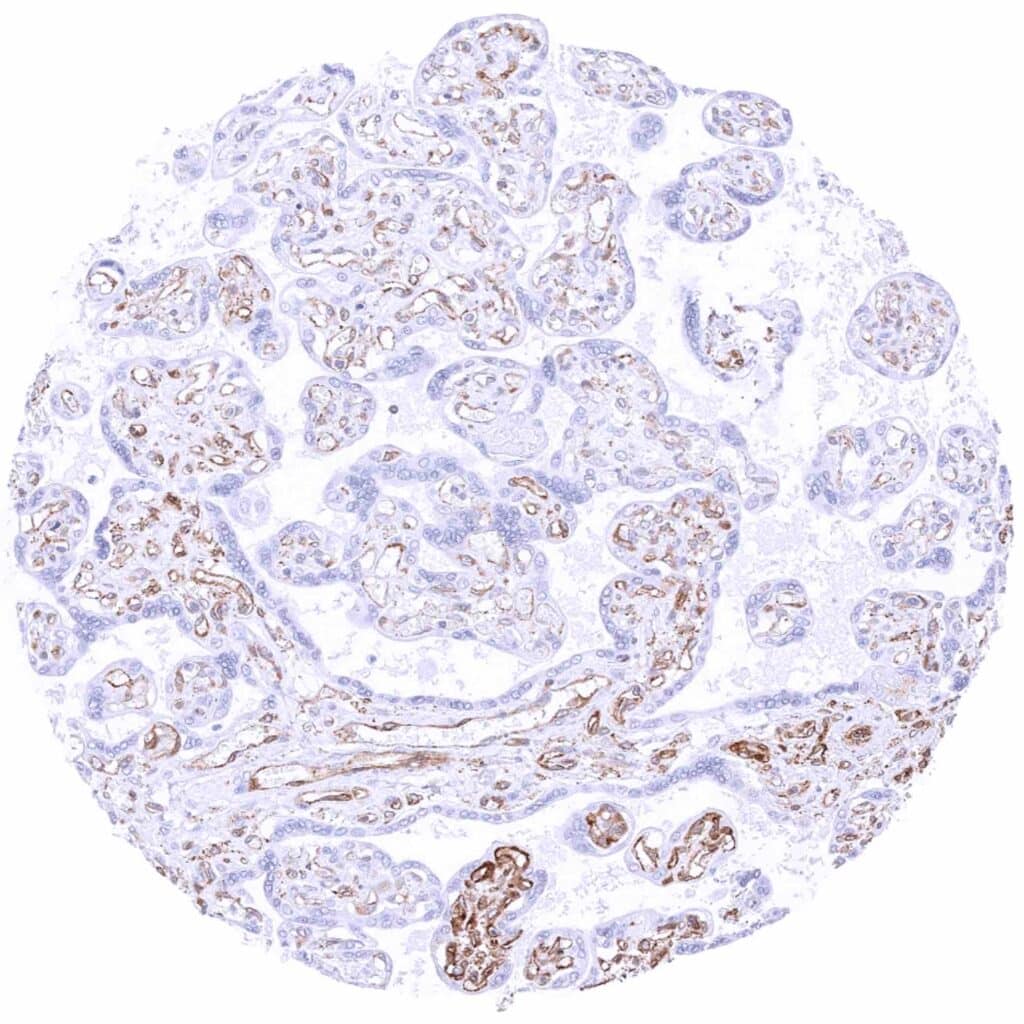
Placenta, mature – Trophoblast cells are MX1 negative. Strong staining is only seen in endothelial cells
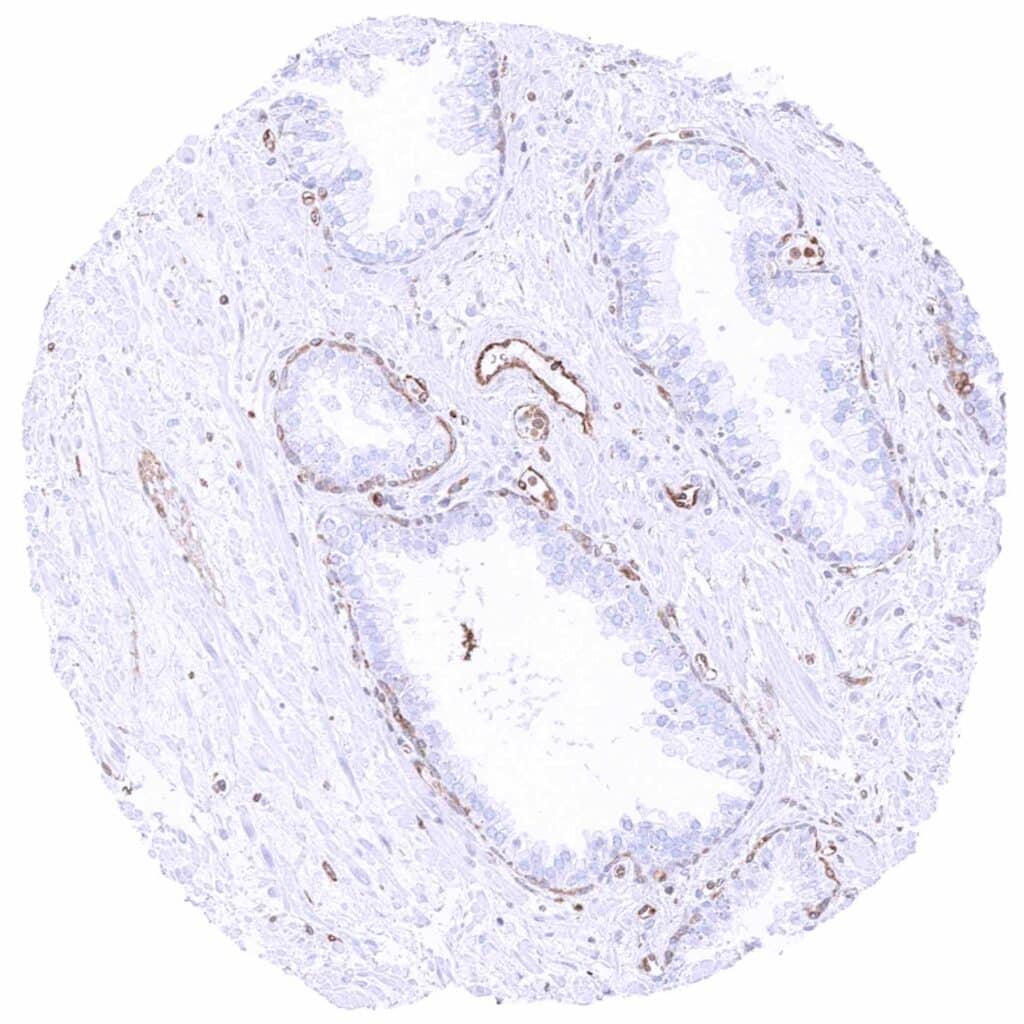
Prostate – Cytoplasmic MX1 staining of basal cells and of the endothelium of small vessels.
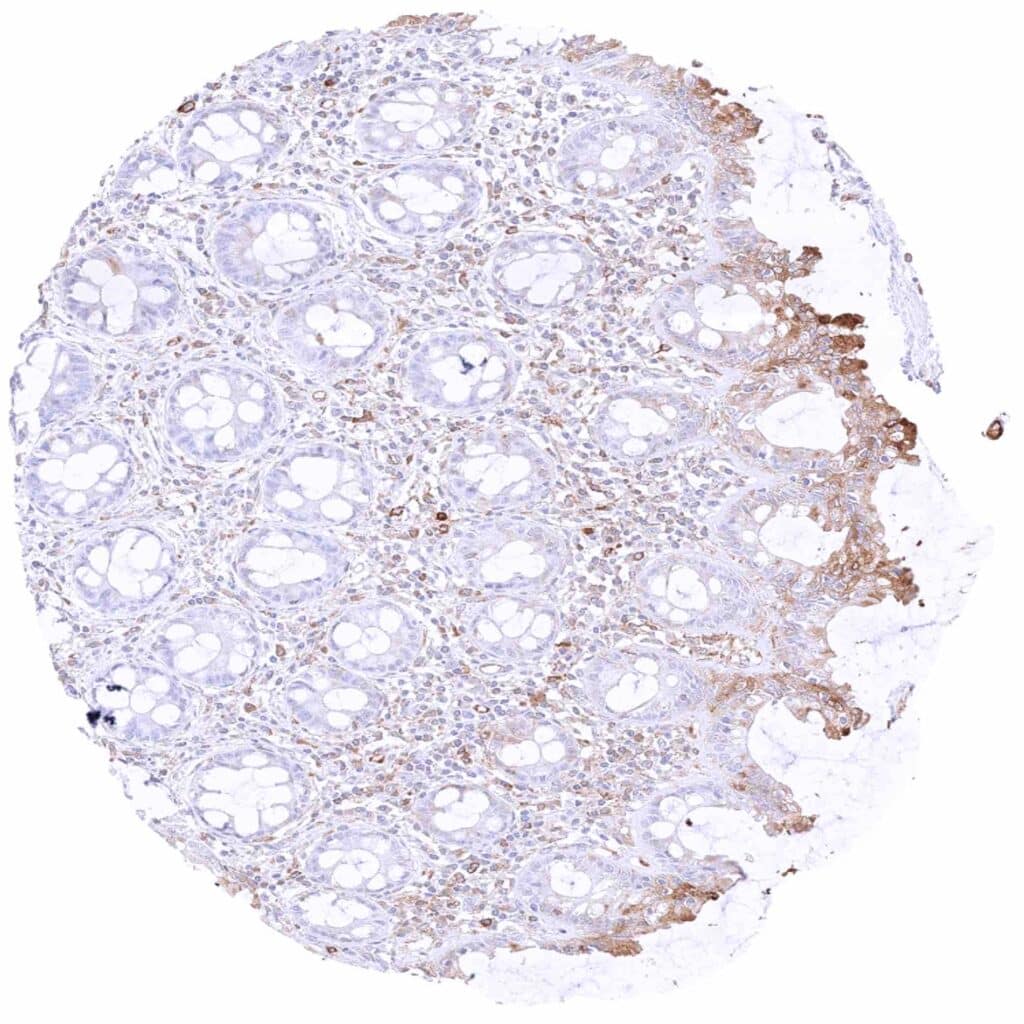
Rectum, mucosa – MX1 staining of epithelial cells is largely restricted to superficial cell layers
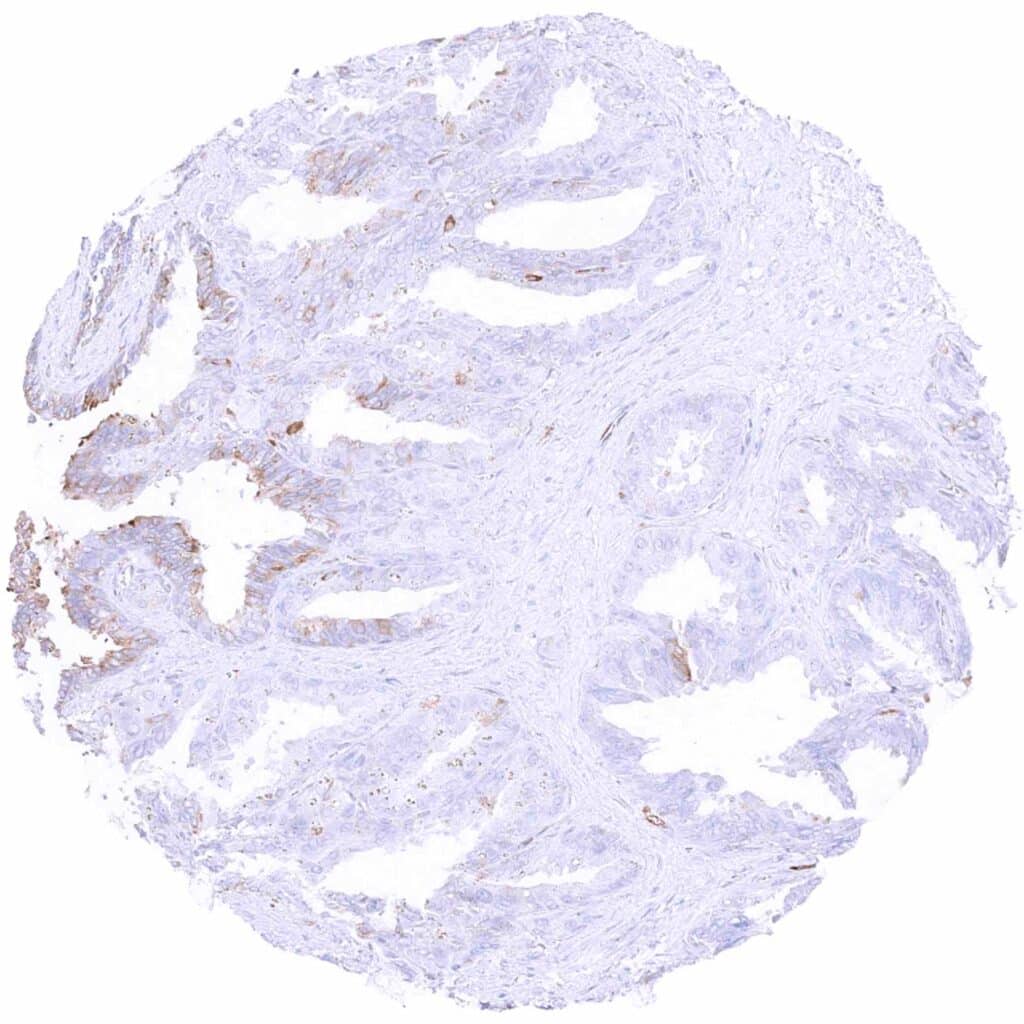
Seminal vesicle – Cytoplasmic MX1 staining of a subset of epithelial cells
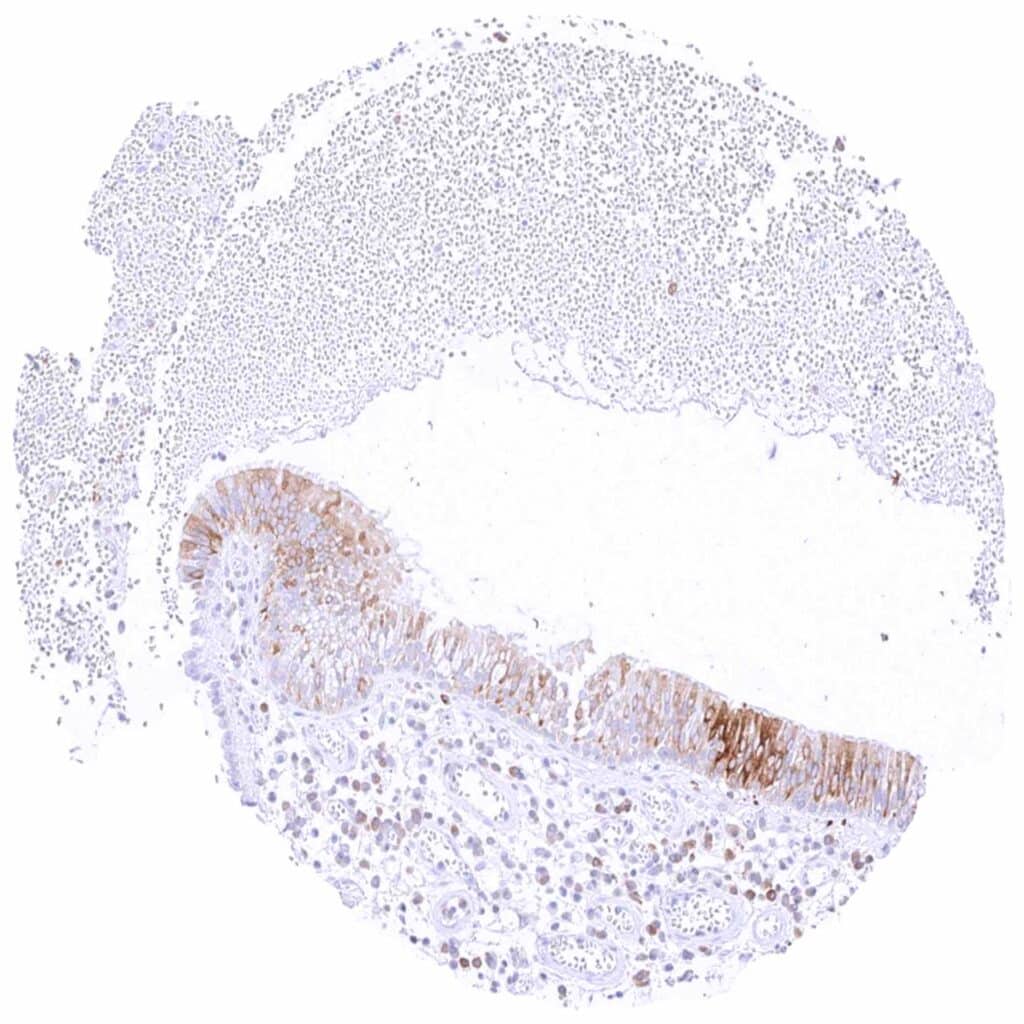
Sinus paranasales – Focal, moderate to strong cytoplasmic MX1 staining in respiratory epithelial cells
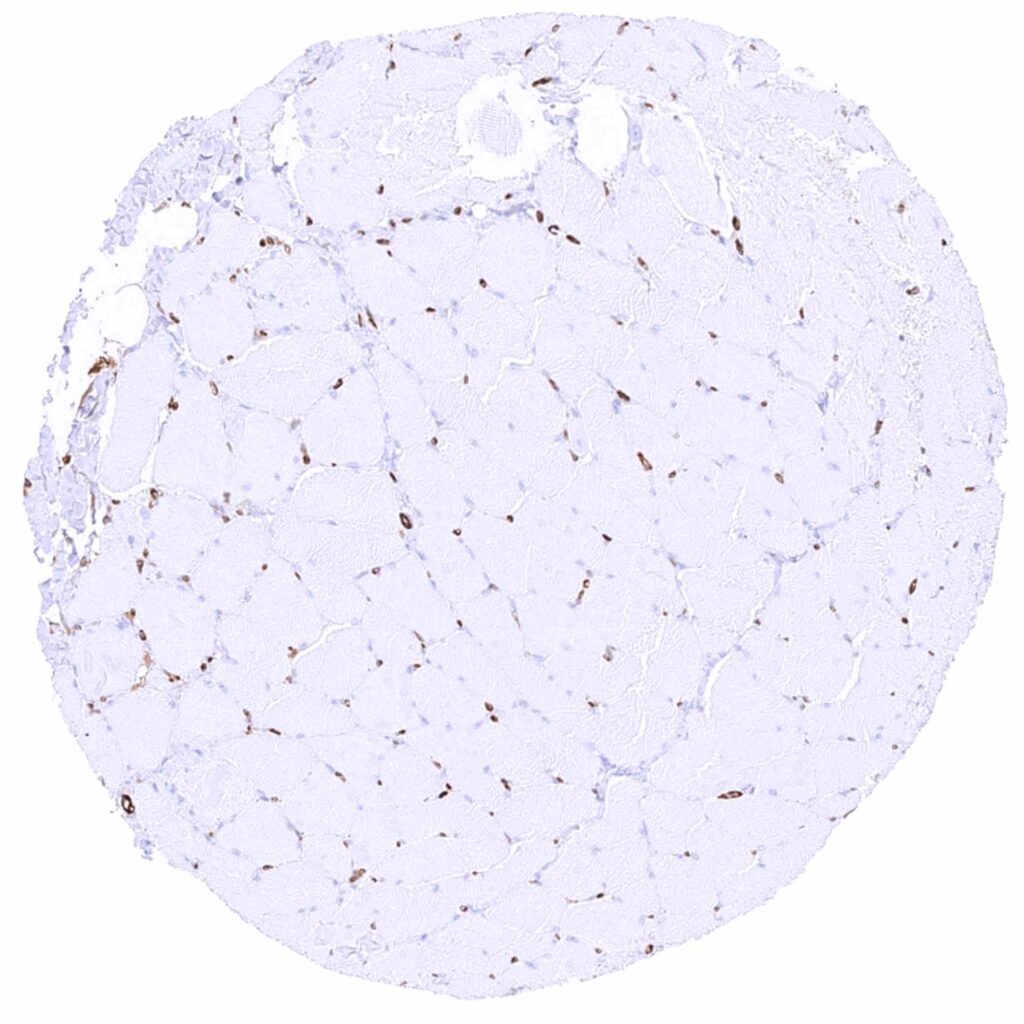
Skeletal muscle – MX1 staining prdominates in the endothelium of small vessels
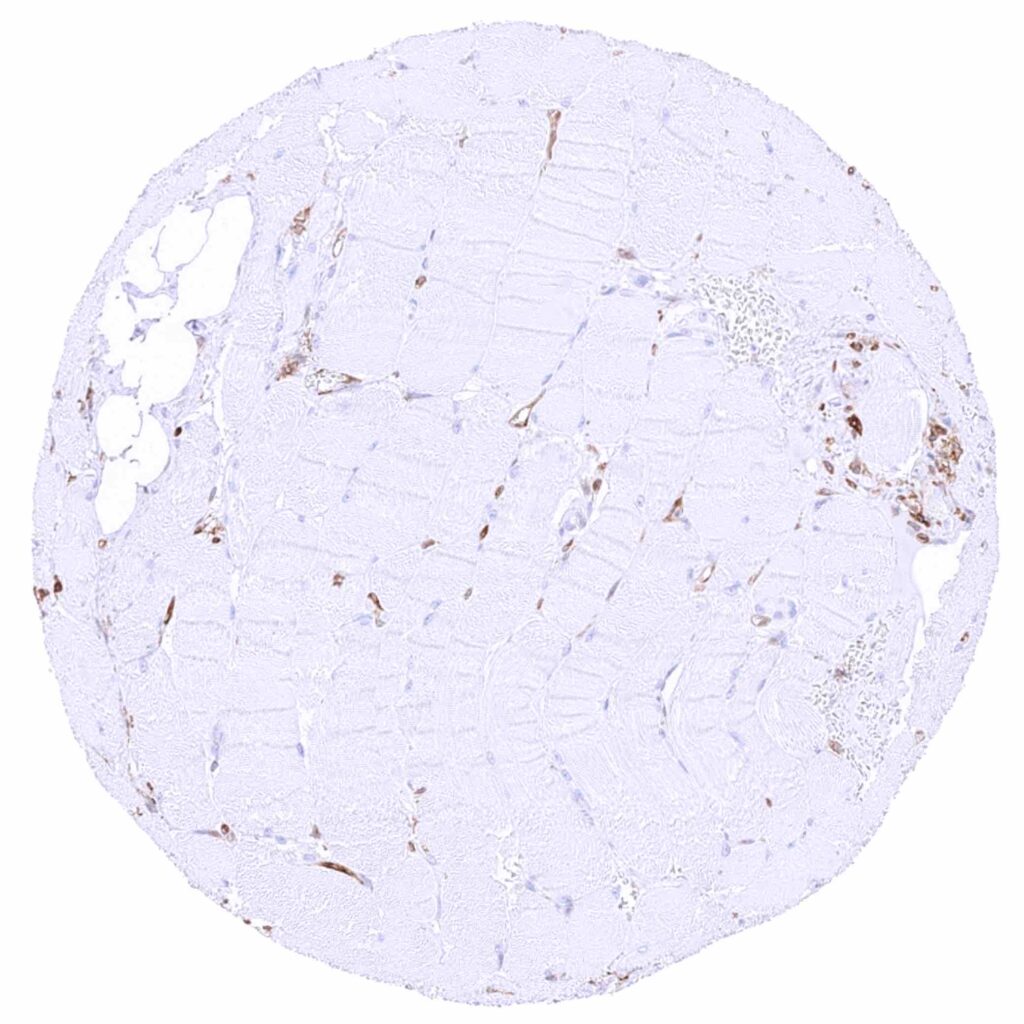
Skeletal muscle.jpeg
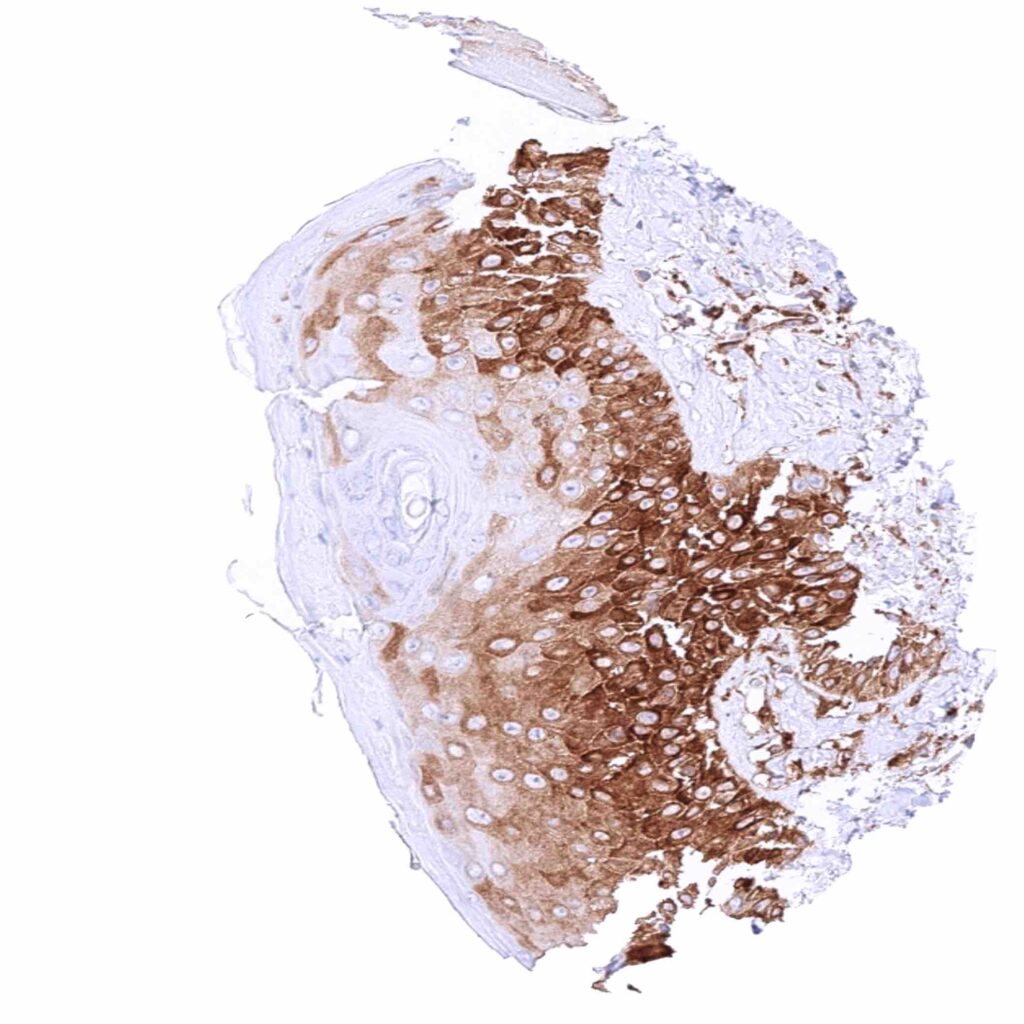
Skin – Strong cytoplasmic MX1 positivity of bottom half of epithelial cells in this sample
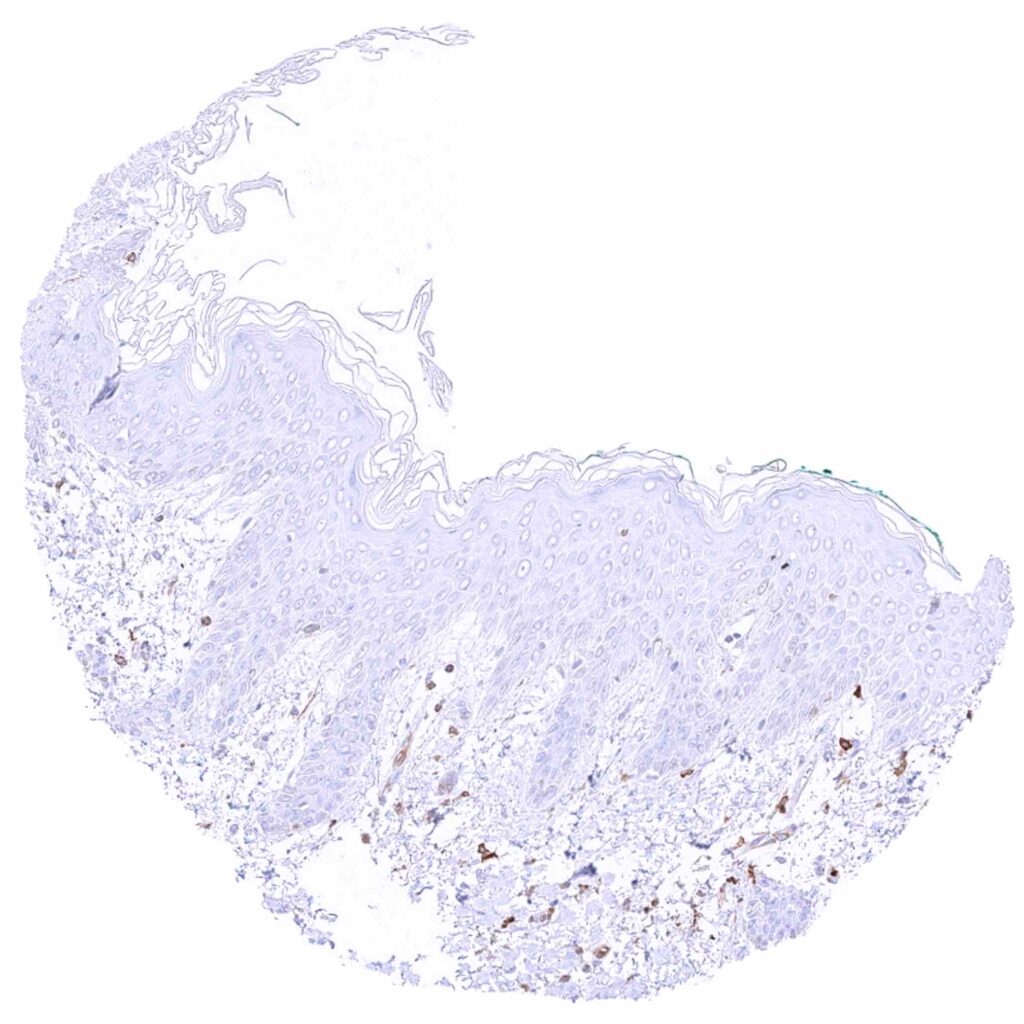
Skin
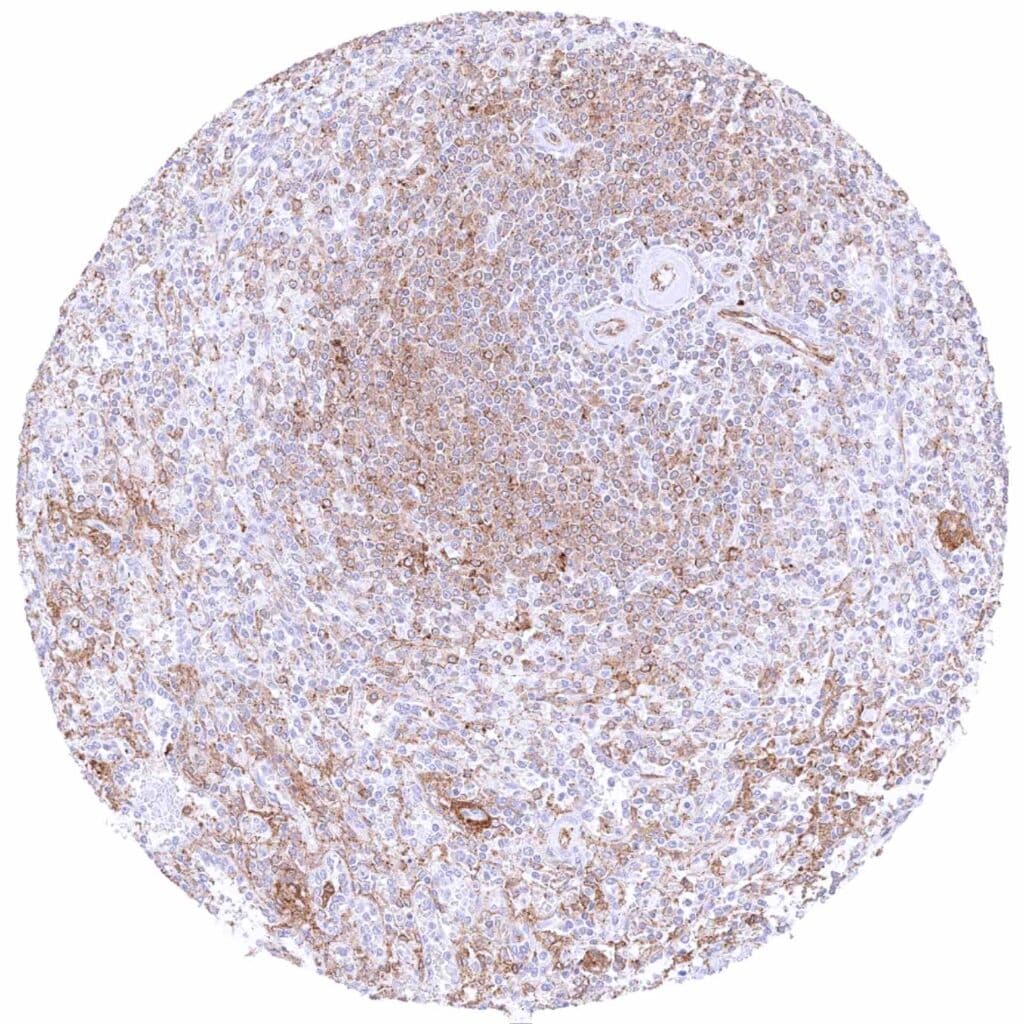
Spleen – Cytoplasmic MX1 staining at variable intensity of a large fraction of cells
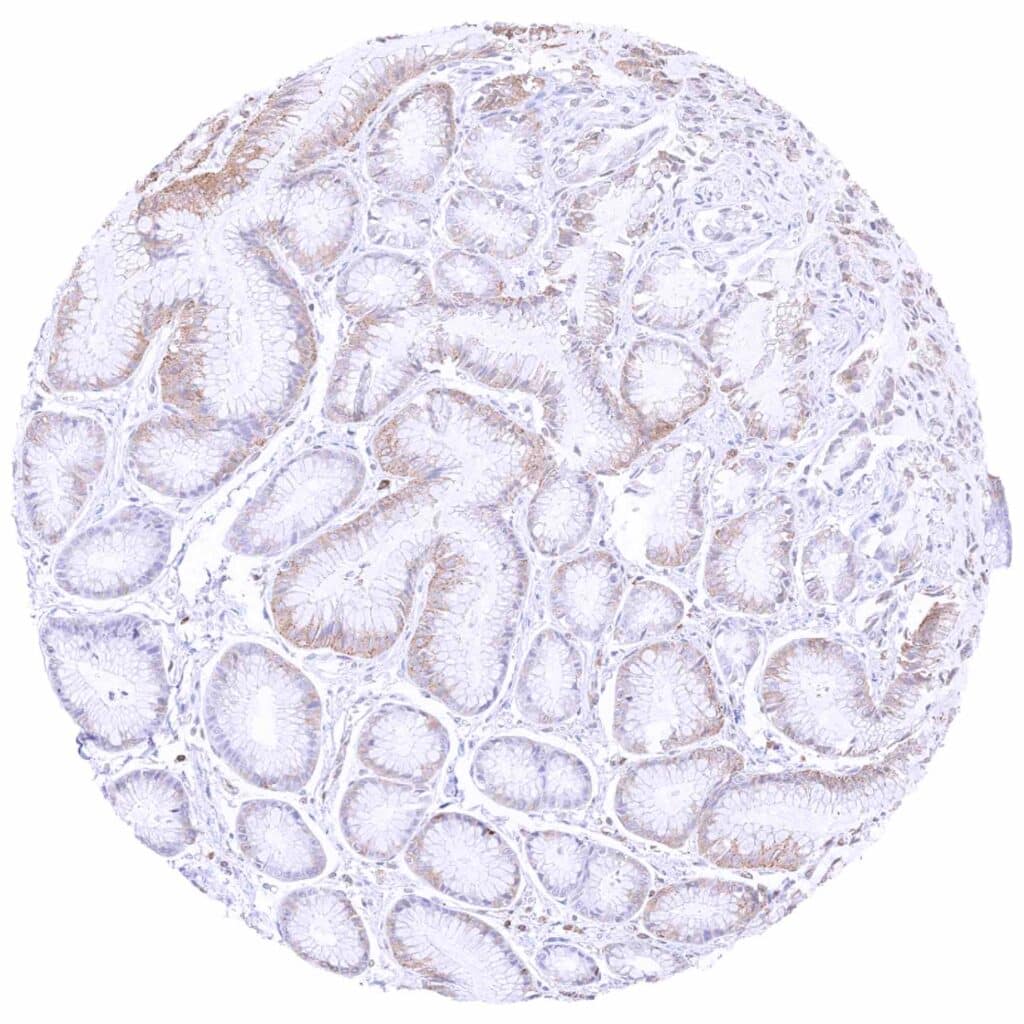
Stomach, antrum – Some cytoplasmic MX1 staining of epithelial cells, mainly of the surface epithelium
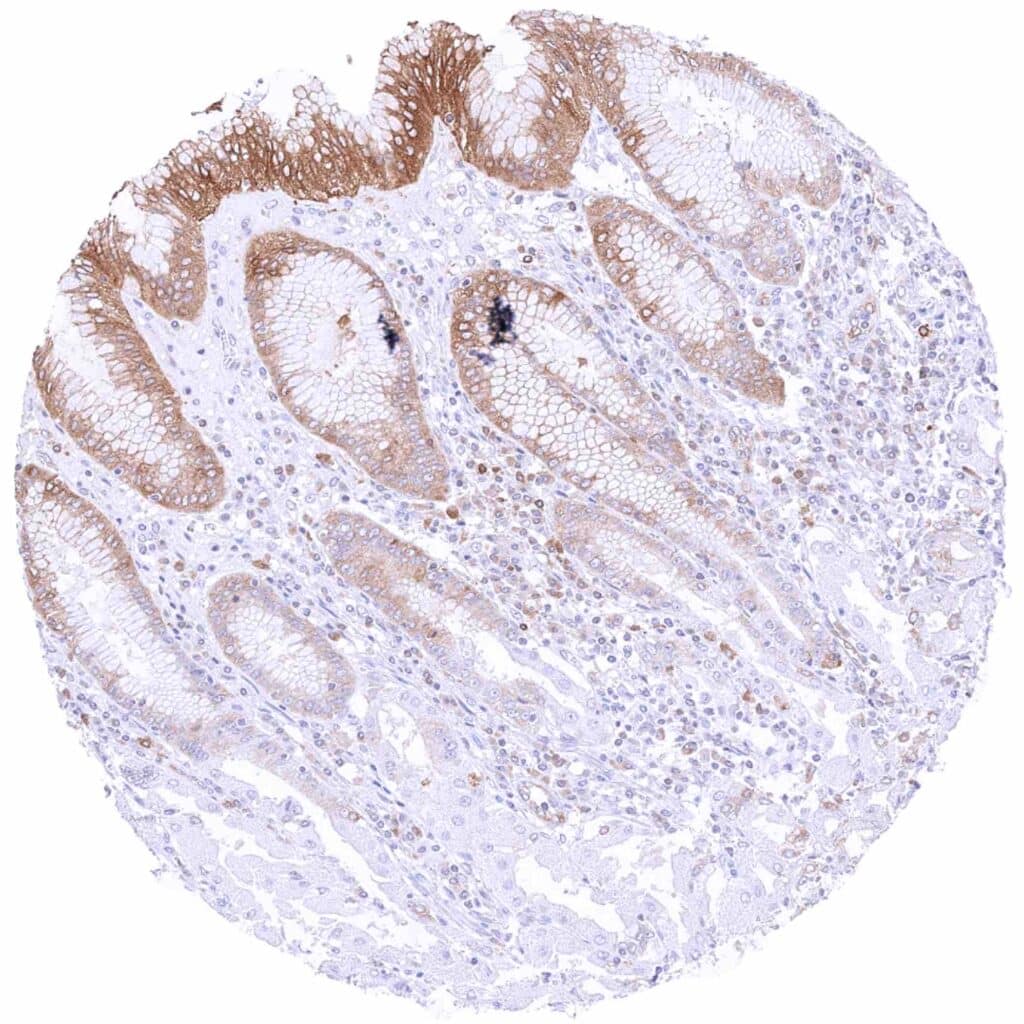
Stomach, corpus – Moderate to strong cytoplasmic MX1 staining of surface epithelial cells in a case with chronic inflammation
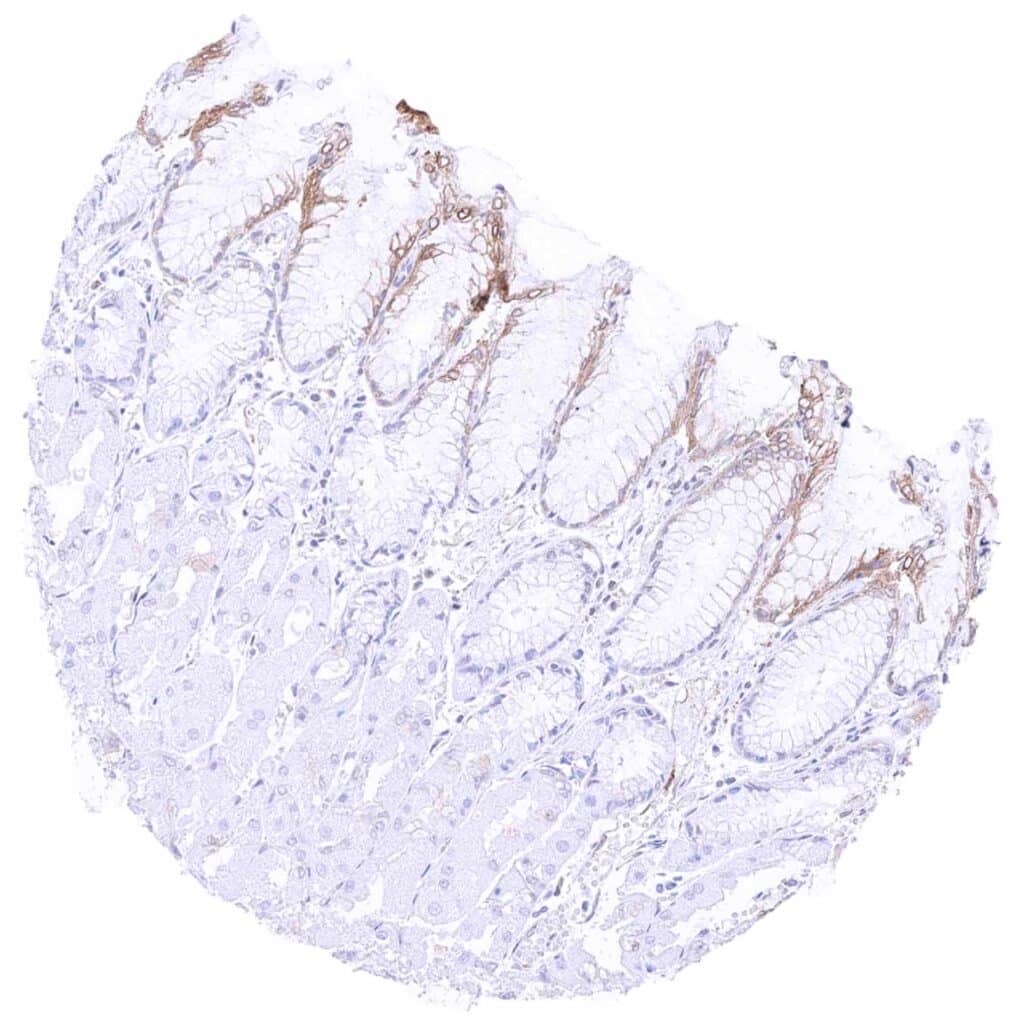
Stomach, corpus – Weak to moderate cytoplasmic MX1 staining of surface epithelial cells
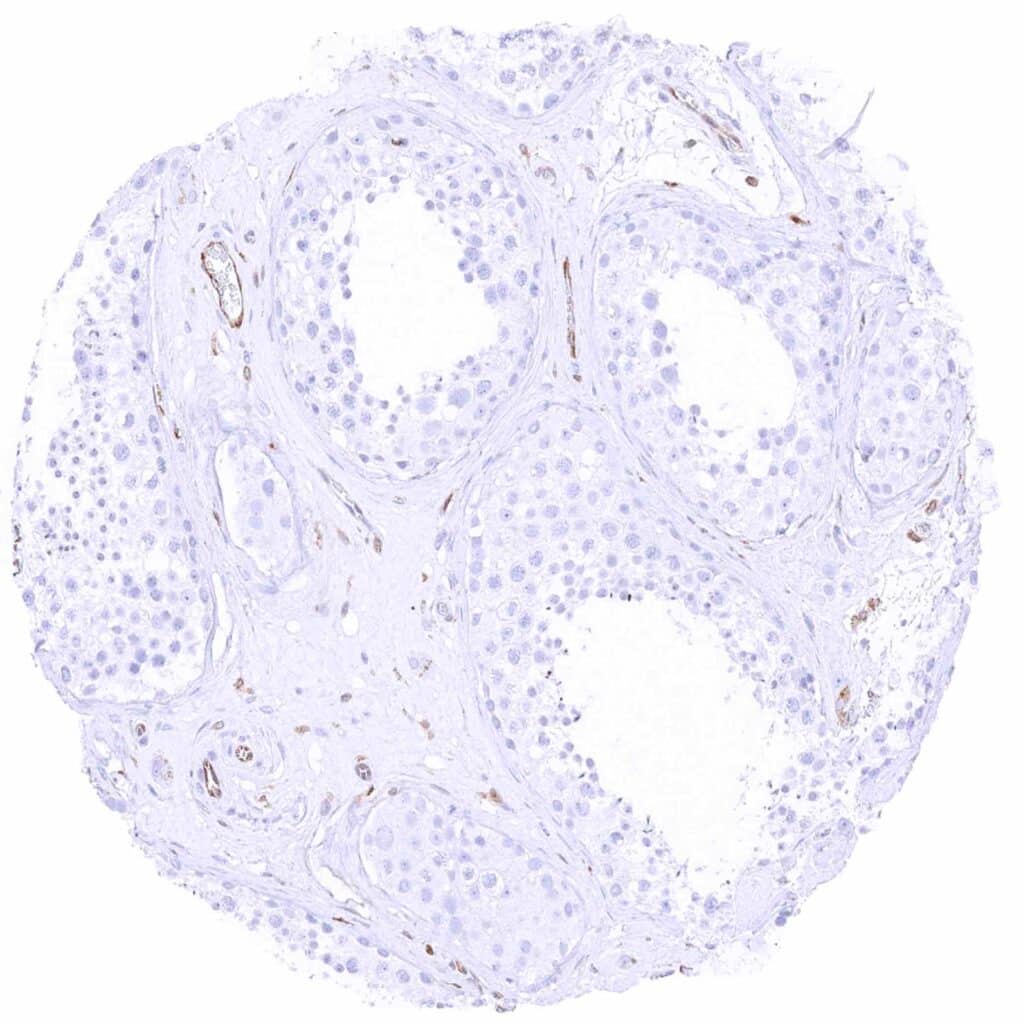
Testis – Cytoplasmic MX1 staining is restricted to endothelial cells.jpeg
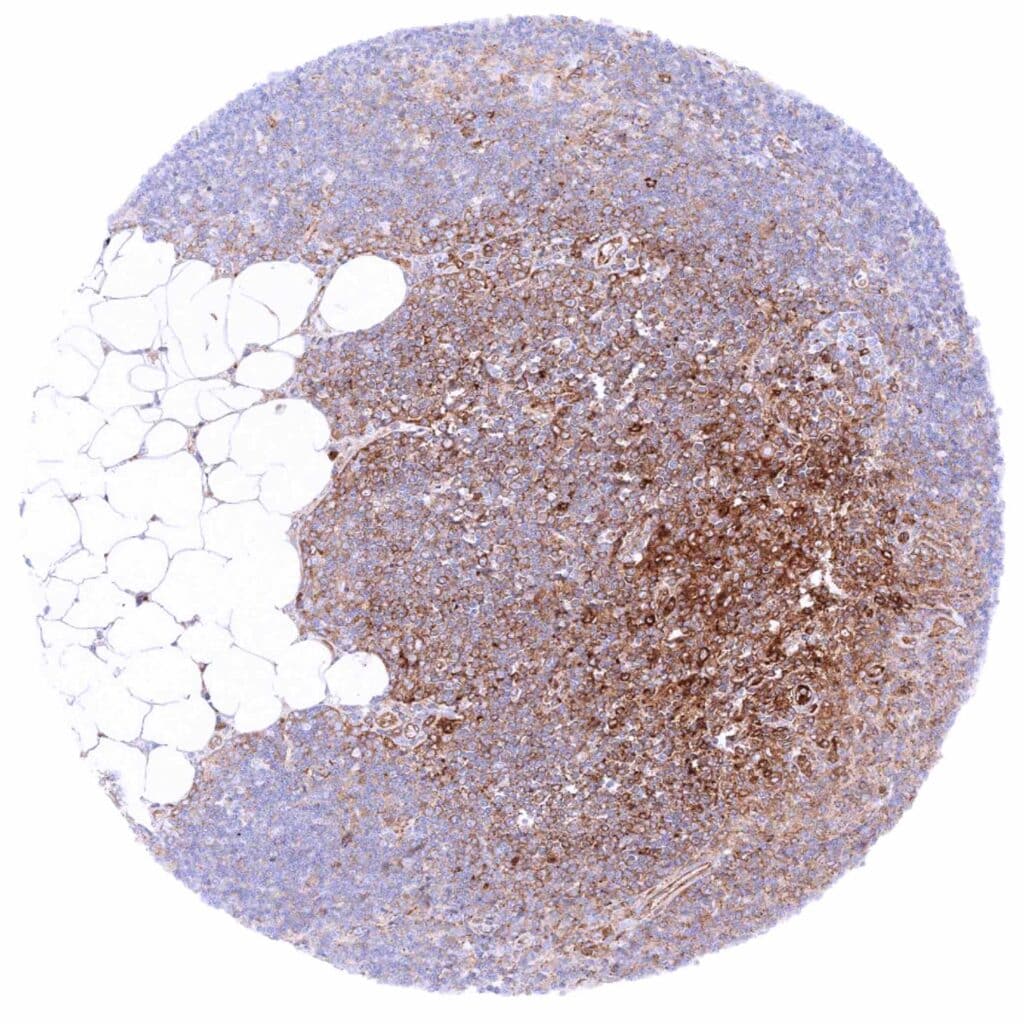
Thymus – Cytoplasmic MX1 staining at variable intensity of a large fraction of cells
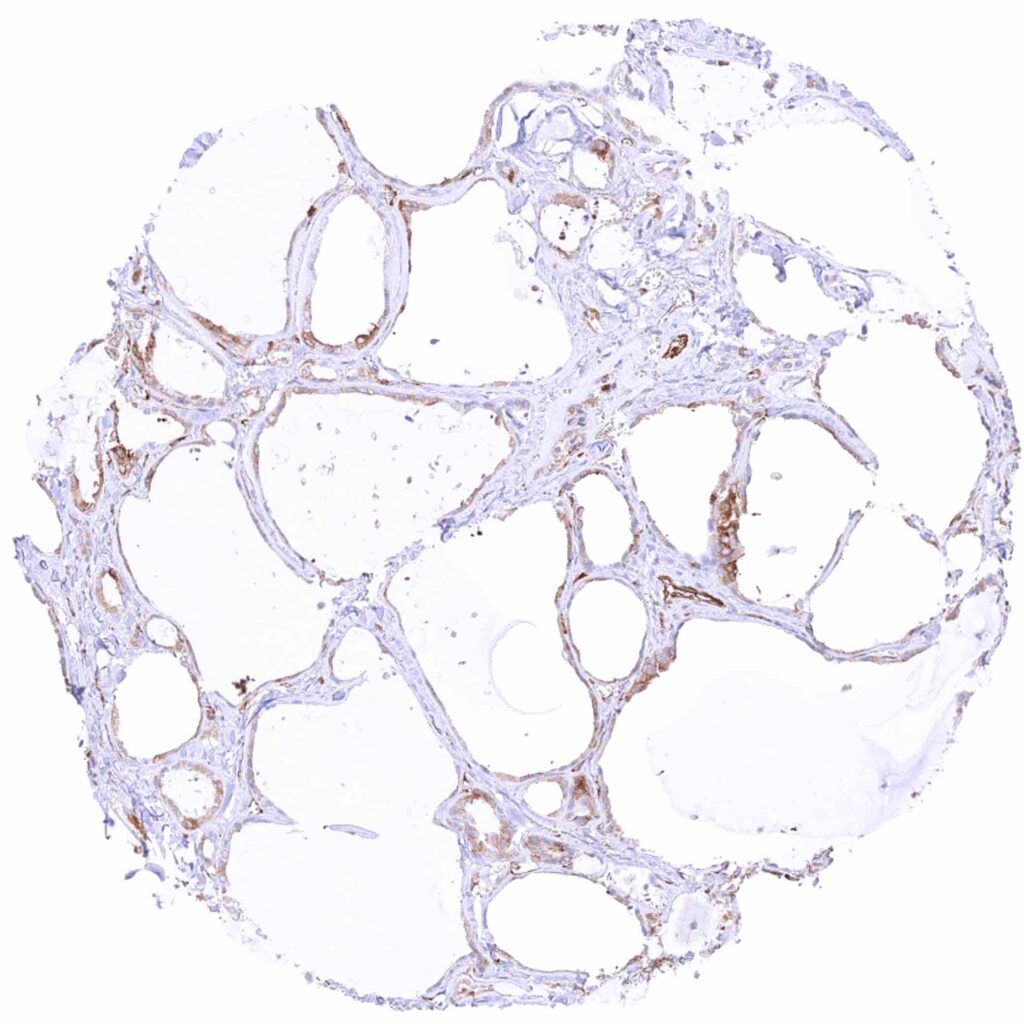
Thyroid gland – Weak to moderate cytoplasmic MX1 staining of follicular cells
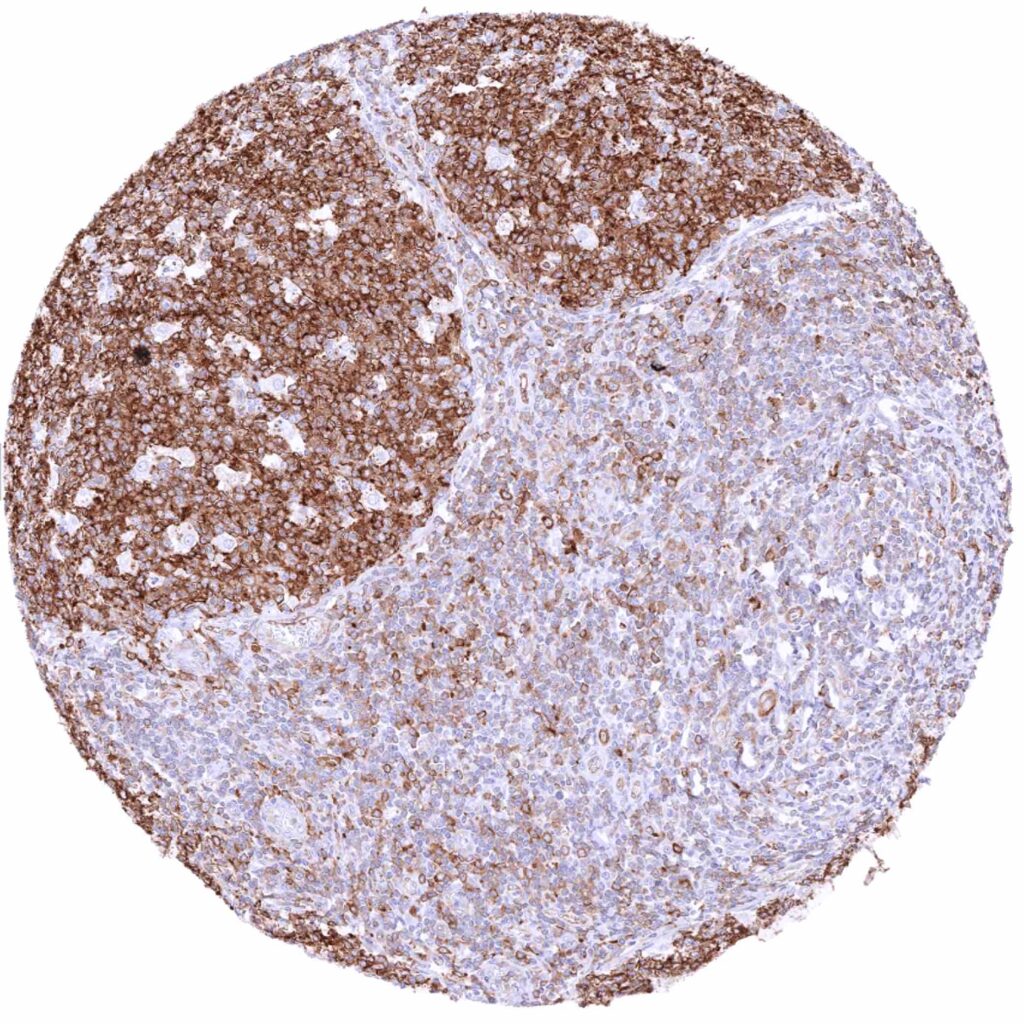
Tonsil – Cytoplasmic MX1 staining of lymphocytic cells is most intensive in germinal centres
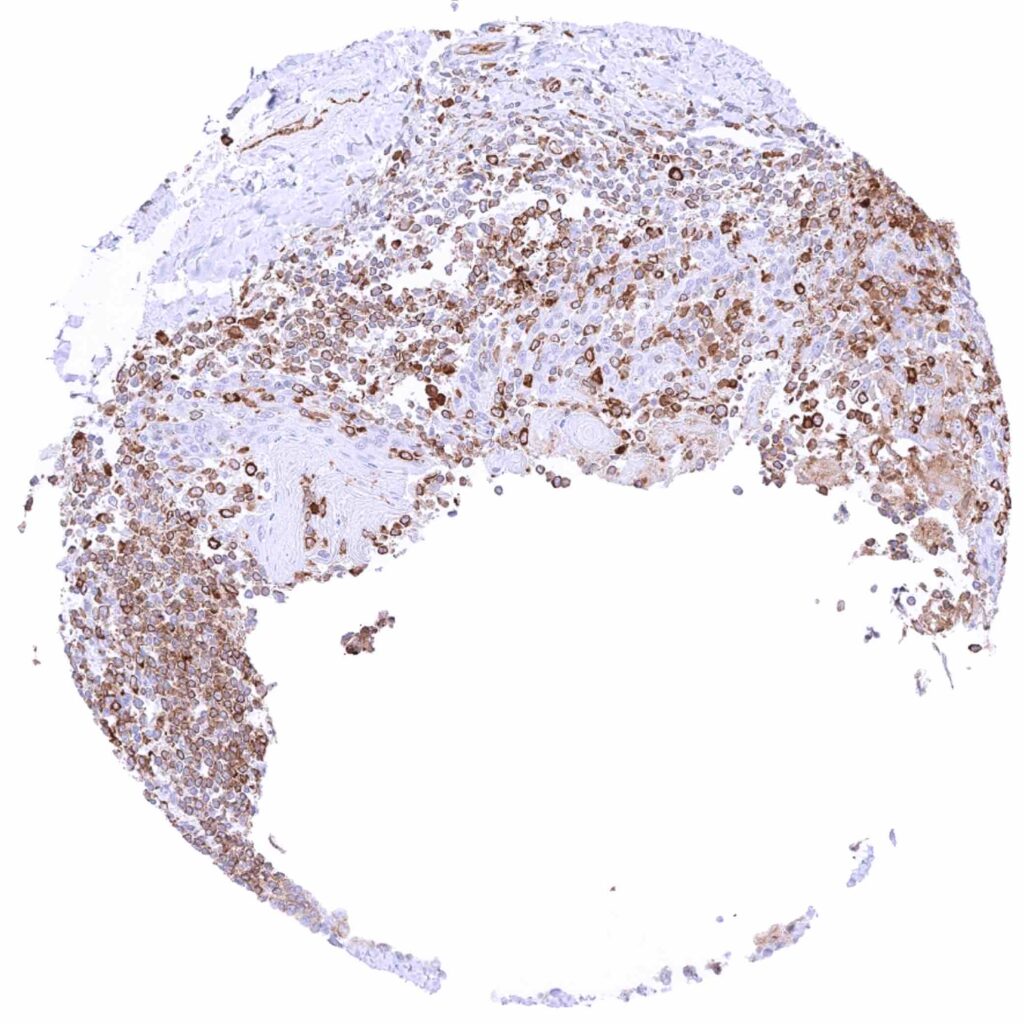
Tonsil – Cytoplasmic MX1 staining of most lymphocytic cells at variable intensity while crypt epithelial cells are largely negative
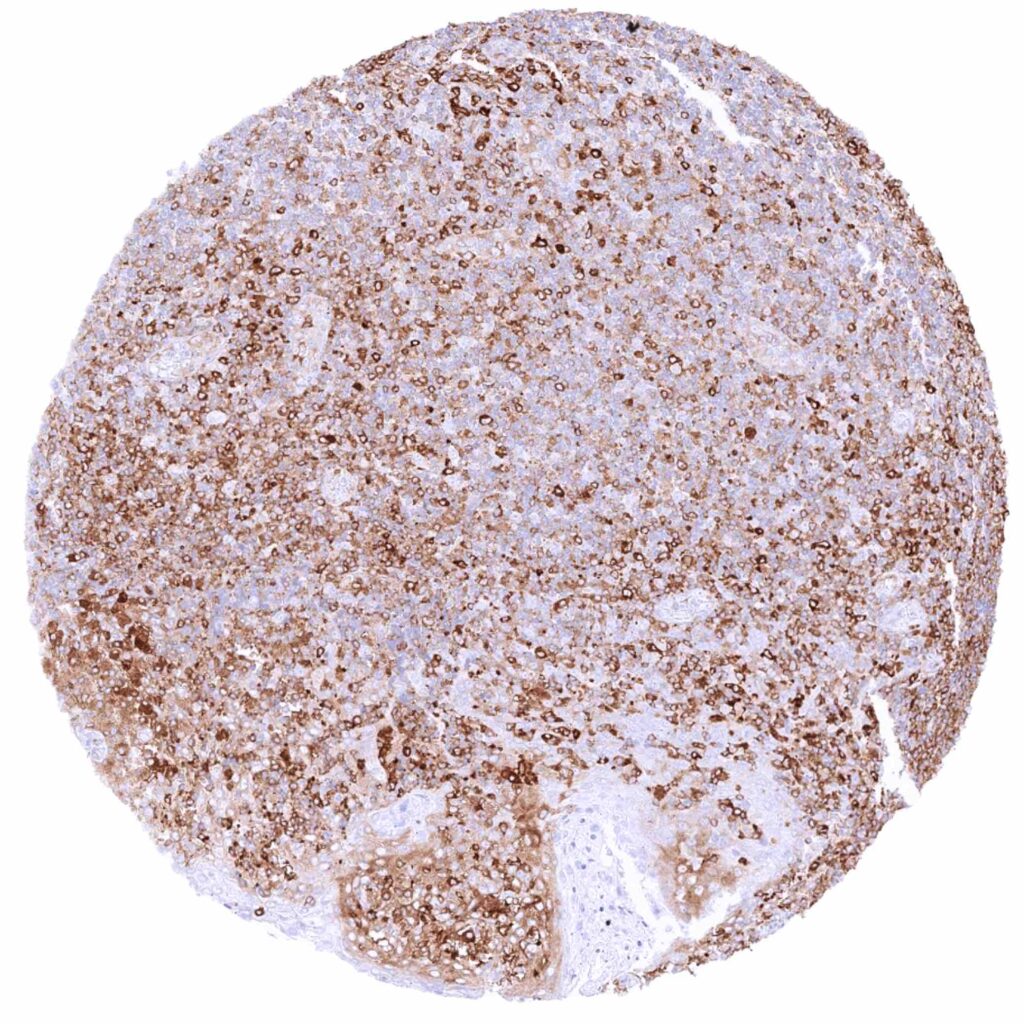
Tonsil, surface epithelium – Abundant cytoplasmic MX1 staining of lymphocytic cells while epithelial cells remain negative
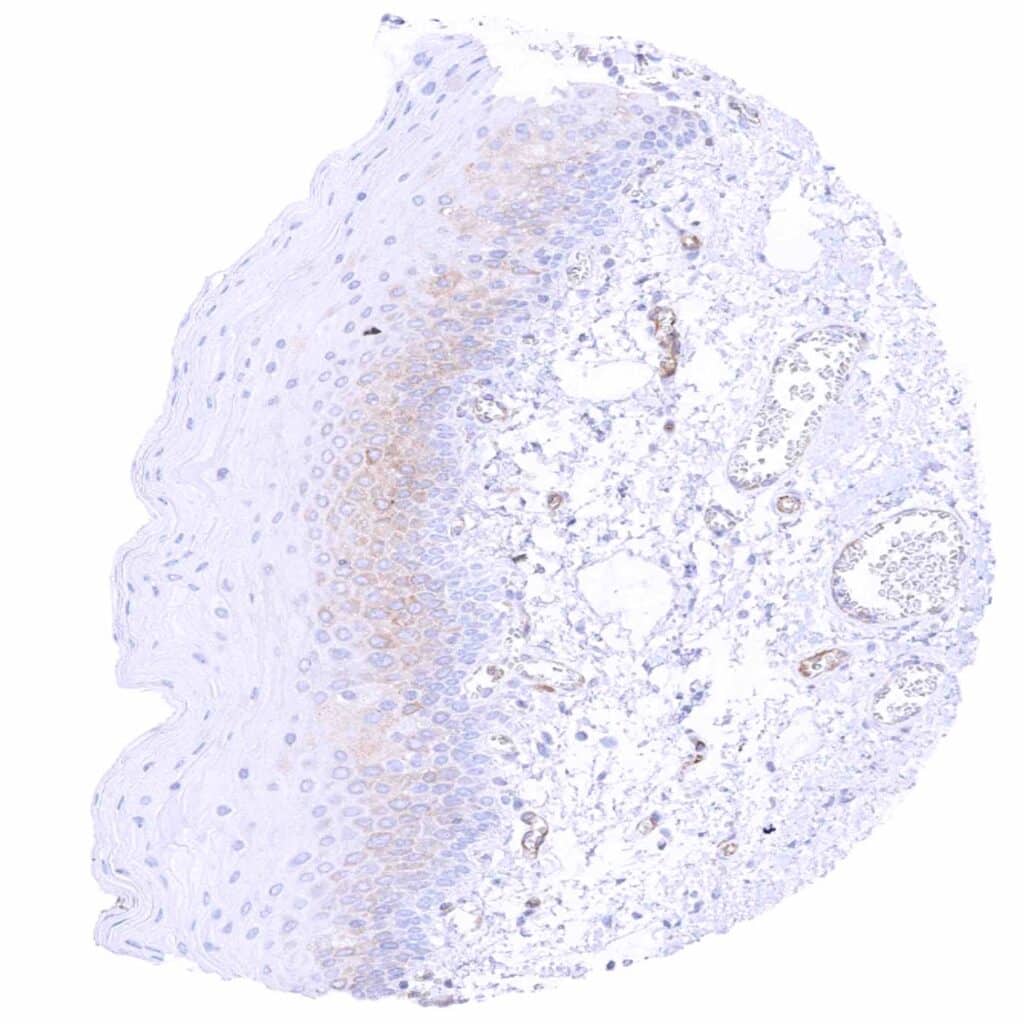
Tonsil, surface epithelium – Weak cytoplasmic MX1 staining of lowest third of epithelial cells in this sample
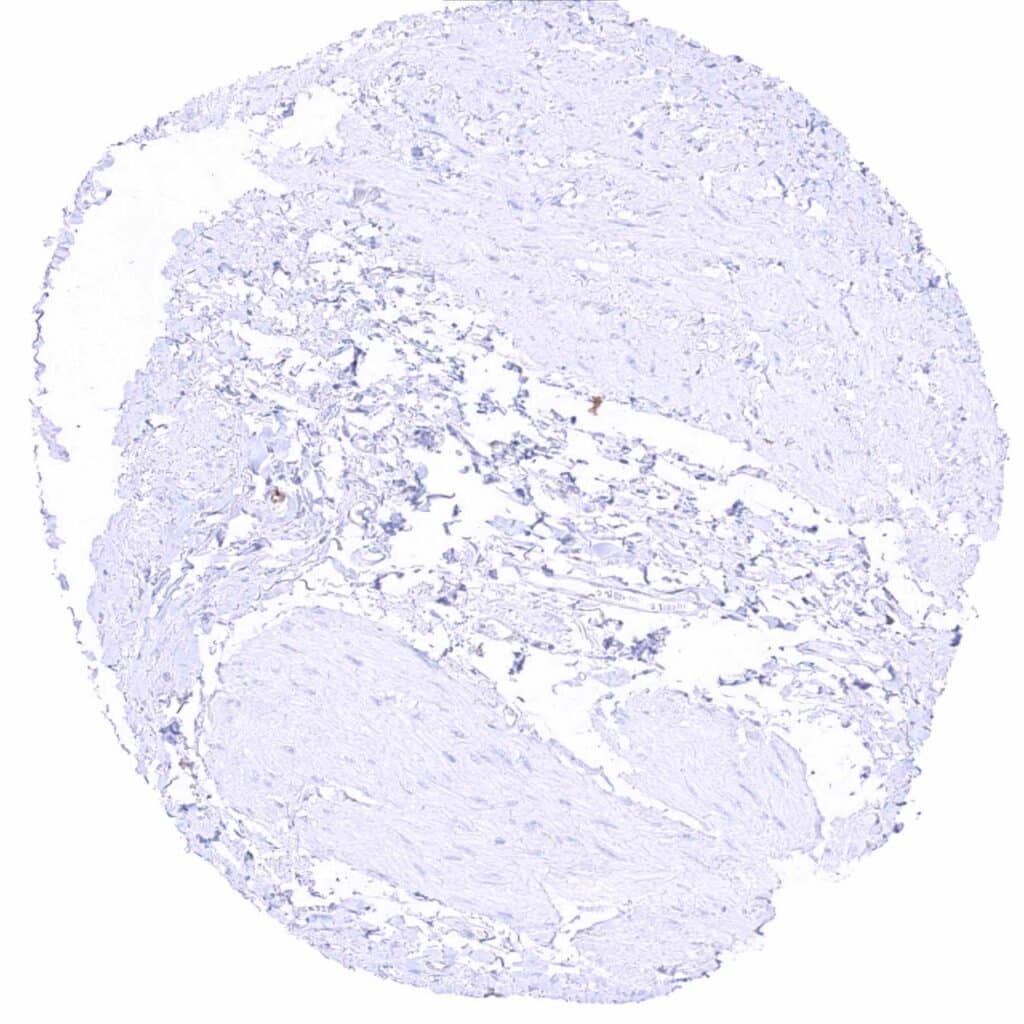
Urinary bladder, muscular wall – MX1 staining prdominates in the endothelium of small vessels
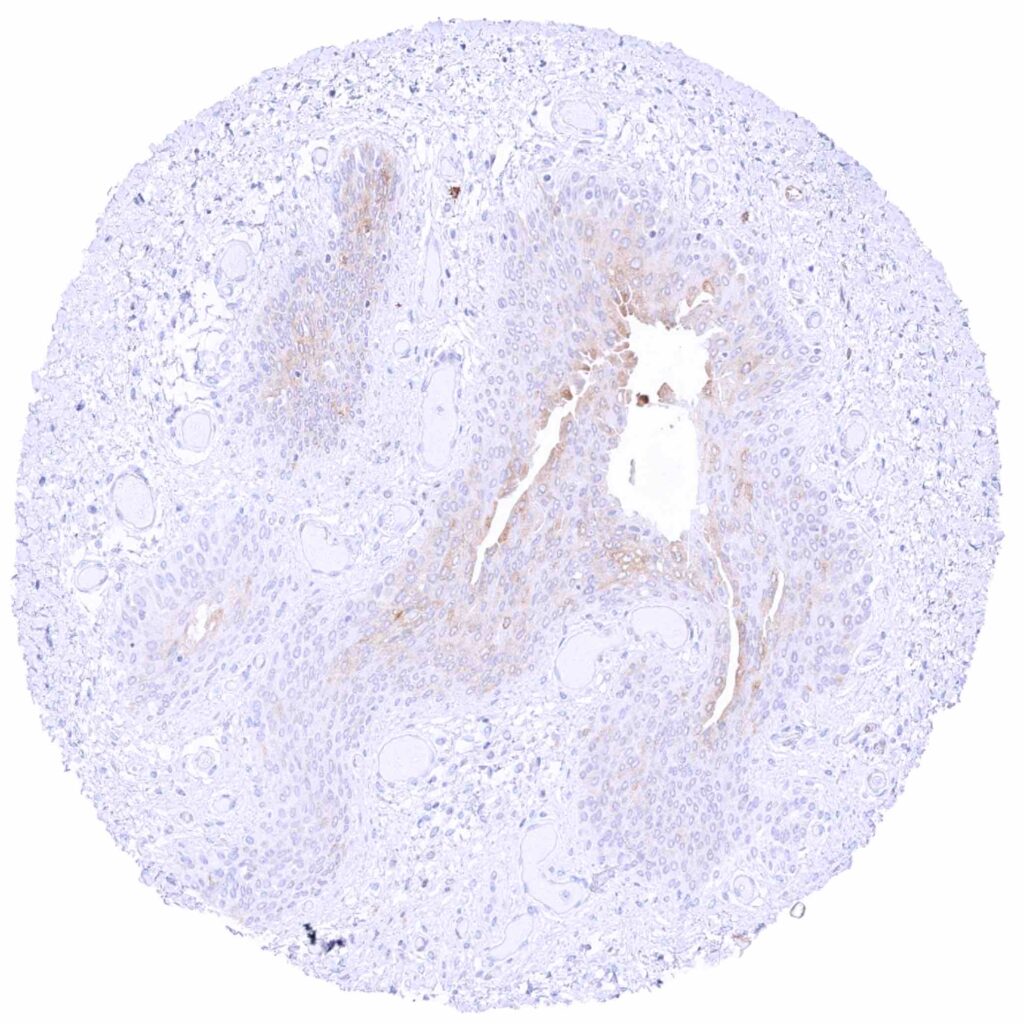
Urinary bladder, urothelium – Weak cytoplasmic MX1 staining of upper-half of urothelial cell layers
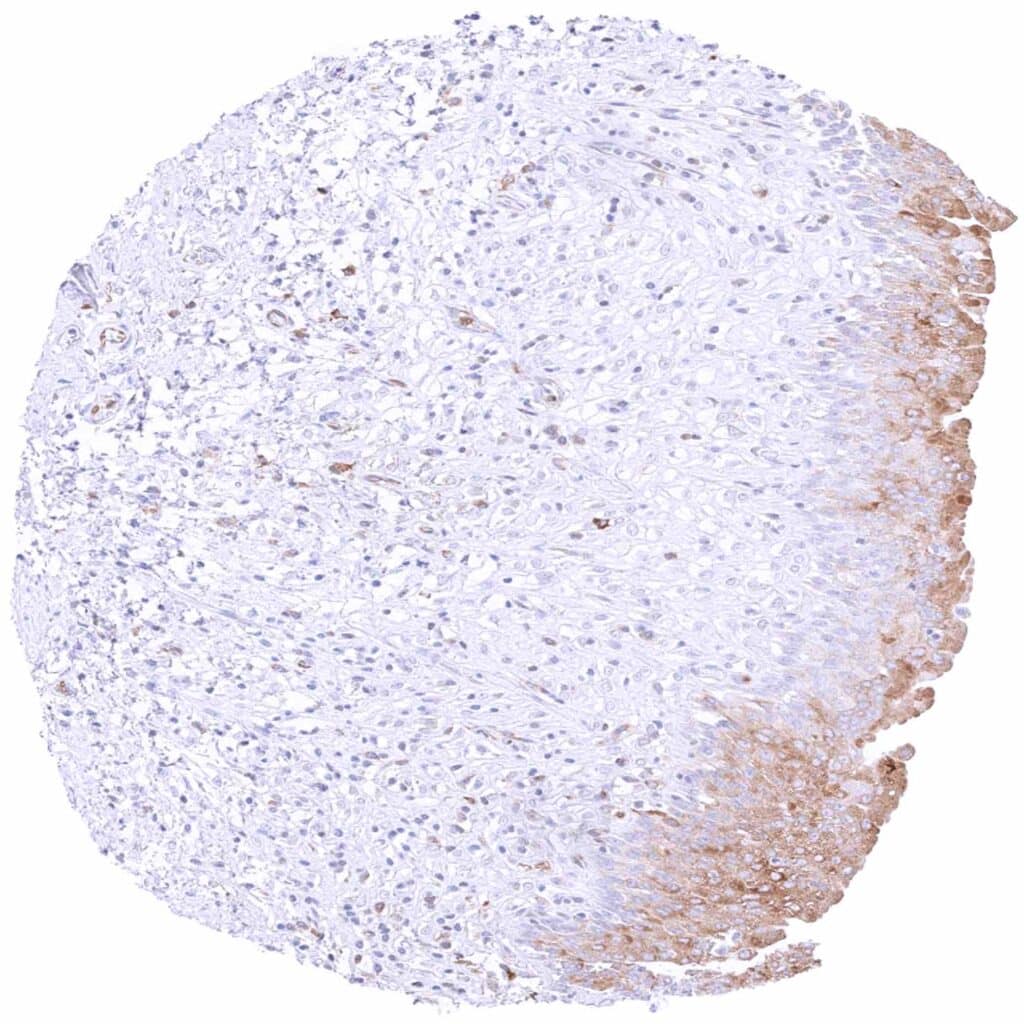
Urinary bladder, urothelium – Weak to moderate cytoplasmic MX1 staining of upper-half of urothelial cell layers
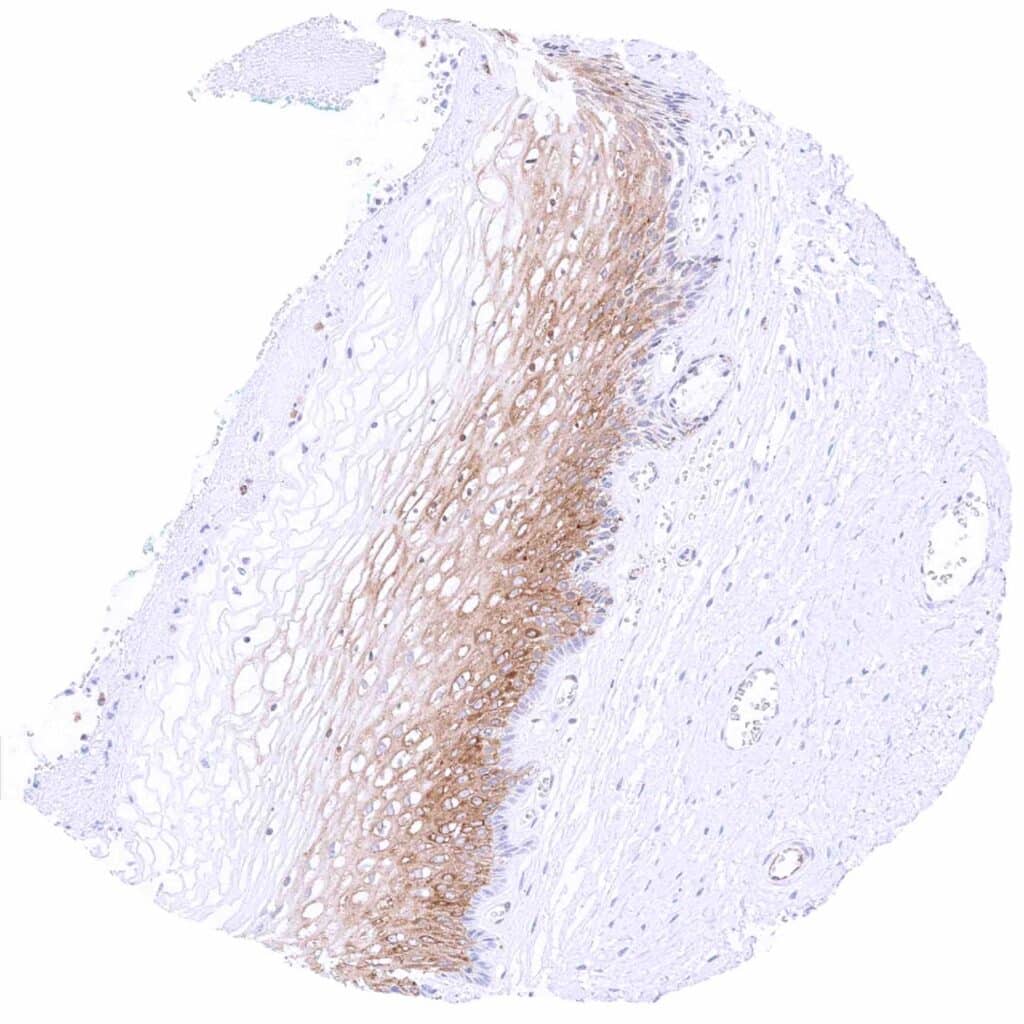
Uterus, ectocervix – Moderate cytoplasmic MX1 staining of suprabasal cell layers
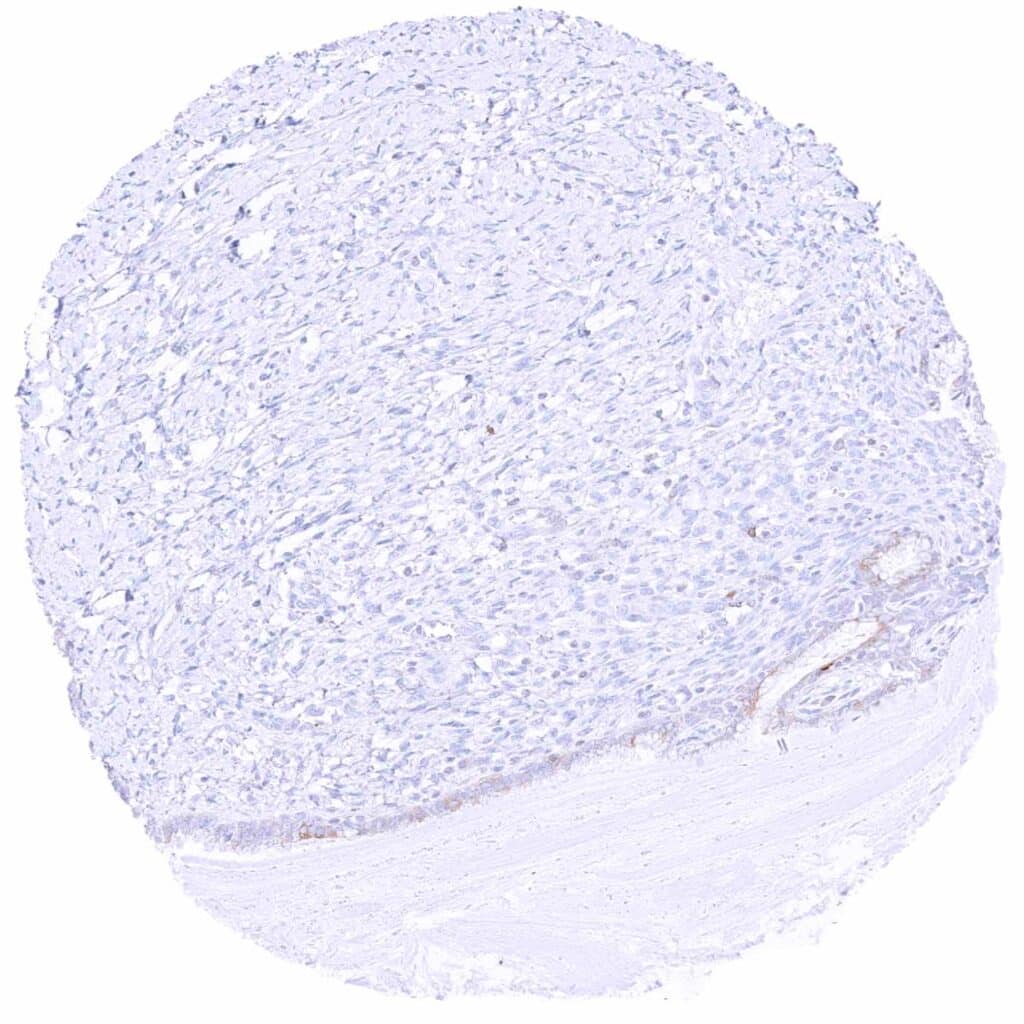
Uterus, endocervix – Faint MX1 staining of some epithelial cells.jpeg
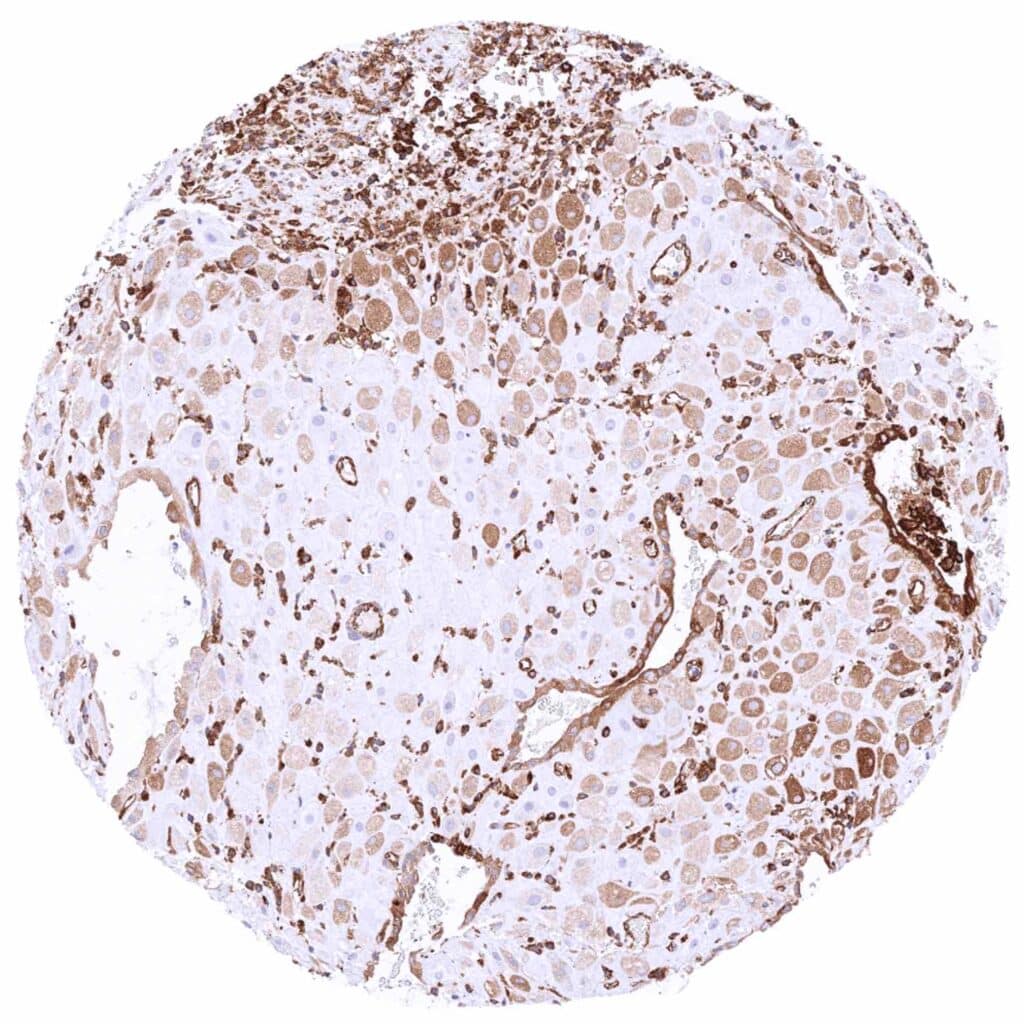
Uterus, endometrium (pregnancy) – Strong MX1 staining of endometrium cells. Moderate intensity MX1 staining of decidua cells
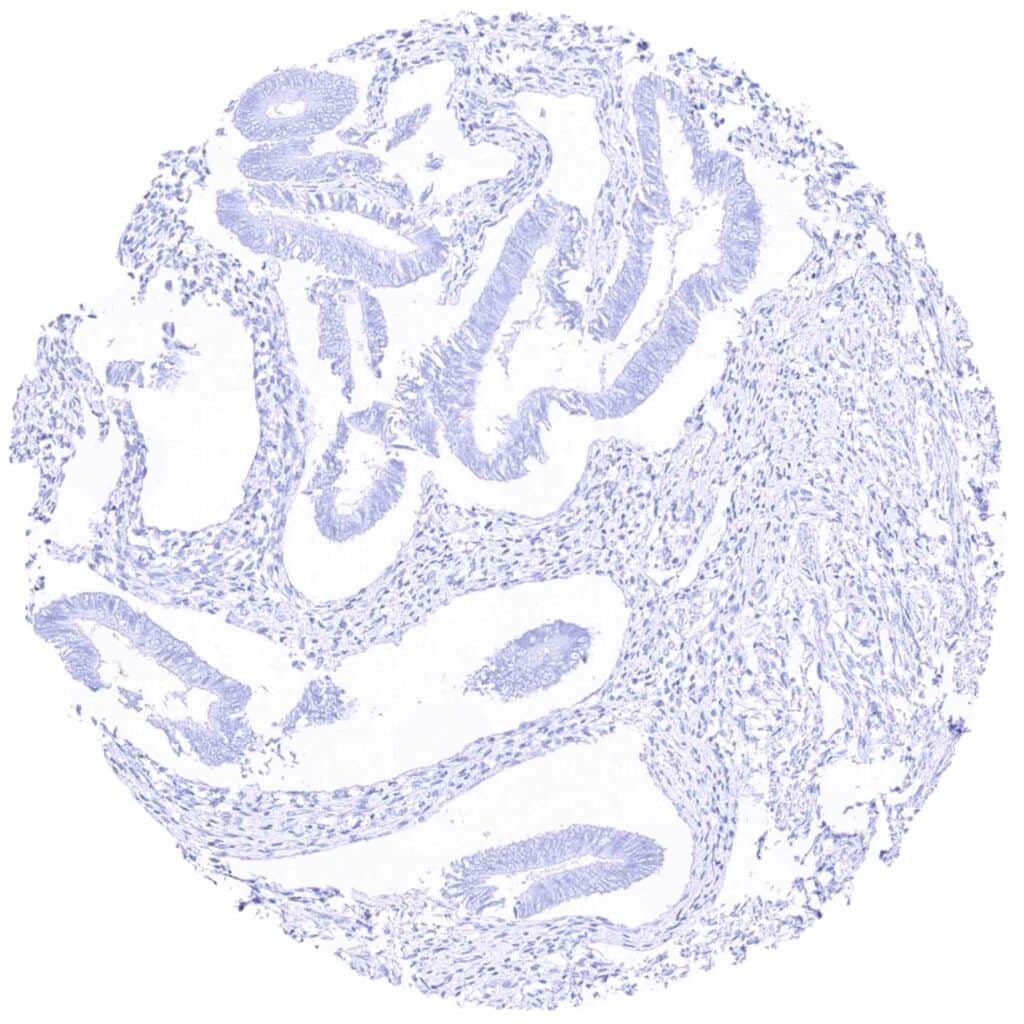
Uterus, endometrium (proliferation)
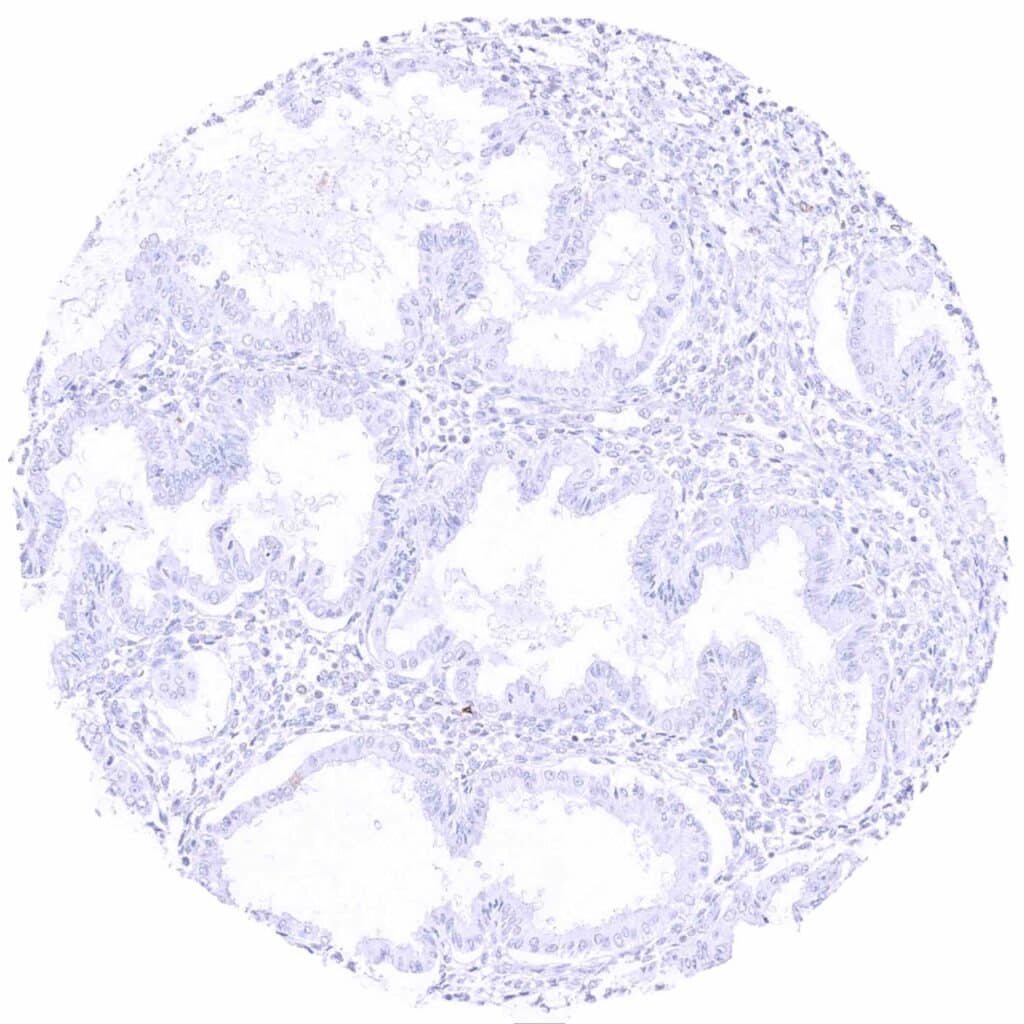
Uterus, endometrium (secretion)
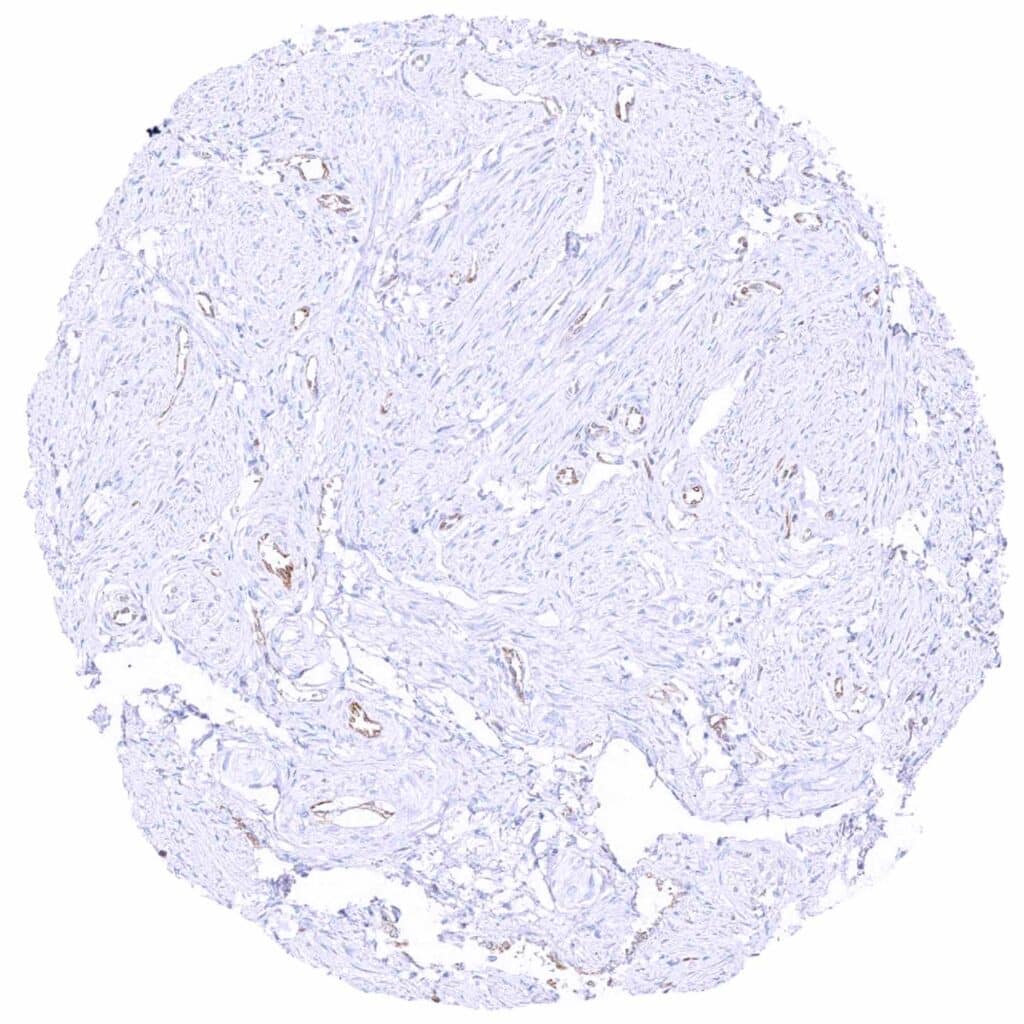
Uterus, myometrium – MX1 staining prdominates in the endothelium of small vessels
